Chapter 20: Electron Transport Chain
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Mitochondria
In eukaryotic cells, aerobic processes occur in the _____
Cytosol
In eukaryotic cells, glycolysis (anaerobic), occurs in the _____
NADH and FADH2; O2
ETC involves a series of intermediate carries that transfer electrons from _____ to _____
Inner mitochondrial membrane
ETC reactions take place in the _____
Oxidative phosphorylation
Process for generating ATP
→ depends on the creation of a pH gradient (proton gradient) within the mitochondrion as a result of electron transport
Proton gradient
Difference between the hydrogen ion (H+) concentrations in the mitochondrial matrix and that in the intermembrane space, which is the basis of coupling between oxidation and phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation in ETC
Bulk of ATP produced in the system occurs in _____
Oxidized; Reduced
In ETC, NADH and FADH2 are _____, and O2 is _____
Proton gradient
Created by electron transport from one carrier to another
Coupled to the production of ATP in aerobic metabolism
I, III, IV
Which complex has proton pumping ability?
Reduced
Molecule with a high reduction potential tends to be _____ if it is paired with a molecule with a lower reduction potential
Higher
Electron flow favors ____ reduction potential
NADH-CoQ oxidoreductase
Enzyme for Complex I
NADH-CoQ oxidoreductase
Catalyzes the transfer of electrons from NADH to CoQ
Integral part of the inner mitochondrial membrane
Includes several proteins that contain an iron-sulfur cluster and the flavoprotein that oxidizes NADH
Flavoprotein has a flavin coenzyme called flavin mononucleotide (FMN)
Flavoprotein
Involved in Complex I and II; oxidizes NADH
Flavin mononucleotide (FMN)
Flavin coenzyme of flavoprotein that can accept and pass on electrons
Hydroquinone
Reduced form of quinone
Succinate-coenzyme Q oxidoreductase
Enzyme for Complex II
Succinate-coenzyme Q oxidoreductase
Catalyzes the transfer of electrons from succinate to CoQ
Cytochromes
Groups of heme-containing proteins in the ETC
→ In each heme group, the iron is successively reduced to Fe(II) and reoxidized to Fe(III)
Cytochromes
When CoQ is reoxidized, electrons are passed to _____
Side chain
All cytochromes contain a heme group; what differentiates them from one another?
CoQH2-cytochrome c oxidoreductase
Enzyme for Complex III
CoQH2-cytochrome c oxidoreductase
Catalyzes the oxidation of reduced CoQ (CoQH2)
2
How many molecules of cytochrome c are required for every molecule of coenzyme Q?
Q cycle
Provides the link between two-electron transfers and one-electron transfers
Involves the flow of electrons via a cyclic path from CoQH2 to other components of the complex
Depends on the fact that coenzyme Q can exist in three forms
One electron is passed from CoQH2 to the iron–sulfur clusters to cytochrome c1, leaving coenzyme Q in the semiquinone form
Provides a mechanism for electrons to be transferred one at a time from coenzyme Q to cytochrome c1
Complex III results in proton pumping and supplies enough energy to drive ATP production because of the reaction that it catalyzes
Semiquinone
A partially reduced form of coenzyme Q (CoQ) that occurs when it gains one electron
Semiquinone form
After one electron is passed from CoQH2 to the iron-sufur clusters to cytochrome c1, CoQH2 turns into _____
Cytochrome c oxidase
Enzyme for Complex IV
Cytochrome c oxidase
Catalyzes the transfer of electrons from cytochrome c to O2
Complex IV
Contains cytochromes a and a3, as well as two Cu2+ ions that are involved in electron transport
Cu2+ ions
Intermediate electron acceptors that lie between cytochromes a and a3 in the following sequence:
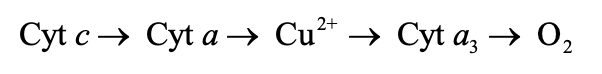
Iron
The _____ of the heme group is involved in a series of redox reactions
Sulfur
Nonheme iron proteins contain _____
Iron is usually bound to cysteine or to S2-
Voltage gradient
Differences in the concentration of ions across the membrane generate a _____
Energy-releasing oxidation reactions
Give rise to proton pumping and a pH gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane, which is used to drive the phosphorylation of ADP
Coupling process
Converts the energy of the electrochemical potential (voltage drop) across the membrane to the chemical energy of ATP
Coupling factor
Needed to link oxidation and phosphorylation
ATP synthase (mitochondrial ATPase)
Complex protein oligomer that is responsible for the production of ATP in the mitochondria
F0
Portion of ATP synthase
Spans the membrane (Integral)
Consists of 3 different kinds of polypeptide chains (a, b, c)
F1
Portion of ATP synthase
Projects into the matrix
Consists of 5 different kinds of polypeptide chain in the ratio α3β3γδε
Site of ATP synthesis
Uncouplers
Inhibit the phosphorylation of ADP without affecting electron transport
Reduce oxygen to H2O but do not enable the production of ATP
Examples
2,4-dinitrophenol
Valinomycin
Gramicidin A
P/O Ratio
Ratio of ATP produced by oxidative phosphorylation to oxygen atoms consumed in electron transport
2.5 ATP
P/O = _____ ATP when NADH is oxidized
1.5 ATP
P/O = _____ ATP when FADH2 is oxidized
Chemiosmotic coupling
Mechanism of coupling that requires a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane
matrix; intermembrane space
Proteins that serve as electron carriers take up protons from the _____ when they are reduced and release them to the _____ when they are reoxidized
NADH, CoQ, O2
Reactions of _____, _____, _____ require protons
F0
Protons flow back into the matrix through channels in the _____ unit of ATP synthase
F1
Flow of protons is accompanied by formation of ATP, which takes place in the _____
Conformational coupling
Proton gradient leads to conformational changes in a number of proteins, including ATP synthase
There are three sites for substrate on ATP synthase and three possible conformational states
Open (O)
Conformational site on ATP Synthase
Low affinity for substrate
Loose-binding (L)
Conformational site on ATP Synthase
Not catalytically active
ADP and Pi bind at a site in this conformational
Tight-binding (T)
Conformational site on ATP Synthase
Catalytically active
ATP is bound at a site in this conformation
T to O
This transition occurs when the tightly bound ATP is released
L to T
This transition happens when the loosely bound substrates (ADP and inorganic phosphate) are converted into tightly bound ATP
Shuttle mechanisms
Transport metabolites between the mitochondria and the cytosol
Glycerol-phosphate shuttle
Mechanism for transferring electrons from NADH in the cytosol to FADH2 in the mitochondrion
Reduction of DHAP
How is glycerol phosphate produced?
FADH2
Product of the glycerol-phosphate shuttle mechanism, which passes electrons through the electron transport chain
Glycerol-phosphate shuttle
NADH is oxidized to NAD+, and FAD is reduced to FADH2
Malate-aspartate shuttle
Found in mammalian kidney, liver, and heart
Uses the fact that malate can cross the mitochondrial membrane, while oxaloacetate cannot
Transfer of electrons from NADH in the cytosol produces NADH in the mitochondrion
Cytosolic malate dehydrogenase
Oxaloacetate is reduced to malate by _____
Cytosol
Oxaloacetate is reduced to malate by cytosolic malate dehydrogenase
Cytosolic NADH is oxidized to NAD+
Aspartate is converted to oxaloacetate in the cytosol
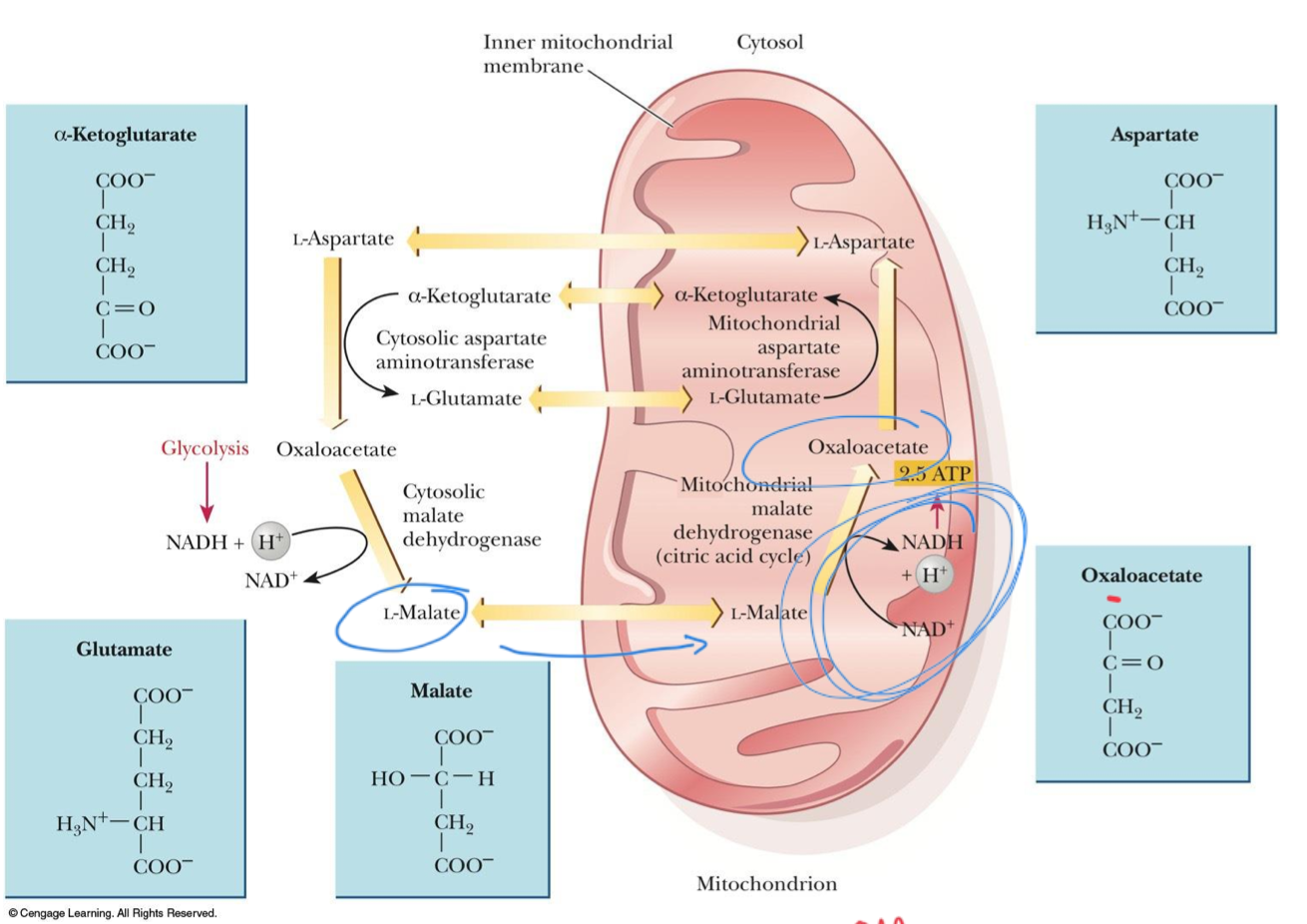
Mitochondrion
Conversion of malate back to oxaloacetate is catalyzed by mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase
Oxaloacetate is converted to aspartate, which can cross the mitochondrial membrane
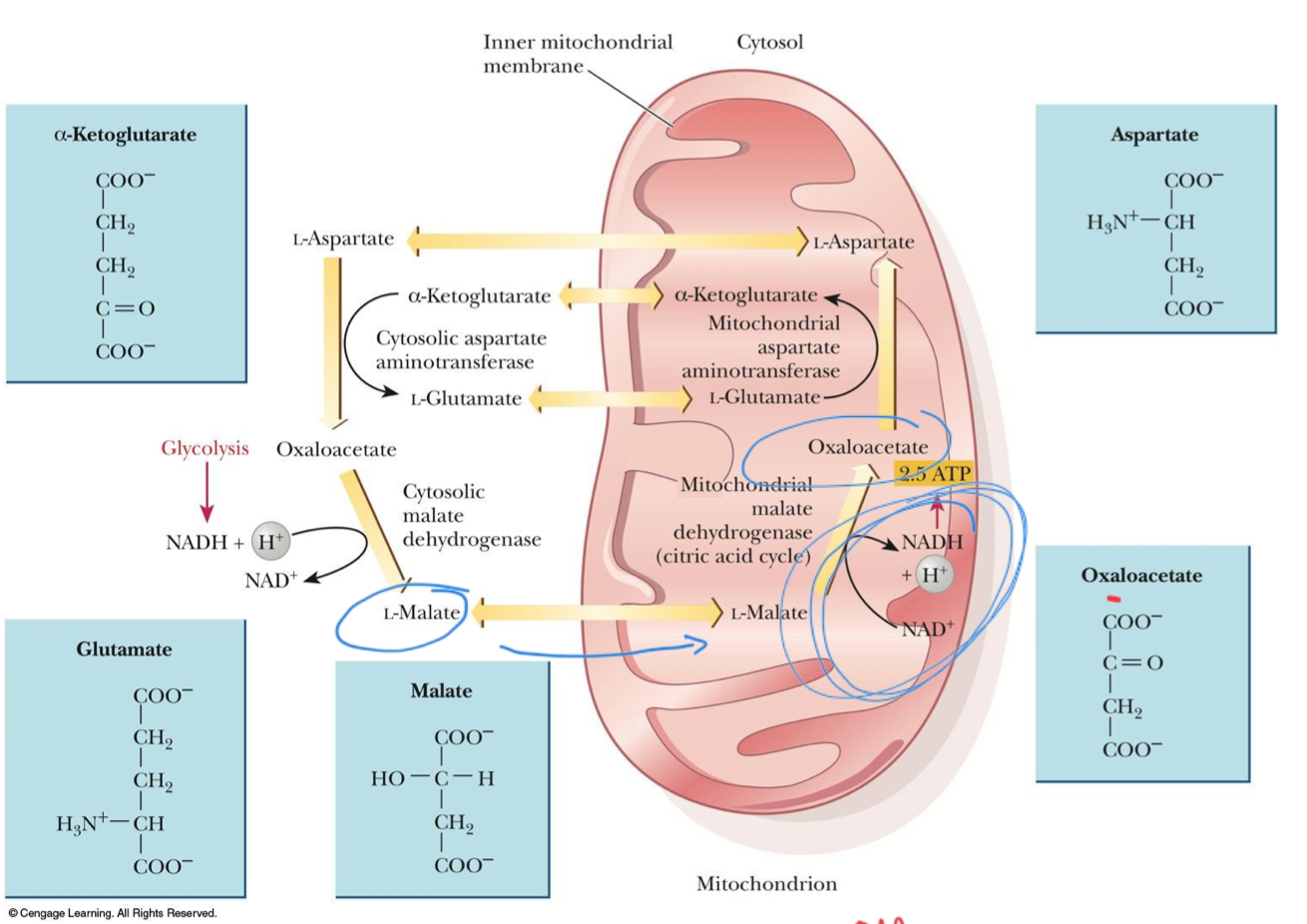
Mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase
Conversion of malate back to oxaloacetate is catalyzed by _____
30 (glycerol) or 32 (malate)
Total ATP produced when:
Pyruvate generated from glycolysis can enter the citric acid cycle
NADH and FADH2 molecules that result from the citric acid cycle are reoxidized through the electron transport chain