Upper Extremity Skeleton + Musculature
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
More stability indicates less _
mobility
More mobility indicates less _
stability
Appendicular muscles move both the upper + lower limbs, and strengthen the joint area
True; they do move both upper + lower limbs
Appendicular muscles only stabilize the pectoral girdle, not the pelvic girdle
False; Appendicular muscles stabilize both the pectoral + pelvic girdles
Appendicular muscles assist with absorbing shocks + jolts as you walk, run, or jump
True; this is a function of Appendicular muscles
Muscles that position the pectoral girdle
originate on the axial skeleton
—> insert on clavicle and scapula
Muscles that move the arm
originate on pectoral girdle + thoracic cage
—> insert on humerus
Extrinsic muscles of hand + digits (fingers)
originate primarily on humerus, radius, ulna
—> insert on metacarpals + phalanges
Intrinsic muscles of hand
originate primary on carpals + metacarpals
—> insert on phalanges
What actions are associated with the positioning of the pectoral girdle?
Elevation; depression; protraction; retraction;
superior/upward rotation; inferior/downward rotation
What actions are associated with moving the arm at the shoulder?
Flexion; extension; abduction; adduction;
internal/medial rotation; external/lateral rotation
What actions are associated with moving the forearm at the elbow?
Flexion; extension
What actions are associated with moving the hand at the wrist?
Flexion; extension; abduction (radial deviation); adduction (ulnar deviation)
What actions are associated with the movements of the individual fingers?
Flexion; extension; abduction; adduction; opposition (thumb & pinky)
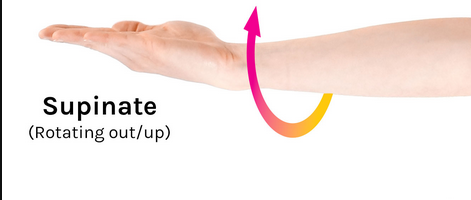
Supination
rotating out/up
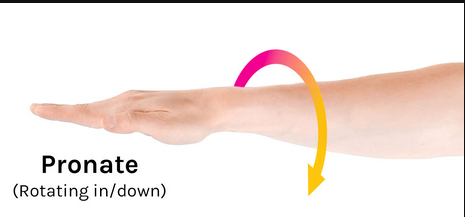
Pronation
rotating in/down
Supination and Pronation both occur at the _ joint (of which there are 2)
radioulnar
The proximal radioulnar joint is near the _
elbow
The distal radioulnar joint is near the _
wrist
Spurt
Muscle that inserts close to the joint
Shunt
Muscle that inserts far away from the joint
Agonist muscles
Prime movers; perform an action
(i.e. biceps brachii flexes the elbow)
Antagonist muscles
perform an opposing action
(i.e. triceps brachii extends the elbow)
When an agonist is active, the antagonist __
relaxes
Synergistic muscles
assist the agonist/prime mover
Stabilizer muscles(i.e. brachioradialis assists with elbow flex)
Stabilizer muscles
stabilize a joint or area for optimum movement of the agonist muscles
(i.e. rotator cuff muscles of the shoulder)