chemical tests
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
test for hydrogen
hold a lit splint near the top of the test tube
hear a squeaky pop
test for oxygen
use a glowing splint
it will reignite
test for carbon dioxide
bubble the gas through limewater
limewater turns cloudy
test for ammonia
use damp red litmus paper
turns blue
test for chlorine
use damp litmus paper
turns white (bleaches)
flame test
used to show the presence of certain metal ions (cations) in a compound.
A platinum or nichrome wire is dipped into concentrated hydrochloric acid to remove any impurities.
The wire is dipped into the salt being tested so some salt sticks to the end.
The wire and salt are held in a non-luminous (roaring) bunsen burner flame.
The colour is observed.
Properties of the platinum or nichrome wire is:
Inert
High melting point
colours in flame tests
lithium-red
sodium-yellow
potassium-lilac
calcium- orange-red
copper- blue-green
colours of ions formed after adding sodium hydroxide
ammonium- will turn damp red litmus paper blue
copper (II)- blue precipitate
iron (II)- green precipitate
iron (III)- brown precipitate
test for carbonates
add hydrochloric acid- if present fizzing will occur
test b checking for the presence of carbon dioxide using limewater
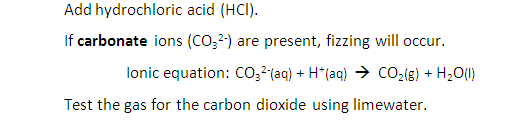
test for halides
other impurity is sulfides

test for sulfates
other impurity is sulfides

chemical test for presence of water
Add anhydrous copper (II) sulfate (CuSO4) to a sample.
If water is present the anhydrous copper (II) sulfate will change from white to blue.
physical test for presence of water
If the sample is pure water it will boil at 100oC