3.5.1 Demand for labour
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
what happens if demand for labour is elastic
then an increase in the wage rate will result in a more than proportional decrease in the quantity of labour demanded by firms,firms will be very responsive to changes in wage rates, rapidly hiring workers when wages fall and firing workers when wages rise
demand for labour graph
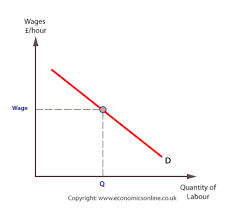
what type of demand is labour
derived demand
why id demand for labour derived demand
as the demand for labour depends on the demand for goods/services
marginal revenue roduct
additional revenue gaines by the firm from employing one extra worker
marginal physical product
the extra output produced by one extra worker
MRP equation
MPP X price of good sold
marginal physical product in short run
in short run as we add more workers to a fixed amount of capital the MPP is assumed to rise until the law of diminishing marginal returns sets in
when will firms hire to with MRP
MRP= wages
factors influencing demand for labour
consumer demand
market rice of good/servce
labour productivity
employment subsidy
cost of capital equipment
wage rate
how does price of product influence demand for labour
If the selling price of the product increases, it increases the marginal revenue product of labour and the firm will demand more labour
Higher priced products incentivise firms to supply more (law of supply) and demand for labour will continually increase with increasing prices
how does demand for product influence demand for labour
As demand for labour is a derived demand, when an economy is booming, then demand for normal goods/services will be high, and the demand for labour will be high
Conversely, when an economy is in a recession demand for normal goods/services will be lower, and the demand for labour will be lower
how does cost of capital machinery influence demand for labour
Firms will regularly evaluate whether it is more cost-effective to switch production from using labour to capital (machinery)
If it is more cost-effective, then demand for labour will fall
how does productivity of labour influence demand for labour
If the productivity of labour increases (possibly through training), this will lower average costs, and firms will likely demand more labour
elasticity of demand for labour
responsiveness of demand for labour when there is a change in the market wage rate
elasticity of demand for labour equation
%change in quantity demanded / % change in wage rate
examles of elastic labour
tourism,retail,cleaner
examles of inelastic laboyr
financial services,healthcare
factors affecting elasticity of labour demand
labour costs as % of total costs
availability of factor substitutes
PED for final product
time period
marginal cost of labour
cost of hiring one additional worker
number of jobs lost to technology 2040
47% of jobs in 2040