Day 3
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Energy
The capacity to do work.
Power
The rate at which energy is flowing.
What does 1 W equal?
1 J/s
What does 1 Hp equal?
740 W
Internal Energy
How fast the atoms and molecules in the object are moving.
Temperature
A measure of the internal energy of an object.
Unit conversion from Celsius to Kelvin
K = C + 273.15
Photons
Small discrete packages of energy.
Wavelength
Characteristic size.
Visible
Seen with the human eye.
Infrared
Beyond the red end of the visible spectrum.
Ultraviolet
Wavelength is beyond the violet end of the visible spectrum.
Blackbody
Idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation.
Wien’s Displacement Law
Relationship between an object’s temperature and the peak of its emission spectrum.
Wien’s Displacement Law Formula
λmax = 2897/T
T = Temperature (K)
λmax = Wavelength of the peak of the emission spectrum (µ)
Stefan-Boltzmann Equation
Relationship between the total power radiated by a blackbody and temperature.
Stefan-Boltzmann Equation Formula
P/a = σT4
P/a = Power emitted by a blackbody unit of surface area (W/m2)
σ is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant, σ = 5.67 x 10 -8 W/m2/K4
T = Temperature (K)
What happens to internal energy and temperature when Ein > Eout?
Increases
What happens to internal energy and temperature when Eout > Ein?
Decreases
What happens to internal energy and temperature when Eout = Ein?
Not changing
Grey Body (still an approximation)
A real-world object that, like a blackbody, has a spectral distribution of radiation that is a constant fraction of a blackbody's radiation at the same temperature, but that fraction is always less than one, making it an imperfect emitter.
Where in the EM spectrum is the visible range?
C
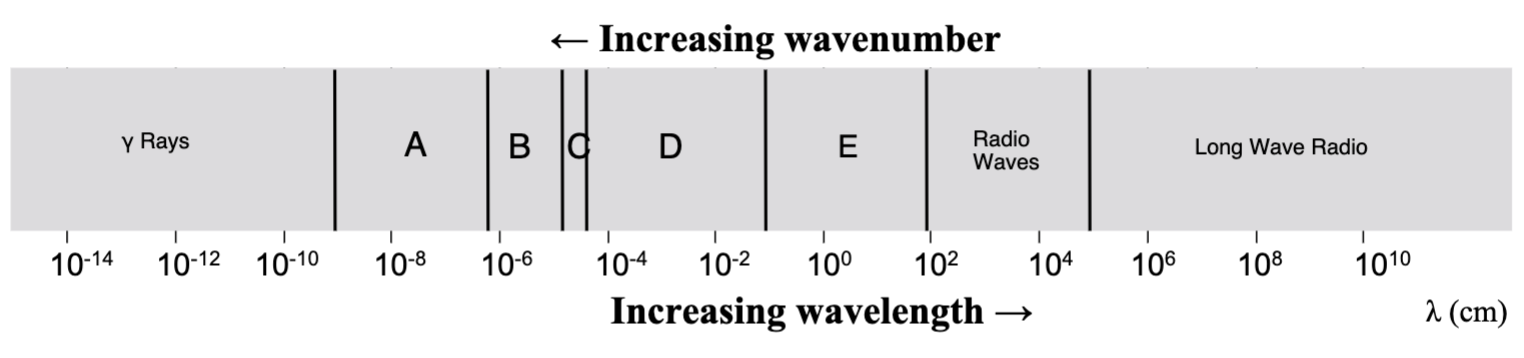
Wavenumber
Number of wavelengths per centimetre
Wavenumber formula
n = 1/λ
An EM wave has a wavenumber of 200 cm -1. What is the distance between its wave peaks?
1/200 cm -1 = 0.005cm
Why do we use both variables λ and n?
Wavelength is more intuitive to most people. It allows you to visualize the size of objects that will interact with the wave you are studying (e.g. a 50 meter boat doesn’t care about λ=1 cm waves or λ=100 km waves )
But wavenumber can be more easily generalized to three dimensions, and can encode directionality
Energy Flux
The rate of energy transfer through a surface.
What are the units for energy flux
W/m2
A solid cube has a volume of 1 m3, and is emitting a flux of 1 W/m2. What is the total power radiated from the cube?
6W, all sides of the box.
Which of the following is FALSE?
(A) All objects absorb and emit electromagnetic radiation
(B) A blackbody emits the same flux at every wavelength
(C) The total emitted flux depends on the temperature of the object
(D) A blackbody is able to absorb all wavelengths of EM flux equally well
(E) The total flux emitted by a blackbody is the area (integral) under the Planck function
Blackbody radiation: Planck Curve
All objects absorb and emit electromagnetic radiation!
Radiation occurs over a spectrum of wavelengths
Warmer objects emit more EM radiation
Only blackbodies are able to absorb at all wavelengths
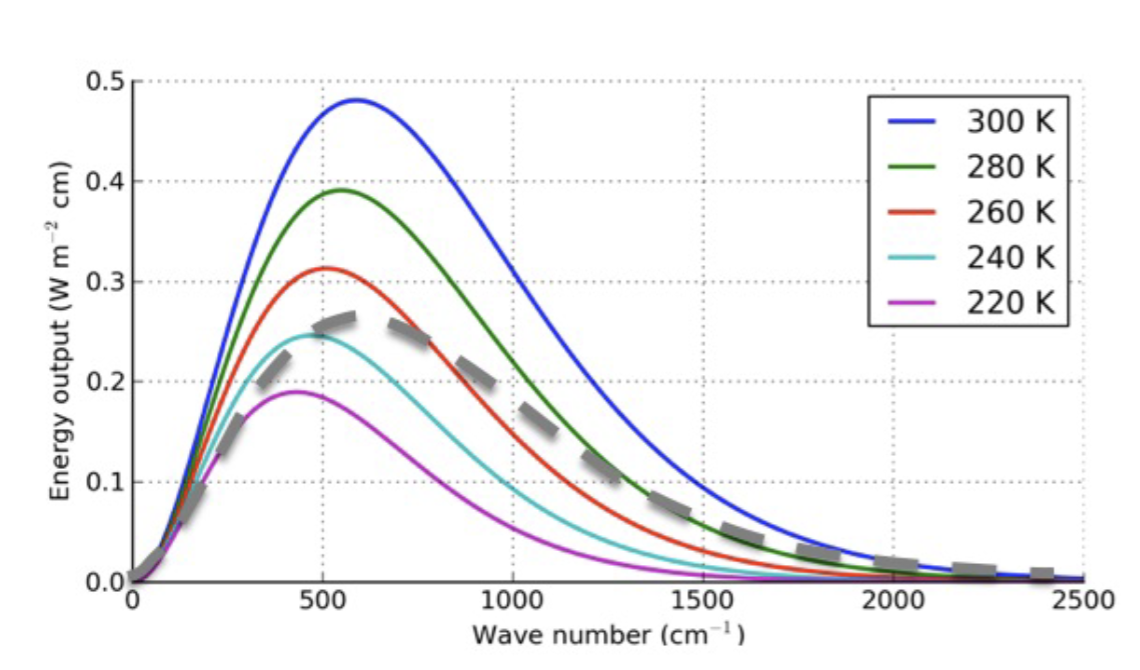
If you integrate this curve (e.g. for 220K, calculate the area of the grey shaded region), the units of the integral are:
W/m2
Estimate the total flux (W/m2) emitted by a 300 K blackbody between 500 and 1000 cm-1
Area = 500 × 0.5 = 250 W/m2
The area is smaller than 5 boxes
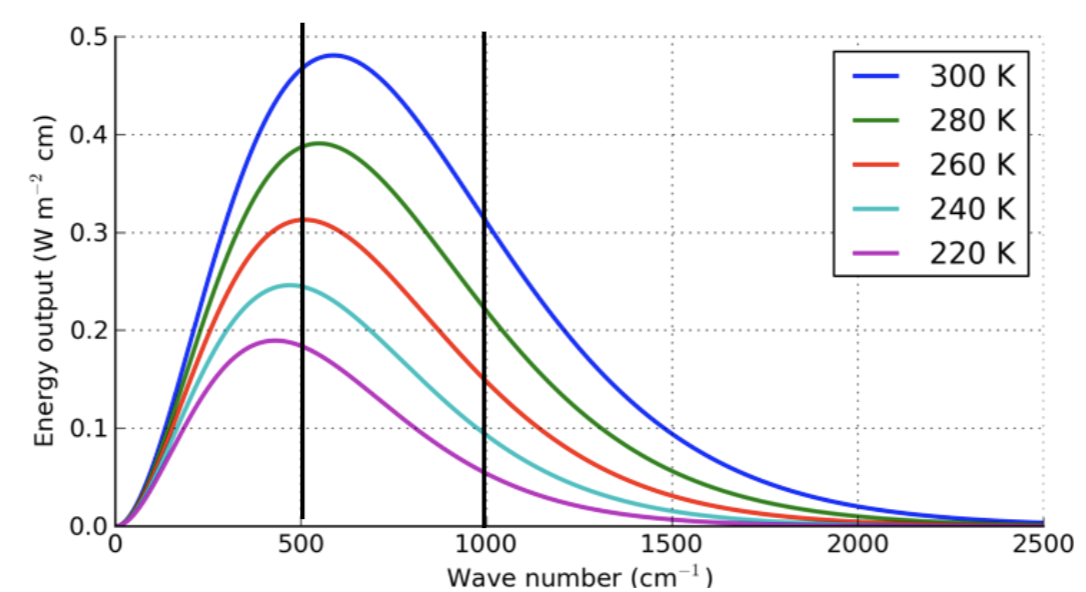
If you want the flux in a particular wavelength range
Estimate the area under the Planck curve.
If you want the total flux over all wavelengths
Use Stefan-Boltzmann equation AS the integral of the Planck curve: I = σT4
Grey Body Formula
I = εσT4
Emissivity (ε)
The RATIO of the actual energy emitted to that which a blackbody would emit.
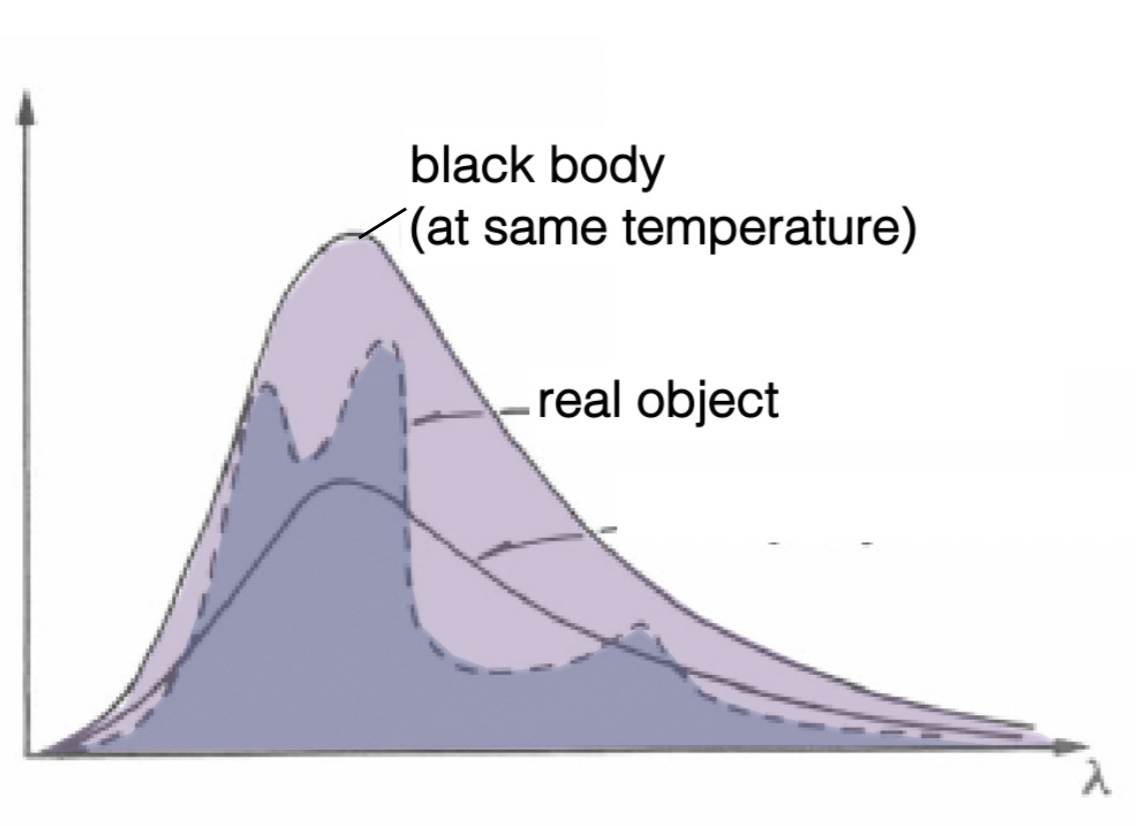
Is the black body (at the same temperature) a reasonable approximation of the real object?
No: the black body emits more total energy than the real object
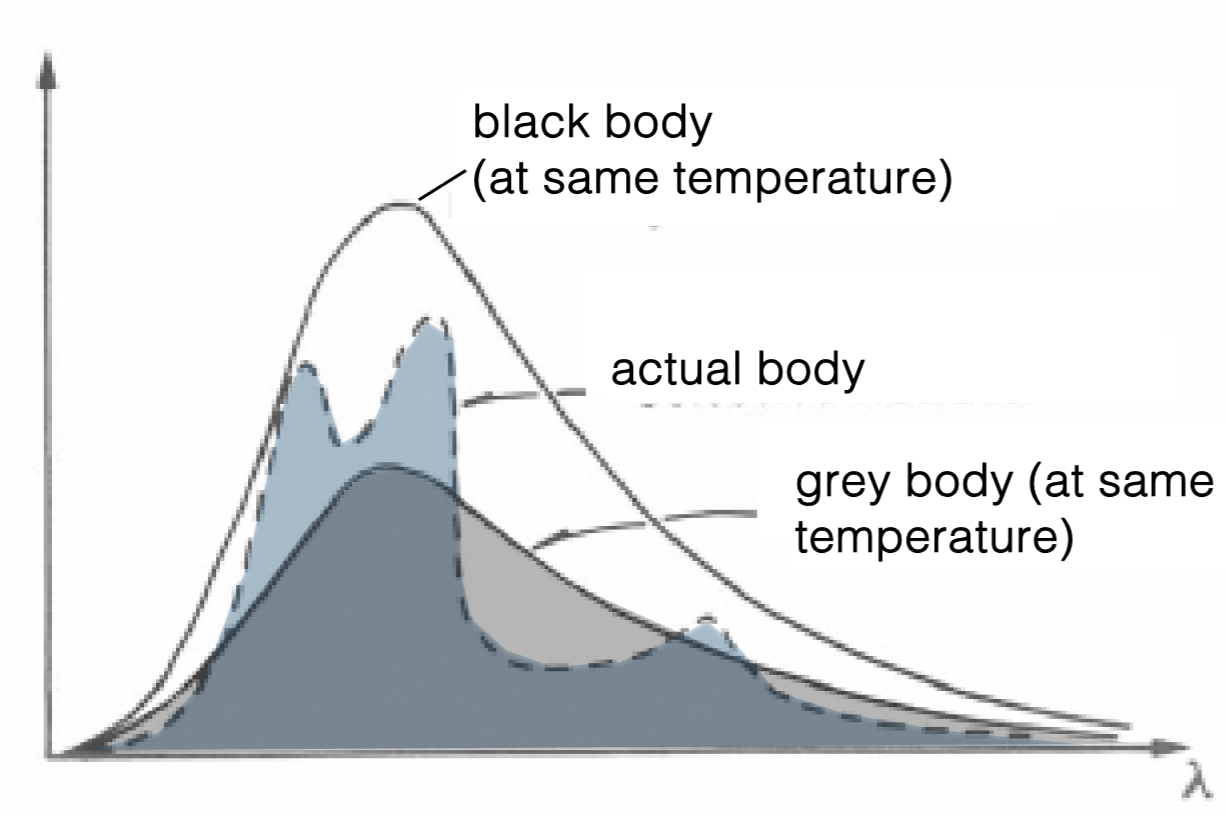
Is the grey body a reasonable approximation of the real object?
Yes: total energy emitted is similar
Important note about grey bodies
For graybodies, emissivity is NOT a function of temperature. I changes with temperature, the wavelength of maximum emitted radiation changes with temperature, but ε does not.
What does the grey curve represent?
The grey curve is from a grey body, with a temperature of about 300K.
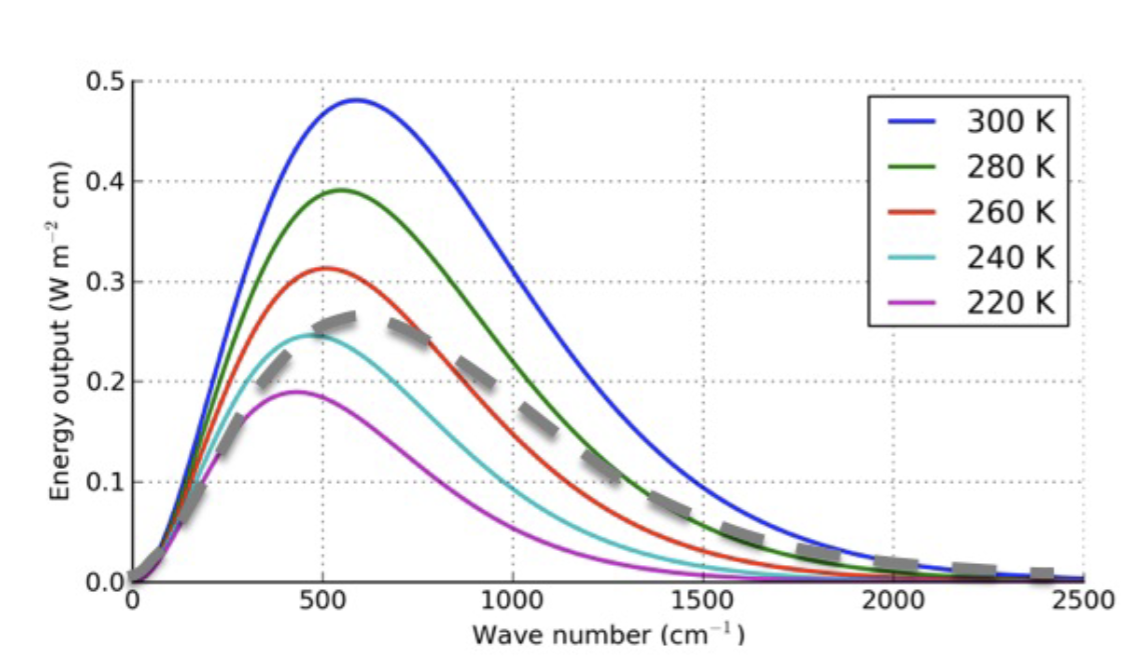
A blackbody at 280K emits the same total energy as a graybody with emissivity ε = 0.8. What is the temperature of the graybody?
296K
Electromagnetic (EM) Radiation
EM radiation hitting an object (e.g. a gas layer in the atmosphere) can either be reflected, absorbed, or transmitted.
Energy conservation
1 = 𝛼 + abs + tr
1st Law of Thermodynamics
Energy is conserved – it cannot be created or destroyed.
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
“Energy cannot be transferred from a colder body to a hotter body without work being done on the system”.
Two walls are an isolated system. The left wall is initially hotter than the right wall (TL > TR). Is a net heat transfer from the left to the right wall physically possible?
Yes
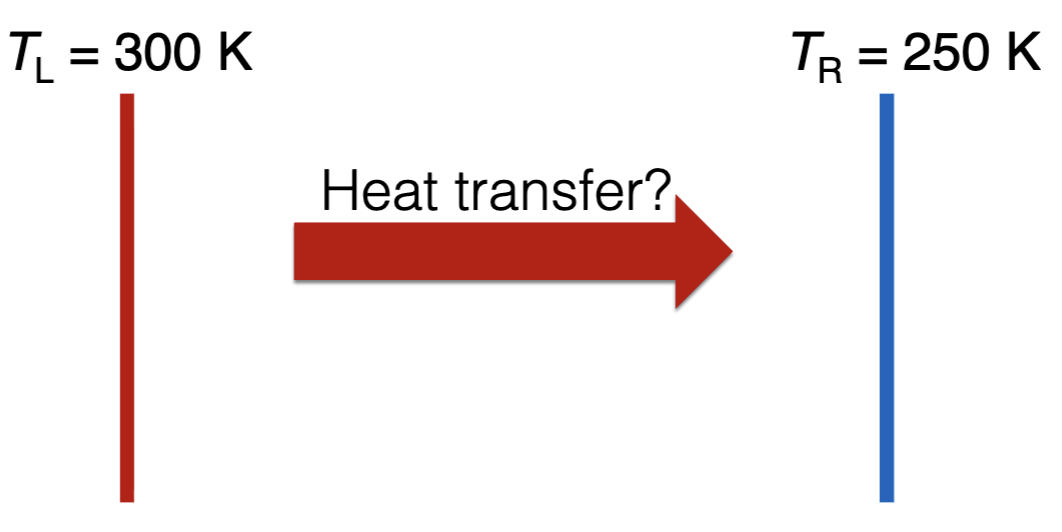
Two walls are an isolated system. The left wall is initially hotter than the right wall (TL > TR). Is a net heat transfer from the right to the left wall physically possible?
No

Is there a net transfer of energy from
Not at all

Which wall will emit the most radiative flux?
TR

The right wall is emitting more radiative flux than the left wall But the temperatures of the walls aren’t changing So, what can we say about how much flux is absorbed by the right wall compared to the flux absorbed by the left wall thinking about the conservation of energy?
Right wall must absorb more radiative flux than the left.

Notes about emissivity
If a body in equilibrium emits the same amount of flux as it absorbs does not mean that the outgoing radiation will be at the same wavelength (e.g. the Earth’s surface absorbs shortwave and longwave radiation and emits only longwave radiation)
This is key for the greenhouse effect!
Different surfaces/layers have different colors because their reflectivity changes with wavelength
Their emissivities and absorptivities also change with wavelength