3. Citric Acid Cycle
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is the schematic diagram of a mitochondria with all membranes and spaces labeled?
DRAW IT
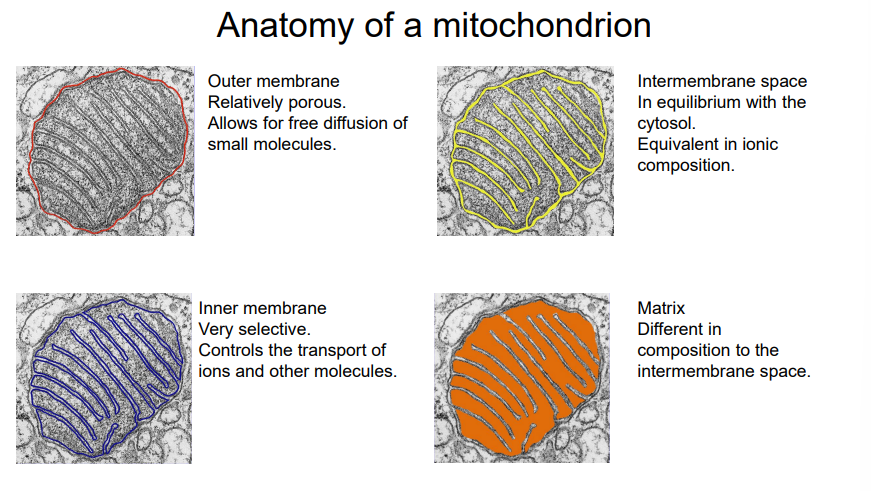
Where do glycolysis, pyruvate decarboxylation, and CAC take place in human cells?
Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis - Cytosol
Pyruvate Decarboxylation + CAC - Mitochondrial Matrix
What is the net reaction for the generation of acetyl-CoA from Pyruvate?
Pyruvate + CoA-SH +NAD+ —> Acetyl-CoA + CO2 + NADH (Twice b/c 2 Pyruvate)
Decarboxylation - release energy
Oxidation - NAD+ oxidizes Pyruvate —> NADH
Form thioester bond - require energy
What becomes “activated” after hydrolysis and what ΔG°’ is associated with it?
CoA-thioesters and large -ΔG°’
What are the two resonance structures that stabilize the negative charge that results from abstraction of a proton from acetyl-CoA?
Enolate ←→ Ketone
DRAW IT
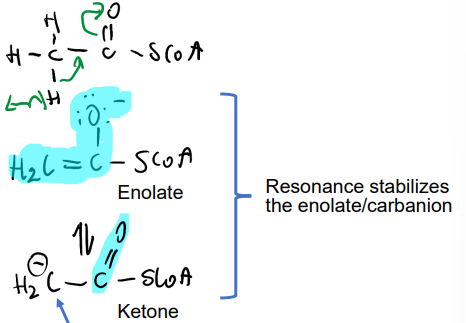
What is the nucleophilic species that attacks the electrophilic carbonyl group of oxaloacetate?
The carbanion H2C-
How is Step 2 of the CAC a setup rxn for oxidative decarboxylation in Step 3?
It makes the hydroxyl group of citrate accessible to oxygen (isomerize tertiary carbon to a secondary carbon) which is necessary for decarboxylation
What is the movement of electrons that occur in decarboxylation in the intermediate in Step 3?
DRAW IT
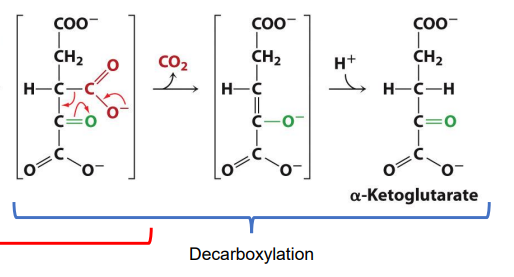
How is Step 4 of CAC similar to Step 3 chemistry wise?
Both use oxidative decarboxylation that produce NADH and CO2
Why is the generation of acyl-phosphate from CoA-thioester in Step 5 thermodynamically feasible?
The breaking of a thioester bond is coupled with the formation of a phosphoanhydride bond
What is the phosphoryl group donor to GDP in Step 5?
Succinyl-Phosphate
It is similar to Step 7 in Glycolysis where acyl-phosphate donates a Phosphate to ADP
Where do the CO2 molecules that are lost in Oxidative Decarboxylation in Steps 3 and 4 come from?
Oxaloacetate
What are Steps 6-8 of CAC?
DRAW AND MEMORIZE
Succinate —> Fumarate —> Malate —> Oxaloacetate
What are the mitochondrial locations of the redox cofactors NADH and QH2?
NADH - Mitochondrial Matrix (CAC) + Cytosol (Glycolysis
QH2 - Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
What is the yield of nucleoside triphosphate and reduced cofactors for one turn of the CAC?
3 NADH + 1 QH2+ 1 GTP
What is organ responsible for fructose metabolism when fructose is consumed in large quantities?
The liver
What is the overall metabolism of fructose including uptake?
Fructose —> Fructose (Blood) + Fructokinase —> Fructose 1-P + Aldolase B —> DHAP (then to glycolysis/glycogenesis/gluconeogenesis) or Glyceraldehyde —> Glyceraldehyde 3-P (then to glycolysis/glycogenesis/gluconeogenesis)
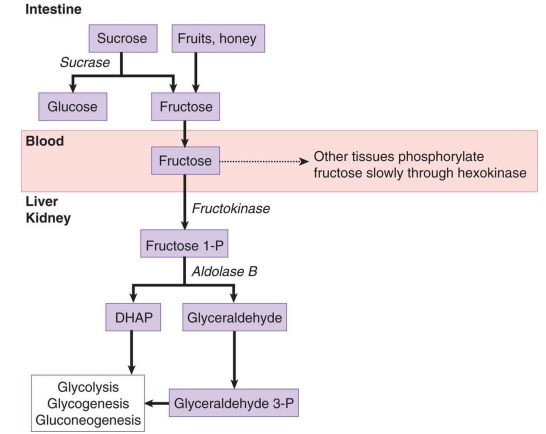
What can lead to a crash in ATP levels in fructose metabolism?
The phosphorylation of Fructose 1-P by Fructokinase is not regulated by feedback inhibition which can lead to rapid phosphorylation of which uses ATP
What are the potential outcomes of high levels of fructose metabolism in the liver?
ATP depletion, increased fat synthesis, and elevated uric acid
What can be used to turn into Pyruvate, Acetyl CoA, or G3P to produce energy?
Anything from glycerol, fatty acids, and amino acids