Barrons AP Psychology Flashcards ALL
1/277
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
278 Terms
memory
learning that has persisted over time
information-processing model
- model of memory
- also called the three box model
- involves the sensory memory, short-term/working memory, long-term memory, and the processes of encoding and retrieval
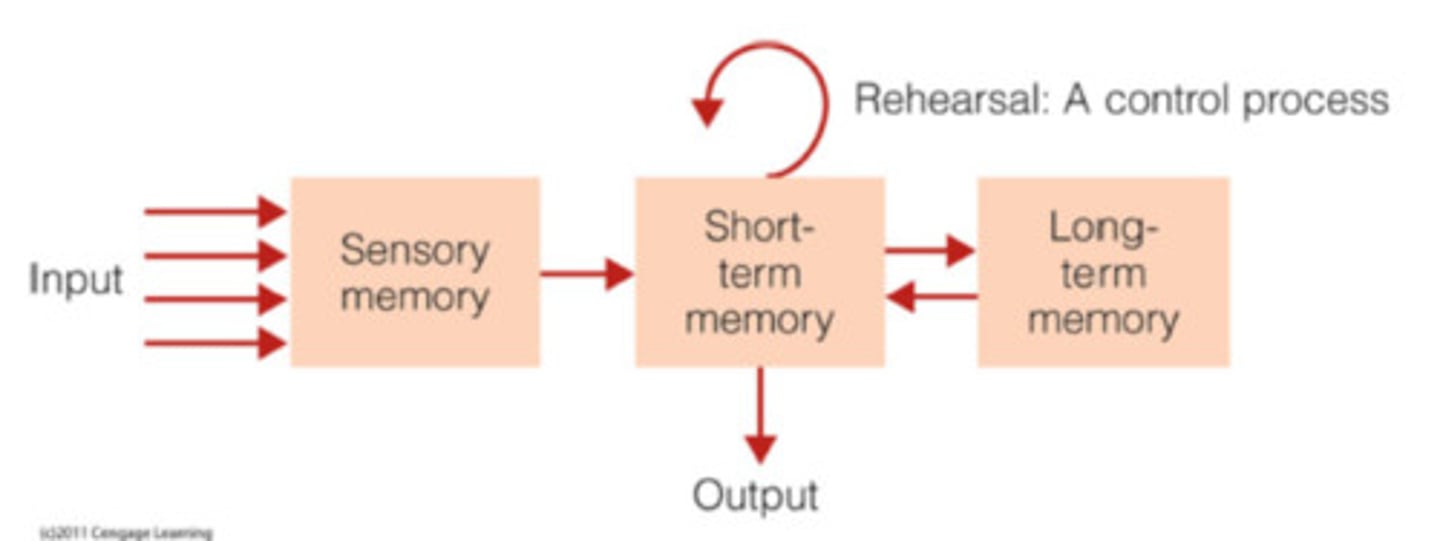
sensory memory
split-second holding tank for incoming sensory information
- encoded to short-term memory based on selective attention
types: iconic and echoic
iconic memory
type of sensory memory where a split-second photograph of a scene is temporarily in your minds eye
echoic memory
a 3-4 second sensory memory for sounds
short-term/working memory
the memories we are currently working with and are aware of in our consciousness
- temporary; lasting 10-30 seconds
mnemonic devices
memory aids (like chunking)
long-term memory
essentially unlimited storage space of memories in the mind
- formats: episodic, semantic, and procedural
episodic memory
memories of specific events, stored in sequential series of events
semantic memory
general knowledge of the world, stored as facts, meanings, or categories rather than sequentially
procedural memory
memories of skills and how to perform them

explicit memories (declarative memories)
conscious memories of facts or events we actively tried to remember
implicit memories (nondeclarative memories)
unintentional memories that we might not even realize we have
levels of processing model
model of memory that explains why we remember what we do by examining how deeply the memory was processed or thought about
- sees memories as deeply or shallowly processed
retrieval
getting information out of memory so we can use it
recognition
type of retrieval; process of matching a current event or fact with one already in memory
- multiple choice test
recall
type of retrieval; retrieving a memory with an external cue
- short answer question
primacy effect
predicts that we are more likely to recall items presented at the beginning of a list
recency effect
demonstrated by our ability to recall the items at the end of a list
serial position effect
- when recall of a list is affected by the order of items in a list
- primacy and recency effect
-researched by Hermann Ebbinghaus

tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon
temporary inability to remember information --> partially explained by the semantic network theory
semantic network theory
memory theory that states our brain might form new memories by connecting their meaning and context with meanings already in memory, creating a web of interconnected memories
flashbulb memories
a vividly clear memory of emotionally significant moment or event
- possibly explained by the semantic network theory --> the event was important so we also encode the context of the event
- Sept 11th 2001

mood-congruent memory
the greater likelihood of recalling an item when our mood matches the mood we were in when the event happened
state-dependent memory
the phenomenon of recalling events encoded while in a particular states of consciousness
decay
forgetting because we do not use a memory or connections to a memory for a long time
interference
when other information in your memory competes with what you are trying to recall
- two types: proactive and retroactive
proactive interference
older information learned previously interfering with the recall of information learned more recently
forward acting interference
retroactive interference
when learning new information interferes witht he recall of older information
backwards acting interference
anterograde amnesia
caused by damage to the hippocampus
- inability to create new memories
long-term potentiation
the idea that neurons can strengthen connections between each other through repeated firings, leading to long-term memory
phonemes
the smallest units of sound used in language
morphemes
the smallest unit of meaningful sound in language
syntax
the grammar of a language; how words are used in a particular organized manner
stages of language aquisition
babbling --> holographic --> telegraphic
overgeneralization
the tendency to combine words with improper syntax in young children
"He hitted my head so I throwed the truck at him"
critical period
a window of opportunity during which we must learn a skill or our development will permanently suffer
typically applied to learning language
concepts
cognitive rules we apply to stimuli from our environment that allow us to categorize and think about the things we encounter
prototype
what we think is the most typical example of a particular concept
algorithm
a rules that guarantees the right solution by using a formula or other foolproof method
heuristic
a rule of thumb - a rule that is generally, but not always, true that we can use to make a judgement
availability heuristic
judging a situation based on examples of similar situations that easily/initially come to mind
representativeness heuristic
judging a situation based on how similar the aspects to prototypes the person holds in his or her mind
belief perserverence
our tendency to maintain a belief even in the face of contradictory evidence
rigidity (mental set)
the tendency to fall into established thought patterns; using solution or past experience to try and solve novel problems
functional fixedness
example of rigidity where people have an inability to see a new use for an object
confirmation bias
tendency to look for evidence that confirms our beliefs and ignore evidence that contradicts what we think is true
framing
the way a problem is presented that can drastically change the way we view our ability to solve it
convergent thinking
thinking pointed towards one solution
divergent thinking
thinking that searches for multiple possible answers
motivations
feelings or ideas that cause us to act toward a goal
Robert Rescorla
revised the Pavlonian model of learning to include more cognitive, circumstantial factors

Albert Bandura
conducted the Bobo Doll experiments that showcased observational learning
- cognitive learning scientist

instincts
automatic (inborn) behaviors performed in response to specific stimuli
drive reduction theory
the theory that our behavior is solely motivated by biological needs and resulting drives
homeostasis
a balanced internal state emphasized by the drive-reduction motivation theory
arousal theory
motivation theory that states we seek an optimum level of excitement/arousal
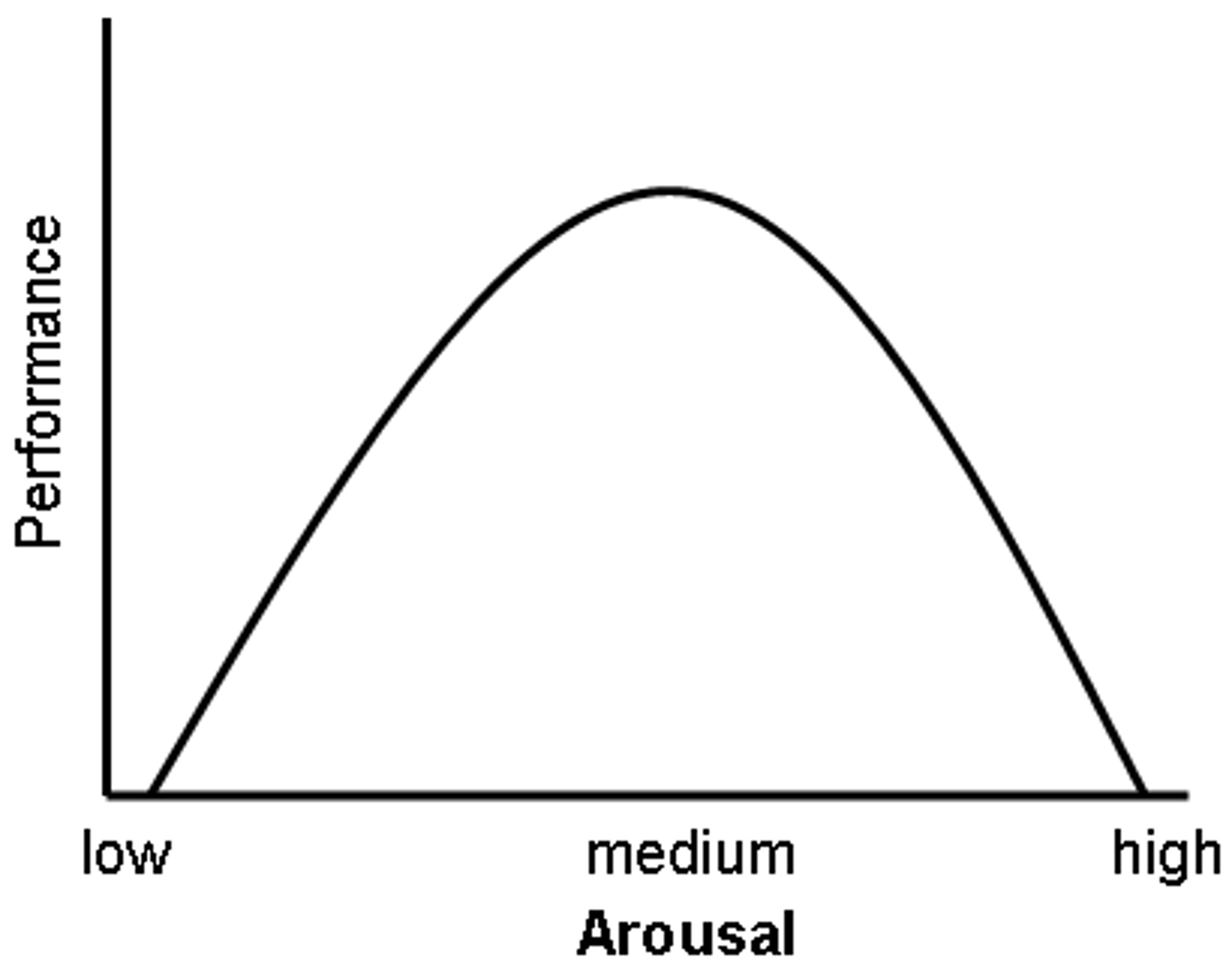
Yerkes-Dodson Law
the concept that we perform best with an optimum level of arousal, which varies with different activities and difficulty levels
opponent-process theory of motivation
theory of motivation which states that people have a baseline state that motivates us to perform behaviors that keep us at that baseline
incentives
stimuli that we are drawn to due to learning and positive/negative associations
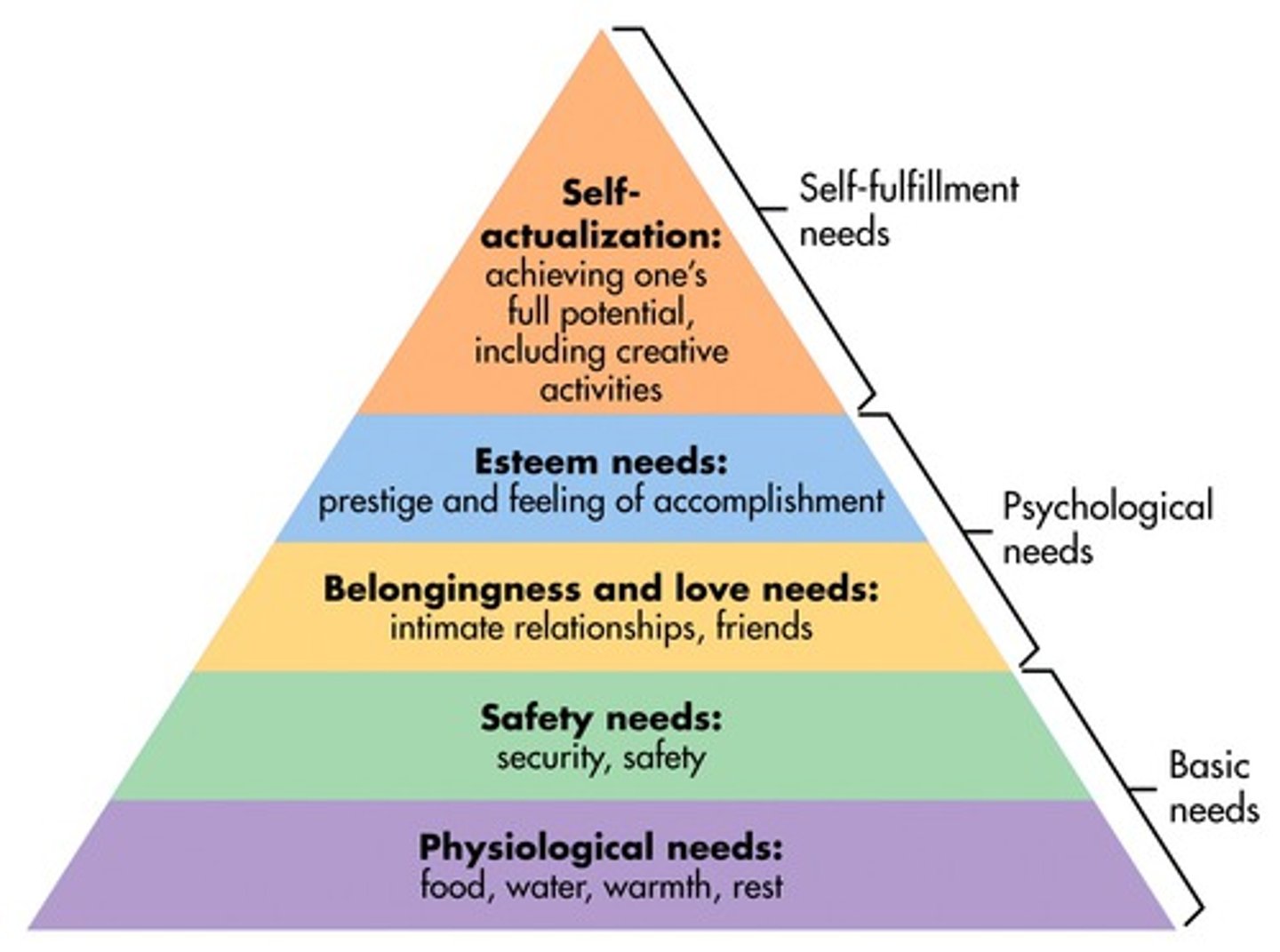
Maslow's hierarchy of needs
predicts which needs we will be motivated to satisfy first
created by Abraham Maslow
survival/safety --> emotional needs (love/self esteem) --> satisfaction and self-actualization
lateral hypothalamus
hunger center of the brain
causes feelings of hunger
ventromedial hypothalamus
part of the hypothalamus that causes an animal to stop eating
set-point theory
describes how the hypothalamus controls our hunger and metabolic rate
- everyone has a "set point" weight that our brain helps us maintain (more or less)
bulimia
eating disorder characterized by eating large amounts of food in a short period of time (binging) and then getting rid of the food (purging)
- tend to stay around their average weight or even above
anorexia
eating disorder characterized by starving oneself and refusing to eat because of an obsession with weight
obesity
eating disorder characterized by a BMI over 30 (being severely overweight)
achievement motivation
theory that explains why some are constantly motivated to challenge themselves, master complex tasks, reach personal goals, and figure out the world
extrinsic motivation
motivation to reach a goal based on the external rewards (money, prizes, recognition, etc)

intrinsic motivation
motivation to reach a goal based on your personal, internal drive to succeed or want for enjoyment and satisfaction

approach-approach conflict
conflict that occurs when you must choose between two desirable outcomes
avoidance-avoidance conflict
conflict that occurs when you must choose between two unattractive outcomes
approach-avoidance conflict
conflict that occurs when one event or goal has both attractive and unattractive features
multiple approach-avoidance conflicts
conflicts in which you must choose between two or more things, each of which has both desirable and undesirable features
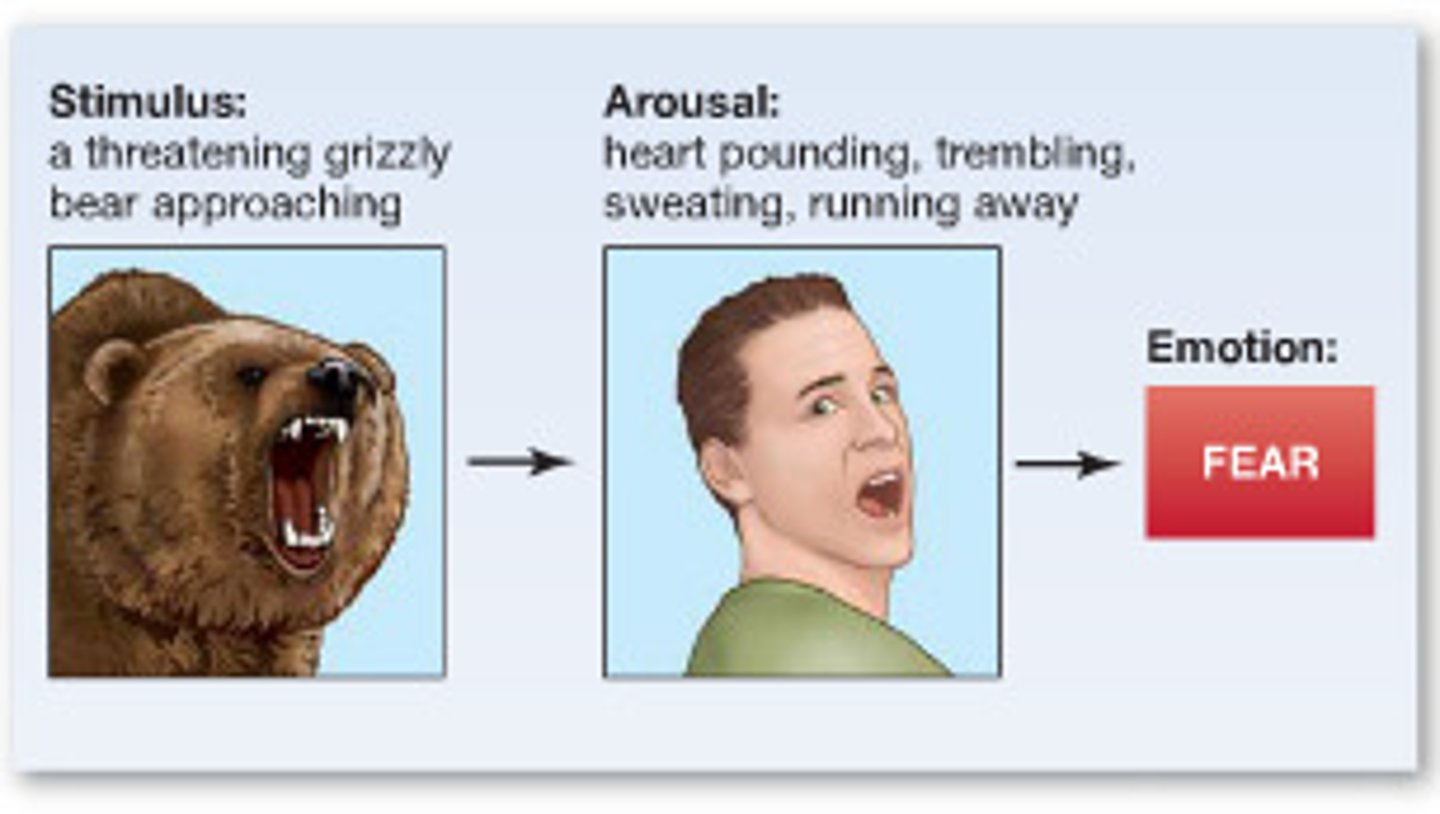
James-Lange theory of emotion
theory of emotion that stated we feel emotion because of biological changes caused by stress
stressor --> biological action --> emotion
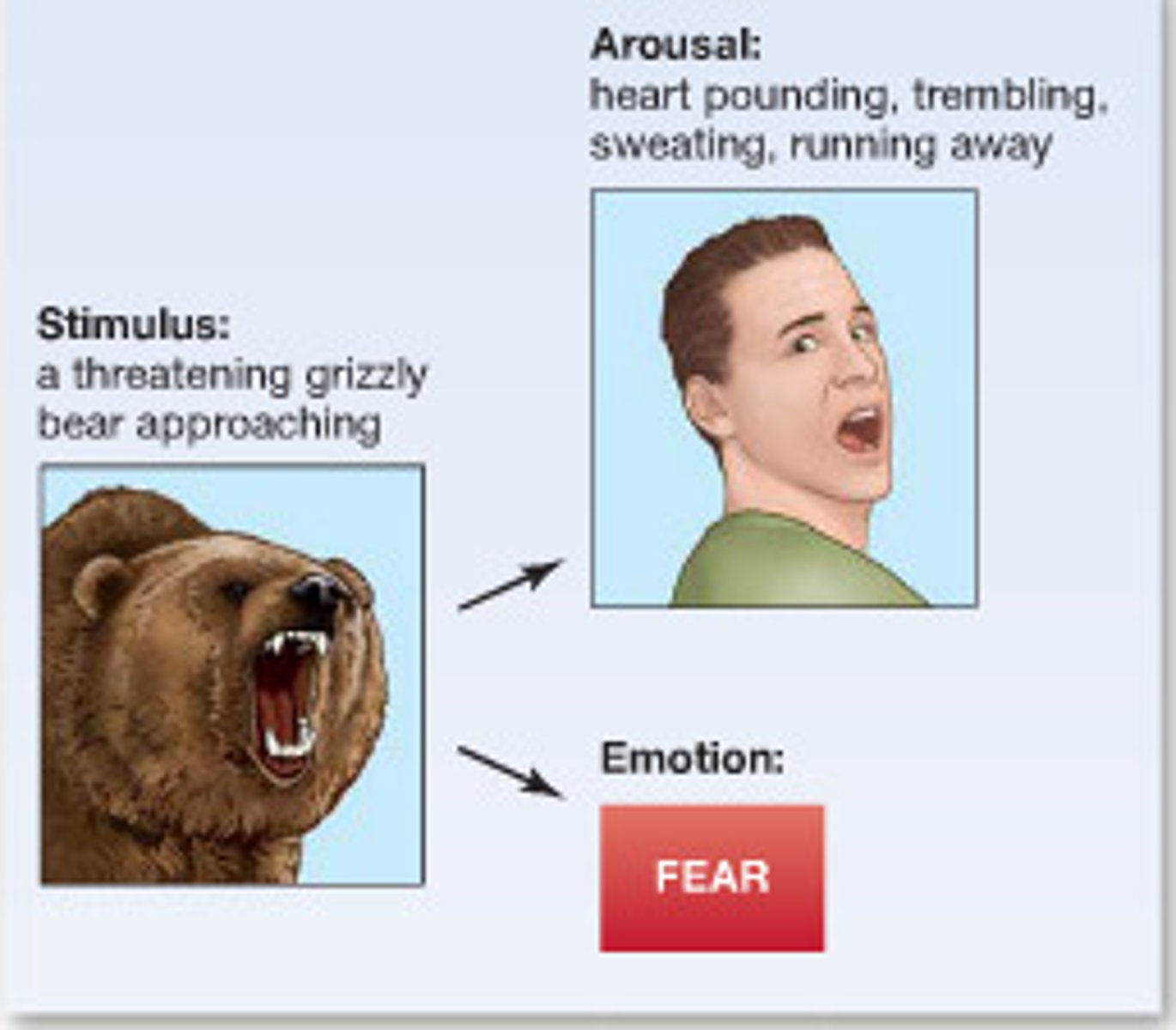
Cannon-Bard theory of emotion
theory of emotion that theorized the biological change and the cognitive awareness of an emotional state occurs simultaneously
stressor --> emotion AND biological action
two-factor theory
theory of emotion that demonstrates how emotion depends on the interaction between two factors: biology and cognition
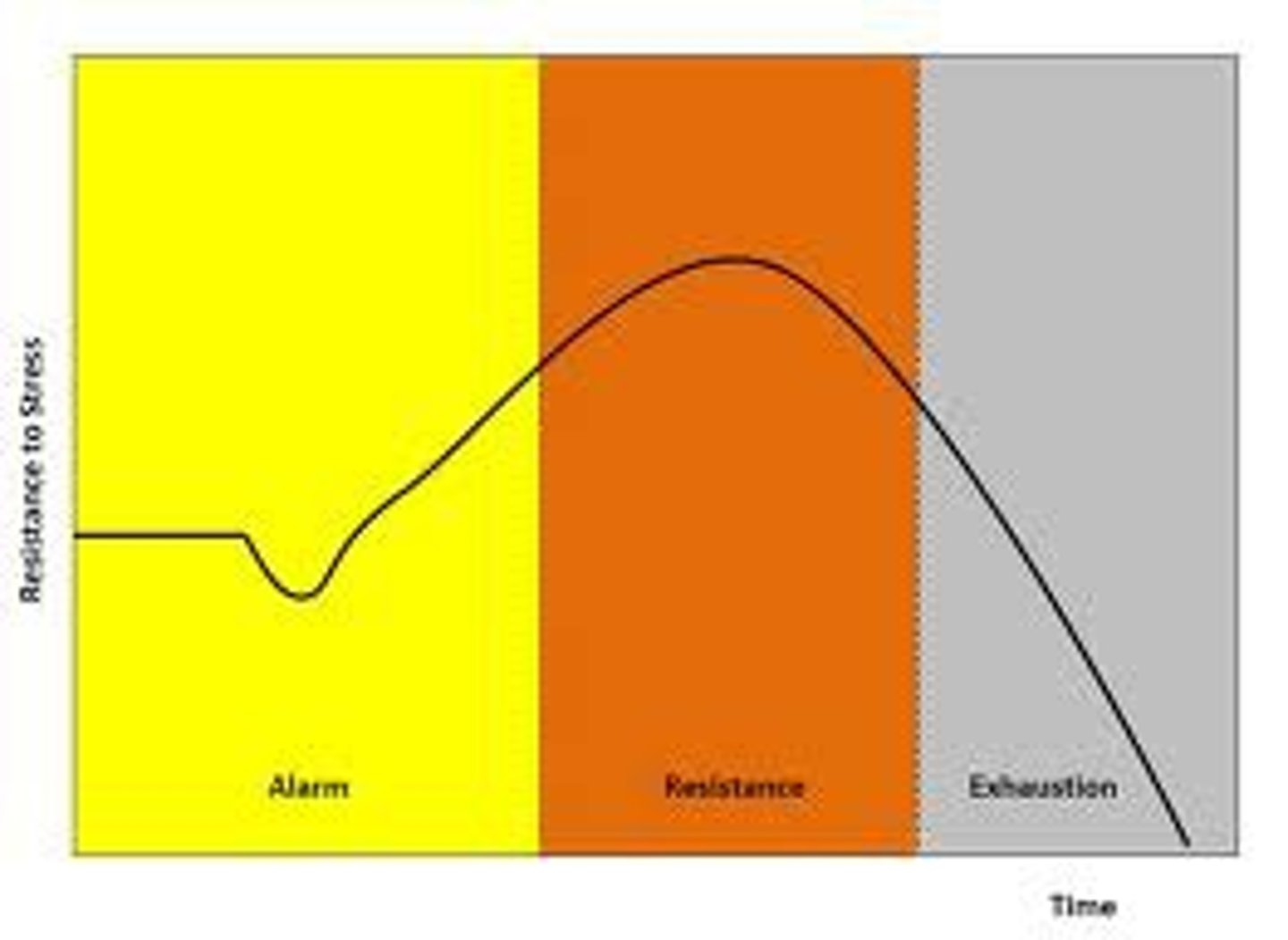
General adaptation syndrome (GAS)
describes the general response animals (including humans) have to a stressful event
alarm reaction --> resistance --> exhaustion
developmental psychologist
psychologists that study how our behaviors and thoughts change over our entire lives (from birth to death)
nature vs nurture
debate evaluating the influences of genetic factors and environmental factors on development

cross-sectional research
type of research common in developmental psychology that uses participants of different ages to compare how certain variables may change over the life span

longitudinal research
type of research common in developmental psychology that examines one group of participants over time

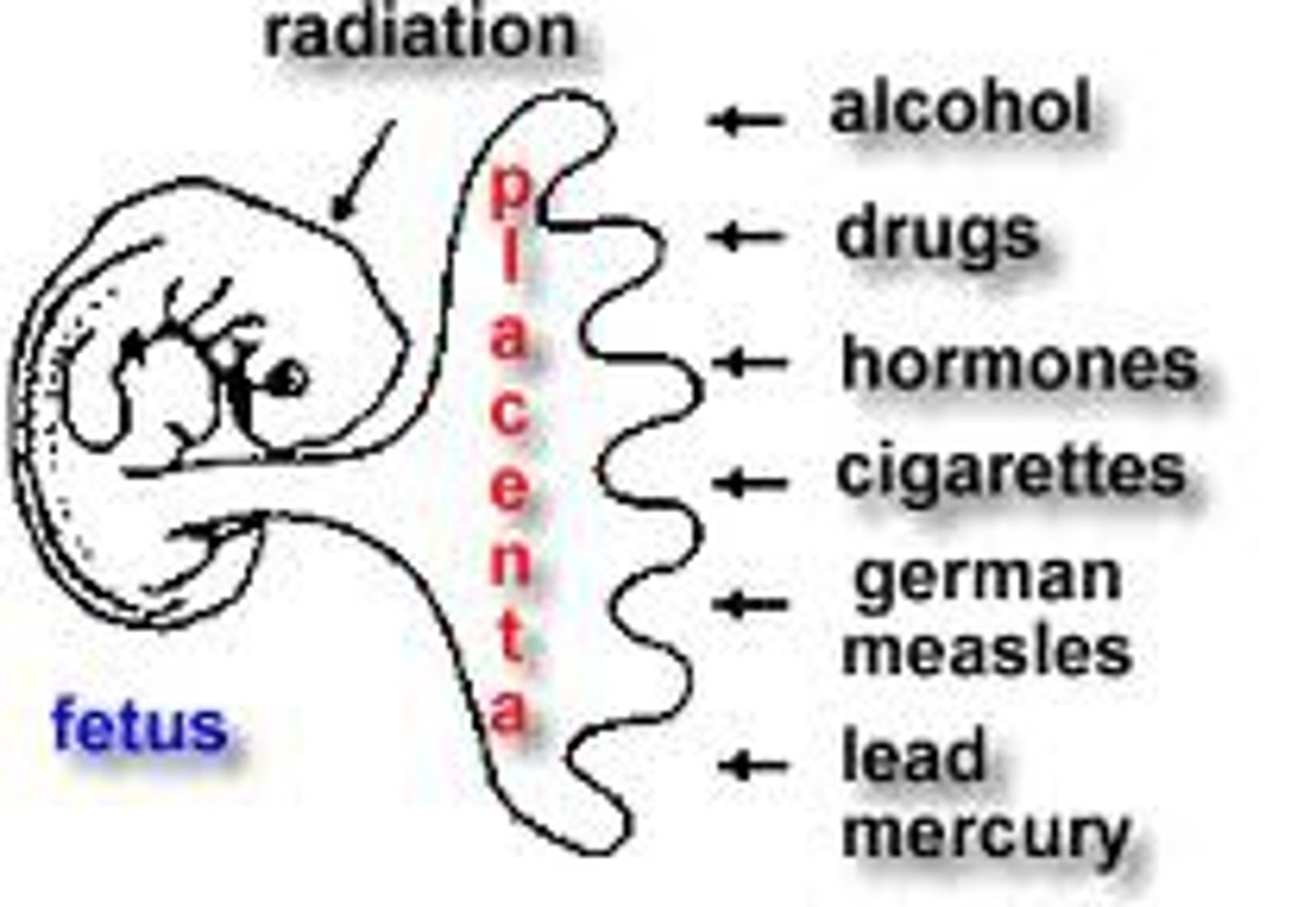
teratogens
certain chemicals or agents that can cause harm to the fetus if ingested or contracted by a pregnant mother
fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)
displayed by children of mothers who drink heavily during pregnancy, small, malformed skulls and intellectual disability are symptoms

newborn reflexes
specific, inborn automatic responses to certain specific stimuli
- rooting reflex, sucking reflex, grasping reflex, moro reflex (stretching out body and arms), Babinski reflex (spreading toes when foot is touched)

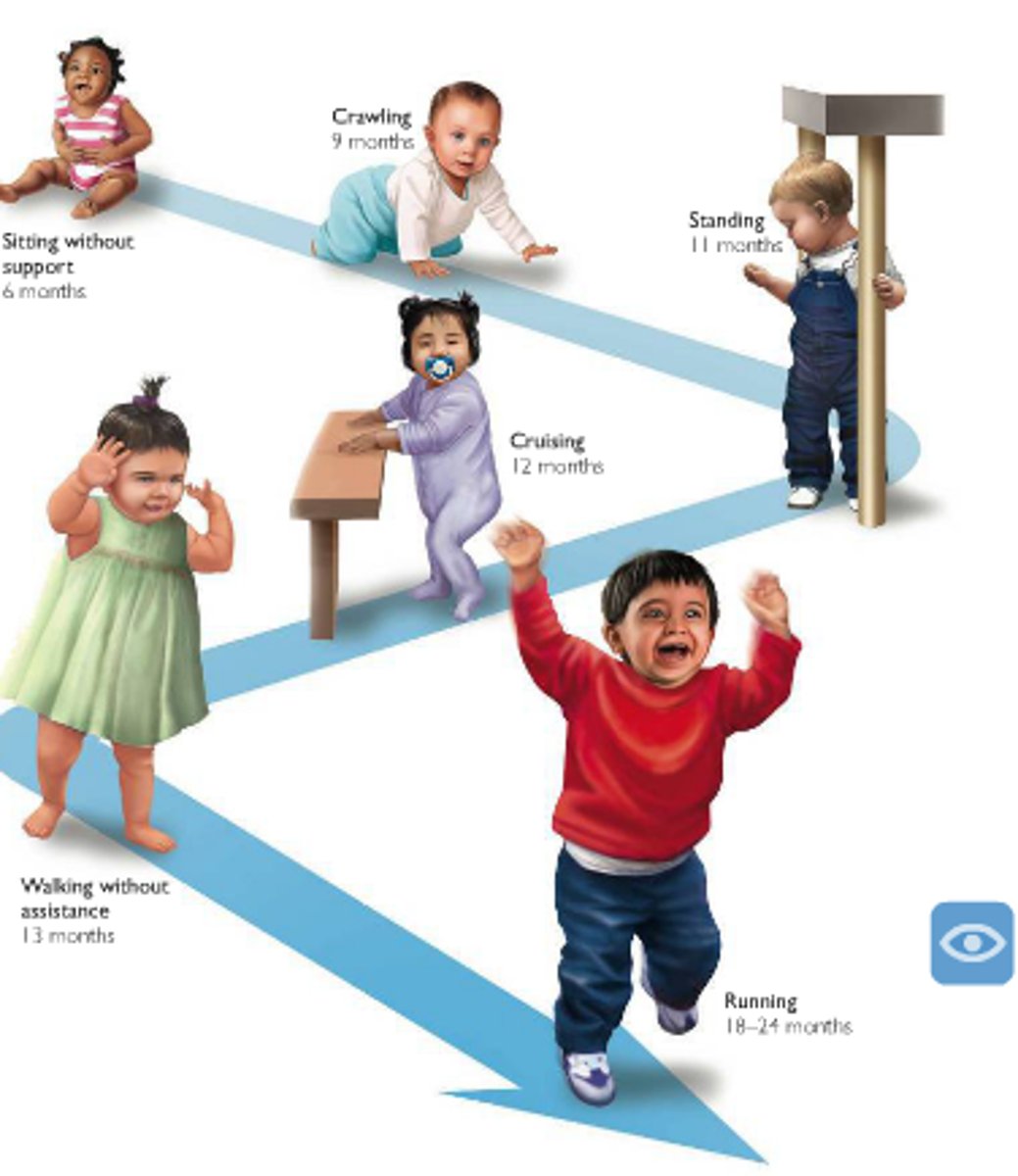
sequence of motor development
all human children follow the same basic motor skills in the same sequence (though the timing of each one may differ from person to person)
- roll over --> sitting up --> standing --> crawling --> walking
attachment
reciprocal relationship between caregiver and child
- affects development and emotional security
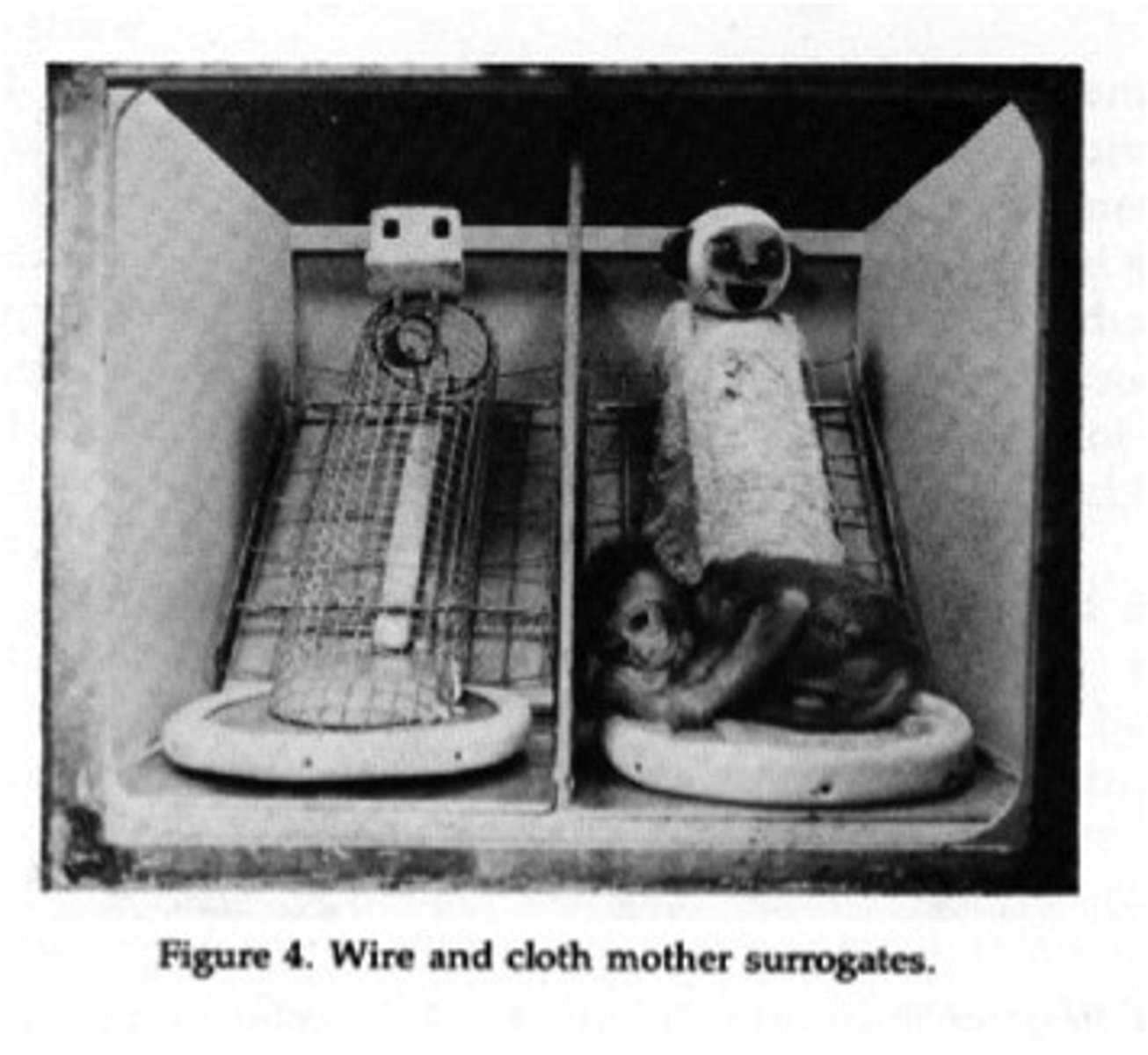
Harry Harlow's attachment research
- research conducted with baby monkeys that displayed the importance of physical comfort in establishing a secure attachment
- displayed the importance of a secure attachment to developing confidence and curiosity

Mary Ainsworth's strange situation
- research conducted with babies and their parents to show the different types of attachment
- parents would leave the room and come back to see the reaction of their children
secure attachments
in Mary Ainsworth's experiment; infants confidently explored their novel environment while the parents were present, were mildly distressed when they left, and were glad when their parent's returned
avoidant attachments
in Mary Ainsworth's experiment; infants who resisted being held by the parents and explored the novel environment, and did not go to their parents for comfort when they returned
anxious/ambivalent attachments
in Mary Ainsworth's experiment; infants who had ambivalent reactions to their parents, showing extreme stress when the parents leave but resisting comfort once they return
authoritarian
parenting style with low warmth and high control
- children are more likely to be distrusting and withdrawn from peers
permissive
parenting style with high warmth and low control
- children are more likely to have emotional control issues and be dependent on others
authoritative
parenting style with high warmth and high control
- produces the most socially capable and academically successful children
continuity vs discontinuity
the debate evaluating if we develop continually, at a steady rate from birth to death, or discontinuously, with some periods of rapid development and relatively little development
stage theories
- discontinuous theories of development
- Freud's psychosexual model, Erik Erikson's psychosocial stage theory, Jean Piaget cognitive development theory, Lawrence Kohlberg's moral development theory
fixated (fixation)
- related to Freud's psychosexual model
- becoming preoccupied with the behaviors associated with specific stage
- if we fail to resolve a significant conflict in our lives during of the the psychosexual stages, we could become ____________.
oral stage
- 1st stage of Freud's psychosexual model
- infants seeking pleasure through their mouths
- associated problem: overeating, smoking

anal stage
- 2nd stage of Freud's psychosexual model
- develops during toilet training
- associated problem: retentive (controlling) or expulsive (out of control) behaviors