1A Anatomy - Cell part 3-5
1/214
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
215 Terms
Glycogen
Type of cytoplasmic inclusion that is the storage form of carbohydrates
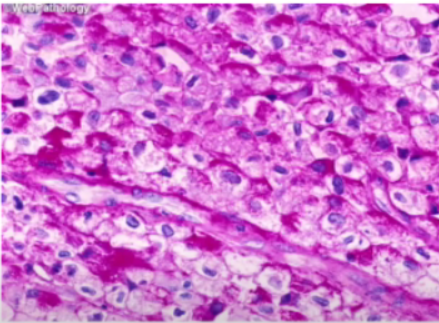
Pars fibrosa
The electron-dense area formed by rRNA molecules produced in the nucleolar organizing region
phagocytosis
The engulfing of solid substances to bring them into the cell
Ribonucleoprotein or ribosomal subunits
An rRNA molecule linked to proteins from the cytoplasm is called ___.
Stop codon (i.e., UAG, UAA, UGA)
It signals the ribosome to end the process of protein synthesis.
Amino acids
What are the monomers that make up proteins?
TRUE
Lamins A and B are part of the nuclear lamina (fibrous lamina). (True or False)
catalase
This enzyme converts hydrogen peroxide to oxygen and water.
mitochondrial DNA
___ is the only DNA in the cells that is found outside the nucleus.
Between / Intermediate
Compared to microfilaments and microtubules, their size is ___ the two.
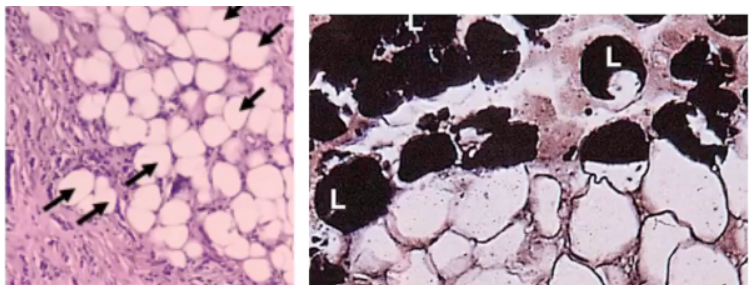
Fat/lipid droplets
Type of cytoplasmic inclusion present in adipose cells
Crystals
Cytoplasmic inclusions present in very few cell types and of unknown exact chemical composition and functions
Ribosome
It translates the mRNA code into polypeptide chains.
Skeletin filaments
Desmin is also known as ___.
TRUE
The ER is the most extensive membrane-bound structure in the cytoplasm. (True or False)
macropinocytosis
The engulfing of large amounts of liquid into the cell
glycocalyx
What is the term for the cell coat formed by the projection of glycolipid and glycoprotein from the outer surface of the cell membrane?
oxidases
This enzyme is responsible for the detoxification and catabolism of various substances.
TRUE
The chemicals in the lysosomes are hydrolytic enzymes bound by unit membranes. (True or False)
active at pH = 5; inactive at pH = 7.2
At what pH is the lysosome active and inactive?
mitochondria
The human genome contains the total amount of DNA present in the chromosomes and in the ___.
5
Only about __% of the DNA molecules in the chromosomes encode for genes.
Heterophagy - digestion of foreign substances brought into the cell via phagocytosis; Autophagy - digestion of the cell's own unneeded structures
What is the difference between heterophagy and autophagy?
mRNA
What connects polyribosomes/polysomes together?
FALSE
In males, somatic and sex chromosomes are homologous. (True or False)
diplosome
Two centrioles are collectively called ___.
Exocytosis
What is the process of transporting secretory products out of the cell?
TRUE
More than one ribosome can translate an mRNA at the same time. (True or False)
endoplasmic reticulum
Organelle made up of interconnecting tubules, vesicles, and sacs known as cisternae
Nucleus
Where does tRNA transcription occur?
G-actin (globular actin)
Half of the actin in cells exists as F-actin while the rest exists as ___.
increased number of ribosomes (numerous phosphate groups of the RNA in ribosomes)
What makes the cytoplasm basophilic?
FALSE
All cells are capable of phagocytosis. (True or False)
microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs)
Microtubules are surrounded by ___ that strengthen and stabilize their walls.
To produce ribosomal units
What is the function of the nucleolus?
Nuclear pores
These are hundreds to thousands of circular openings that perforate the nuclear envelope.
ribosomes, centrosome
What organelles are not delimited by unit membranes?
order
In the human chromosomal genome, there are 3 billion nitrogen-containing bases arranged in a specific ___.
Nucleolar organizing region
Area where chromosomes containing nuclear organizers (genes that code for rRNA) gather then transcribe and produce rRNA
FALSE (chromatin is not RNA)
Clumps of RNA are attached to the nuclear lamina. (True or False)
keratinocytes
Keratin filaments are only present in epithelial cells, especially in ___. Their primary function is to protect cells from mechanical and nonmechanical stresses.
Anticodon
What is the trinucleotide sequence located at one end of the tRNA?
lysosomes
These are pouches made of unit membranes and hydrolytic enzymes from the Golgi complex.
endocytosis
The engulfing of extracellular substances to bring them into the cell
22
How many somatic pairs of chromosomes do humans have?
TRUE
Crystals are NOT membrane-bound. (True or False)
Pore diaphragm
What structure covers the nuclear pore as a thin film?
Ribosome
It translates the mRNA code into polypeptide chains.
- Maintains cell shape and integrity of the cytoplasm
- Stabilizes cytoskeletal interactions
- Provides support and anchor cytoplasmic organelles
What are the functions of vimentin?
FALSE (each membrane is 7 to 8 nm thick while the perinuclear space is 10 to 30 nm thick)
Each individual membrane of the nuclear envelope is thicker than the perinuclear space. (True or False)
carrier transport
It uses carrier proteins to move molecules across.
Hemoglobin
The iron-containing pigment responsible for the color of red blood cells
TRUE
Cytosol is viscid, translucent and colloidal in nature. (True or False)
Genes
These are "codes" that produce nucleic acids and proteins.
FALSE
Proteins from free ribosomes are exported out of the cell through exocytosis. (True or False)
rod
Crystals are most often __-shaped.
FALSE (it has 2, an inner and an outer membrane)
The nuclear envelope/membrane has a single unit membrane. (True or False)
Polymerization of alpha-tubulin and beta-tubulin
How are microtubules formed?
TRUE
Cytoplasm refers to the material within a living cell, excluding the nucleus. (True or False)
Lipochrome/lipofuschin
Pigment granules that appear yellowish-brown; are of coalesced residual bodies common in long-lived cells
generates most of the cell's energy for performing metabollic processes, degradation process of the enzymes in the mitochondrial matrix yields a lot of ATP molecules
Why are mitochondria called the "powerhouses" of the cell?
centrioles
It is a tubular structure consisting of an electron-dense wall of assembled microtubules surrounding an electron-lucent space.
Melanocytes; keratinocytes
Melanin is produced by then transferred to for storage.
1
How many pairs of sex chromosomes do humans have?
FALSE
Large and small ribosomal subunits find their way to the cytoplasm together via nuclear pores. (True or False)
Skin; nerve cells of substantia nigra; locus coeruleus of brain; pigment epithelium of retinas
Melanin is present in , , , and .
FALSE
All living things are multicellular. (True or False)
Nuclear lamina (also fibrous lamina)
What structure stabilizes the nuclear pores?
TRUE
The lysosomes can digest nearly all organic substances in the cell. (True or False)
Due to several types of keratin subunits
Why does the biochemical composition of keratin filaments vary depending on cell type?
It houses chromosomes where genes are stored
Why is the nucleus considered as the data bank of the cell?
Zymogen granules
Proteins from the Golgi complex to be released extracellularly via exocytosis; also known as secretory granules
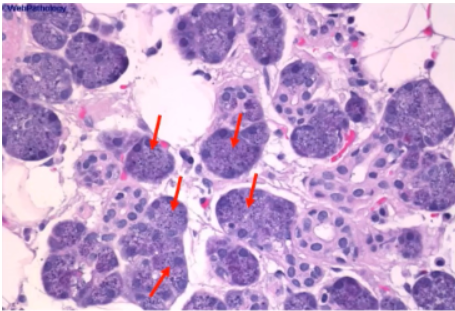
Transfer vesicles
What are the small membrane-bound vesicles released by the rER towards the Golgi complex?
Centrioles bud and grow out of the lateral surface on each centriole. The procentrioles elongate to form daughter cells and set perpendicularly to their mother cells. The mother-daughter centrioles make up a diplosome and acquire centriolar satellites to form a centrosome.
How do centrioles replicate?
TRUE
Microfilaments are scattered haphazardly in the central area of the cell. (True or False)
rough endoplasmic reticulum
The perinuclear space can be regarded as a specialized portion of the ___.
Pars granulosa
This is formed when rRNA from the pars fibrosa and imported proteins from the cytoplasm get linked together.
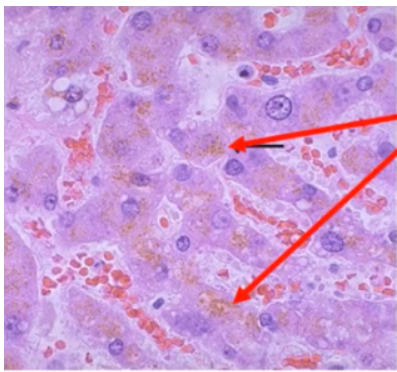
Hemosiderin
Pigment granules that appear brown in color; pigment produced from the lysosomal digestion of hemoglobin
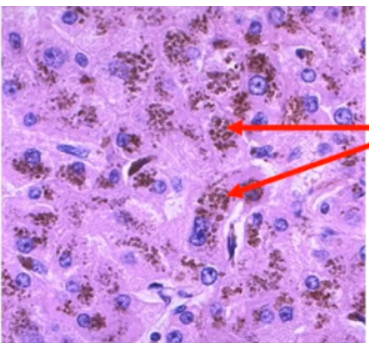
phagocytosis
What is the process of engulfing materials such as microorganisms and senescent red blood cells?
TRUE
The inner membrane of the mitochondrion is folded to form the cristae that projects into the intercristal space. (True or False)
centrosome
It is the site of microtubule assembly and production.
Iron
What component of hemosiderin allows it to be distinguishable from other pigments via special staining?
chromatin
Chromosomes are the highly condensed form of ___.
cell
A ___ is capable of independent existence as long as its environmental conditions are favorable
5
There are ___ pairs of chromosomes with nucleolar organizers in humans.
phagocytes
What is the term for cells that are capable of phagocytosis?
Nucleolus (produce mRNA, tRNA, rRNA)
What structure inside the nucleus serves as the site for RNA synthesis?
FALSE (Are membrane-bound)
Residual bodies are NOT membrane-bound. (True or False)
46
How many chromosomes are present in diploid cells?
Adipose
In __ cells, the nucleus is pushed to the periphery due to the large amount of stored lipids.
Epithelial cells; keratinocytes
Keratin filaments are only present in ___, especially in ___ or the main cell type in the epidermis.
Protecting epithelial cells from mechanical and non-mechanical stresses; cell-to-cell attachment
The primary function of keratin filaments is ___, but they are also involved in ___.
rough endoplasmic reticulum
It is the site of protein synthesis and it receives and processes the proteins from the attached ribosomes.
proteins
The nuclear lamina is made of lamins, nuclear intermediate filaments, and nuclear lamin-associated membrane ___.
Cytoplasmic inclusions
Generally temporary and inert structures found in cells of variable size, shape, and content
Chromosomes
In what structure within the nucleus are genes stored?
Movement of organelles and cellular structures; changes in cell shape
The cytoskeleton is mainly involved in ___ and ___.
Euchromatin
Pale areas in the nucleus that do not take up stains
Myocardial muscle cells; Sertoli cells in testes
Give two examples of cells that may contain lipofuschin granules.
FALSE
The human genome consists of the total amount of DNA present in the chromosomes only. (True or False)