Multiple choice answers for Developmental Final
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
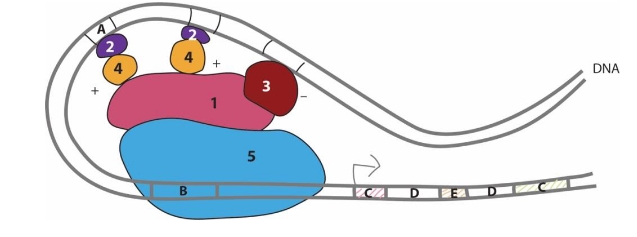
In the accompanying diagram, the protein marked #3 is a(n)
Repressor
Which of the following is a "show it" experiment?
In situ hybridization to examine spatial gene expression
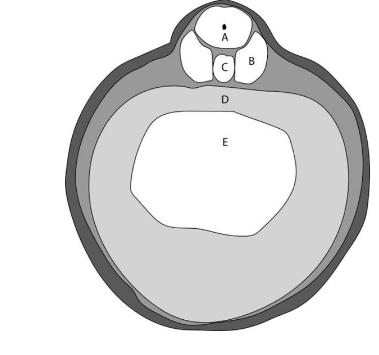
In the accompanying diagram, the structure labeled “C” arises from which germ layer?
Mesoderm.
Where does the Spemann organizer form?
At the dorsal vegetal region
Which embryonic tissue gives rise to the nervous system?
Ectoderm
Which characteristic does not make an organism a good developmental model?
Ethical restrictions on embryo use
What would happen if Chordin is knocked out in the frog embryo?
Ventralization of embryo
Which signaling pathway is responsible for dorsal identity in frogs?
Wnt/β-catenin
Which of the following is not a function of the Spemann organizer?
Activate zygotic transcription
What is the defining feature of terminally differentiated cells?
Stable, specialized function
Which cells become the endoderm?
Cells in the vegetal pole
Which stage comes immediately after gastrulation?
Neurula
What is the role of transcription factors?
Bind promoters and regulate gene expression
The ______________ receives signals from the organizer to form neural tissue.
Ectoderm
Why is studying development in humans challenging?
Ethical and practical limitations restrict experimental manipulation
What do you predict is likely to happen if vegetal cytoplasm is transplanted to the animal pole?
Animal cells would adopt mesodermal fates
What is the function of the dorsal lip of the blastopore?
Organizer of embryonic body plan
What induces mesoderm formation in the marginal zone?
Nodal-related signals from vegetal cells
Which maternal determinant promotes endoderm fate?
VegT
Which protein is encoded by maternal VegT?
T-box transcription factor
Which cell type initiates the highest Nodal expression?
Nieuwkoop center cells
Which term describes the spatial arrangement of cells during development?
Morphogenesis
Which organism is best suited for large-scale mutagenesis screens in development?
Fly
What term defines the state when a cell will follow a fate even if it is moved?
Determined
Which statement best describes the concept of epigenesis?
Structures in the embryo arise progressively through interactions and differentiation
What did John Gurdon's nuclear transplant experiments in frogs demonstrate?
Differentiated nuclei retain full genetic potential
What does the occurrence of identical nonuplets suggest about the early human embryo?
Blastomeres from early cleavage divisions are totipotent
Which tissue originates from the mesoderm?
Muscle
____________ refers to the ability of a cell to respond to a signal.
Competence.
Which experiment led to the discovery of the organizer?
Spemann-Mangold transplantation
Which molecule is a BMP antagonist?
Chordin
Where is the frog blastocoel located?
Between vegetal and animal poles
Which best defines developmental potential?
All possible fates a cell can adopt
If you wanted to clone your pet dog, Daisy, you can do a somatic cell nuclear transplant experiment. For this, Daisy would have to be:
The somatic cell nucleus donor
Which of the following does not always apply to a maternal determinant?
It is uniformly distributed throughout the embryo
A triploblast is _
An animal with three germ layers
The endoderm gives rise to the
Gut
Which result would you expect if you applied an antagonist of the Wnt signaling pathway to an early 4-cell C. elegans embryo?
Both EMS daughters adopt an MS fate.
Which best describes planar cell polarity?
Coordinated orientation within the plane of a tissue
What would be the likely consequence of a mutation that disrupts spatial colinearity in a Hox gene cluster?
Homeotic transformations, where one segment develops characteristics of another
Which signaling pathway is centrally involved in establishing planar cell polarity in both Drosophila and vertebrates?
Non-canonical Wnt/Frizzled pathway
Embryos from a mother homozygous for a loss-of-function mutation in nanos will likely show defects in their:
Posterior structures
Engrailed is an example of a:
Segment polarity gene
The P4 cell in C. elegans is similar in function to which cell(s) in Drosophila?
Pole cells
What is the ploidy of the Arabidopsis endosperm?
Triploid
What is the fundamental difference in how the BMP signaling gradient is established along the D- V axis in frog versus fly embryos?
In frogs, BMP signaling is blocked dorsally by antagonists secreted from the organizer; in flies, a gradient of Dpp (BMP homolog) activity is shaped by localized production and modulation
How would a mutation in a gap gene like Kruppel affect the expression of pair-rule genes like even-skipped?
The striped pattern of even-skipped expression would be disrupted or altered in the region normally specified by Kruppel.
What is the main function of PIN proteins in Arabidopsis embryos?
Transport auxin directionally
In vertebrate development, failure of planar cell polarity signaling during gastrulation would primarily disrupt:
Anterior-posterior axis elongation
If two cell populations express different types of cadherins, what will likely happen?
They will selectively segregate
How does the Bicoid protein gradient affect the transcription of the hunchback gene?
It activates hunchback transcription at high concentrations
In vertebrates like frogs, the dorsal organizer is functionally similar to which Drosophila region?
Neuroectoderm
The primary body axes in an Arabidopsis seedling are:
Apical-Basal and Radial
What is a key similarity between frog and fly embryos in terms of signaling gradients and nervous system specification along the D-V axis?
Both use a BMP gradient, with low levels specifying neural tissue.
In frog embryos, what event marks the start of gastrulation?
Apical constriction of bottle cells
Radial intercalation results in:
Thinning and spreading of tissue
The APX-1 ligand in C. elegans interacts with which receptor to induce ABp fate?
GLP-1
BMPs (Bone Morphogenetic Proteins) are vertebrate signaling molecules involved in D-V patterning. What is the Drosophila homolog of BMPs in this context?
Decapentaplegic (Dpp)
How does the Dorsal morphogen gradient specify different cell fates along the D-V axis?
By activating or repressing different target genes at different threshold concentrations.
The diagram shows a synthetic transgene. If this transgene is introduced Drosophila, where would you expect to observe GFP expression in the embryo?
GFP would be expressed in an anterior-to-posterior gradient in the embryo

Which is the correct temporal order of Drosophila embryogenesis stages?
Syncytial blastoderm → Cellular blastoderm → Gastrulation → Segmentation
The post-translation modification of cactus protein that happens when Toll receptor is activated is:
Phosphorylation
What are the key similarities in Hox genes between flies and mice that highlight their conserved roles in development?
They are clustered on the chromosome and exhibit spatial colinearity with their expression domains.
The diagram shows the expression of a zygotic segmentation gene in Drosophila. Which class does it most likely belong to?
Pair-rule gene

A novel mutation in Drosophila prevents translational repression of maternal hunchback mRNA by Nanos. Predict the effect on the embryo:
Loss of posterior structures
How does the syncytial nature of the early Drosophila embryo facilitate the establishment of morphogen gradients?
It allows for free diffusion of molecules throughout the cytoplasm before cellularization
The diagram indicates how a hypothetical gene X is regulated by threshold concentrations of its regulatory transcription factors A and B. Factor A forms an anterior-to-posterior gradient (high anterior), and Factor B forms a posterior-to-anterior gradient (high posterior). Where would gene X be expressed?
Only in the extreme anterior region.

In Drosophila, a cactus mutant is expected to have:
Expanded ventral mesoderm
How does the timing of gene expression differ between maternal effect genes and zygotic genes and how does this relate to their roles in early development?
Maternal genes are expressed early and establish initial axes; zygotic genes are expressed later and refine these patterns.
Convergent extension relies primarily on which cellular behavior?
Coordinated medio-lateral intercalation of cells.
What cell lineage in C. elegans sets up the posterior fate?
P2
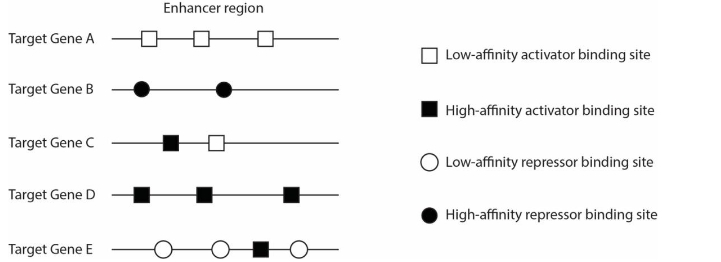
The diagram shows the enhancer regions of 5 different target genes. Which gene is most likely to be expressed in the zone where the concentration of the transcription activator is the lowest?
Target gene D
Which class of segmentation gene is first expressed after fertilization in Drosophila?
Gap
In Drosophila, pole cells are important because they:
Form the germline
A major difference between plant and animal development is that:
Plants do not undergo gastrulation
If a mutation in a maternal-effect gene results in all offspring of a homozygous mutant mother lacking terminal structures, what would you expect to observe in the offspring of a heterozygous mother? Assume the mutation is recessive.
None of the offspring will show the defect
Spatial colinearity in Hox gene clusters refers to the phenomenon where:
Hox genes at one end of the cluster are expressed at the anterior
On a fate map of a Drosophila embryo, the mesoderm is derived from cells located in the:
Ventral-most region