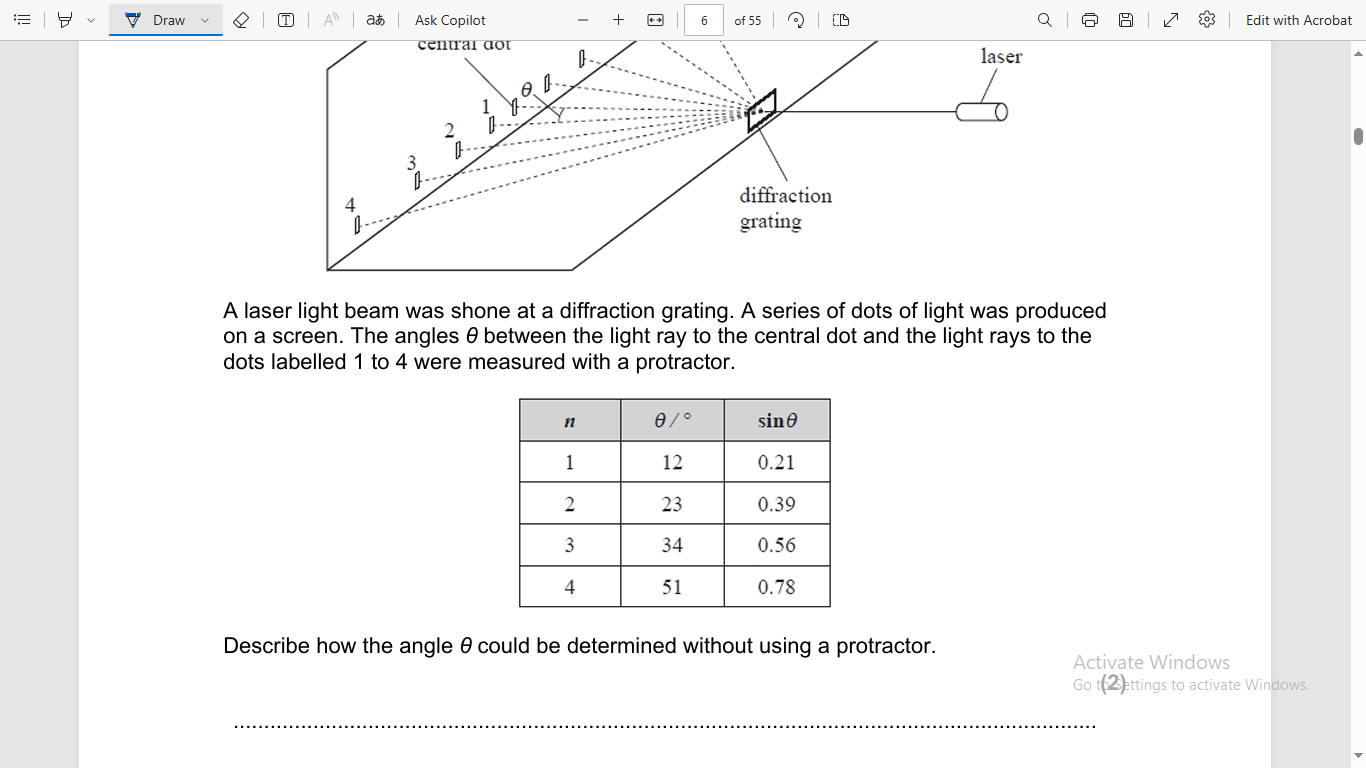
Interference and diffraction
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
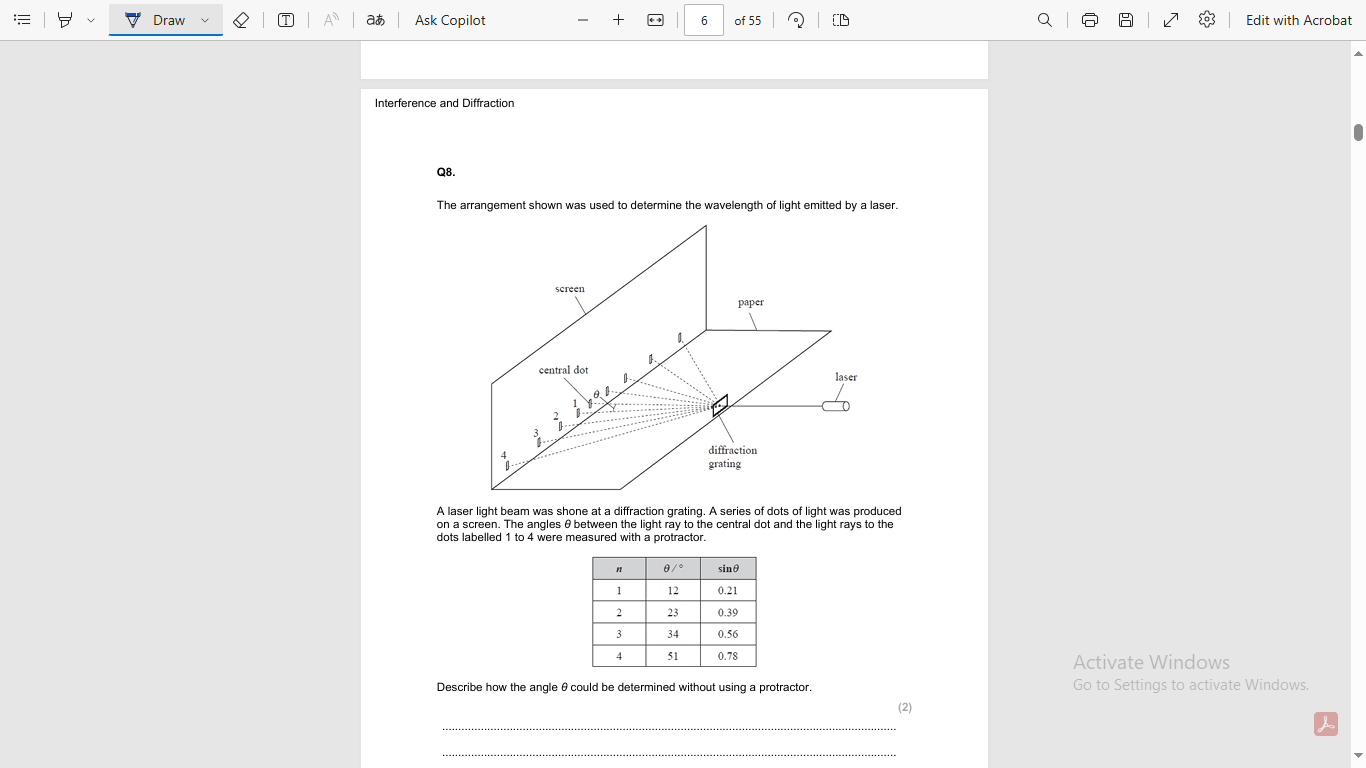
measure larger angle
to reduce percentage uncertainty
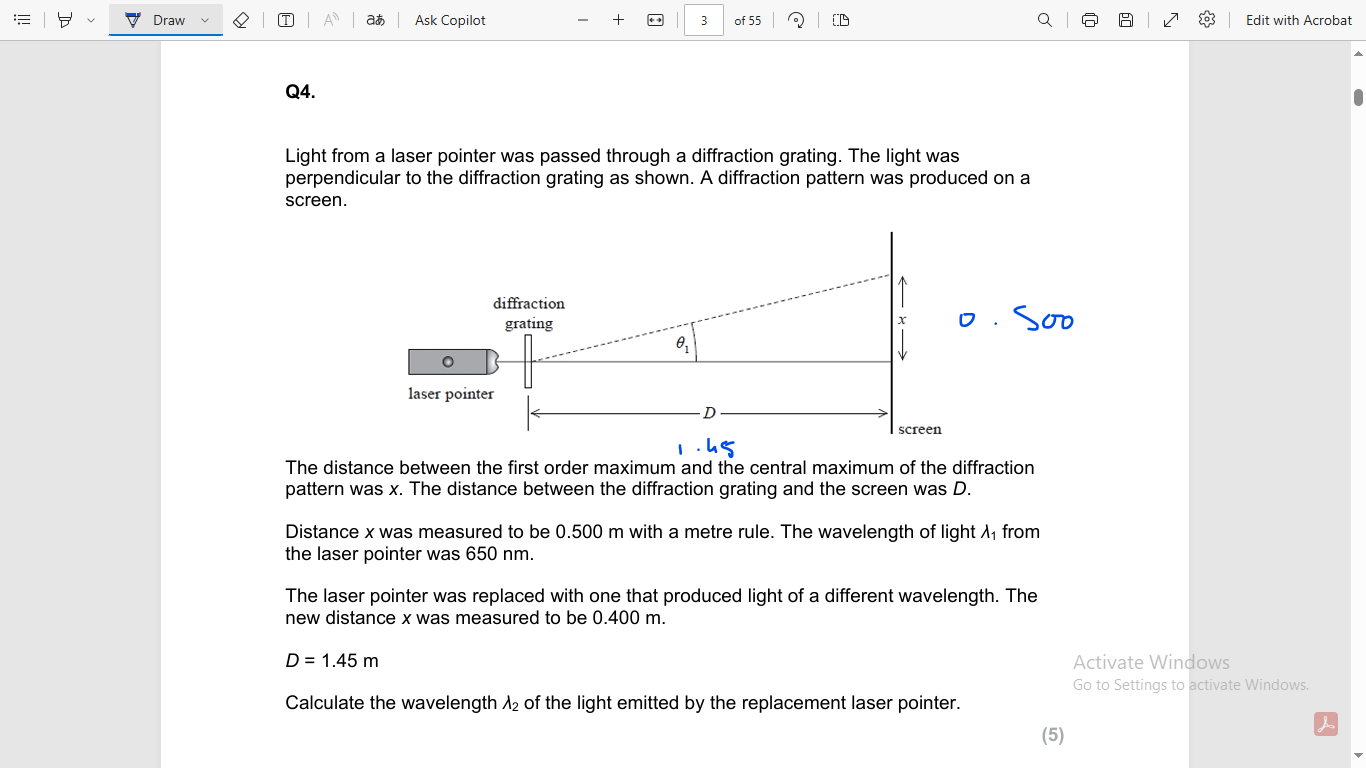
d sin θ = nλ
sin 0.500 / 2 = 19
19 x sin 0.400
5.29
measure distance of grating to screen (l)
and from centre to dot (x)
tan θ=x/l
gradient
gradient=d/λ
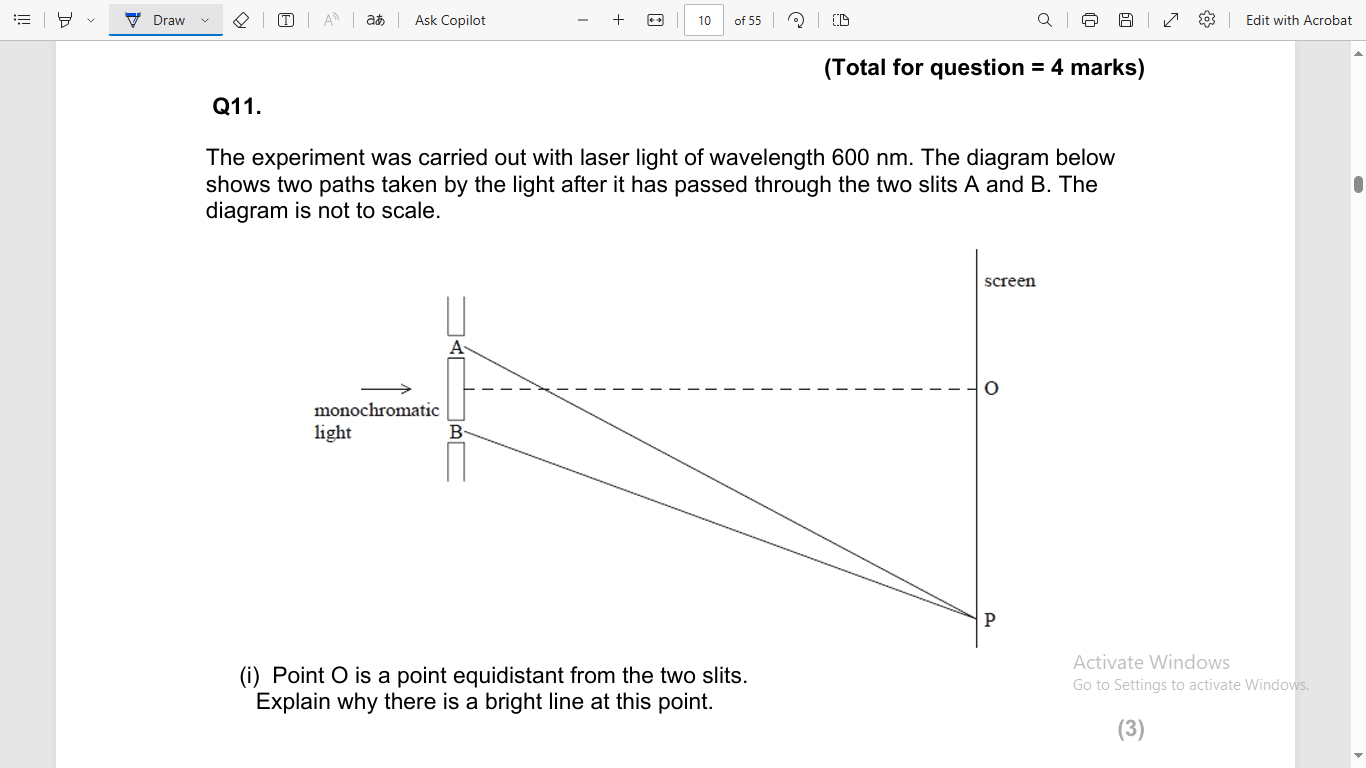
path difference is zero
phase difference is zero
so superposition takes place
diffraction grating
set up grating parallel to screen
measure distance between grating and screen
measure the distance between 1st order images on the screen
how diffraction pattern is created
waves passing through a narrow gap spread out
light reaches the wall from each part of the slit with differing wavelengths
when waves meet constructively interfere if in phase so brighter region is seen
red v green wavelength
red has longer wavelength than green
means red diffracts more
more dark points would be closer to the centre

diffraction occurs when light is reflected from cd surface
each ring on cd acts as a diffraction centre scattering light in all directions
interference occurs
in directions in which there is a path difference equal to a whole number of wavelengths and constructive interference occurs
white light is a range of wavelengths
hence each wavelength of light reinforces in a different direction which explains why a spectrum is seen
coherent waves monochromatic
coherent waves have a constant phase relationship
coherent waves have the same frequency
however for each frequency present the two reflected wavelengths are coherent
with a non chromatic source a set of dark rings for each frequency would be produced
hence with a white light source you would see a set f coloured rings
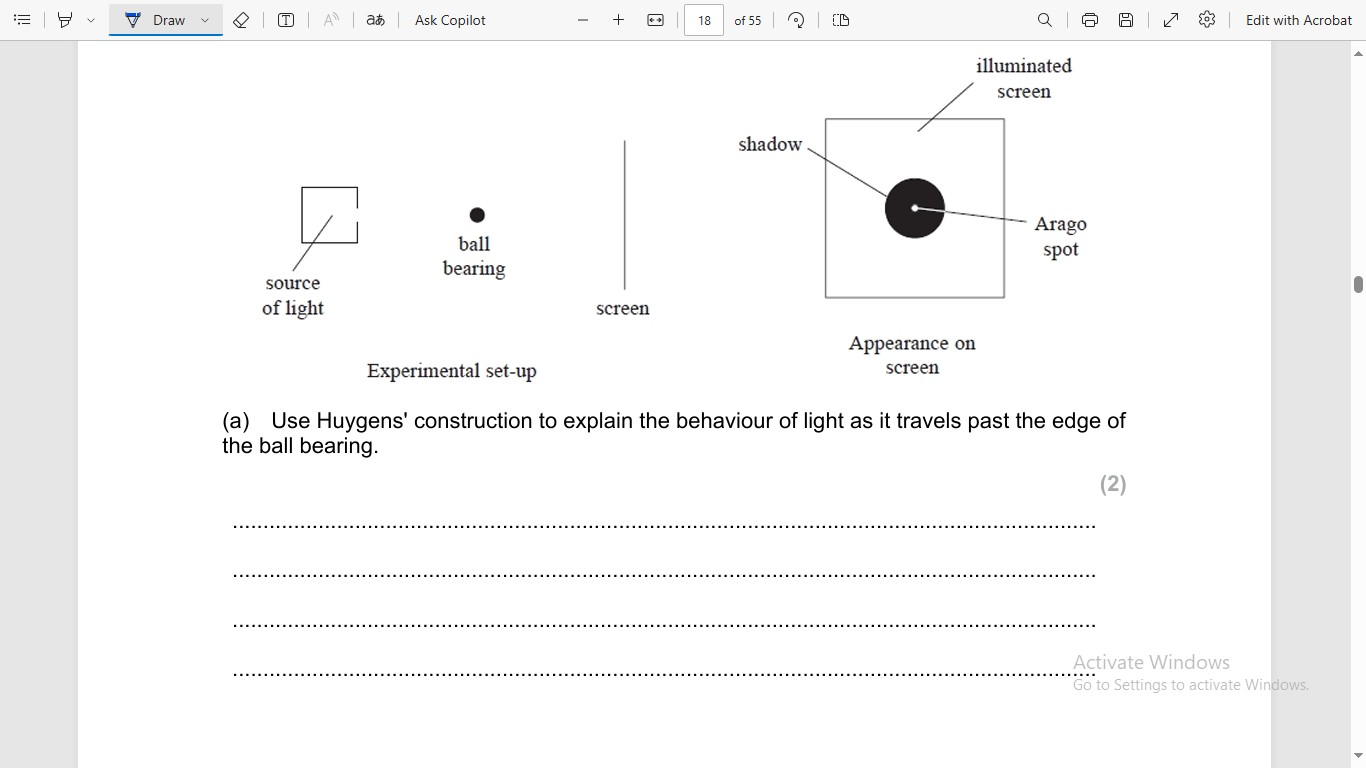
light is diffracted
each point on the wave front acts as a source for secondary wavelets
Huygens construction through gap
wave spreads out
each points acts as a secondary source for wavelets
they superpose
constructive interference
in phase
max intensity
path difference = nλ
destructive interreference
anti phase
min intensity
path difference=(n+1/2)λ
wavefront
line joining points on a wave that are in phase
why monochromatic light is important in diffraction experiments
emits small range of wavelengths
so smaller variation at each angle
produces a clearer interference pattern

wave and reflection will meet and superposition will take place
where in antiphase destrucive interference takes place
minimum amplitude at nodes so mice wont hear
waves also arrive from other surfaces
complete cancellation unlikely
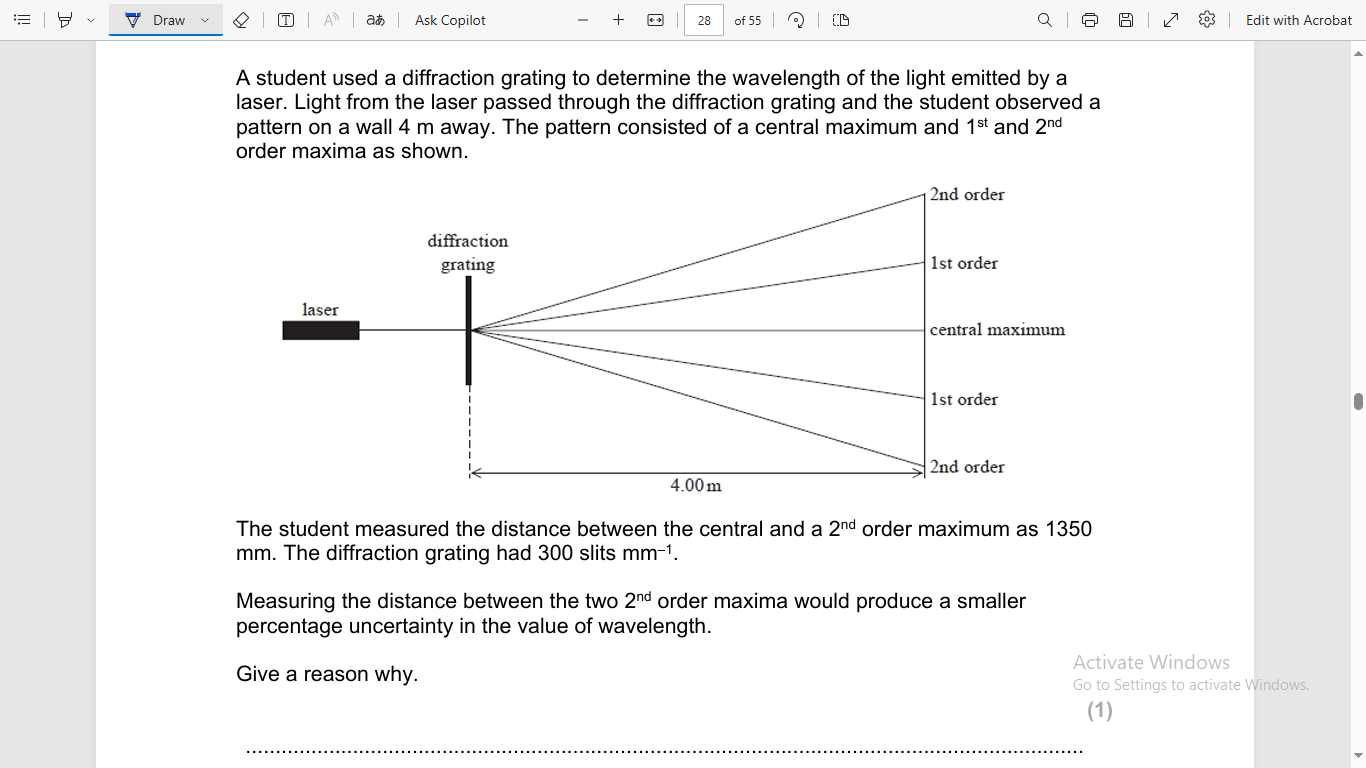
resolution would be same but distance measured would be greater
coherent
constant phase relationship
superposition
two or more waves meet
the resultant displacement at a point is the sum of individual displacements from the individual waves
why x model was accepted
-provided experimental evidence
-supported previous evidence
-can be repeated by others