PDA Lecture 22: Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Inhibitors
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
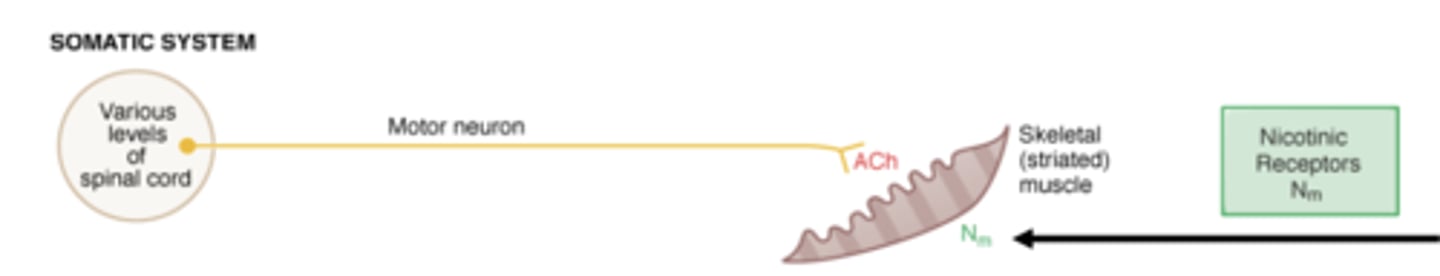
Acetylcholine activates _______________________ in skeletal muscle via the somatic system
muscle-type nicotinic receptors
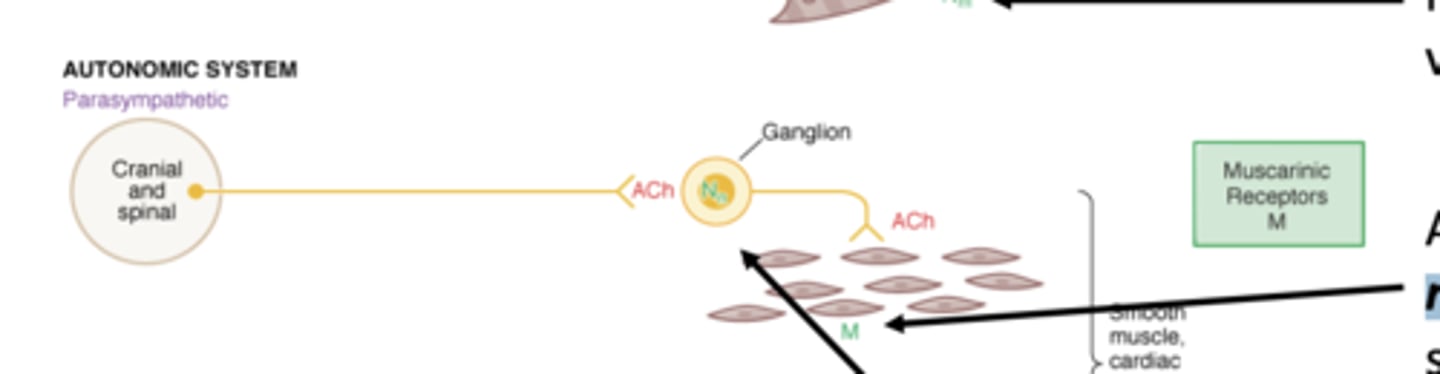
Acetylcholine activates __________________ in smooth muscle via the parasympathetic system
muscarinic receptors
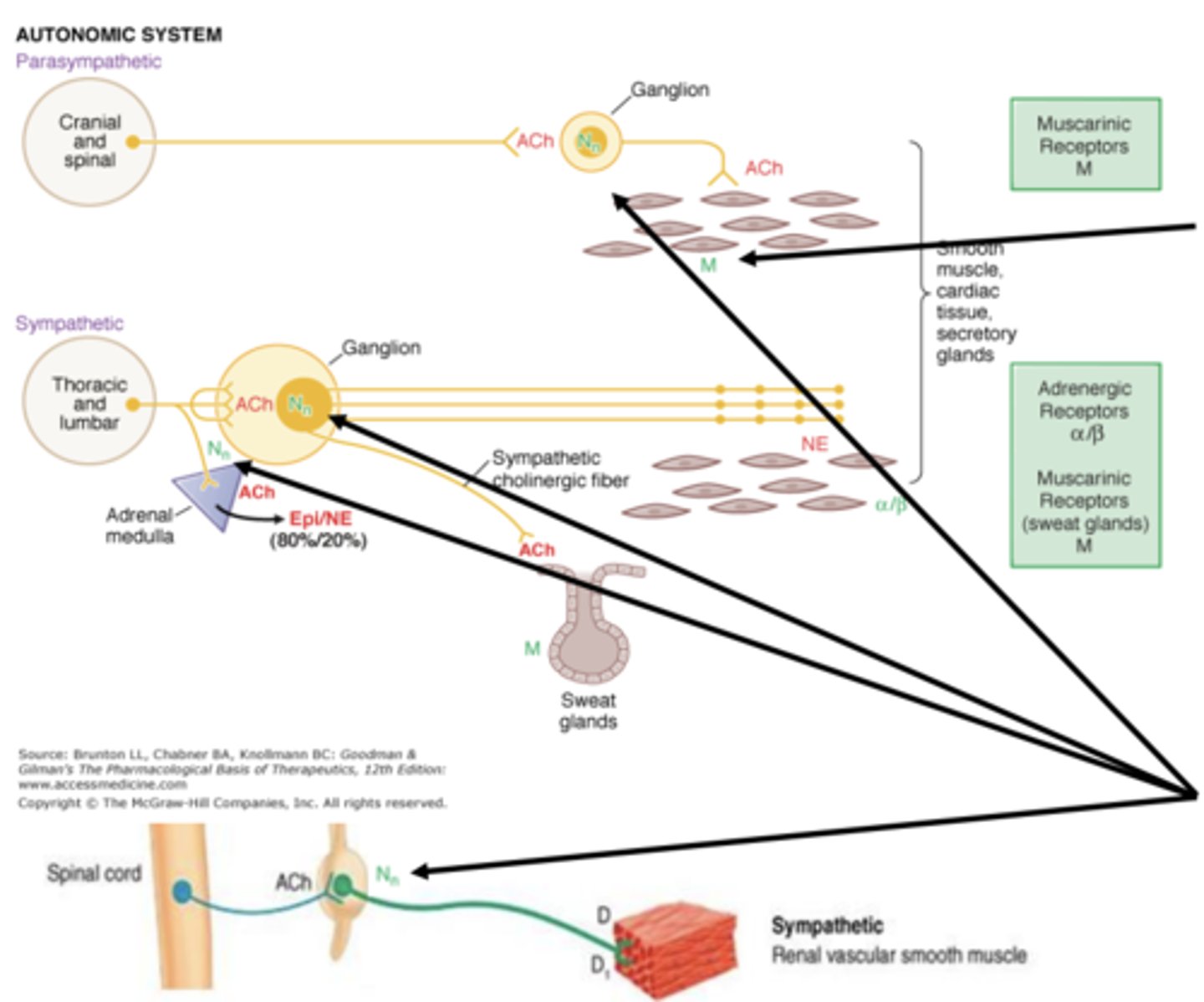
Acetylcholine activates _______________________ in all ganglion and adrenal medulla via sympathetic and parasympathetic system
neuronal-type nicotinic
Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE)
also metabolizes acetylcholine (among other drugs)
- found mainly in liver and plasma
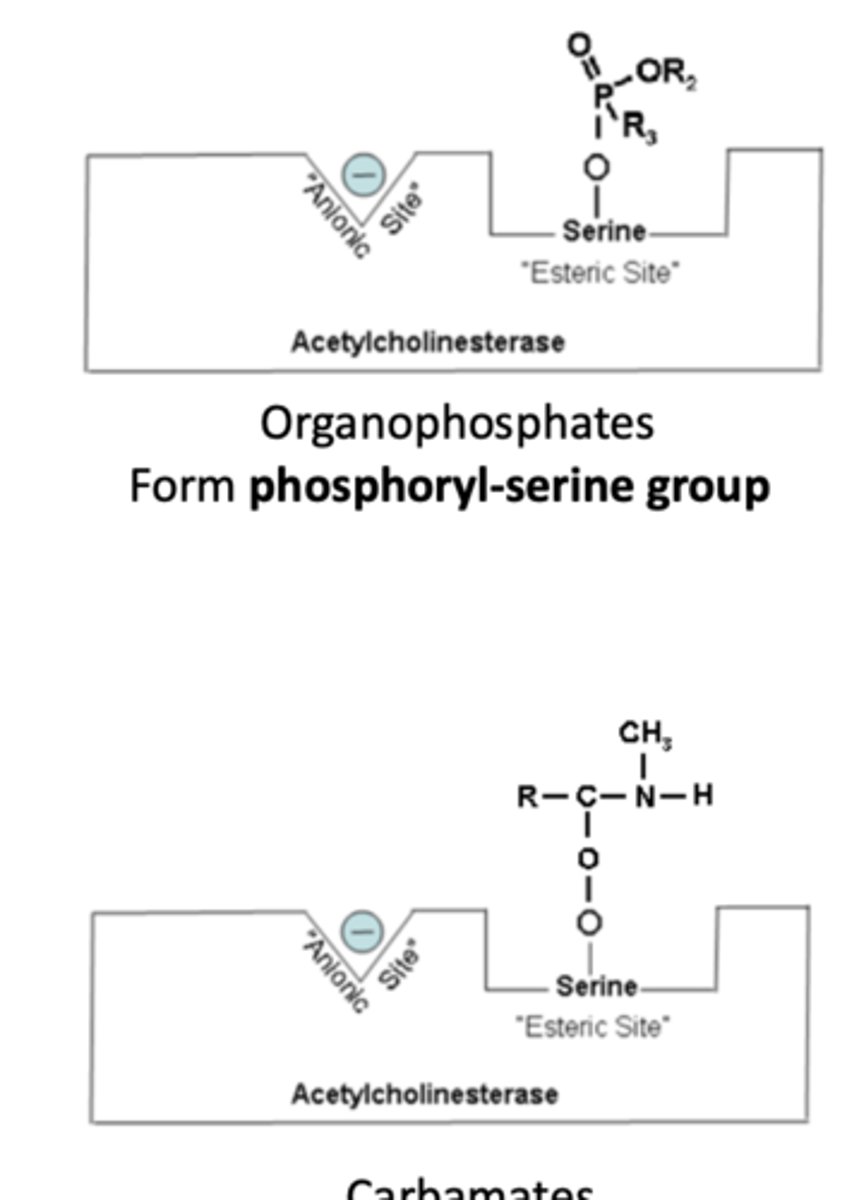
Acetylcholine Esterase Inhibitors (AChEIs) (2)
Organophosphates and Carbamates
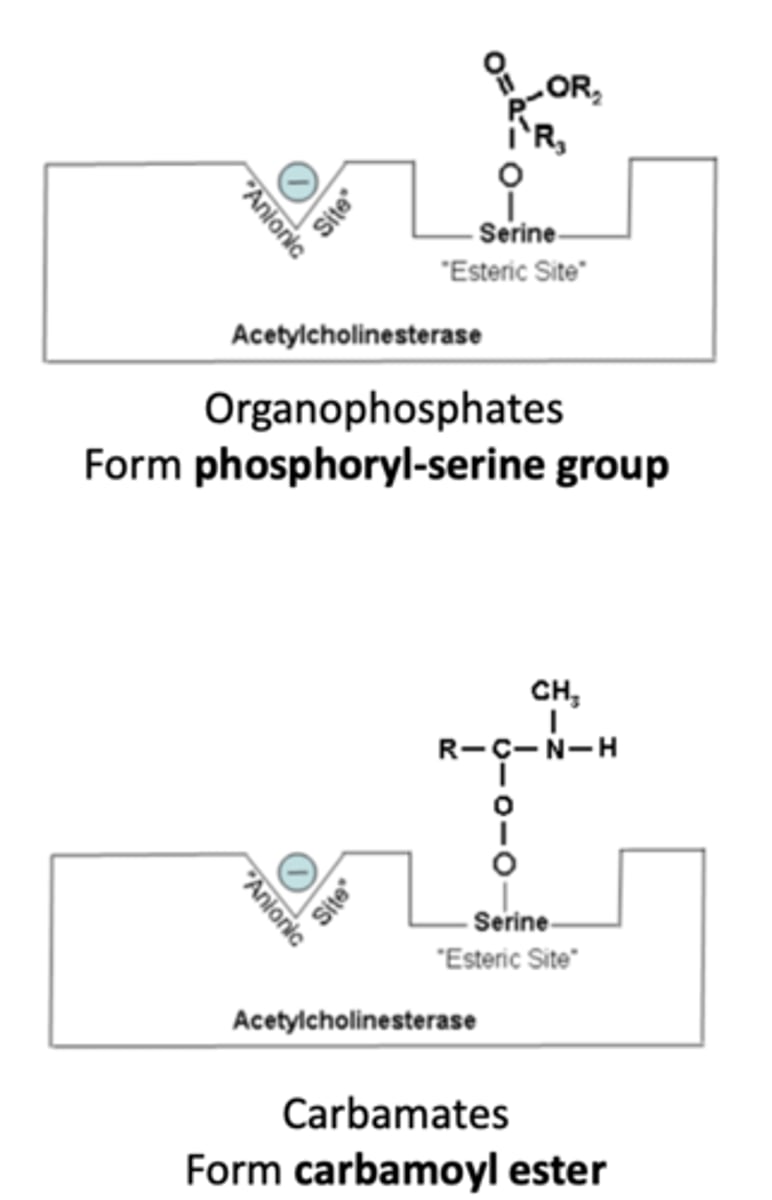
What do Acetylcholine Esterase Inhibitors (AChEIs) (organophosphates & carbamates) do? What is there mechanism of action?
- increase "rest and digest" effects
- increase general cholinergic signaling (agonist effect) by decreasing breakdown of acetylcholine
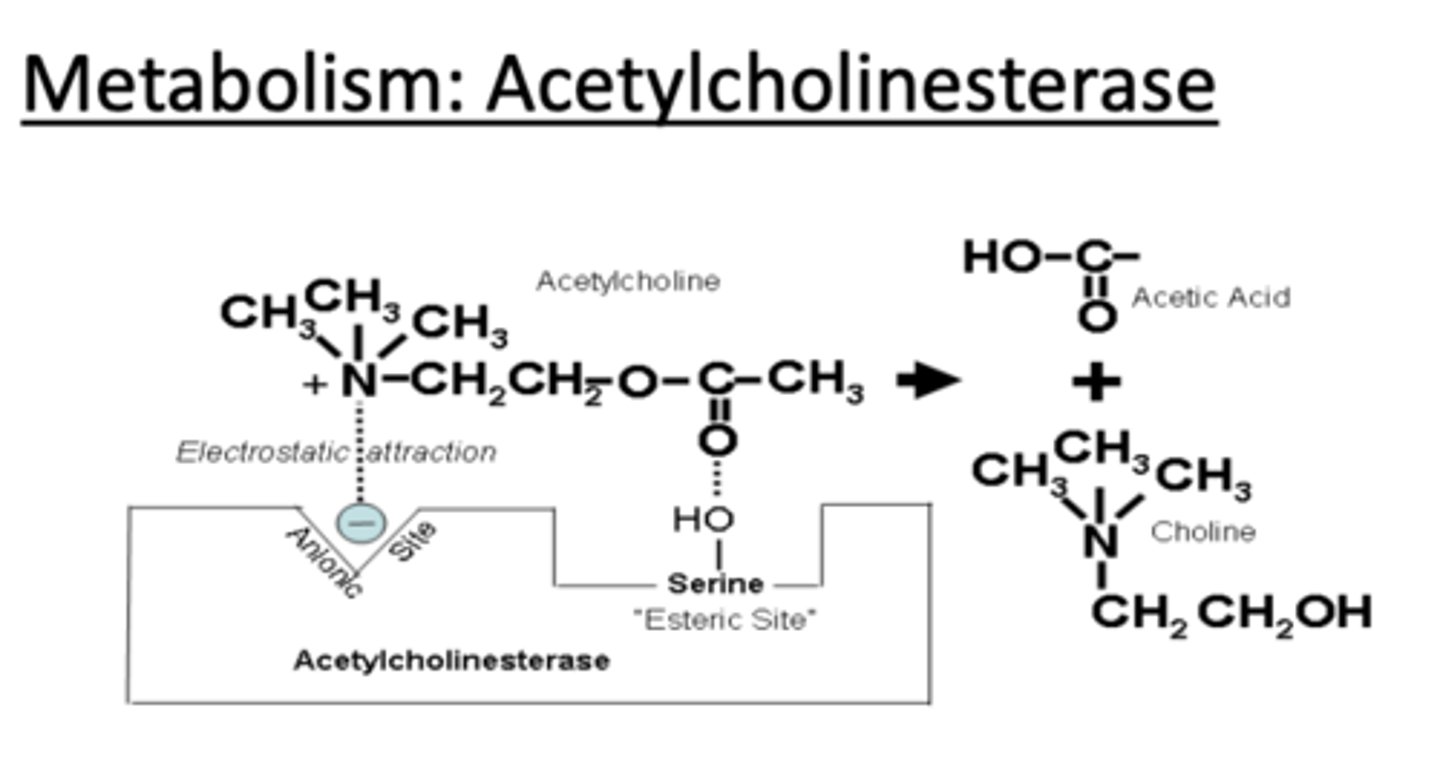
- Block AChE breakdown of acetylcholine by bonding with the serine site
- in a sense, are indirect agonists of all cholinergic receptors (nicotinic and muscarinic)
Acetylcholine Esterase Inhibitors (AChEIs) (organophosphates & carbamates) have variable ___________________
blood brain barrier penetration
Do acetylcholine esterase inhibitors (AChEIs) have clinical uses?
yes have clinical uses, but can be very toxic (cholinergic toxicity)
Are organophosphates or carbamates more toxic? Why?
- Organophosphates are more toxic
- they have a longer duration of action, "irreversible", while carbamates have a shorter duration of action, "reversible
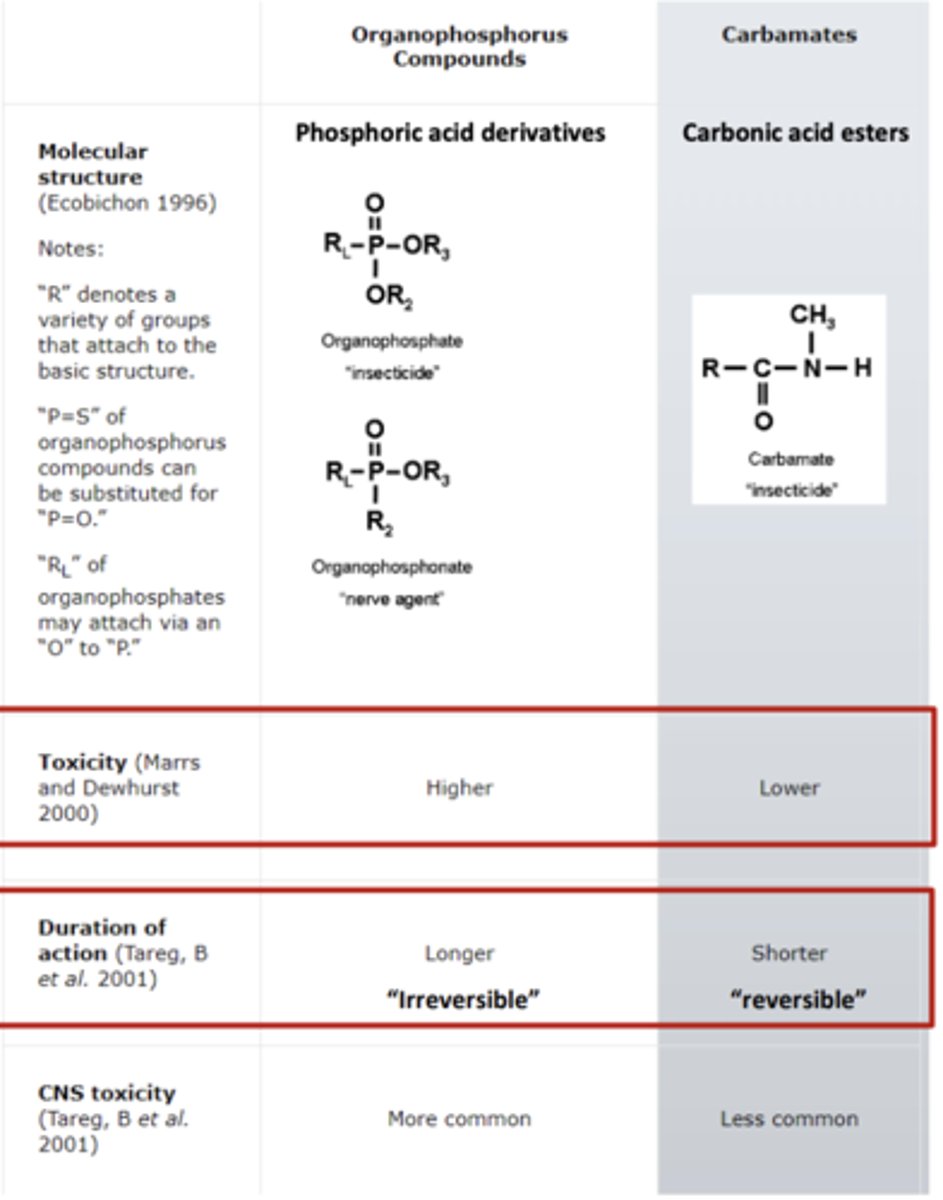
Which is preferred for clinical use: organophosphates or carbamates?
carbamates- they are less toxic
Organophosphates and carbamates can be ___________________ when used in insecticides or nerve agents. Why?
- very toxic
- excellent blood brain barrier penetration
For organophosphates, you cannot break the bond after......
after a few hours
- aged bond is irreversible
What can be used as an antidote for AChEI poisoning?
atropine
- given to troops at risk for nerve gas exposure
Irreversible organophosphates
- Dyflos (DFP)
- Ecothiophate
- Malathion
- Diazinon
- Isoflurophate
Reversible carbamates
- phyostigmine
- neostigmine
- pyridostigmine
- edrophonium
- rivastigmine
- donepezil
- galantamine
- tacrine
AChEIs will increase ________________ functions and decrease ______________ functions
- "rest and digest"
- "fight or flight"
- inhibit acetylcholinesterase, increase acetylcholine, increasing rest and digest
What are organophosphates isoflurophate and echothiophate used for?
What is the MOA?
What are side effects?
- used for glaucoma
- vessels in eye dilate, allowing fluid to drain (vasodilation of rest and digest)
- side effects include eye muscle spasms
What are organophosphates diazinon and malathion used for?
Which is prohibited for residential use? Which is considered "safe" for humans?
- used as insecticides
- Diazinon prohibited for residential use
- Malathion considered "safe" for humans
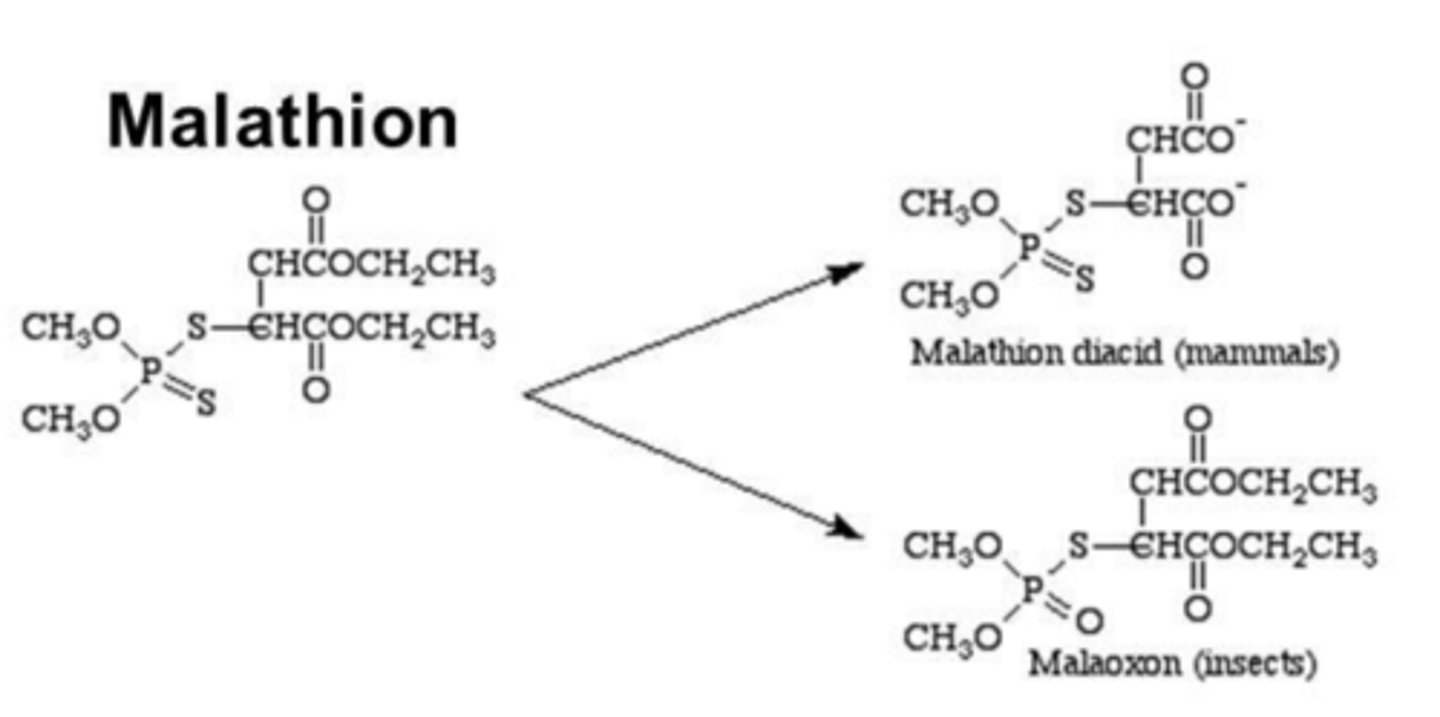
Why isn't the malathion pesticide neurotoxic to humans?
insects and mammals metabolize the 'prodrug' differently
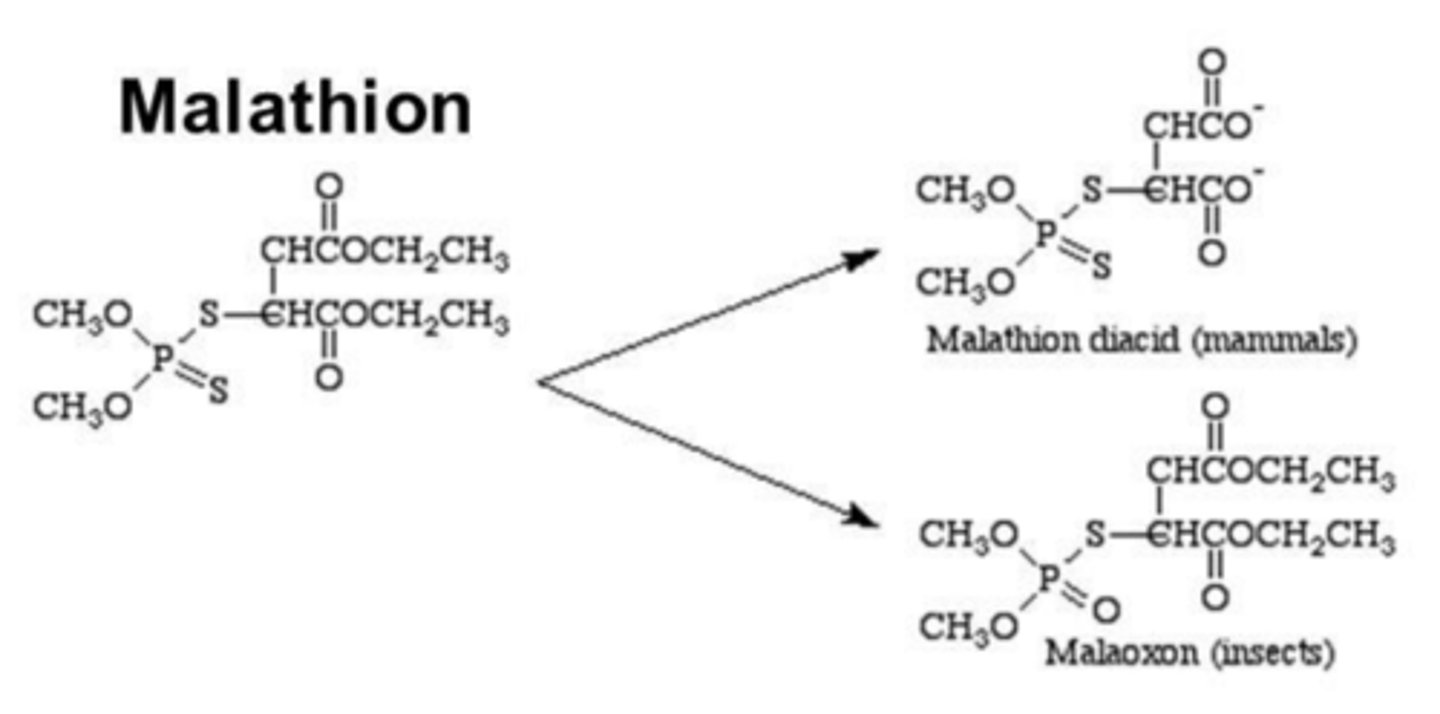
How do insects metabolize malathion?
P450 metabolism
- P-S bond converted P-O bond: molecule becomes malaoxon, in active inhibitor
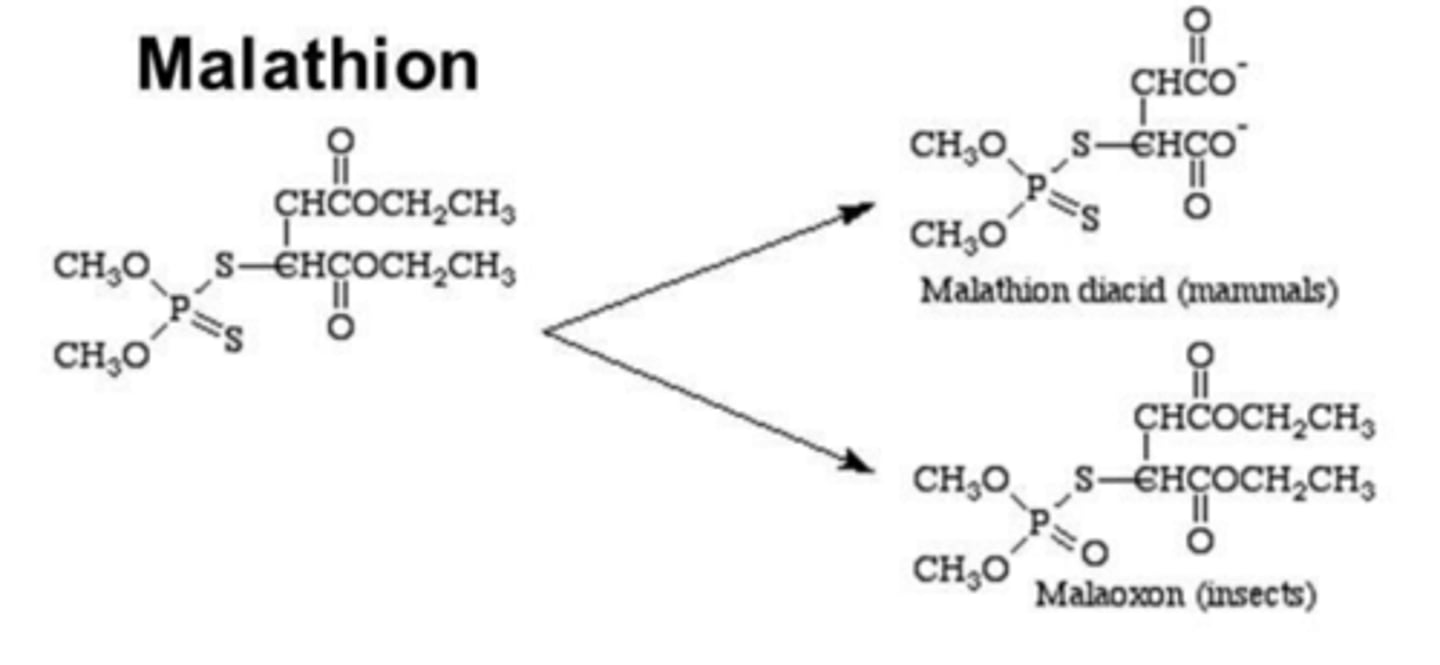
How do mammals metabolize malathion?
esterase activity
- hydrolyzes the molecule into inactive metabolites
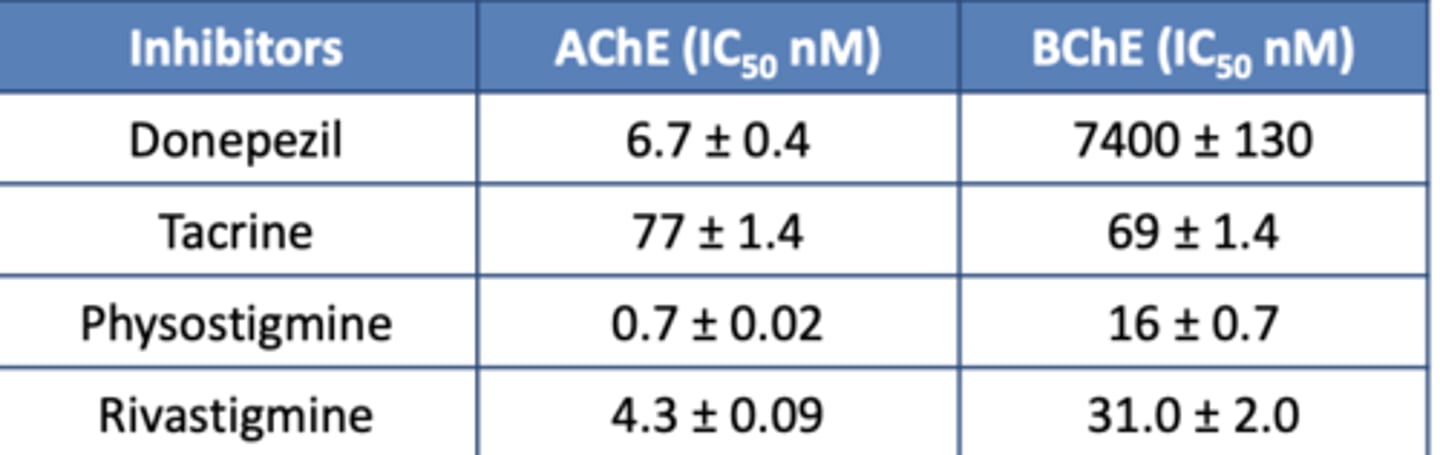
Which carbamate provides the most inhibition of butyrylcholinesterase (BChE)?
The lowest?
Highest: Donepezil
Lowest: Physostigmine
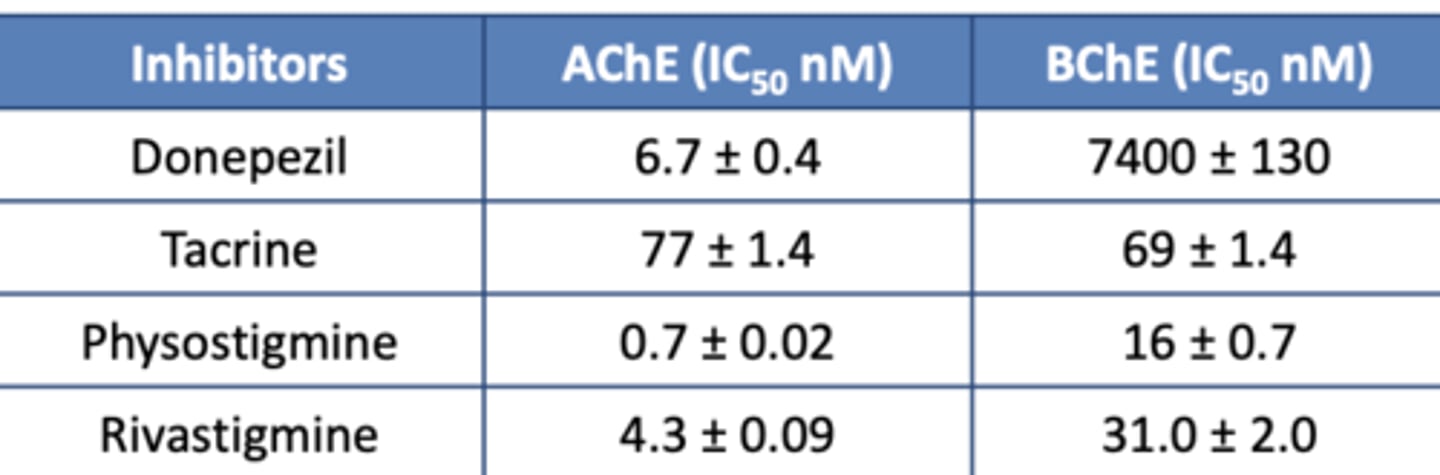
Which Which carbamate provides the most inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)?
The lowest?
Highest: Tacrine
Lowest: Physostigmine
What is the carbamate, endrophonium used for?
used clinically to differentiate myasthenia gravis from choline toxicity (both cause muscle weakness)
Myasthenia gravis
Autoimmune destruction of muscle-type nicotinic receptors
What is endrophonium's effect on myasthenia gravis?
Endrophonium reduces weakness because increase in ACh increases activation of remaining muscle-type nicotinic receptors
Cholinergic toxicity
AChE inhibitor overdose from nerve gas or medication (cholinergic toxicity)
What is endrophonium's effect on cholinergic toxicity?
Endrophonium increases weakness because increase in ACh adds to already high levels of acetylcholine cause by AChE inhibitor
What is the carbamate, physostigmine used for?
- Does it have a short or long duration?
- How is its BBB penetration?
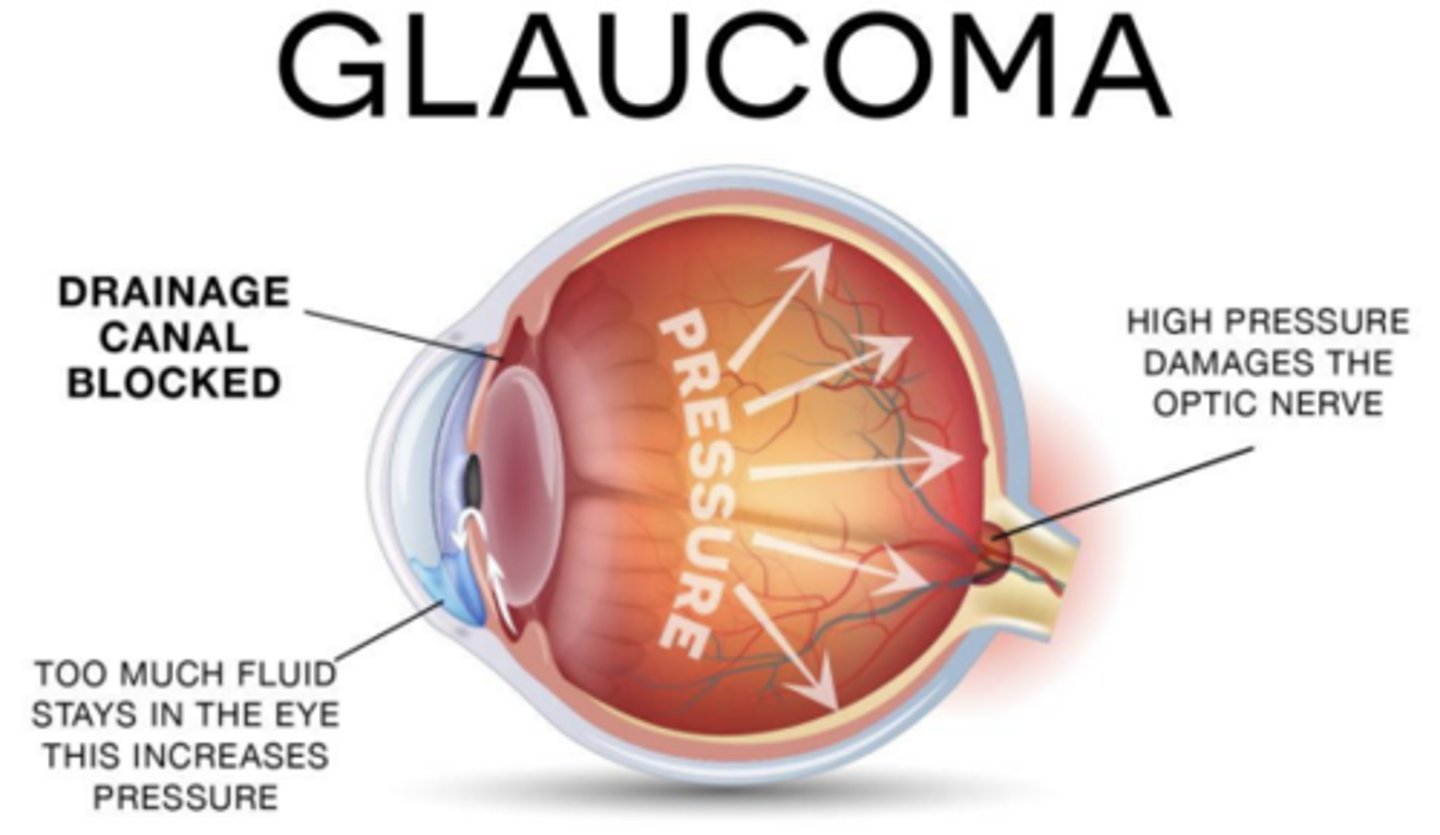
- used to treat glaucoma
- short duration (1-2 hrs)
- excellent BBB penetration
What are the carbamates neostigmine and pyridostigmine used for?
Do they have short or long duration?
- How is their BBB penetration?
- used to treat myasthenia gravis and glaucoma
- neostigmine- moderate duration (3-4 h)
- pyridostygmine, long duration (6-8 h)
- poor BBB penetration
When should you avoid the use of carbamates?
if other drugs requiring inactivation by acetylcholine esterase or butyrylcholinesterase are in patients system
If BChE is busy metabolizing drugs, it will not be available to....
break down increased acetylcholine from carbamate
What is a risk of using carbamates with drugs that require inactivation by AChE and BChE?
Risk of carbamate cholinergic toxicity, similar to that seen with organophosphates.
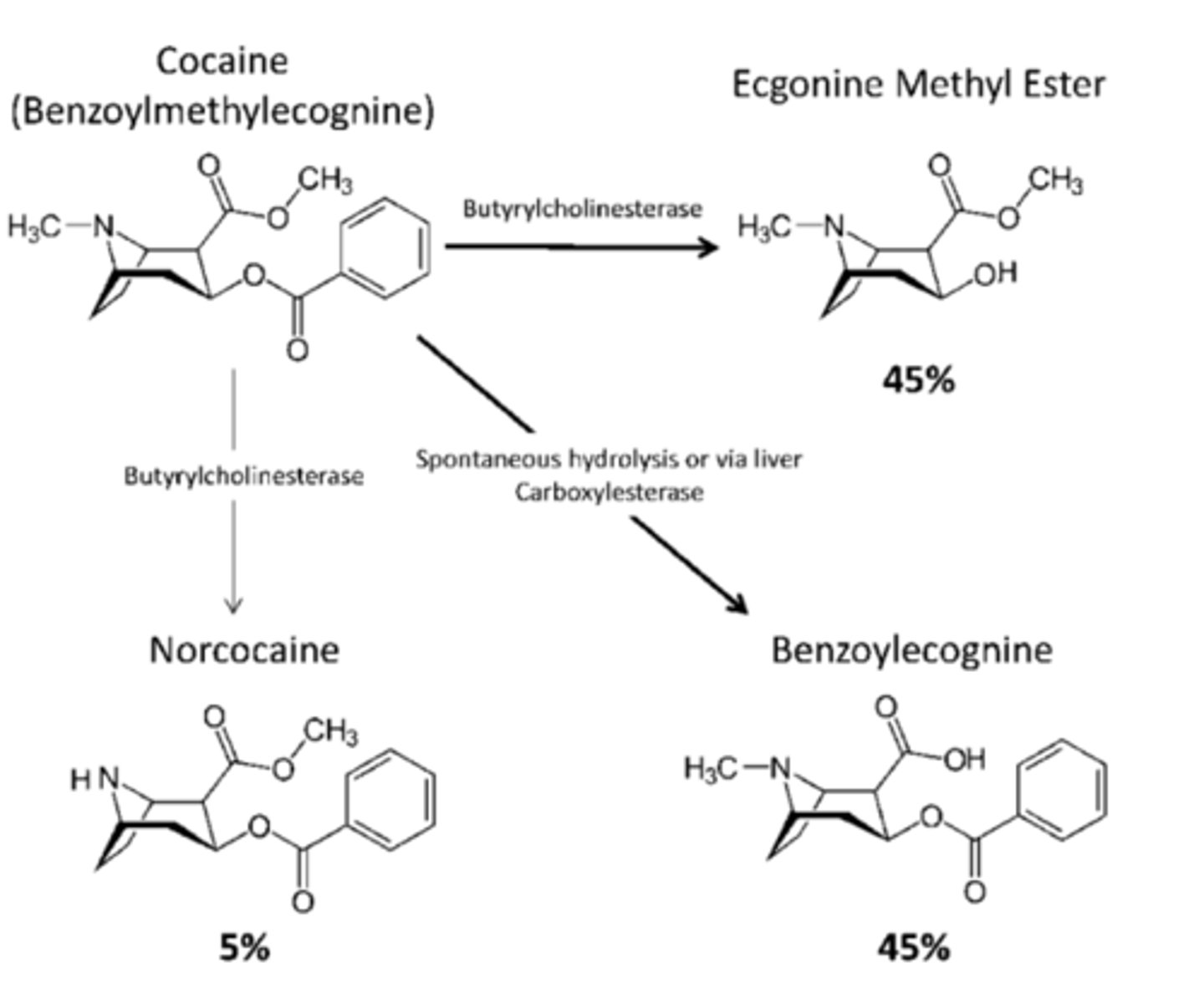
Common drugs metabolized by Butyrylcholinesterase (BChE)
o Mivacurium
o Succinylcholine
o Procaine (i.e. Novocain)
o Cocaine
T/F: Organophosphates and carbamates inhibit AChE by blocking the serine site
TRUE
Troops going into war zones where organophosphates may be used are given microinjections of _____________ as antidotes
a. Epinephrine
b. Atropine
c. Insulin
d. Carbamates
b. Atropine
Carbamates are used for the treatment of glaucoma, primarily because they:
a. Constrict the pupils
b. decrease eye muscle spasms
c. relieve eye pressure
d. dilate the pupils
c. relieve eye pressure
The insecticide malathion is considered safe for humans for which of the following reasons?
a. malathion is not harmful when eaten, only when sprayed directly on
b. amount of malathion used is large enough to kill insects, but has no effect on humans
c. drug is metabolized differently in humans and insects
d. AChE is different in humans and insects
c. drug is metabolized differently in humans and insects