Oceans Atmospheres Climate Exam #2
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Explain the cycle of changing pacific atmospheric circulation from an El Niño to a La Niña event?
The Walker Circulationthe
pattern of rising and sinking air, flips
The rising air, which is associated with heavy rainfall and clouds during El Niño, moves back to the western Pacific and Indonesia.
This causes drier conditions in the central Pacific and wetter conditions in places like Indonesia
Concisely explain the cycle of changing Pacific sea surface temperatures from an El Niño to a La Niña event?
weakened trade winds reverse
Pushes warm pacific waters east towards the Americas
The El Niño weakens
Trade winds strengthen
Pushing the warm water further west
Sketch a map showing sea surface temperatures distributions for both El Niño and La Niña events?
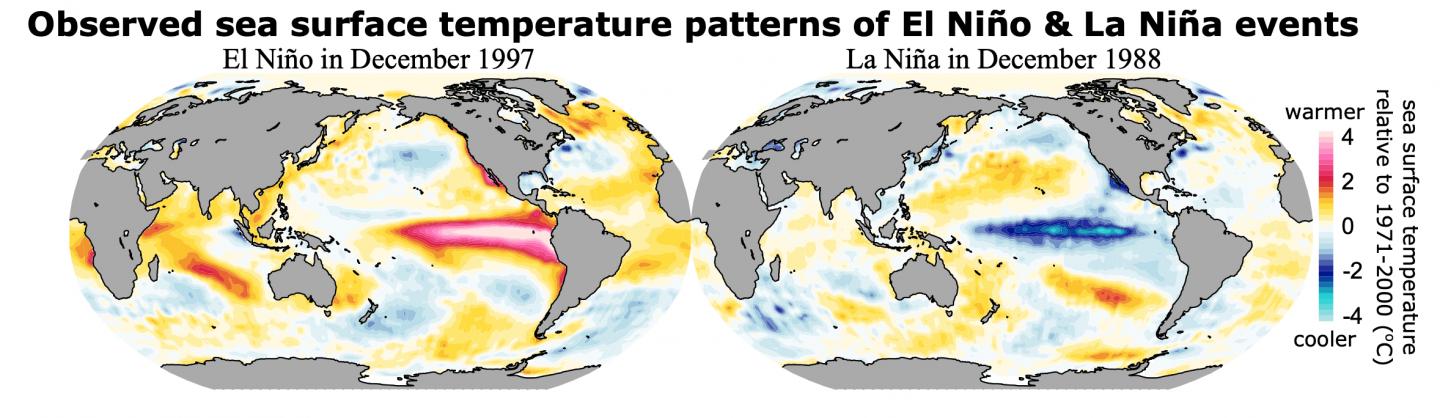
How is precipitation effected along the coast of Peru during an El Niño event?
Precipitation increases, leading to devastating floods and mudslides
How is precipitation effected along the coast of Australia during an El Niño event?
Precipitation would reduce, particularly in the eastern and northern coastal regions
How do ocean currents affect primary productivity (algae growth) in the ocean which in turn impacts the productivity of fisheries?
Ocean currents control the distribution of essential nutrients, this in turn directly affect fisheries because the algae are the base of the marine food web
Does algae growth impact upwelling? If so, how?
Yes, because they are driving or suppressing the vertical movements of water.
What is upwelling?
An oceanographic process where wind-driven currents cause cold, nutrient-rich water from the deep ocean to rise toward the surface.
What and how can we learn from a varied lake record in the Ecuador about the history of the El Niño Southern Oscillation?
This offers a window into the Earths long term climate history, allowing scientists to learn about the frequency, intensity, and impacts of the ENSO.
How can we learn from varied lake records?
These records provide valuable insights into the past climate conditions and how they have changed over time.
What about a lake sediment record from the western tropical Pacific?
This record provides information mostly on the opposite end of the ENSO: the La Niña state.
What is an open gyre?
An open gyre is a large, rotating system of ocean currents that acts like a massive vortex. It is driven by global wind patterns, the Earths rotation, and the boundaries of continents.
How are ocean gyres different in the northern and southern hemisphere?
In the north, the subtropical gyres rotate clockwise, whereas in the south, the subtropical gyres rotate counterclockwise.
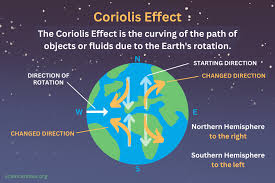
Describe how the Coriolis differs in the northern and southern hemispheres.
In the North, the Coriolis effect deflects moving objects, including ocean currents, to the right. In the South, the Coriolis effect deflects moving objects to the left.
Diagram how the Coriolis Effect differs in the North and South hemispheres?
Name two types of plat boundaries?
Divergent boundary and convergent boundary
What are these plat boundaries role in the carbon cycle?
The divergent boundary adds carbon to the atmosphere, while the convergent boundary is responsible for both removing and releasing carbon into the atmosphere.
At what timescales are these processes active in the carbon cycle?
Divergent boundaries are very continuos, but very slow, process and the carbon removal at convergent boundaries through subduction is a slow, long term process.
What is the age of the oldest ocean crust?
200 million years old
What limits the age of the oldest ocean crust?
It limits its age because of the continuous process of seafloor spreading and subduction, which together acts as a geological conveyor belt.
How do the densities of ocean and continental crust compare?
Oceanic crust is significantly denser than continental crust. The density difference is a primary factor driving plate tectonics and shapes the earths surface
Describe the two different categories of volcanism in the Pacifc ring of fire and the midocean ridges.
In the pacific ring of fire, volcanism is caused by convergent boundaries and subduction zones, while at mid-ocean ridges it is caused by divergent boundaries and sea floor spreading.
Sketch out how volcanism is different in that Pacific ring of fire and the mid ocean ridges.
Are the sources of magma different in the two volcanism systems in the ring of fire and the midocean regions?
Yes they are different, in the midocean regions the magma originates from hot, solid mantel beneath the separating plates. The subduction zones magma is generated in the mantle wedge.
Draw a map of the Atlantic’s mid ocean ridge showing how the age of crust changes moving away from the ridge.
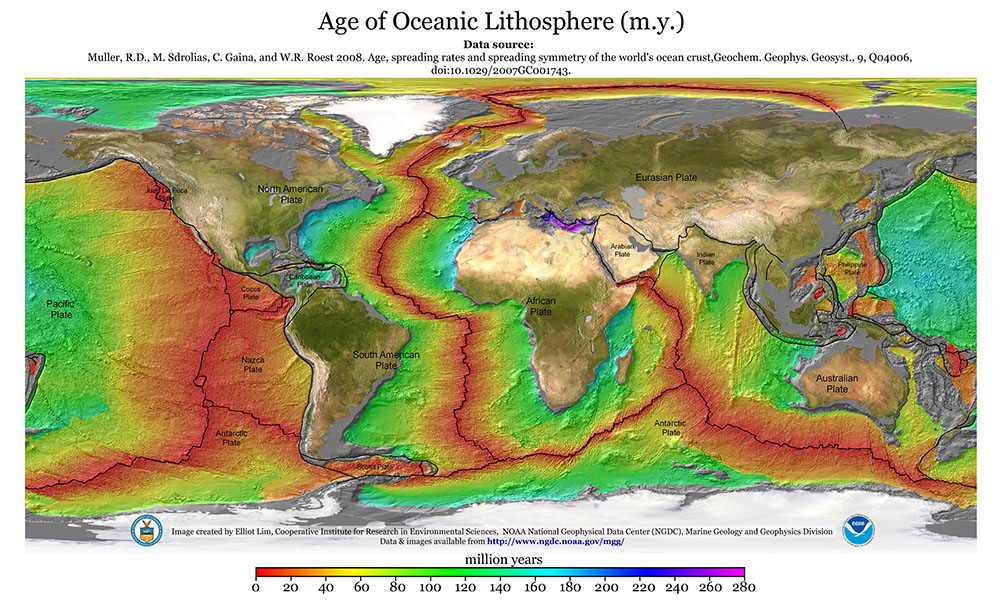
Explain the paleomagnetic signal archived in the basaltic ocean crust.
This is a magnetic record of earths past magnetic field. It is recorded as a pattern of magnetic stripes that run parallel and symmetrically on both sides of a mid-ocean range. This record is created through the behavior of iron-rich minerals in cooling magma.
How is this information of the paleomagnetic signal useful for understanding rates of plate movements?
This is crucial for understanding plate movements because it provides a reliable, long term timeline for seafloor spreading. By combining the magnetic striping pattern with the GPTS, scientists can effectively date the ocean floor and calculate the speed at which plates have moved in the past.
Does the rate of plate movements change over time?
Yes, the rate of plate movement changes over time because of slab pulling and ridge pushing.
Diagram the biological pump
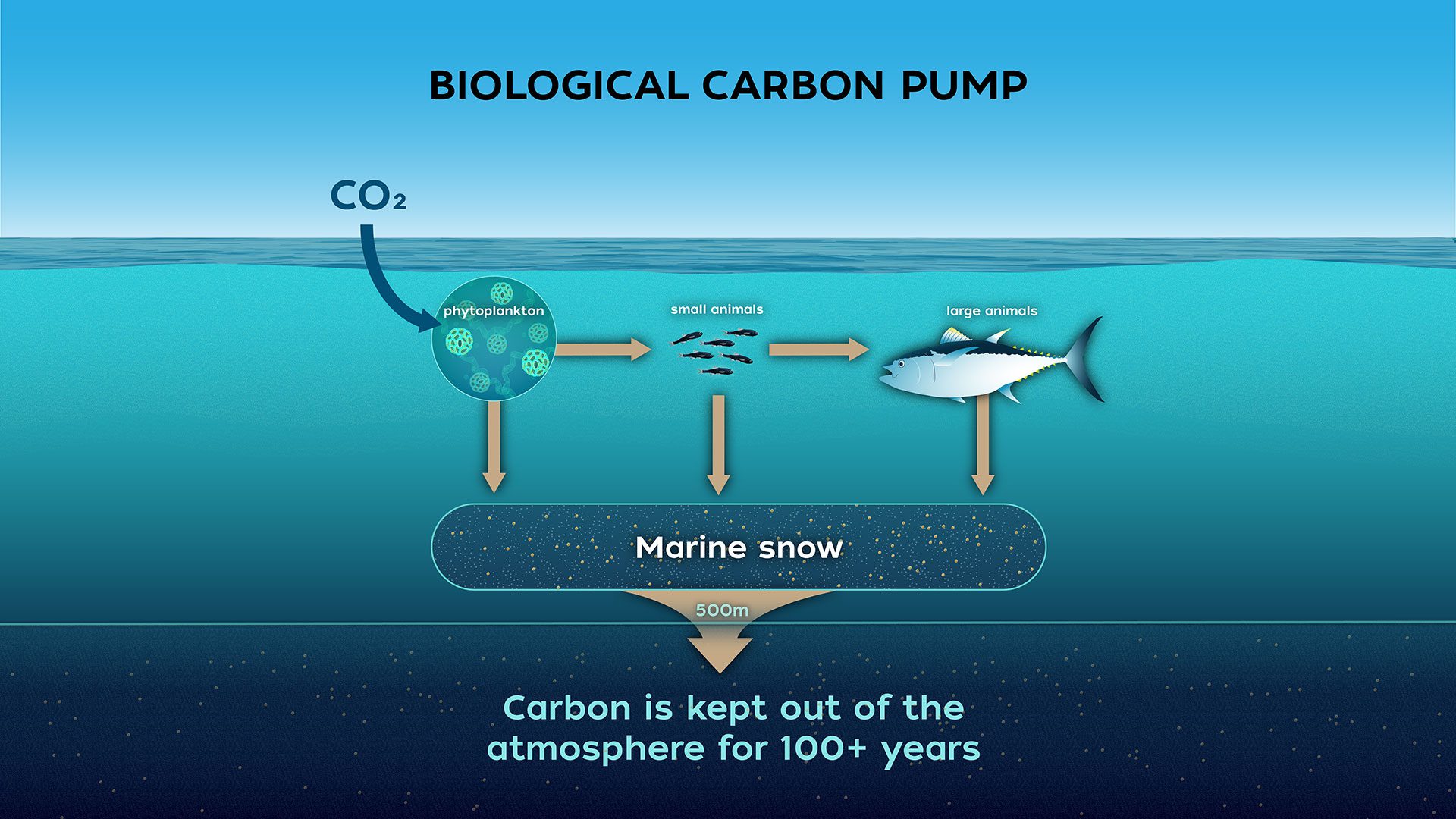
Describe the biological pump
The biological pump is a process by which carbon is transferred from the atmosphere to the deep ocean, where it can be stored for long periods.
What is the role of the biological pump in the carbon cycle?
The biological pump is a key component of the carbon cycle, removing carbon from the atmosphere and putting it into the deep ocean.
Describe the process of photosynthesis and respiration using basic chemical formulas
Photosynthesis: 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2. Respiration is just the opposite.
How can changes in the rock weathering rates impact the carbon cycle?
Changes in rock weathering rates can impact the carbon cycle, primarily by influencing the long-term balance of atmospheric carbon dioxide. This occurs through chemical weathering, a process that removes CO2 from the atmosphere and stores it in the ocean and sediments.
How can changes in continental uplift unchanged as the formation of the Himalayas impact the carbon cycle?
Through accelerated rock weathering, organic carbon burial, and altered climate patterns.
What are the major carbon reservoirs?
The major carbon reservoirs are the Atmosphere, Oceans, Biosphere, Geosphere, and Soils.
Which carbon reservoirs exchange carbon over annual to century timescales?
Solis, Atmosphere, Ocean, and Biosphere
Which carbon reservoir take a millennium or more?
The Deep ocean and the Geosphere
Which carbon reservoirs take millions of years?
The Geosphere
Rank them in terms of largest capacity to store carbon to the least.
Geosphere, Oceans, Soils, Biosphere, and Atmosphere
Describe how nutrient concentrations are different in upwelling zones?
Nutrient concentrations are exceptionally high in upwelling zones compared to the surrounding surface waters of the ocean.
What are sea surface temperatures like in upwelling zones?
Sea temperatures are typically much colder than in the surrounding surface waters.
Name or describe the location of two upwelling zones?
Coast of Peru and West Africa
What controls climate on biological timescales?
CO2, Photosynthesis, Respiration, and Circulation
Why is there very little ocean crust older than about 1.5 million years old?
It gets recycled through subduction
which is the largest reservoir of carbon?
The deep ocean