BSCI222 - Sex determination and linkage
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What are the different types of sex determination system?
Environmental
Chromosomal haplodiploidy
Haploid (n) v. diploid (2n)
X0 v. XX
Paired chromosomes
XY or XX
ZZ or ZW
What is environmental sex determination?
Sex influenced by temperature
Females = hot
Males = cold
Seen in: turtles and crocodiles
What is chromosomal sex (haplodiploidy full set) determination?
Haploid v. Diploidy (haplodiploidy)
Females = 2n
Males = n (not fertilized)
Seen in: bees, wasps, ants
What is chromosomal sex (haplodiploidy ONE chromosome) determination?
Sex chromosome haploid v. diploid
Females = XX
Males = X or X0
Seen in: grasshoppers, dragonflies, many spiders
What is paired sex chromosomes (XX and XY)?
Specific sex chromosomes
Females: XX (homogametic)
Males: XY (heterogametic)
Seen in: all placental mammals, some insects, some reptiles
What is paired sex chromosomes (ZW and ZZ)?
Specific sex chromosomes
Females: ZW (heterogametic)
Males: ZZ (homogametic)
Seen in: birds and butterflies, some amphibians, some fishes
What is heterogametic v. homogametic?
Heterogametic - half of the gametes receive one allele and the other half receive the other allele (ex. X and Y)
Homogametic - all gametes receive the same allele (ex. X and X)
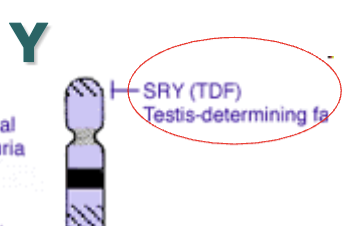
What’s the role of the SRY gene?
Known as the “guy” gene
Induces the development of testes
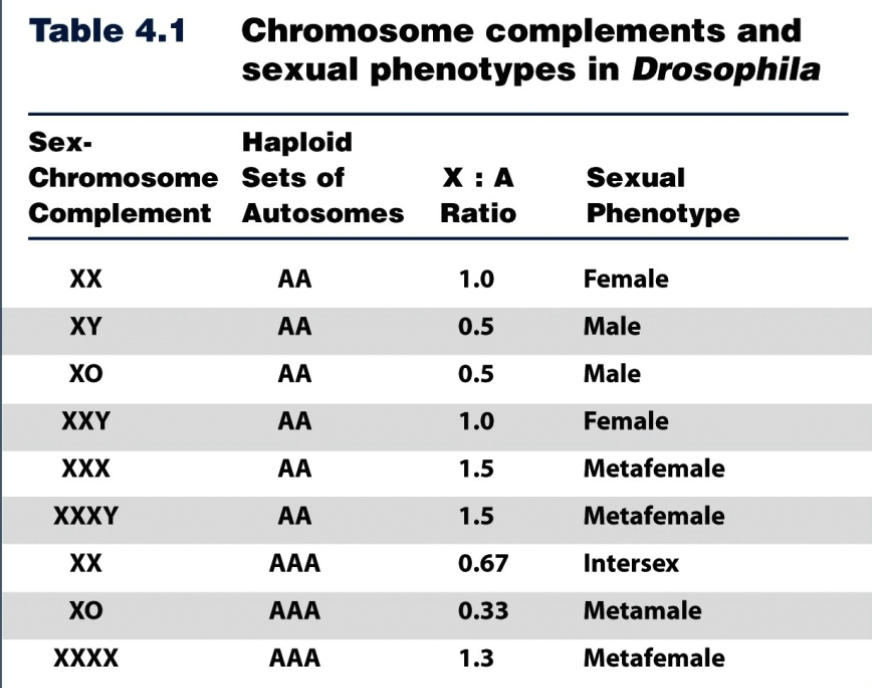
How does sex determination function in drosophilia?
Follows XX and XY but the Y does NOT play a role in sex determination
based on the ratio of proteins coming from X chromosomes and proteins made by the autosomes
1:1 is female
Less than 1:1 is male
What is dosage compensation (name the 3 types)?
Dosage compensation is a mechanism that equalizes amount of gene product of x chromosomes
double X activity in males (Drosophila)
halve X activity of genes on both X in females (nematodes)
inactivate one of the x in females (mammals)
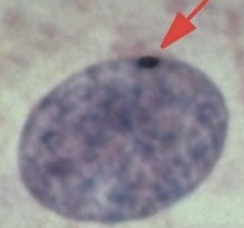
What is a barr body?
An inactivated X chromosome in the somatic chromosome (ONLY IN FEMALE)
seen as a densely packed spot in the nucleus of the cell
dosage compensation
How does DNA inactivation occur?
RNA coats the chromosome and compacts it!
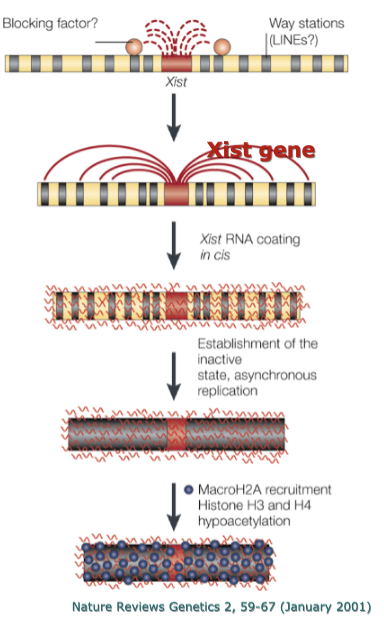
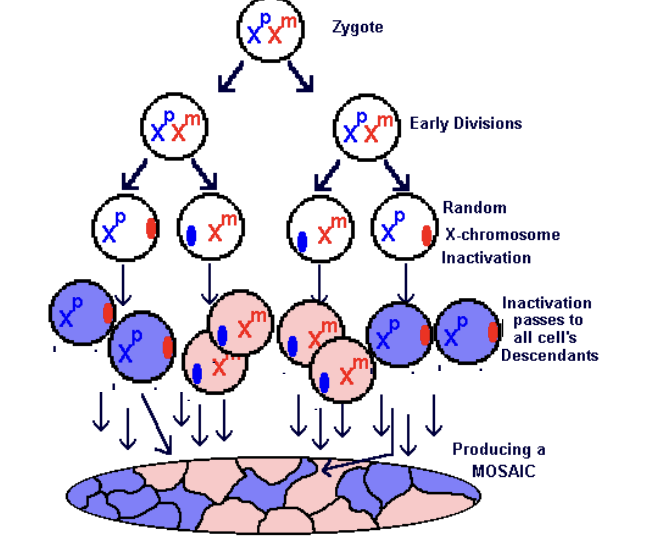
What is the genetic result of X inactivation in humans?
Produces a mosaic in tissue (not all cells are the same since inactivated X is random)
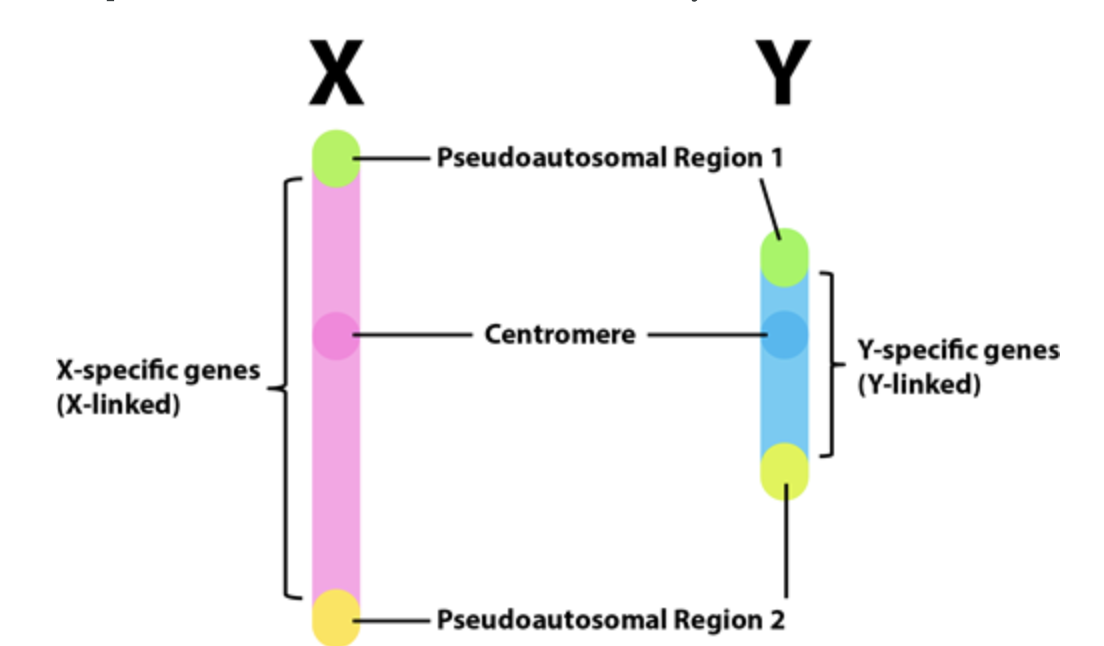
How does the pseudoautosomal region on the X and Y provide function and properties of the few genes in that region?
Critical for pairing in meiosis in the male (recombine).
Behaves like an autosome here!
What is the pattern of inheritance for the Y chromosome and how is it useful?
Doesn’t get recombined (except at the ends)
Only the males get the Y (passed from father to son like a clone)
What is the nature of mitochondrial DNA inheritance?
Mitochondrial DNA is passed from the mother to all her offspring but only the daughters can continue passing the trait.
What types of diseases are associated with mutations in mitochondrial DNA?
Depends on the mitochondrial genes that is affected!
Some examples: myopathy, neuropathy (NARP), hearing loss
What is Klinefelter’s Syndrome?
XXY (male)
What is Turner’s Syndrome?
X0 (female)
How does inactivation work in Klinefelter’s and Turner’s Syndrome?
Nothing is inactivated in Turner’s (already missing an X)!
One X is inactivated in Klinefelter’s!
What are psuedoautosomal regions?
Homologous regions on the X and Y chromosome (at the tips) that match to allow for the sex chromosomes to pair up