ECON 204 Final
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Econ 204 ualberta final. supply and demand, market structures, internation trade.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Economics
Study of choices people make regarding the allocation of scarce resources to satisfy their needs and wants.
Judging economic efficiency
efficiency
equity
moral and political consequences
Correlation Fallacy
incorrect belief that correlation means causation
Post Hoc Fallacy
error of reasoning that a first event causes a second because if occurred first
Fallacy of Composition
what is true for the individual is not true for the group
Opportunity Cost
benefit given up by not using the resources in the next best alternative way
Law of Increasing Costs
in order to produce extra amounts of one good, society must give up ever increasing amounts of the other
Rationality Assumption
the assumption that individuals make decisions aimed at leaving themselves better off
Three Players in the Market
Households
Firms
Government
Circular Flow Diagram
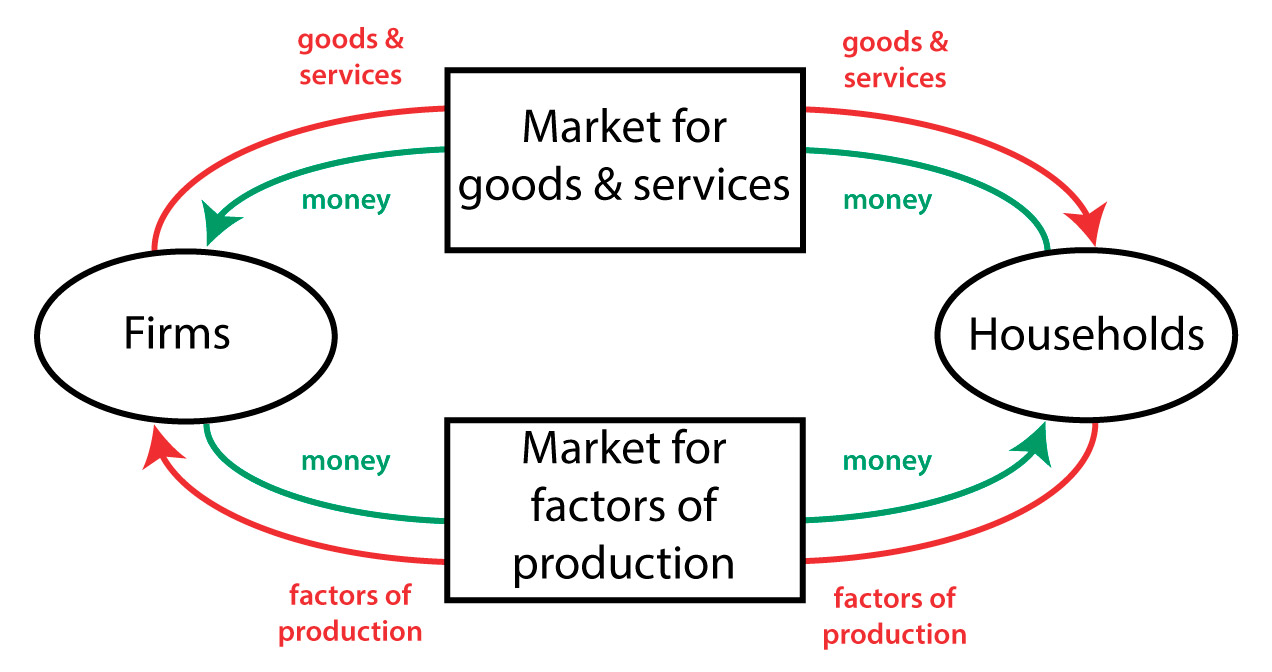
Law of Demand
As the price of a good decreases, the quantity demanded increases, and vice versa.
Law of Supply
As the price of a good increases, the quantity supplied increases, and vice versa.
Equilibrium
quantity demanded equals quantity supplied
Price Floor
Government set min price. High price floor causes surplus
Price Ceiling
government sets max price. Low price ceiling causes shortage.
Quota
government sets maximum quantity (reduces supply)
Elasticity
measures responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns
as each new unit of the increasing input is added, the marginal output gets smaller. (less efficient)