Molecular and Cellular Biology
1/126
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Atom
The smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons.
Molecule
chemical structure of 2 or more atoms held together by chemical bounds
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space, including atoms and molecules.
Elements
chemical substance where all atoms have same number of protons
Nucleus
the center of an atom that holds protons and nuetrons, contributes to atom mass
Protons
positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom, defining the element's atomic number.
Neutrons
neutral particles within the nucleus, adds to atomic mass, can determine isotopes
Electrons
negatively charged particles outside the nucleus, found orbiting in shells, plays key roll in chemical bonding
Valance shell
outermost shell that holds valence electrons which are involved in chemical reactions and bonding, atoms are most reactive if valence shell is imcomplete
Octet Rule
with the exception of the innermost shell, atoms are more stable when they have 8 electrons in their valence shell (outermost shell) This rule explains why atoms tend to form bonds, as they seek to achieve a full valence shell for stability.
Isotopes
different forms of elemts that have same number of protons but differing neutrons, alters atomic mass
Atomic Number
number of protons in nucleus, determines its identity (element)
atomic mass
calculated mean of mass for its naturally occuring isotopes + protons
electron shells
electron usually exists in the lowest energy shell available which is the closests to the nucleus
Chemical reactivity
the tendency of a substance to undergo chemical reactions, forming new substances, ability to combine and chemically bond with other elements or compounds.
Chemical Reactions
make and break bonds, reactants “react” together, start of reaction, products are “produced” end of reaction
Ions
atoms or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons.
Chemical bonds
attractions that keep atoms close together and form molecultes, protons and electrons attract like magnets
Covalent Bonds
chemical bonds that share a pair of electrons, strong bonds. Can be non-polar or polar
non-polar bonds (covalent)
the sharing of electrons is equal
polar bonds (covalent)
sharing of electrons is unequal, creates partial charges called poles
Ionic Bonds
One atom (anion) steals electron, other atom (cation) loses electron, strong bonds///NO SHARING///formed between ions with opposite charges
Cations
Positive ions formed by losing electrons
Anions
Negative ions formed by gaining electrons
Hydrogen bounds
form between poles of H and O in water molecules, weak bonds
Energy Laws
1st Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot be created or destroyed
@nd Law: reactions tend to increase disorder (make energy less available for cells)
Endothermic reactions
take energy
Exothermic Reactions
Release energy
Water Properties
3 states of being, solid is less dense than liquid, adhesion cohesion and surface tension, universal solvent, high specific heat, and evaporative cooling
About Water’s charges
charge on oxygen, contributing to water’s properties of attraction. Water’s charges are generated because oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, making it more likely that a shared electron would be found near the oxygen nucleus than the hydrogen nucleus, thus generating the partial negative charge near the oxygen. As a result of water’s polarity, each water molecule attracts other water molecules because of the opposite charges between water molecules, forming hydrogen bonds.
Adhesion
water molecules will stick to non-water molecules well
Cohesion
water molecules will stick to other water molecules
high specific heat
highest specific heat capacity/amount of heat one gram of substance must absorb or lose to change its temperature by 1 degree
heat of vaporization
amount of energy required to change one gram of a liquid substance to a gas
surface tension
cohesion allows for this, hard to break the surface of water, the capacity of a substance to withstand being ruptured when placed under tension or stress
Universal solvent
pretty much anything can disolve into water, substance capable of dissolving other polar molecules and ionic compounds
High specific heat
takes longer to increase the temperature of one unit o water than other molecules, highest in any liquid (water)
evaporation
turning liquid to gas/steam/etc///When the heat is raised as water is boiled, the higher kinetic energy of the water molecules causes the hydrogen bonds to break completely and allows water molecules to escape into the air as gas (steam or water vapor)///Even when below its boiling point, water’s individual molecules acquire enough energy from other water molecules such that some surface water molecules can escape and vaporize
ice and solidification of water
when the temperature of water is reduced and water freezes, the water molecules form a crystalline structure maintained by hydrogen bonding (there is not enough energy to break the hydrogen bonds) that makes ice less dense than liquid water, a phenomenon not seen in the solidification of other liquids. (ICE CAN FLOAT BC ITS LESS DENSE THAN WATER)///ice insulates lake so animals and plants are ok
acid
substance that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution (pH of <7)
base
provides hydrovide ions (OH-) or other negatively charged ions that combine with hydrogen ions, reuding their concentration in the solution and raising the pH
buffers
absorb excess H+ or OH-, manages pH level
organic molecule
any molecule containing carbon (can contain other molecules like oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen)
monomer
atoms or small molecules that bond together to form more complex structures such as polymers. there are 4 main types: sugars, animo acids, fatty acids, and nucleotides
carbohydraes
provides fast energy, has three types: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides (MADE OF carbon hydrogen and oxygen CHO)
monosaccharides
simple sugars (glucose, fructose, etc), number of carbons is usually 3-7
disaccharides
formed whn 2 mono- undergo a dehydration reaction (sucrose, lactose, maltose)
polysaccharides
long chain of mono- linked by glycosidic bonds (starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin)
glycogen
storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose (animal equivalent of starch)
cellulose
most abundant natural biopolymer, cell wall is mostly made of cellulose, provides structural support to the cell
lipids
energy storage, compounds that are largely non-polar, provides insulation, is hydrophobic (fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, steroids) ///MADE OF carbon hydro
phospholipids
major constituents of the plasma membrane
steroids
fused ring structure (ex. cholesterol which is sinthecized in the liver)
proteins
macromolecule that transports, stores, membranes (MADE OF AMINO ACIDS),formed when amino acids join together thru peptide bonds, unique sequence determines a proteins structure and function
enzymes
produced by livign cells, catalysts in biochemical reactions like digestion
hormones
chemical signaling molecules secreted by endocrine cells that act to control or regulate specific processes
protein types and functions
digestive - amylase, lipase, pepsin, trypsin - help digestion of food by catabolizing nutrients into monomeric units
transport - hemoglobin, albumin - carry substances in blood or lymph thruout body
structural - actin, tubulin, keratin - constructs structures like cytoskelton
hormones - insulin, thyroxine - coordinate the actiivty of different body systems
defense - immunoglobins - protect the body form foreign pathogens
contractile - actin, myosin - effect muscle constraction
storage - legume storage proteins, egg white - provide nourishment in eary development of embryo and the seedling
denaturation
changes in pH, temperature and exposure to chemicals leading to permanent changes in the shape of the protein leading to loss of function
animo acids
monomers that make up proteins, there are 20, each has fundamental structure (central carbon atom bonded to amino group, carbozyl group, and hydrogen atom - also has another atom or group of atoms bonded to the central atom known as the R group
peptide bond
bonds amino acids together by a covalent bond, formed by a dehydration reaction, creates peptides…then those make polypeptides
protein structure
primary: unique sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
secondary: folding of polypeptide in some regions (a helix and b pleated sheet)
tertiary: 3d structure of a polypeptide
quarternary: subunits form this
nucleic acids
function: information storage and blueprint for functioning of a cell, made of nucleotides, 2 types: DNA and RNA
nucleotides are made of…
phosphate group, a sugar (deoxyrubose in dna or ribose in RNA), and a nitrogenous base
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid RNA
genetic material found in all living organisms, found in the nucleus of eukaryotes and in the organelles, chloroplasts, and mitochondria. in prokaryotes DNA is NOTE enclosed in membrainous envolope
mRNA
intermediary used to communicate with the DNA and rest of the cell
RNA
mostly involved in protein synthesis
nucleotide
makes up DNA and RNA, can form a polynucleotide
Nitrogen Bases in nucelides and DNA
Adeinine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine, thymine (T) Paris: A + T, G + C
RNA
4 types: messenger RNA mRNA: carries message to DNA, ribosomal RNA (rRna): major constituant of ribosomes on which the mRNA binds proper alignment of the mRNA and ribsomes, transfer RNA tRNA: carries correct amino acid to site of protein synthesis, and microRNA miRNA
transcription
DNA info is copied into a messenger
translation
RNA dictates the structure of protein, process where a cell uses the genetic info carried in mRNA to synthesize proteins
mrmbranes
boundary b/w inside of cell and surroundings, selectively permeable, phospholipid bilayer w/ proteins, other lipids, hybrid molecules
membrane transport (passive and active)
passive: diffusion across membraine; no energy required; somtimes need “doorway”protein with is in membrane
active: movement across membrane requiring energy and “doorway” protein
diffusion (passive transport)
movement of molecules from higher to lower concentrations, each mole moves randomly, no energy needed
osmosis
passive, diffusion of water across membraine from high to low concen.
faciliated diffusion
difussion w/ help of “doorway” proteins
active trans
require energy and doorway protein, useful for moving molecules against their concentration gradients
bulk transport (active)
large moles can pass thru membrane, so uses exocytosis or endocytosis
exocytosis
leaving cell thru vesciles
endocytosis
entering cell thru vesicles
prokaryotic cells
bacteria and archaea, most ancestral living things, simple mostlysingle celled organism that lacksanucleus
plasmamembrane
and cytoplasm,
DNA
ribosomes
NO nucleus or organelles
eukaryotes
animals, fungi, plants, protozoans, evolved from prokaryotes,
membrane bound nucelus
membrane bound organelles
rod-shapped chromosomes
origin of life
3.5 million years ago, bacteria and similar organisms were first, evolution of life
simple organic molecules
some moles able to replicate themselves
membranes, cell division
metabolism
many lines of evidence of common ancestry: cell membranes, metabolism, DNA, fossils
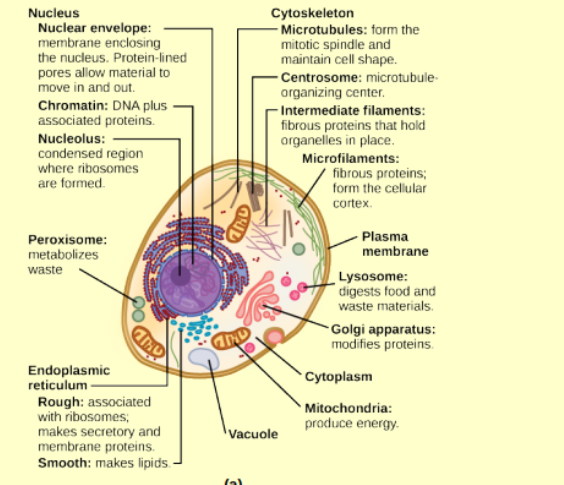
cell structure (animal)
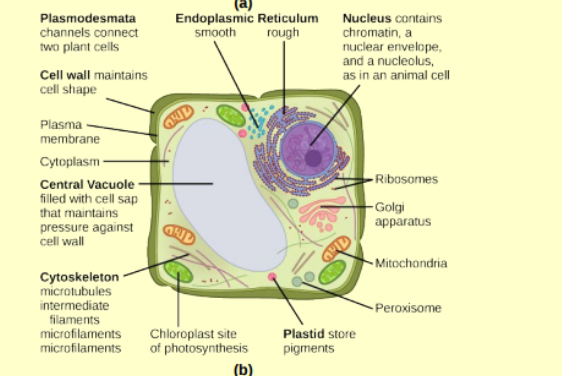
cell structure plant
plasma membrane
in both pro and euk, phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates the internal contents of the cell from its surrounding environments
cytoplasm
entire region of a cell between the plasma membrane end the nuclear envelope
nucleus
membrane bound organelle containing genetic material, double membrane structure with nuclear pores///controls cell activites by regulating gene expression, DNA replication, transcription, and synthesis of rRNA
nuclear envelope
double membrane structure that constitues the outermost portion of nucleus
nucleoplasm
semi-solid fluid inside nucleus where the chromatic and nucleoius are
chromosomes
structures within the nucleus that are made of DNA (humans have 46)
chromatin
unwound protein-chromosome complexes
ribosomes
cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis
mitochonrdria
responsible for making ATP which is cells main energy carrying molecule
peroxisomes
small round organelles that carry out oxidation reactions that break down farry acids and amino acids, detoxyfy many poisons
vesicles and vacuoles
membrane bound sacs that function in storage and transports
animal vs plant cell
animal:
-cnetrioles associated with MTOC: a complex called the centrosome, have centrosome and lysosomes
plant:
-cell wall, chloroplasts and other plastids, large central vacuole
centrosome
microtubule organizing center foundnear the nuclei of animal cells, function not clear
lysosomes
cell’s garbage disposal, enzymeswithin lyso aid in the breakdown of proteins, polysacc, lipids, mucleic acids, and organelles
cell wall
rigid covering that protects the plant cell, provides support, and gives shape to cell