Hearing: cochlea and function and types of deafness
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
sound waves longitudinal or transverse
longitudinal
describe motion of sound waves
push-pull
how can you measure loudness of decibels
add 10 dB = double loudness
Normal hearing=
can hear quiet sounds less than 20 dB HL
mild hearing loss=
hearing between 20-40 dB HL
moderate hearing loss=
hearing loss between 41-70 dB HL
severe hearing loss=
71-95 dB HL
what is lateral 1/3 of external auditory meatus composed of
cartilage
ceruminous and sebaceous glands
produce cerumen= earwax
what are the medial 2/3 of external auditory meatus composed of
bone
lined with thick skin= continuous with tympanic membrane
describe ear drum/tympanic membrane
semi-transparent membrane
externally lined by thick skin
internally lined by mucous membrane
sandwich radial and circumferential collagen fibres
role of ossicles in hearing
movement of ossicles increases force and reduces amplitude of vibrations
what is stapedius
inserts to stapes
when tense→ reduces amplitude of vibrations
what is tensor tympani
inserts into malleus
when tense→ reduces amplitude of vibrations
what cranial nerve branches are involved in inner ear
vestibular branch of CN VIII
Fascial nerve CN VII
Vestibulo-cochlear nerve CN VIII
Cochlear branch CN VIII
components of vestibular system
saccule
utricle
semicircular canals
sound detection occurs in
tectoral membrane
what’s found beneath tectoral membrnae
inner hair cells
outer hair cells with villi which insert into tectoral membrane
where are outer hair cells embedded in
perilymph
describe what happens in organ of corti when calcium channels open
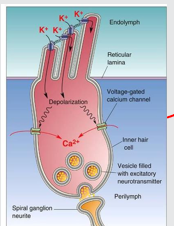
role of outer hair cells
actively amplify sounds
how do we hear
incoming sound= momentary pressure changes in air
collected by outer ear
pinna vibrates the eardrum
vibrates ossicles
which vibrates oval window on outside cochlea
which vibrates fluids inside cochlear
which vibrates basilar membrane where organ of corti is which has inner hair cells
vibrations make stereocilia go backwards and forwards→ pulls and pushes Tip Links
Tip Links pulls open transduction channels
transduction channels allow potassium into inner hair cells
depolarises inner hair cells→ fire off AP which goes to brain through AUDITORY NERVE= SOUND
role of outer ear in hearing
guides sound from outside world into middle ear→ changes in pressure
role of ossciles in hearing
in middle ear
amplify sounds
transmit sounds to inner ear
role of inner ear in hearing
= cochlea
converts changes in pressure into a signal that can be understood by brain
where is perception of sounds perceived
brain
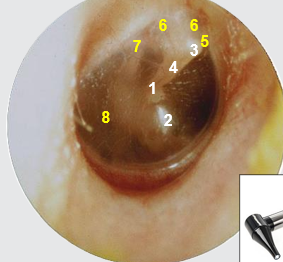
label 1-4
1) umbo
2) cone of light
3) lateral process of malleus
4) handle of malleus
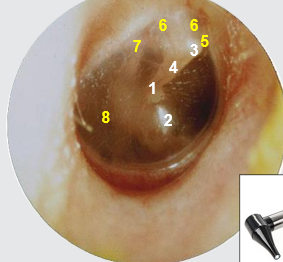
label 5-8
5) anterior mallear fold
6) flaccid part
7) posterior mallear fold
8) posterior inferior quadrant
what causes otitis externa and what is it
= inflammation of ear canal
caused when foreign bod becomes lodges
what is tympanosclerosis
scarring of tympanic membrane
causes calcium deposits to form
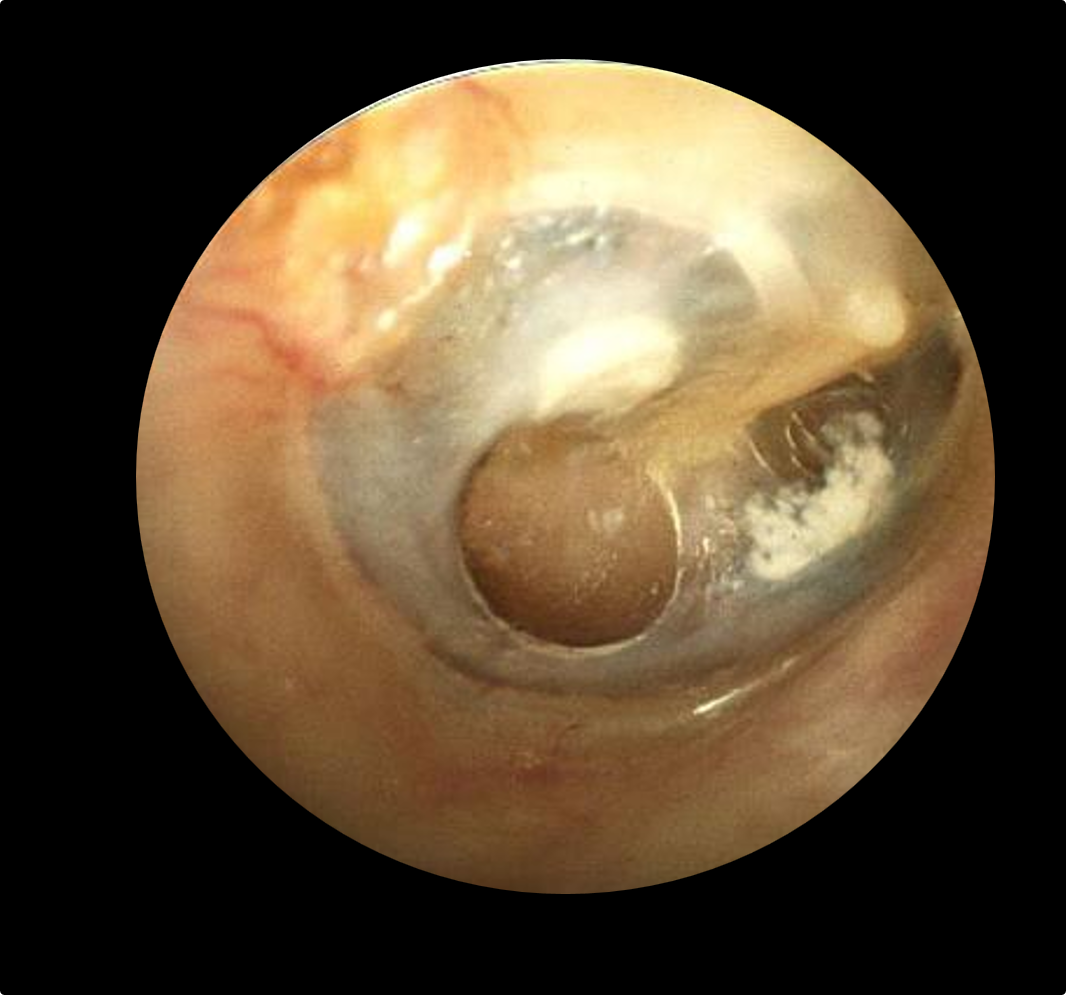
what does this show
perforation
features of otitis media
thick mucus in middle ear
bulging inflamed eardrum
swollen eustachian tube
what is otitis media
inflammation of mucous membrane lining middle ear
treatment for otitis media
grommet surgically inserted in tympanic membrane
describe interaural level differences
head casts an acoustic ‘shadow’
sounds arrives quieter at far ear
describe interaural time differences
sound has to travel further to get to far ear= arrives later
what is conductive hearing loss
if someone has loss by air conduction but not by bone conduction= air-bone gap
3 types of hearing loss
conductive
sensorineural
mixed
causes of sensorineural hearing loss
aging
noise damage
drug side effects
auditory tumours
blast/explosion
causes of mixed hearing loss
genetic disorders
infections
head trauma
causes of conductive hearing loss
fluid
foreign objects
allergies
ruptured eardrum
impacted earwax
what is sensorineural hearing loss
what is microtia
congenital abnormality
failure of auricle and external auditory meatus to develop
pre-auricular appendage
accessory cartilaginous appendage formed anterior and superior to tragus
normal hearing range
between 0-120 dB
describe Weber’s test
tuning fork on top of head
describe Rinne’s test
tuning fork on bone behind ear
patient says when sound stops
describe results for Weber’s test
none= hear best in midline
sensorineural= hear better in normal ear
conductive= hear better in affected ear
results for Rinne’s test
none= air> bone
sensorineural= air> bone
conductive = bone> air
purpose of audiometry
measure softest pure tone that can be detected in very quiet environment at various frequencies in each ear
what occurs in a hearcheck
3 high-frequency tone at decreasing intensities of 75, 55 and 35
then 3 mid-frequency tones at decreasing intensities of 55, 35 and 20 dB HL
results of hearcheck
if you miss:
1 tone at 1 or 3 kHz= mild hearing loss
2 tones at 1 or 3 kHx= moderate hearing loss
3 tones at 1 or 3 kHz= severe hearing loss
when is otoacoustic emissions used
= newborn hearing test
identify children with moderate to profound permanent bilateral deafness within 5 weeks of birth
tinnitus
conscious perception of auditory sensation in absence of corresponding external stimulus