healthcare system study guide
1/309
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
310 Terms
define managed care
system that integrates financing and delivery of appropriate medical care by means of the following:
-contracts with selected physicians and hospitals to provide care for enrollees, usually on a predetermined monthly premium
-utilization and quality controls that contracting providers agree to accepts
-financial incentives for patients to use providers associated with the plan
-the assumption of some financial risk by doctors
True or false: managed care provides cost effective health care
true
what three things are we trying to balance in managed care
access, quality, cost
primary reason for managed care growth
steadily rising and unsustainable health care costs
HMO Act of 1973
-feasibility grants and low-interest developmental loan programs made available to encourage interested parties to develop and build HMOs
-the establishment of procedures through which health plans could become "federally qualified HMOs"
-inclusion of preventative as well as curative health care benefits
-requirement that employers offer federally qualified HMOs to their employees under certain circumstances
what is the differentiating feature of managed care versus fee-for-service
the use of provider networks
network
group of providers, linked through contractual arrangements, supply a full range of primary and acute care services
two common physician reimbursement methods in HMOs
-capitation
-discounted FFS
risk bearing
the amount of risk borne by the provider, which can range from full risk to no risk
physician type
the relationship between the MCO and the physician(s)
relationship exclusivity
addresses whether the physician provides care to patients from one MCO only or to patients from multiple MCOs
out of network coverage
addresses whether care received from a provider who is not in the MCOs network is a covered benefit
MCO characteristics: Place providers at risk
capitation costs for given population are first estimated. providers paid prospectively to provide agreed upon services. providers take risk that the capitation rate will cover all the costs of care for the population. the provider assumes risk that was traditionally underwritten by insurance company
MCO characteristics: Gatekeepers
central component of most HMOs. Gatekeepers are typically primary care physicians. gatekeeper may be financially at risk for medical services
HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) model types
staff, group, network, IPA
Other MCO (managed care organization) models
PPO, POS, EPO, PHO
Health maintenance organizations
organized health care systems that are responsible for both the financing and the delivery of a broad range of comprehensive health services to an enrolled population
staff model HMO
physicians who provide care are employees of the HMO
staff model characteristics
-physicians typically do no see outside patients
-physicians are salaried
-physician mix of generalist and specialist
-have a good degree of organizational control
-high level of control over costs and utilization of services
-pharmacy services provided through in house pharmacies
-do not provide out of network coverage
example of staff model HMO
health partners, Harvard community health plan, group health cooperative of puget sound
group model HMO
organization that contracts with a multi specialty physician's group to provide services to an enrolled group
group model characteristics
-physicians are reimbursed through capitation or are salaried
-physicians see HMO patients only
-no out of network coverage
-pharmacy services provided through in house clinic pharmacies and contacts with network of community pharmacies and mail order
-less organization control
-group practice may be centralized-cant expand to other geographical areas easily
-group practice may be too small to provide a wide range of services
examples of group model HMOs
kaiser health plans, group health alliance plan of Michigan
network model HMO
can be visualized as a group of group practices organized to function as a single group of physicians
characteristic of network model HMOs
-physician networks bear risks
-physicians see HMO and non-HMO patients (non exclusive contracts)
-no out of network coverage
-physicians reimbursed either through capitation or discounted FFS
-pharmacy services offered through in house contracts with community pharmacy networks, and mail order pharmacies
-increases geographic accessibility, patient selection capability and breadth of practitioner expertise
-less organizational control
examples of network model HMOs
health insurance plan of greater New York, healthnet, pacificare, blue plus
IPA (independent practice association)
physicians form their own separate legal entity (usually corporation or partnership) and then contracts with MCO
characteristics of IPA
-most decentralized
-association serves as voice for physicians
-IPA shares risk with MCO
-physicians reimbursed by IPA for services t enrolled patients for a negotiated fee (either through capitation or discounted FFS)
-physicians can see HMO and non-HMO patients
-pharmacy services provided through contracted network of independent and chain community pharmacies and mail order pharmacies
-difficult to adopt policies
examples of IPA
HMO PA-US HealthCare, Medica
advantages of IPA
-maximizes patient choice -low start-up financial requirements -geographic dispersion -community based
disadvantages of IPA
-difficult to standardize policies -difficult to manage utilization -less efficient communication
HMO- summary
-provider network -no out of network coverage -PCP is gatekeeper -prior authorization -most restrictive type of health plan -give least choice to members -lowest out-of-pocket expenses
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
-affiliations of providers that seek contracts with insurance plans
-Less restrictive than HMOs in their choice of health care providers. However, they require greater "out of pocket" payments from members
characteristics of PPOs
-patients have more choice of providers
-channeling through differential cost-sharing
-no gate-keeper PCP; no prior authorization
-financial incentives to use in-network physicians
-DISCOUNTED FEES FOR PROVIDERS
-utilization review (case by case utilization management)
-physicians do not bear any risk
-PPOs exert less control over providers than do HMOs
-grown popular network in recent years
How is PPO different from an HMO?
-physicians bear no risk
-availability of out of network coverage
-don't have "gatekeeper" PCP
Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO)
a form of PPO in which no coverage is provided for care received outside of the provider network
POS (point of service) plan
allows patients to select providers at the same time the service is needed rather then they join the plan. When care is received from a provider outside of the network, some coverage is provided
characteristics of POS
-hybrid of HMO/PPO -has contracted provider network -encourages members to choose PCPs. higher copays for those not choosing to go through PCPs -out of network coverage available
what is a healthcare report card?
a published document that measures and compares the quality of care delivered by health care providers
what is a healthcare report used for?
used to disseminate information on quality MCOs
who uses health care report cards?
employers, government and consumers to compare and understand the performance of the health plan for the purpose of selecting a plan
what is included in a health care report card?
info on both cost and quality
NCQA (National Committee for Quality Assurance)
-independent, not for profit organization dedicated to evaluating and reporting on the quality and performance HMO
-played a major role in the development of standardized report cards
how does NCQA accomplish its mission
through accreditation and performance measurement programs
HEDIS HealthCare Effectiveness Data Information Set
NCQA performance measurement program
What does HEDIS collect?
performance measurements that reflect the achievements of health plans across relevant domains
examples of performance measurements
use of breast cancer screening, availability of providers, member disenrollment rates, average length of stay for maternity care
True or false: more than 90% of HMOs are providing some HEDIS measures
true
Who does NCQA estimate have used HEDIS and accreditation in deciding which plan to purchase
over half of the large employers in the US
why did Pharmacy Benefit Manager (PBM) come into existence
in response to managed care environment
why were PBMs created?
to develop, promote, maintain, and integrate pharmacy and medical benefit programs
carve-out (benefit plan)
payer removes, or carves out, a specific benefit from the internal health plan delivery system and offers the benefit through and external company
What do PBMs provide?
delivery and financing of pharmacy benefits for a defined population
characteristics of PBMs
-have a provider network -offer mail service -negotiate discounts with providers, generic substitution, and rebates -offer electronic claims adjudication -use formularies, prior to authorizations and step protocols to control costs -perform drug utilization review -cost sharing -provider and patient education
two types of employer sponsored health insurance
full insured, self-funded
Define health insurance exchanges
online health insurance marketplace, either state, federal, or jointly run, depending on the state
define self insurance
assume the risk of potential loss rather than purchase insurance
who can self insure?
large companies
list benefits of self insurance
ability to customize benefits, ability to focus on employee health problem trends, improved cash flow, federal employer income tax exclusion
Describe self funded payments
the employer does not pay premiums: instead, it pays fixed costs (administrative fees and stop loss premium) and variable costs (employee health care claims)
self funded: assumption of risk
the employer assumes the risk
self funded: plan design
employers have more control and freedom in their plan designs
Self insured: compliance payments
The Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1947 (EIRSA) pre-empts state regulations
Fully insured: payments
the employer pays monthly premiums to an insurance carrier
assumption of risk: fully insured
the insurance company assumes the risk
Plan design: fully insured
employers are more limited by the insurers' plan design options
compliance payments
the plan must comply with state regulations
list payment methods to physicians
salaries, fee for service, capitation
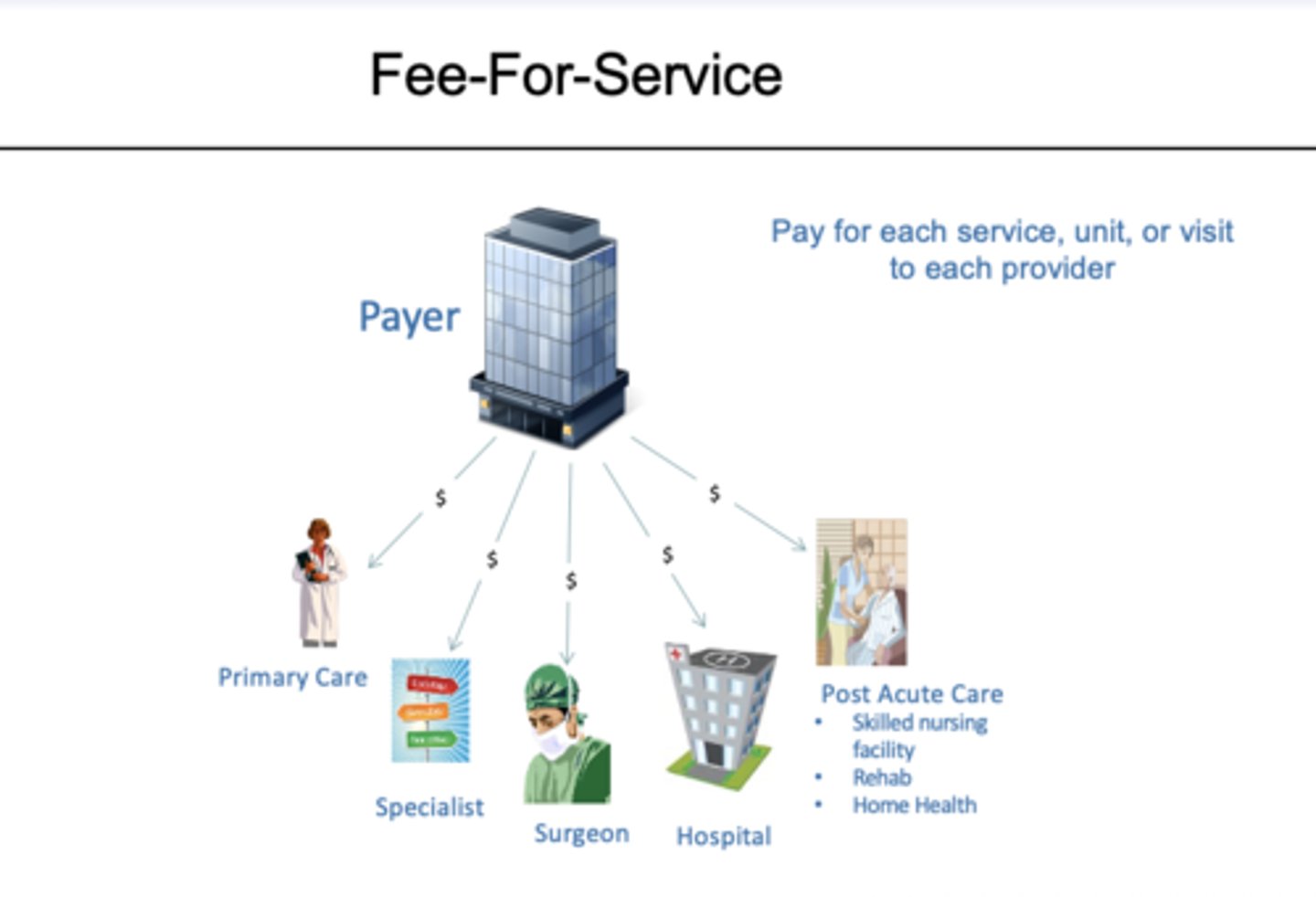
Define fee for service
-payment PER SERVICE
-no risk to providers
-no incentive for efficient production or utilization
define capitation
-payment PER SUBSCRIBER
-provider receives a set dollar amount per person per time period and assumes responsibility for delivery of all needed services during that time
List alternative payment models
P4P, ACOs, Medicare Advantage Plan bonuses, Bundled payments
Define P4P
newer form of payment structure. Providers paid only if they meet certain goals. Provides bonus (or imposes financial penalties) if providers meet or exceed (or fail to meet) quality or performance measures
define ACOs
groups of providers that agree to coordinate care and to be held accountable for quality and costs (group of providers agree to P4P
Define medicare advantage plan bonuses
-bonus payments to medicare advantage plans that achieve at least a four star quality rating
Bundled payments or episode of care payments
Single payment for all clinical services provided during a clinical episode.
What percentage of health care expenditures do physician payments make up
20%
Two methods of reimbursement (if physicians are not salaried or paid by capitation)
-U&C charges
-Fee Schedule (RBRVS)
Define U&C charges
based on actual charges-profiles of charges for each procedure are established by specialty are and geographical area
usual charge
amount typically charged by a physician for a procedure.
customary charge
prevailing amount charged among all physicians in the area.
Disadvantage of U&C charges
great deal of maintenance, profile of each physician needed ,physicians can keep increasing charges in the area and U&C charges will go up
Who uses RBRVS?
Center for medicare and medicaid services and other payers
Relative values of Resource-Based Relative Value Scale (RBRVS)
-depend on length, intensity, and complexity of procedure. Also reflects economic factors like inflation
Elements of Resource-Based Relative Value Scale
-physician work -practice expense -professional liability insurance -geographic practice cost index
Medicare conversion factor of RBRVS
$35.8
Advantage of RBRVS
easy to maintain once relative values have been established
Issues with RBRVS
the issue of balancing billing has arrived
Paying Hospitals: DRGs
-brought financial risk to hospital management
-redefined the unit of production or output to encompass clinical decisions by physicians as well las operation decisions by administrators
-DRGs have reduced medicare expenditures for hospital services: these savings have exceed out of hospital expenses
How are pharmacies paid?
prepaid drug programs
define prepaid drug programs
the only out of pocket payments are copayments per each prescription
Third party programs involve 3 entities
-insurer or underwriter -third party administrator (TPA) -the pharmacy
example of TPA
PAID & PCS
Why are TPAs important
-they adjudicate many claims that represent relative small dollar amounts
-they maintain atomization for verifying insurance
-they maintain pharmacy networks
-they maintain databases for utilization review
What is the cost of a prescription made up of
1. Product cost (AWP-specified %)
2. dispensing or professional fee
Total healthcare expenditures
4.3 trillion dollars
Healthcare expenditures per capita (person)
almost 13000
Total health care expenditures as a percent of GDP
18.3%
Why are rising healthcare costs are a concern?
-not good for the fiscal and economic well-being of the country
-high health spending associated with poor care
-affects affordability and access
two primary reasons health care costs are rising
-high healthcare prices
-aging population (medicare costs expected to increase)
why is the price of healthcare rising?
-innovate healthcare technology
-complexity of the healthcare system leading to administrative waste