Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Anatomy and Physiology are difficult to separate because
physiological functions depend on anatomical structures.
The activities of an anatomist consist of _________, whereas those of a physiologist consist of _________.
observing body parts; studying functions of body parts
Which of the following lists best illustrates the idea of increasing levels of complexity?
Cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism
The removal of wastes produced by metabolic reactions is
excretion.
Homeostasis is the
the tendency of the body to maintain a stable internal environment.
In negative feedback mechanisms, changes away from the normal state (set point)
stimulate changes in the opposite direction.
Positive feedback mechanisms
move conditions away from the normal state (set point).
Which of the following organs is in the abdominopelvic cavity?
The liver
The membrane on the surface of a lung is called the
visceral pleura.
The thoracic cavity lies ______________ the abdominopelvic cavity.
superior to
Blood cells are produced in the organs of the _____________ system.
skeletal
A parietal layer of a serous membrane__________, whereas as visceral layer of a serous membrane_____________.
lines cavities; covers organs
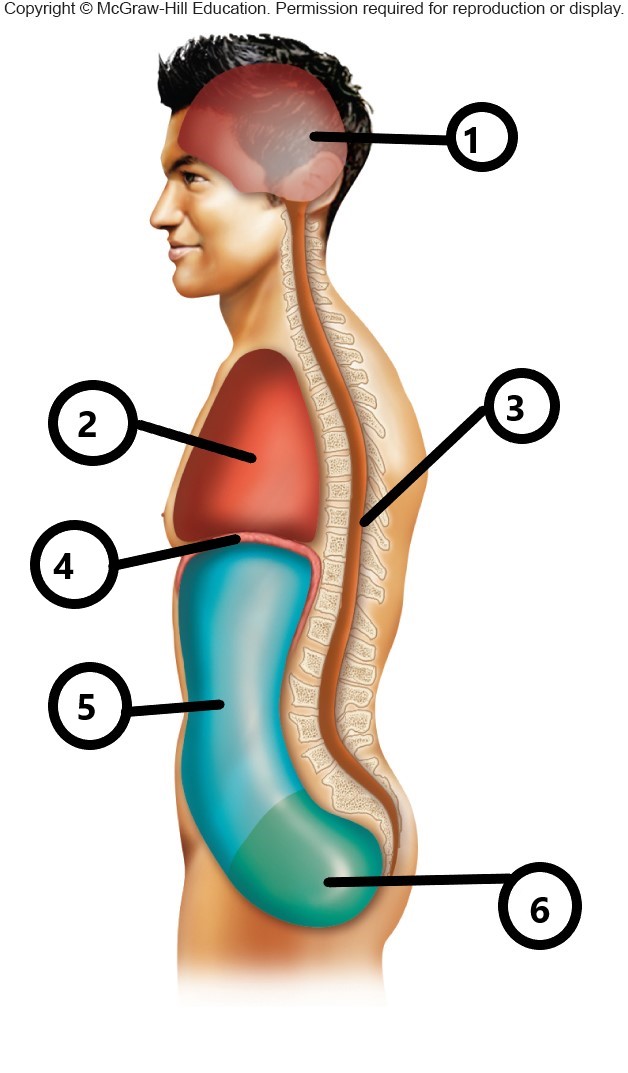
1
cranial cavity
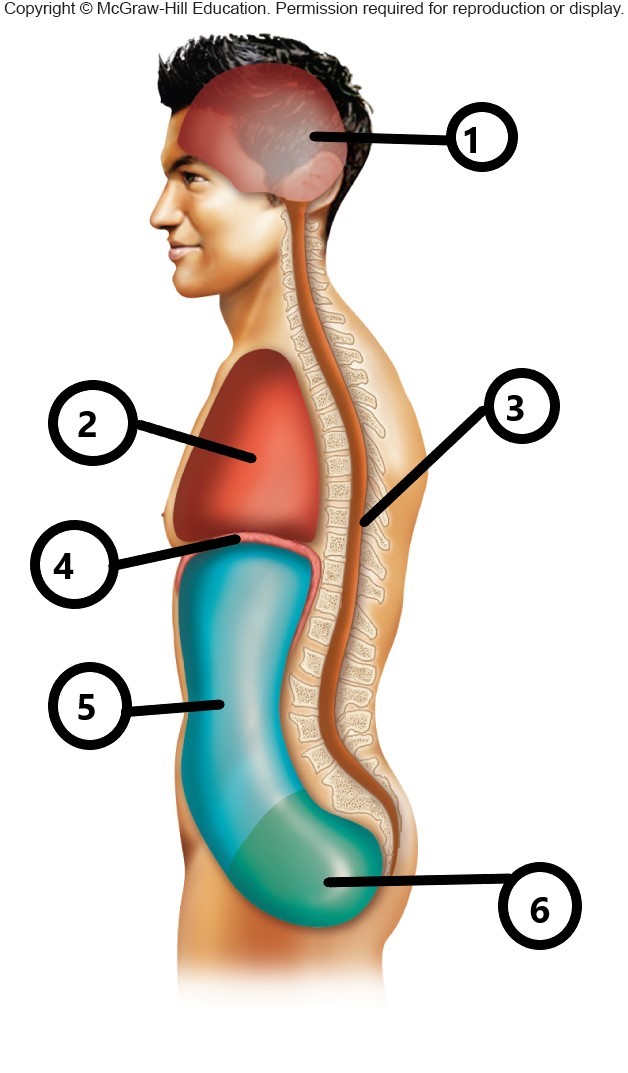
2
thoracic cavity
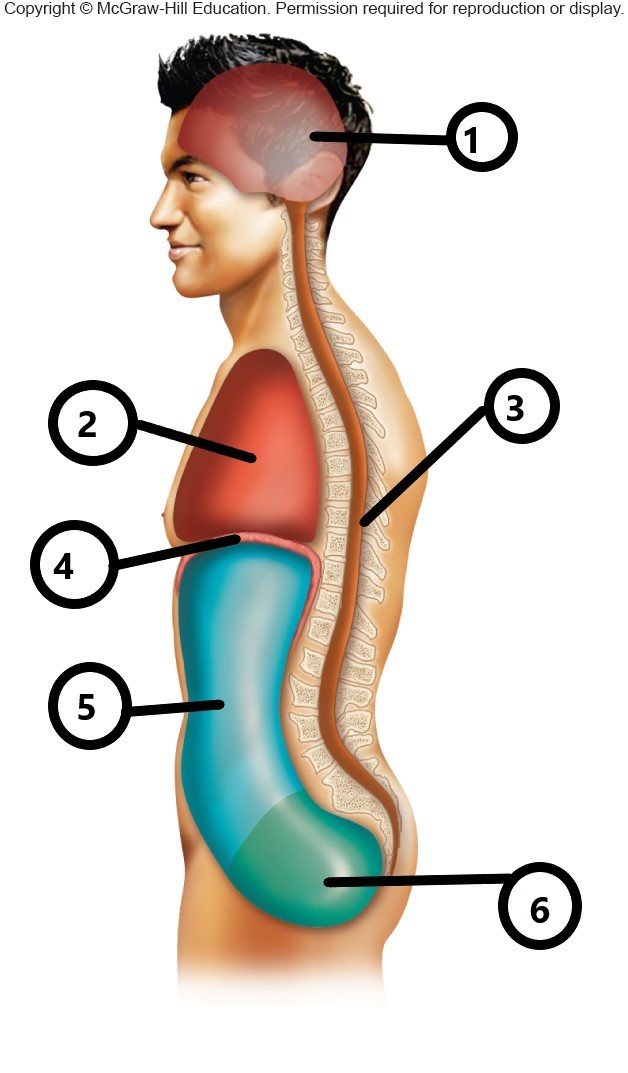
3
vertebral cavity
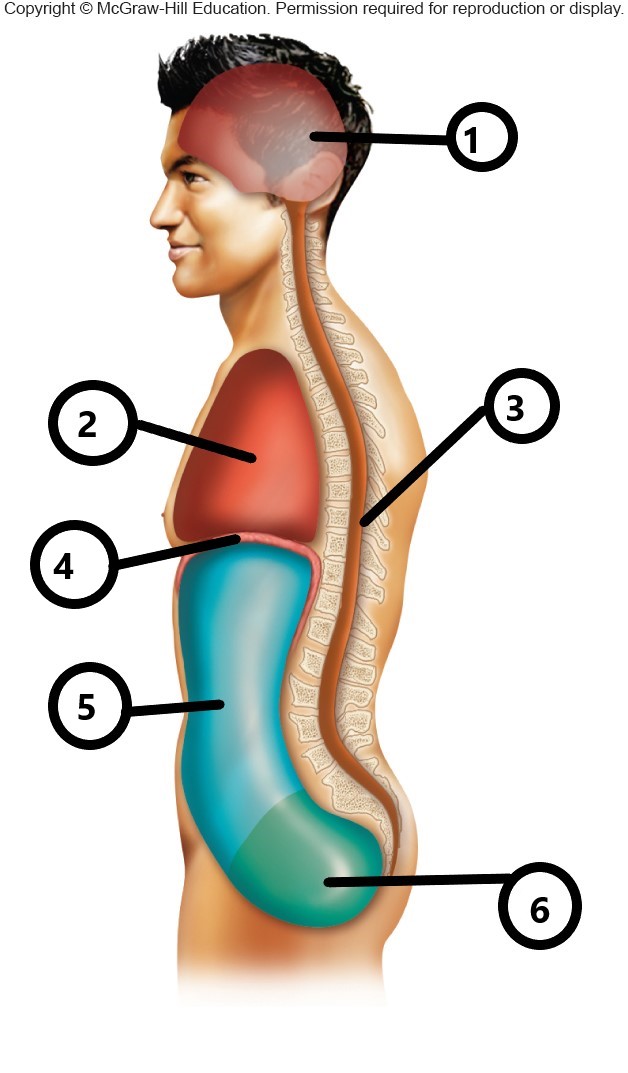
4
diaphragm
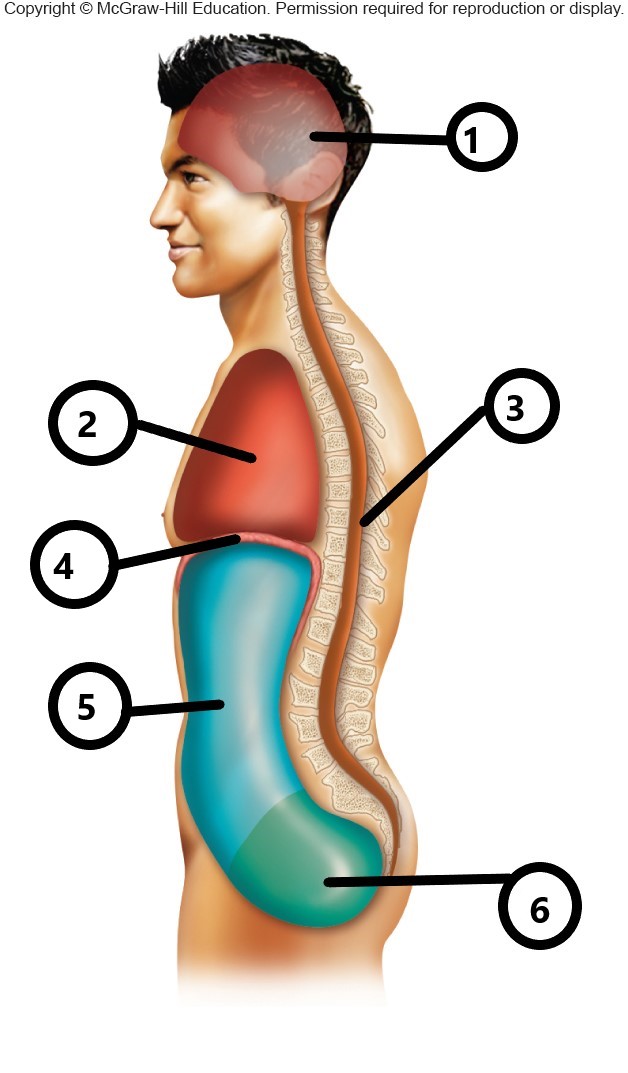
5
abdominal cavity
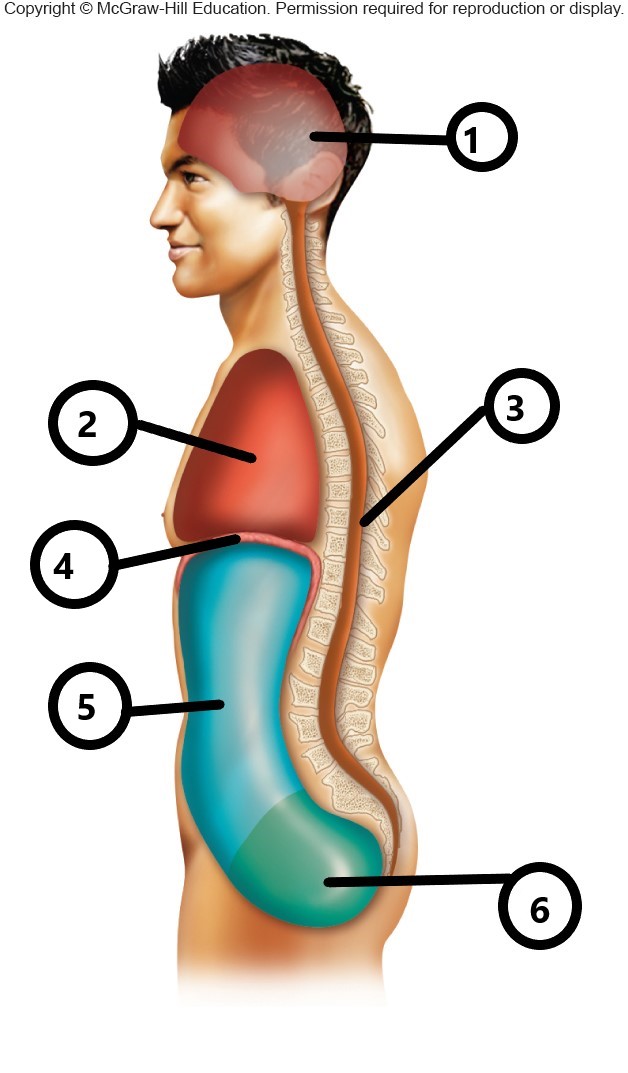
6
pelvic cavity
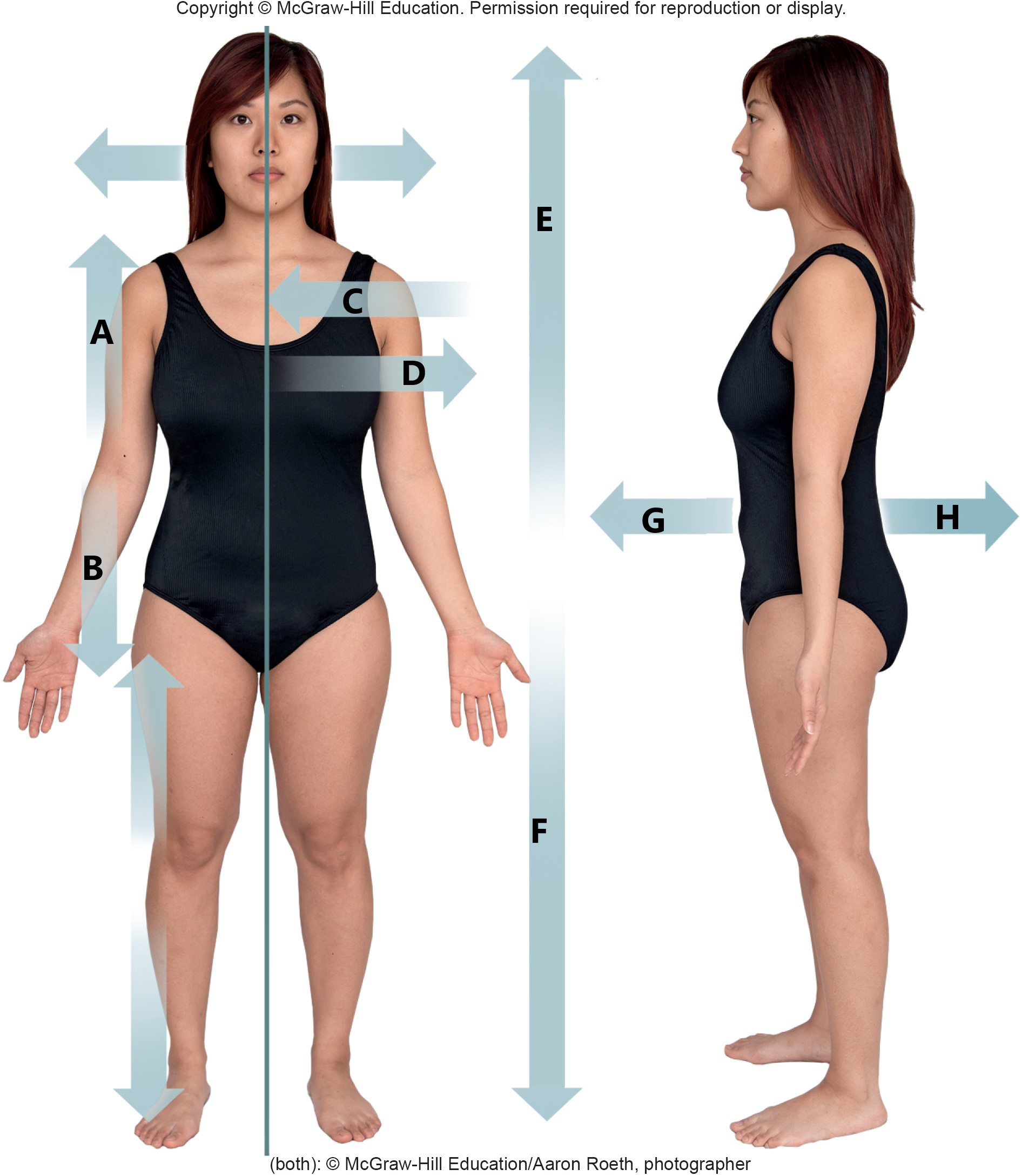
A
proximal

B
distal
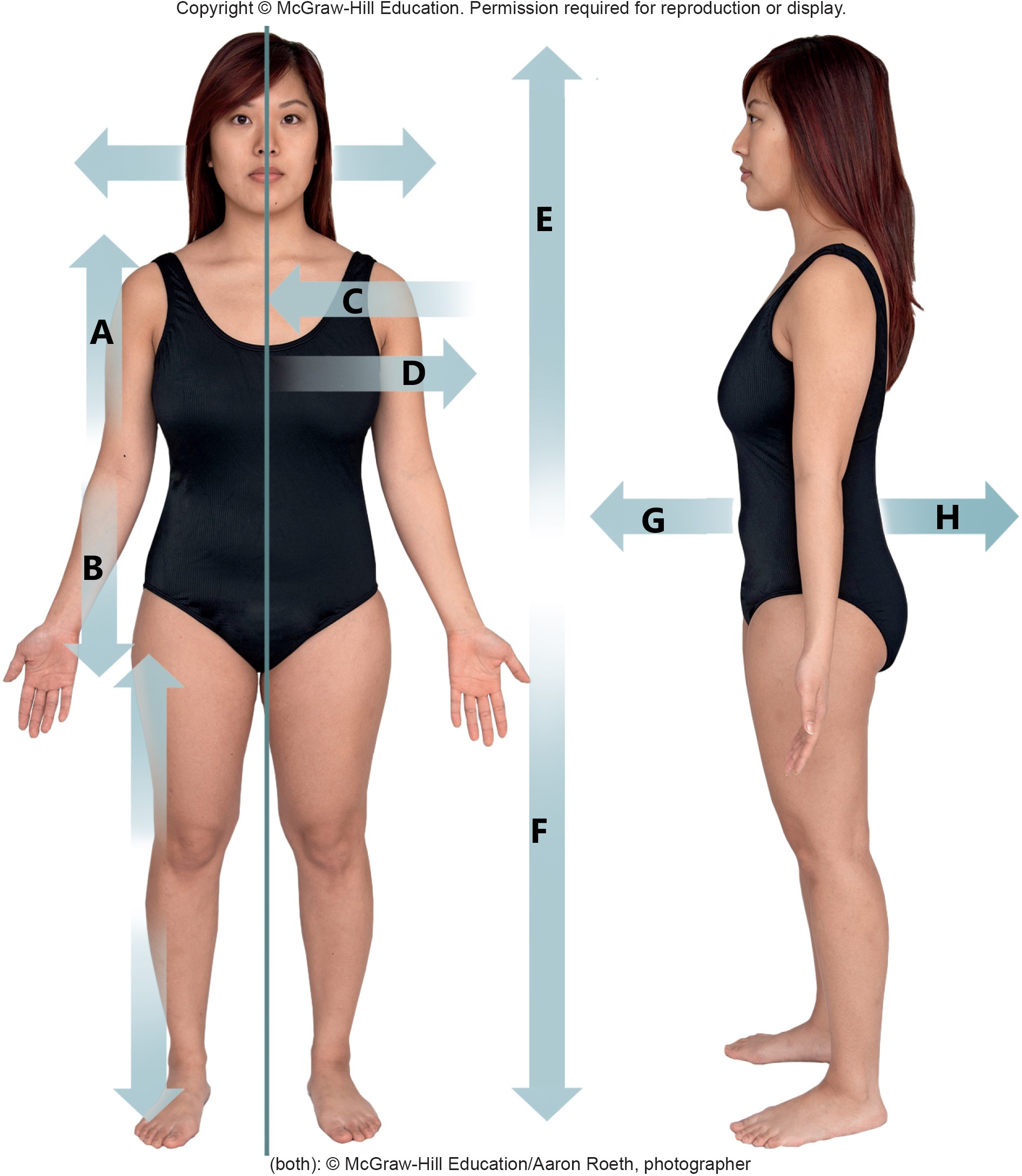
C
medial
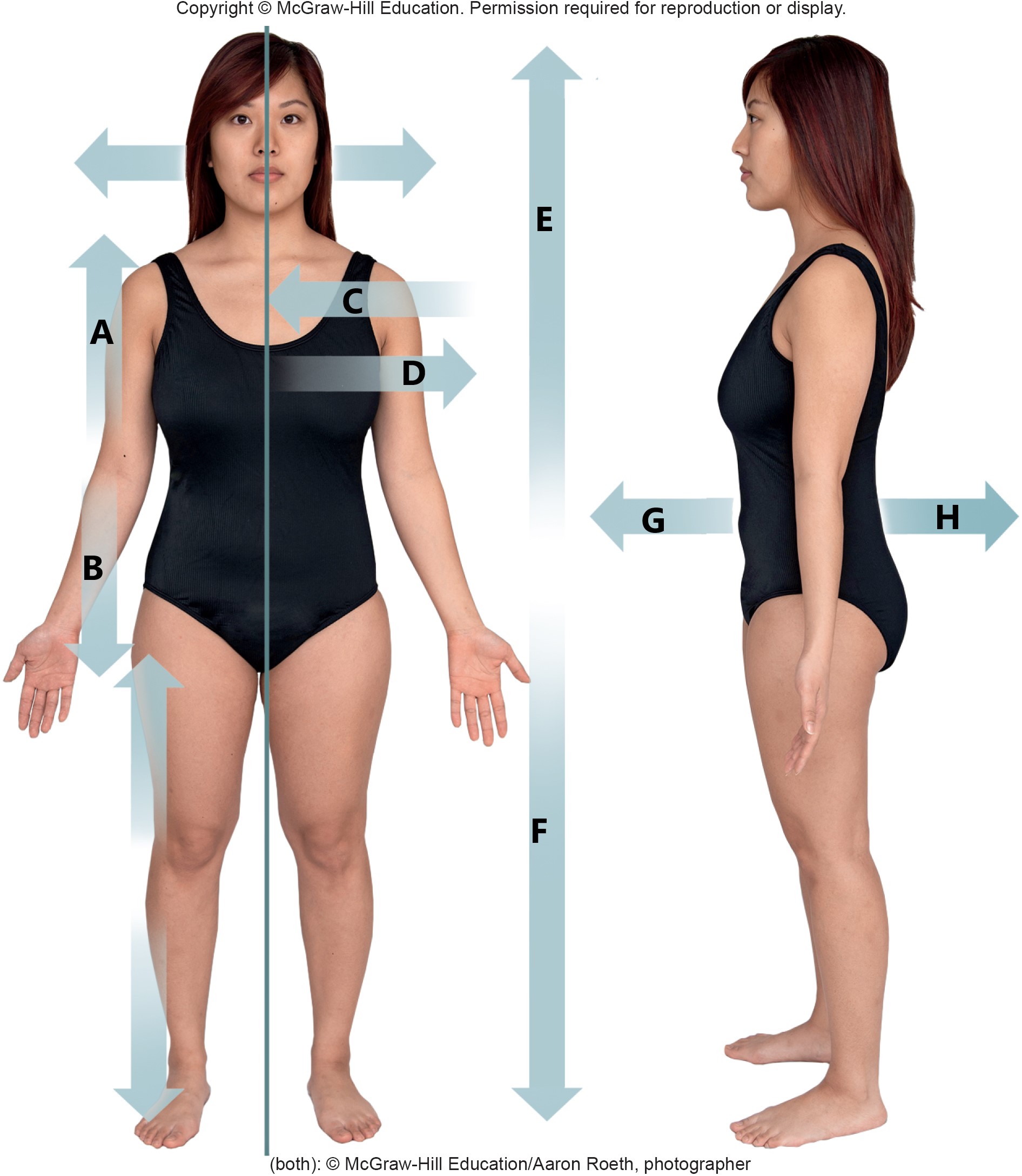
D
lateral
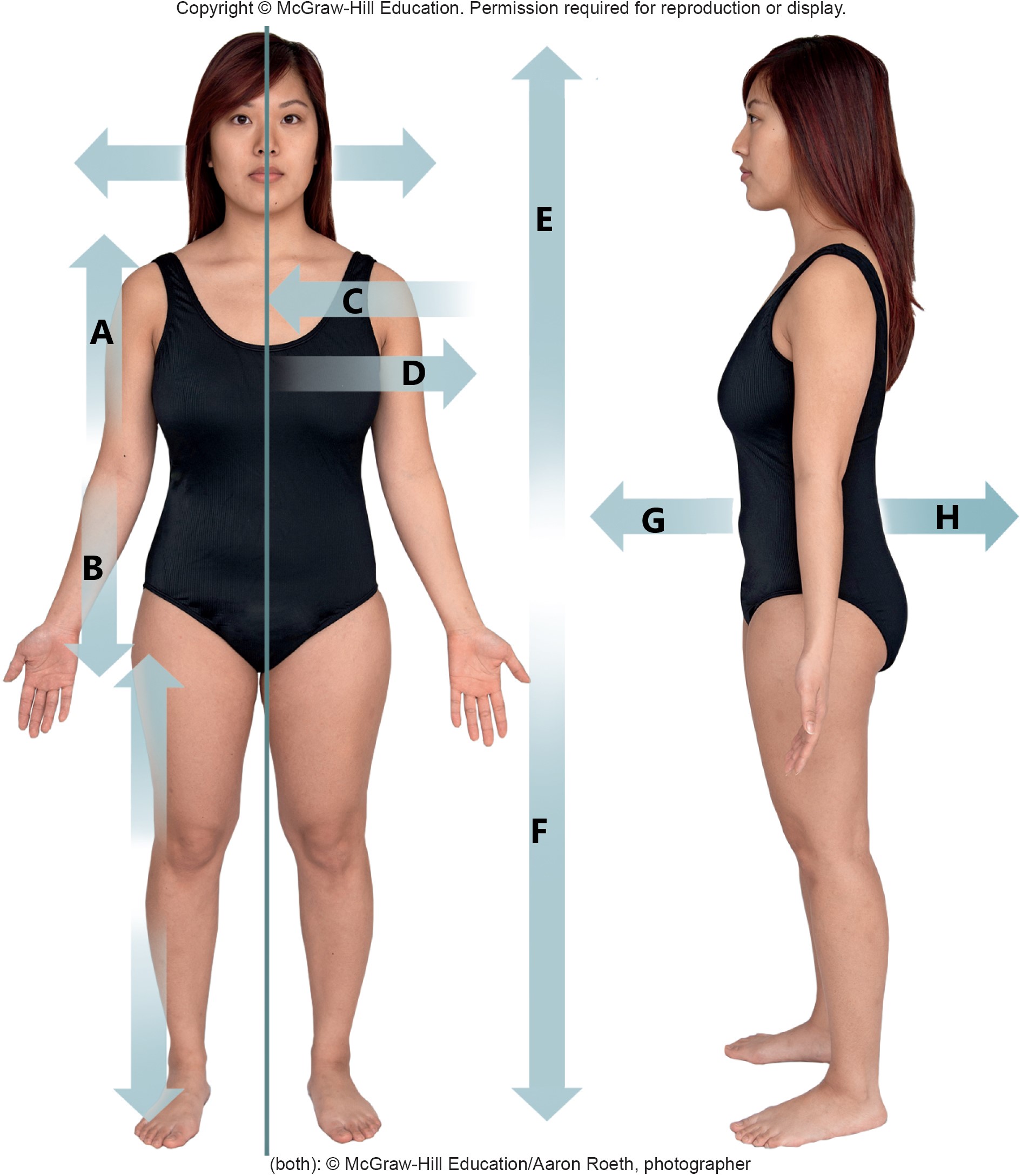
E
superior
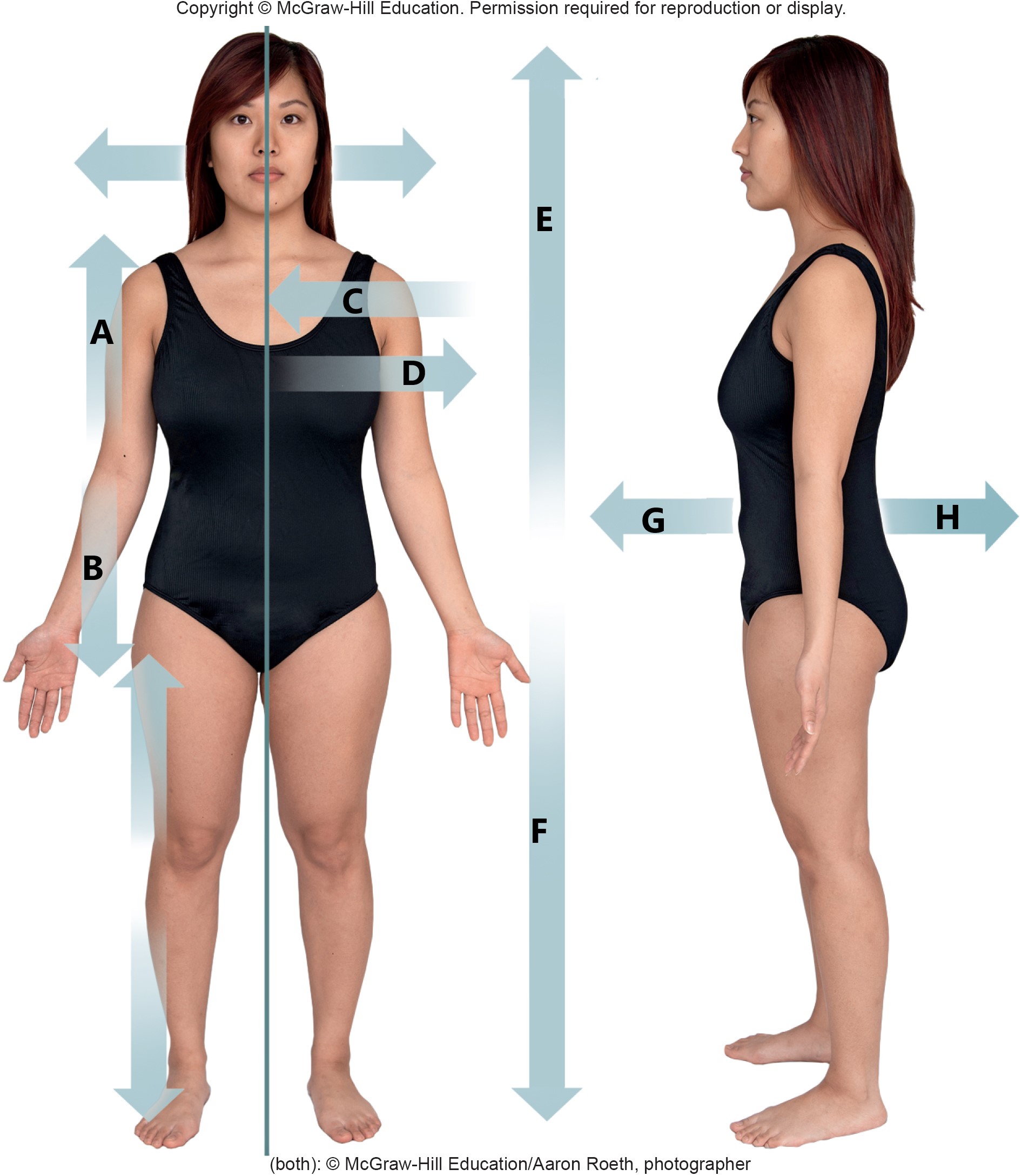
F
inferior
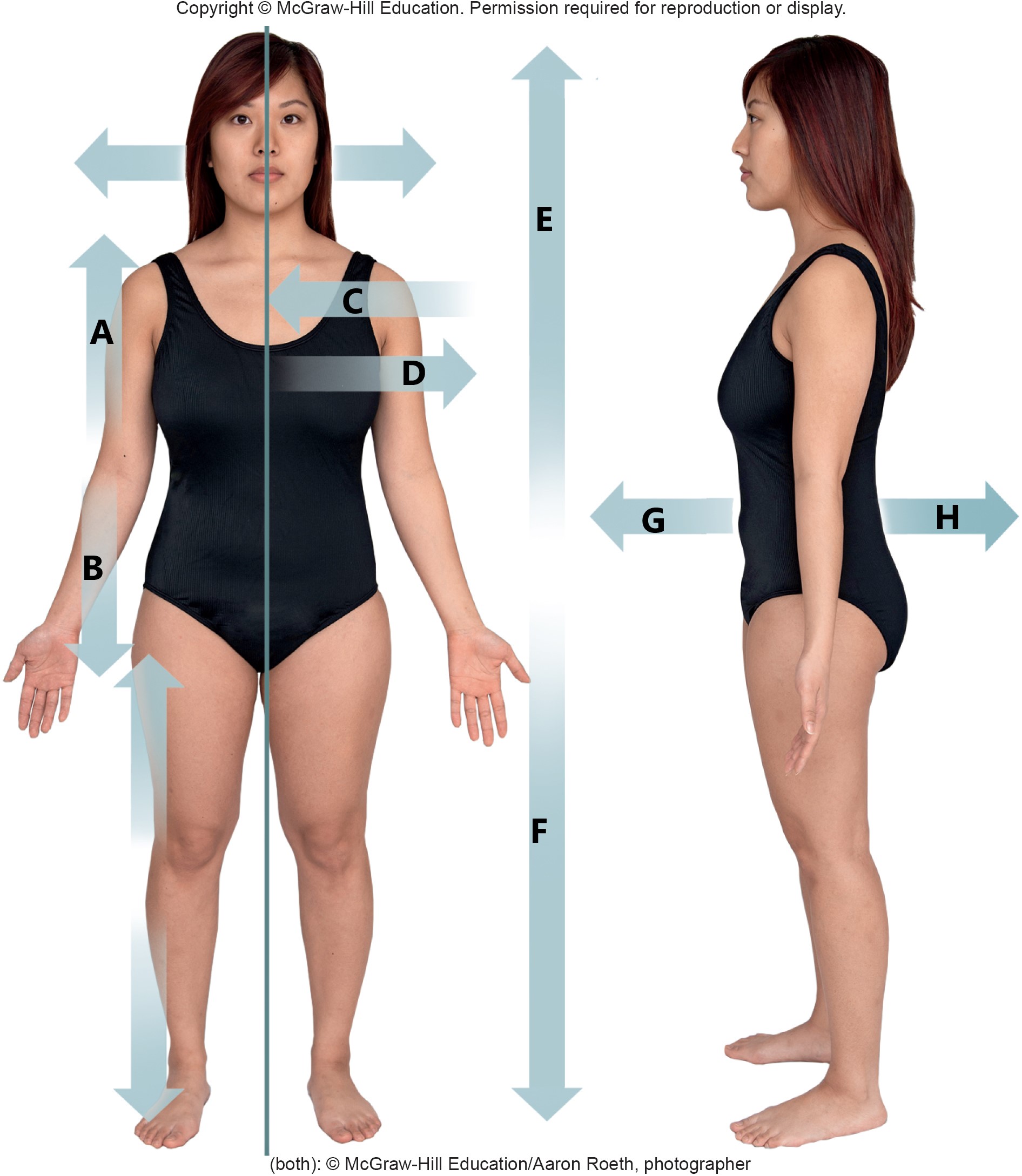
G
anterior
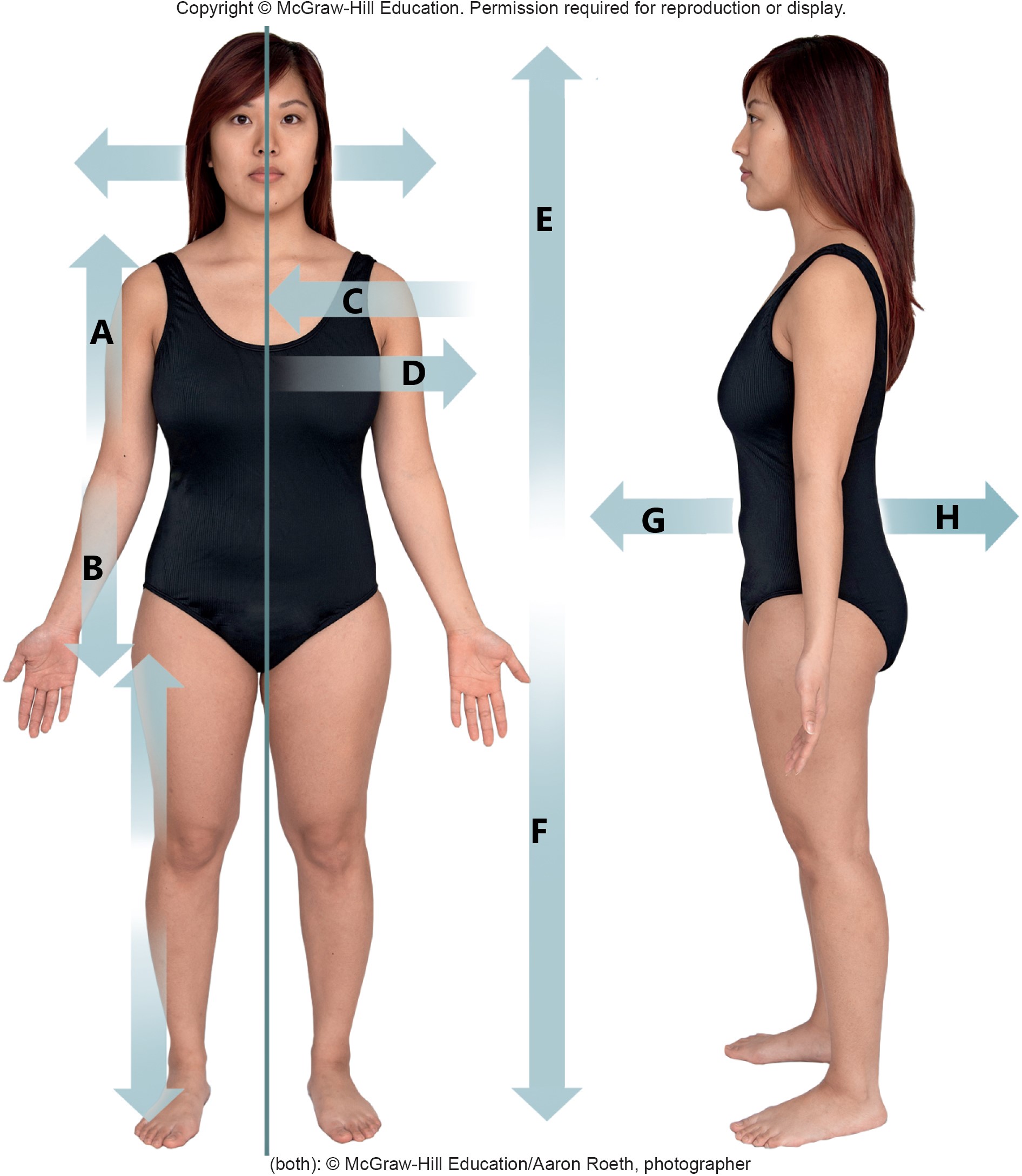
H
posterior
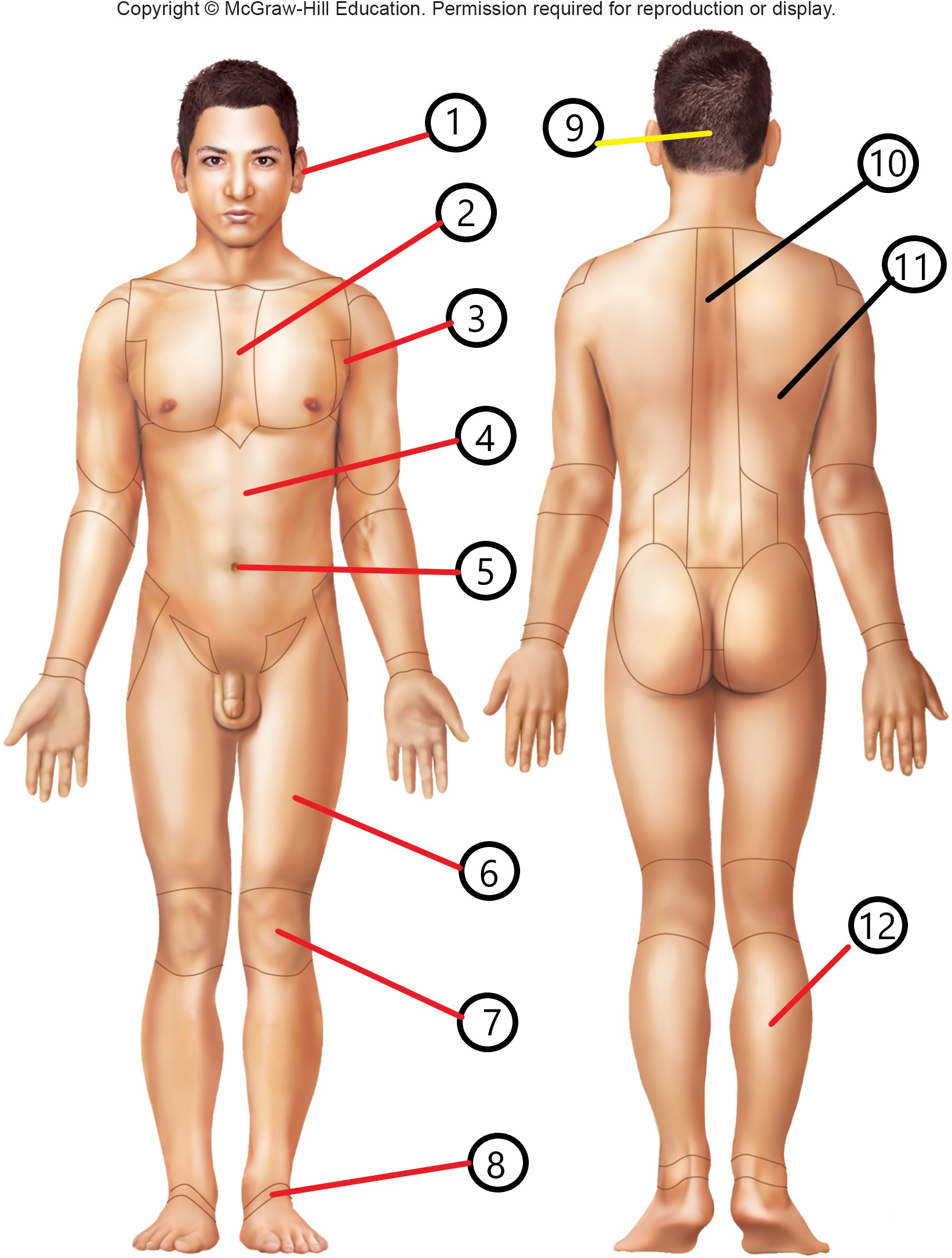
1
otic
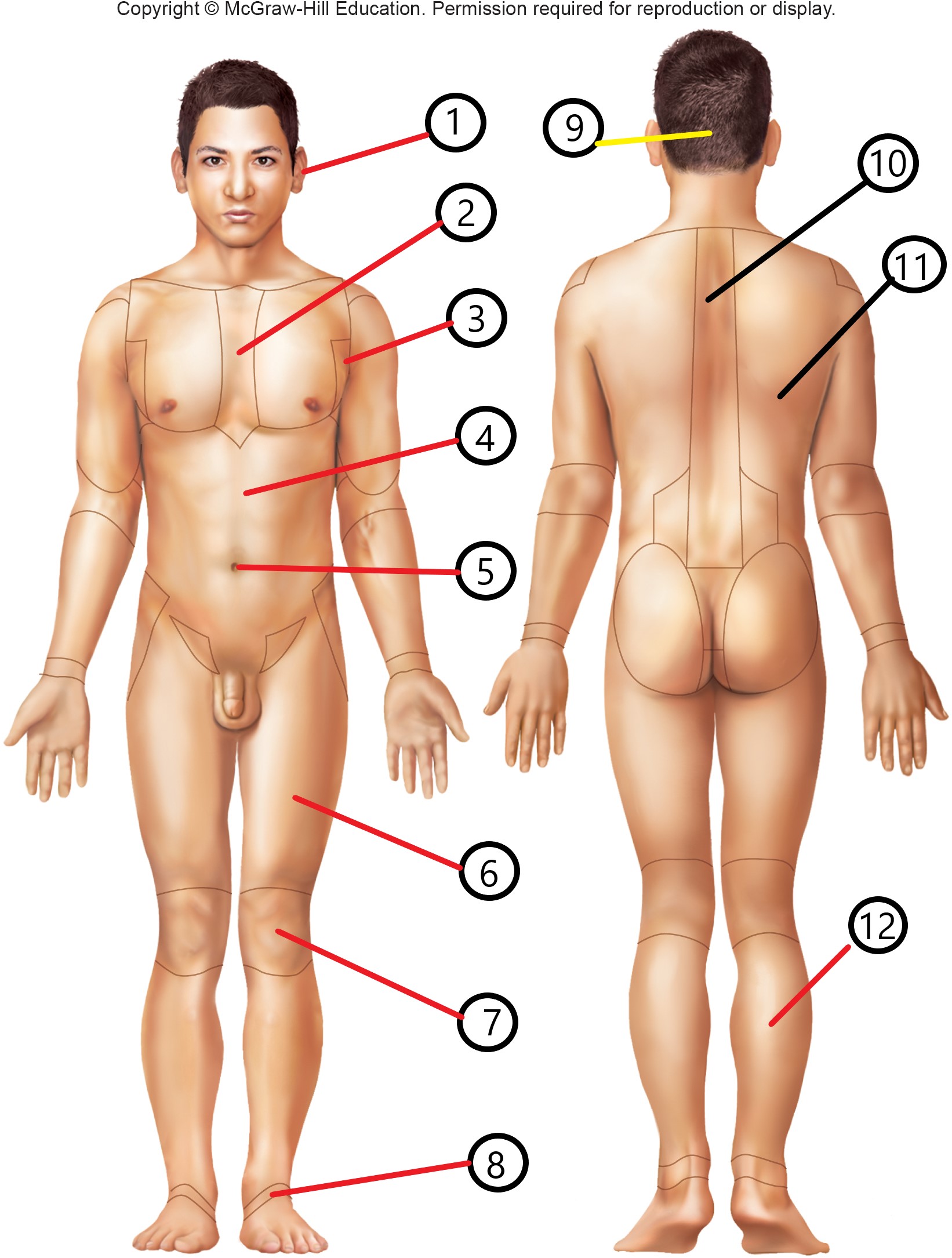
2
sternal
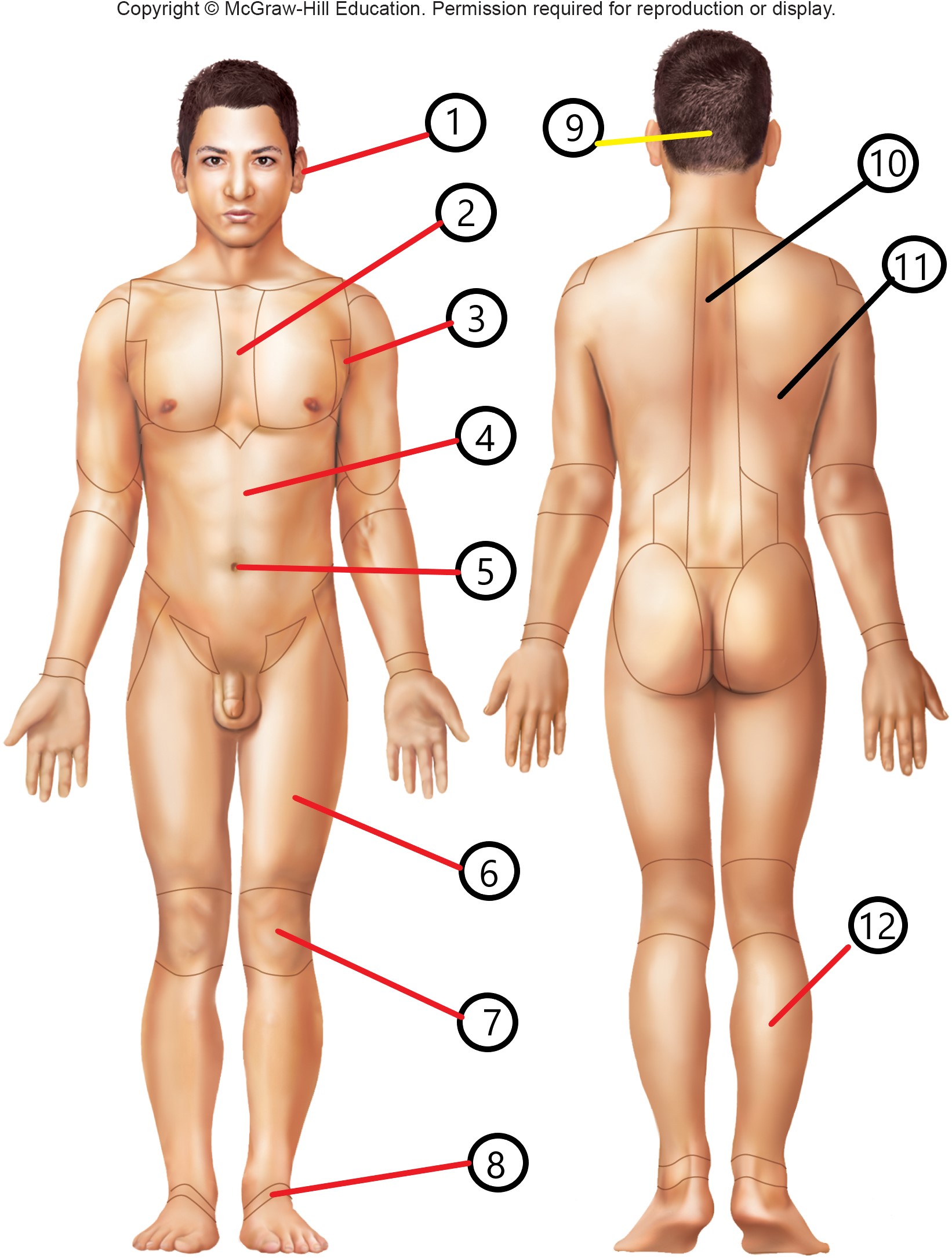
3
axillary
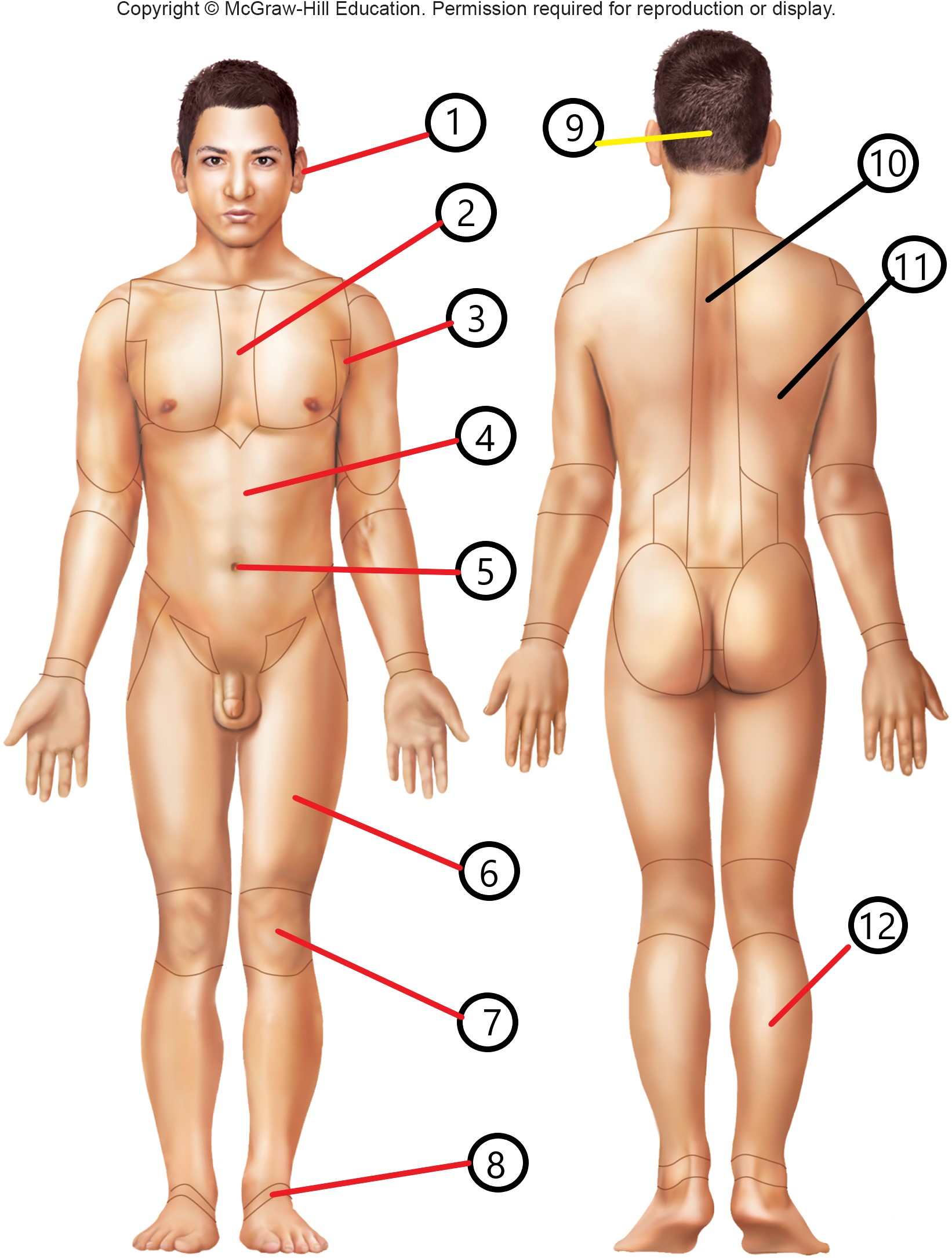
4
abdominal
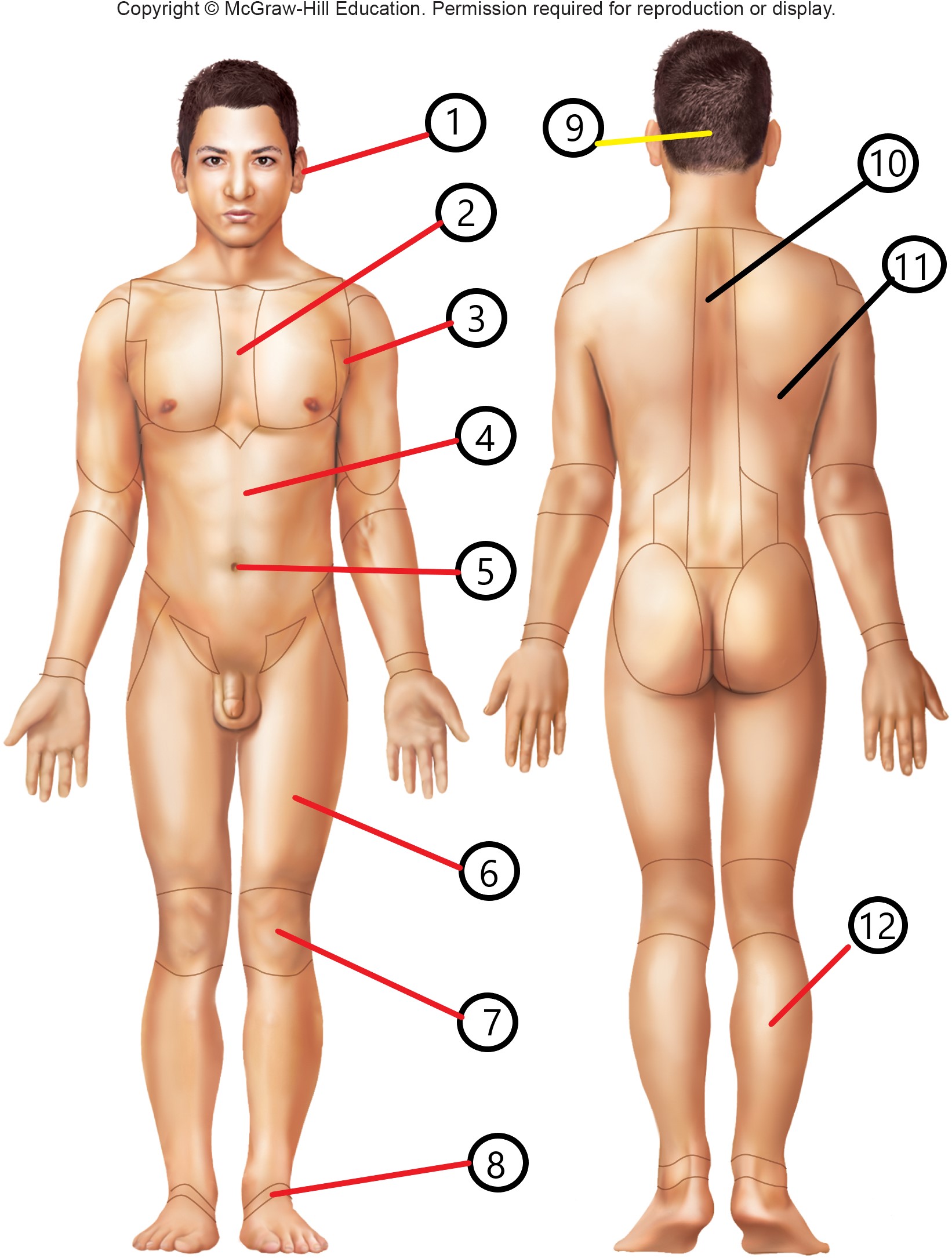
5
umbilical
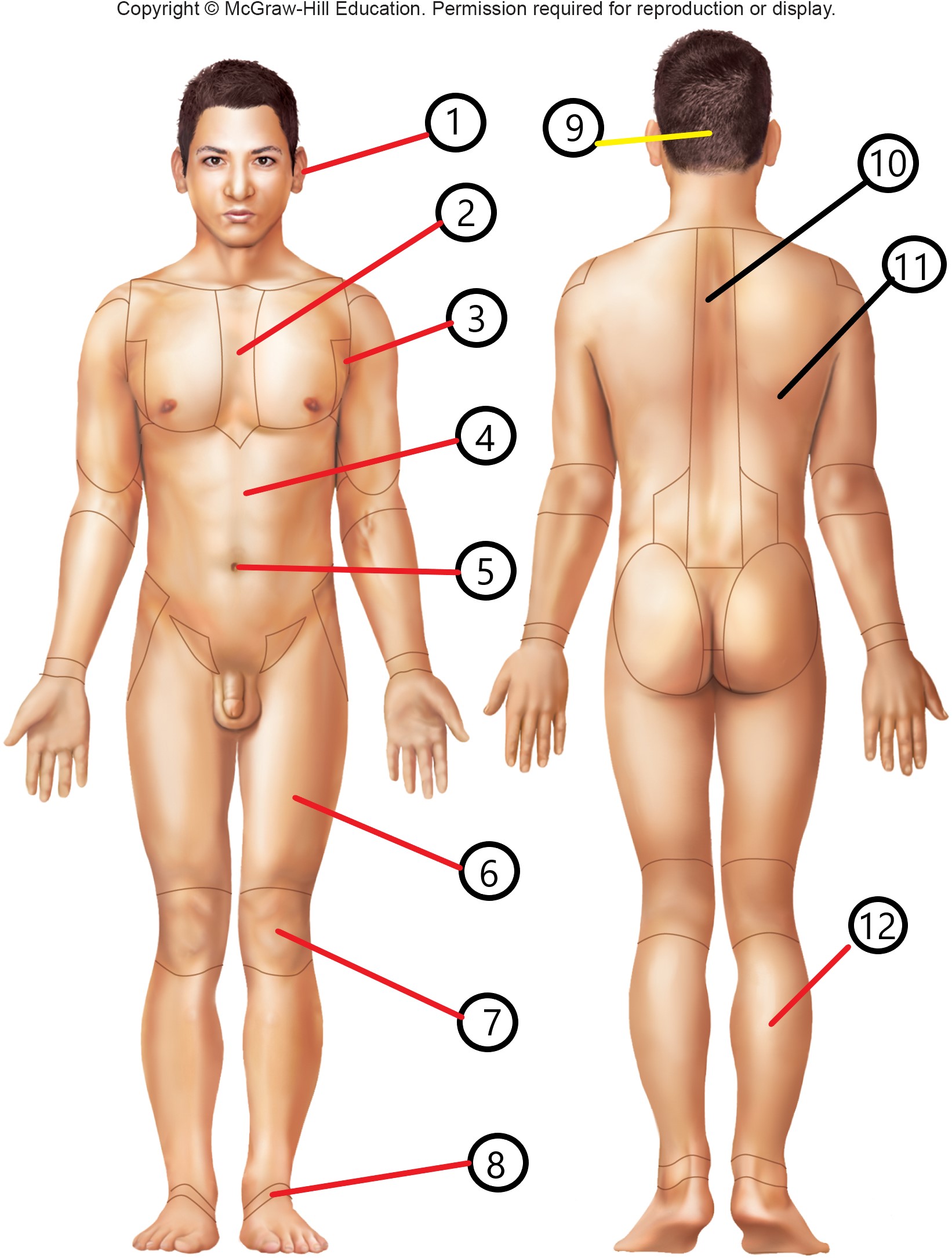
6
femoral
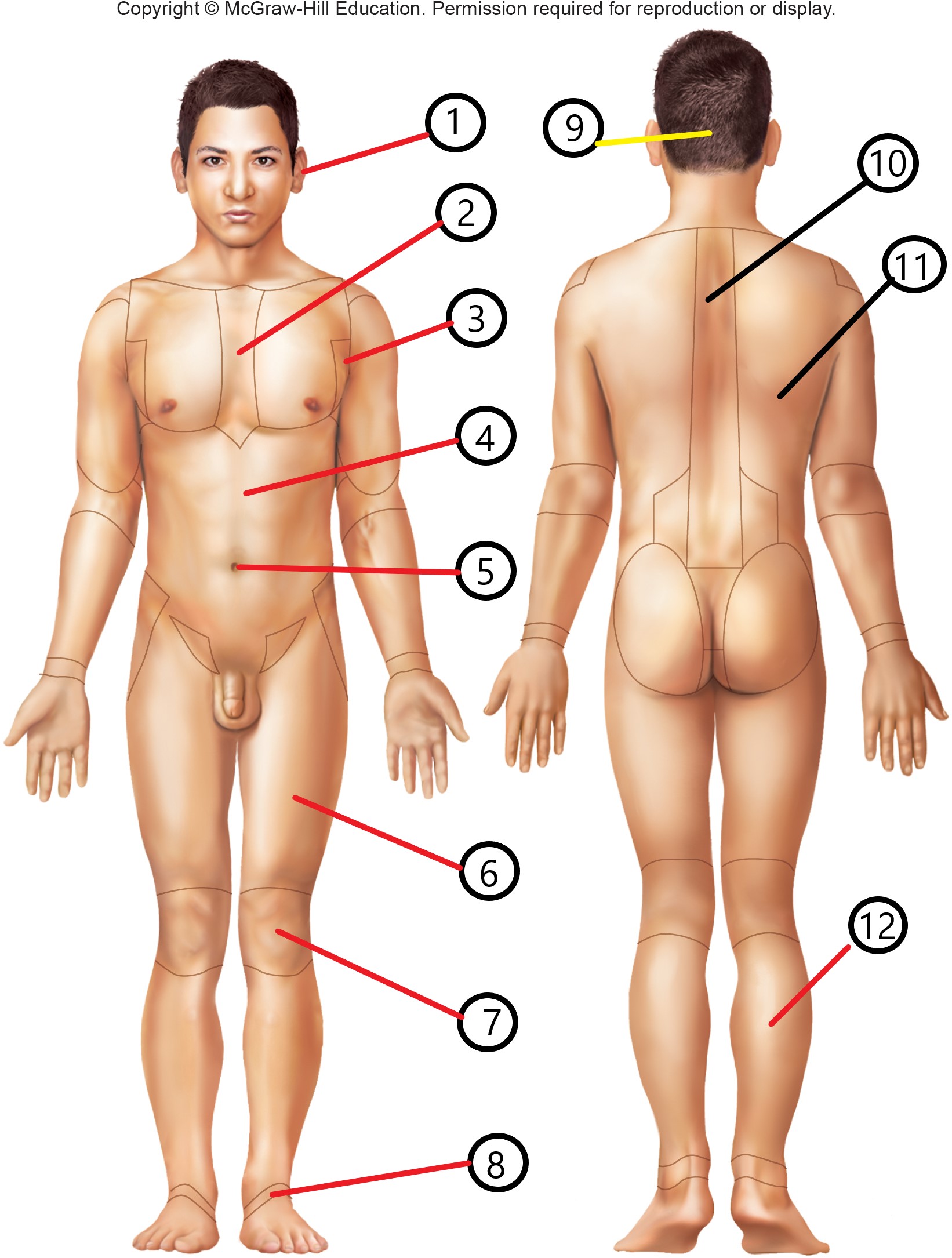
7
patellar
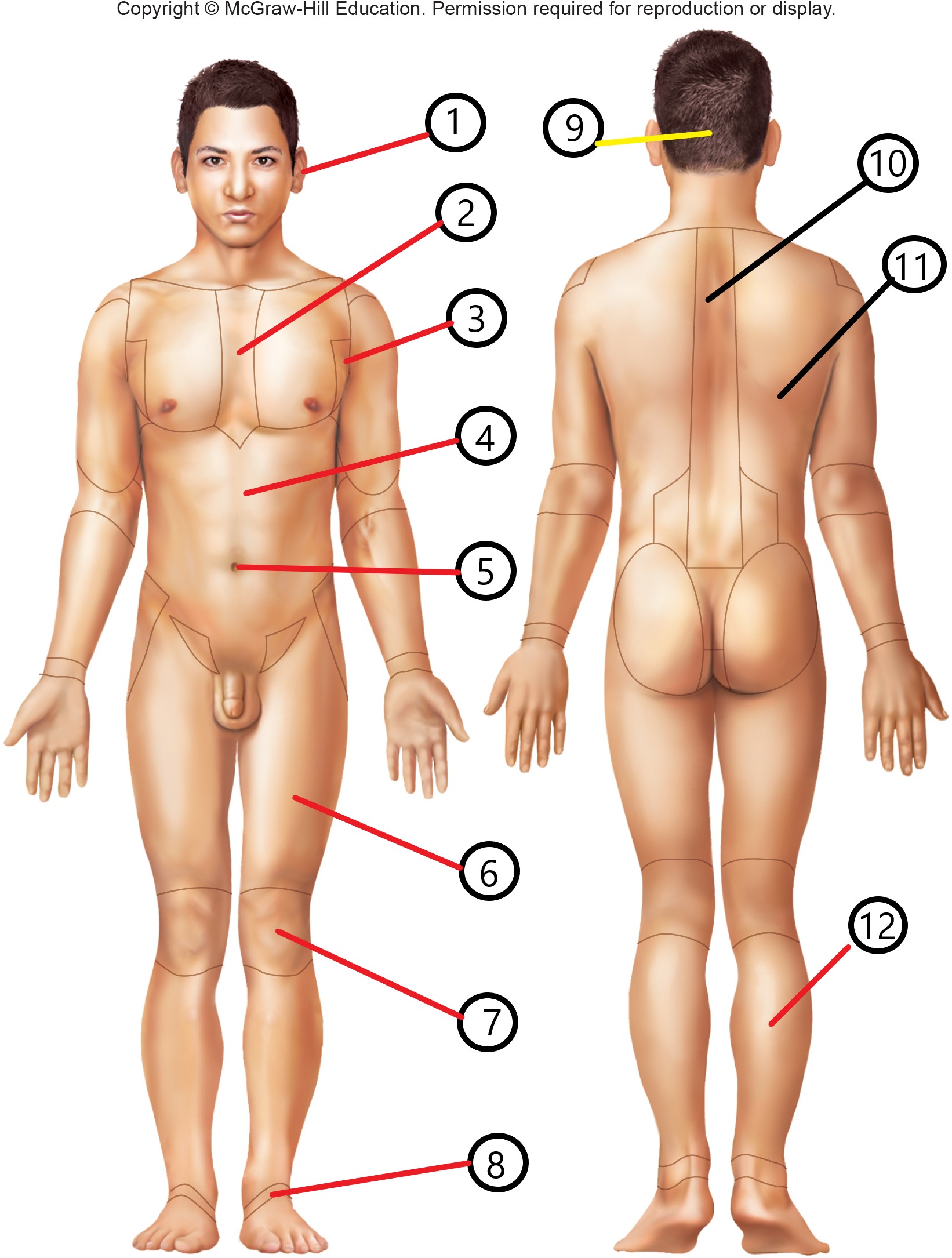
8
tarsal
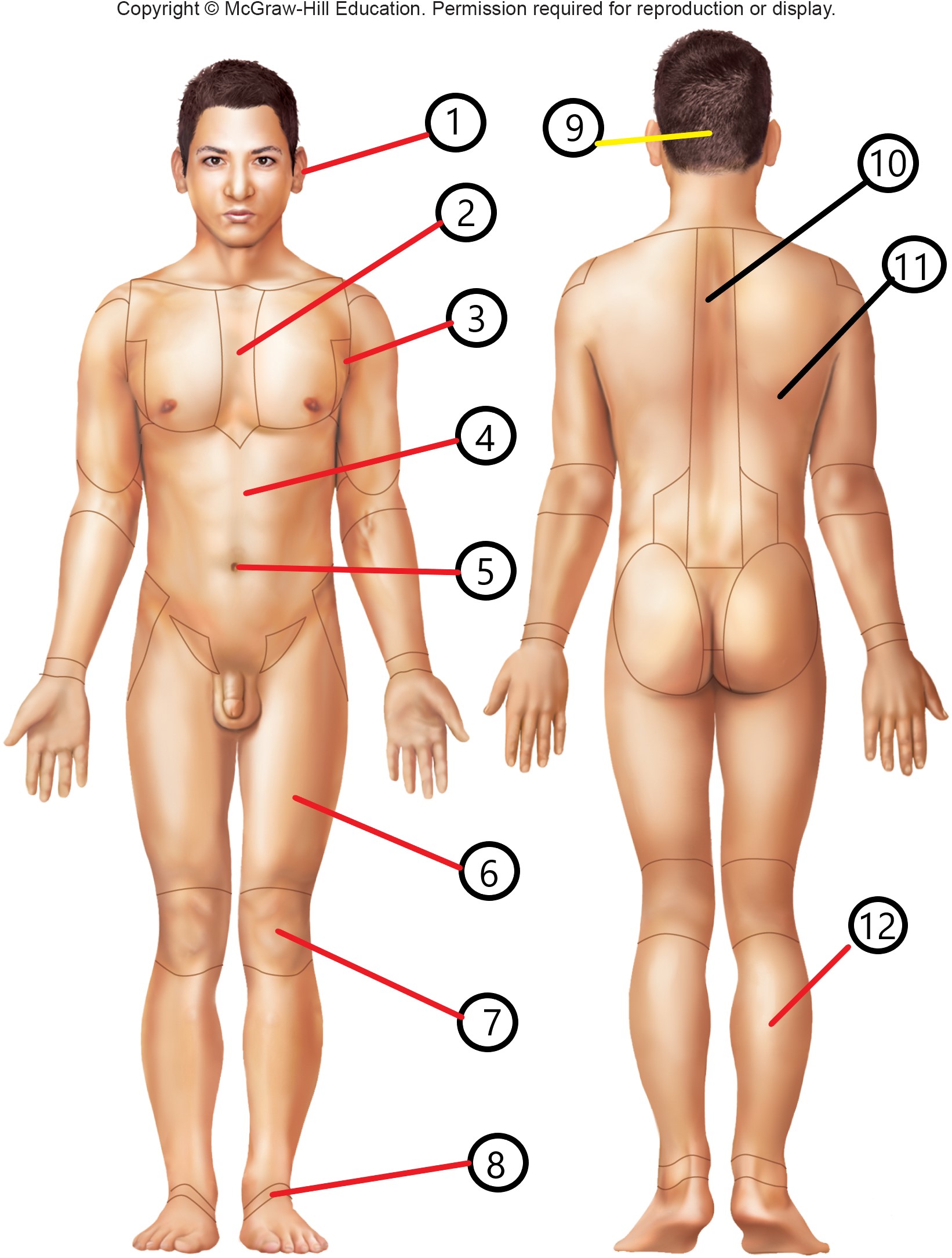
9
occipital
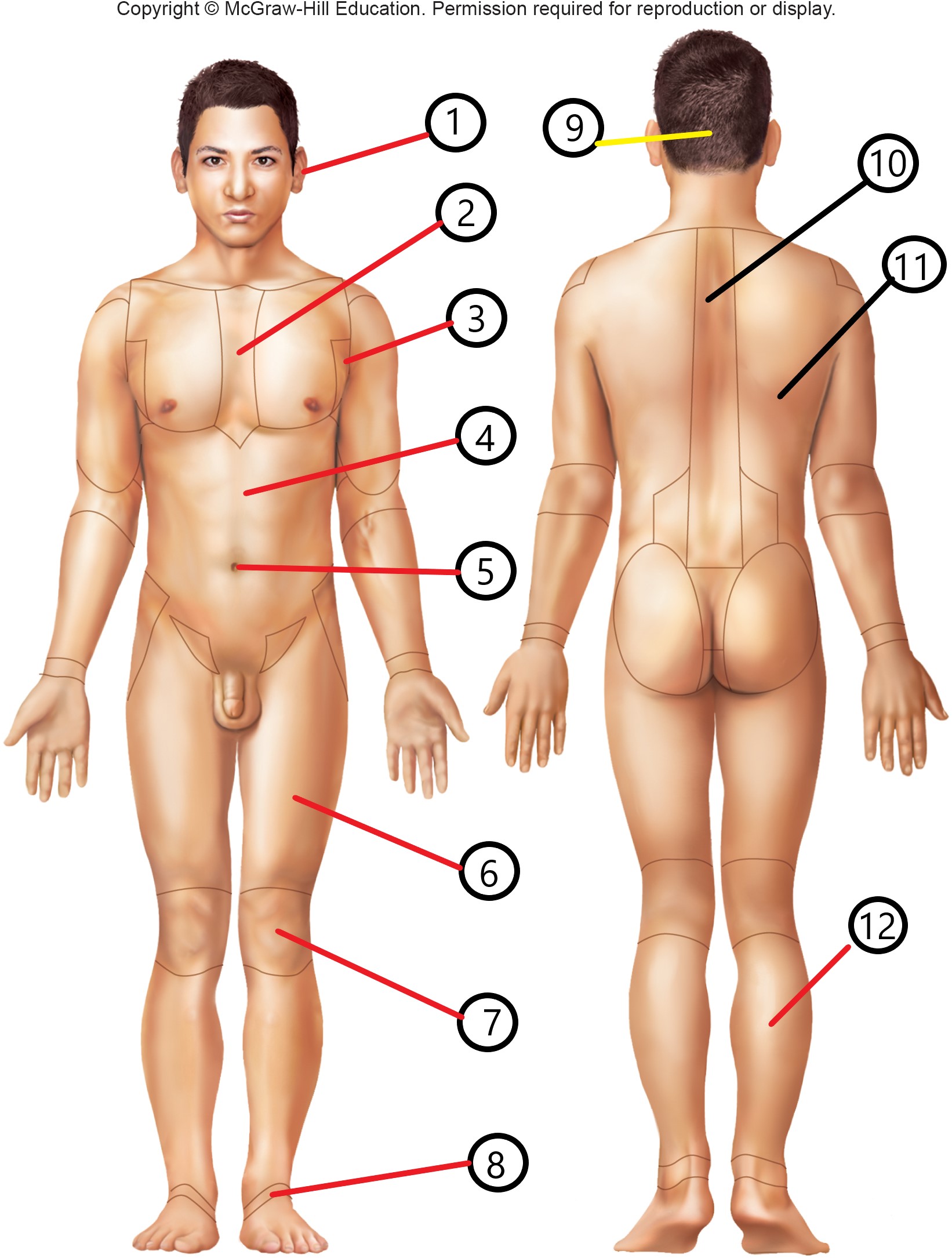
10
vertebral
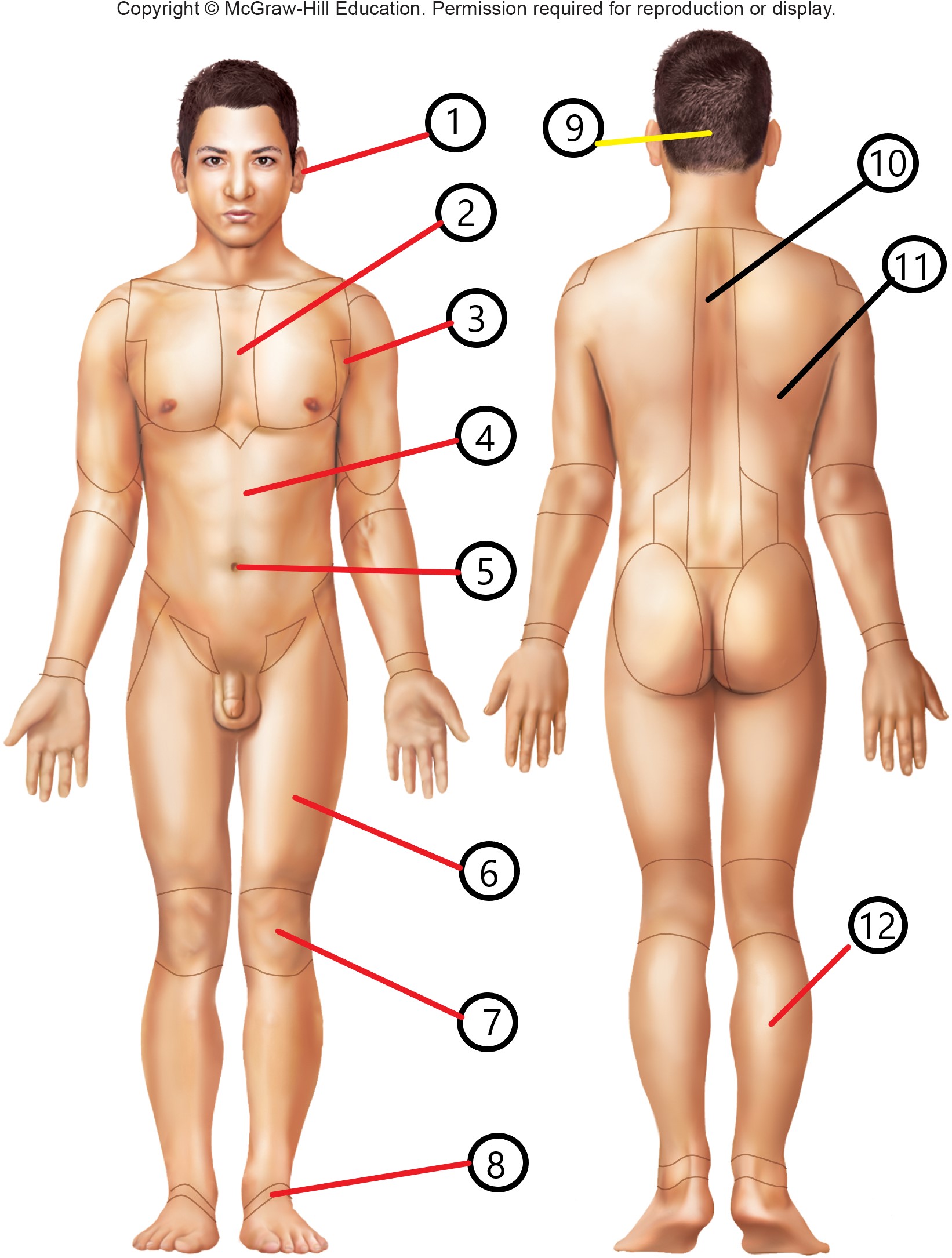
11
dorsal
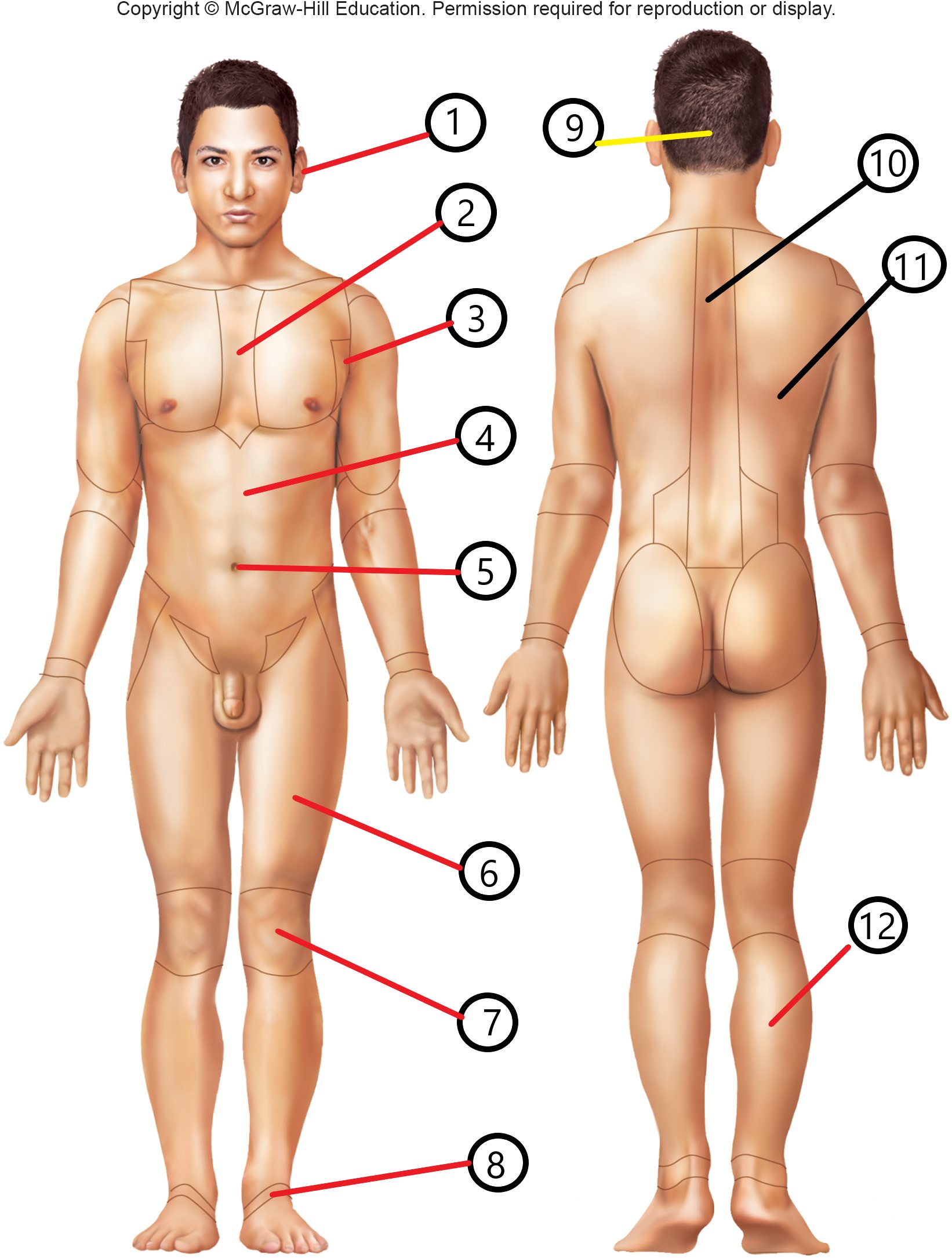
12
sural
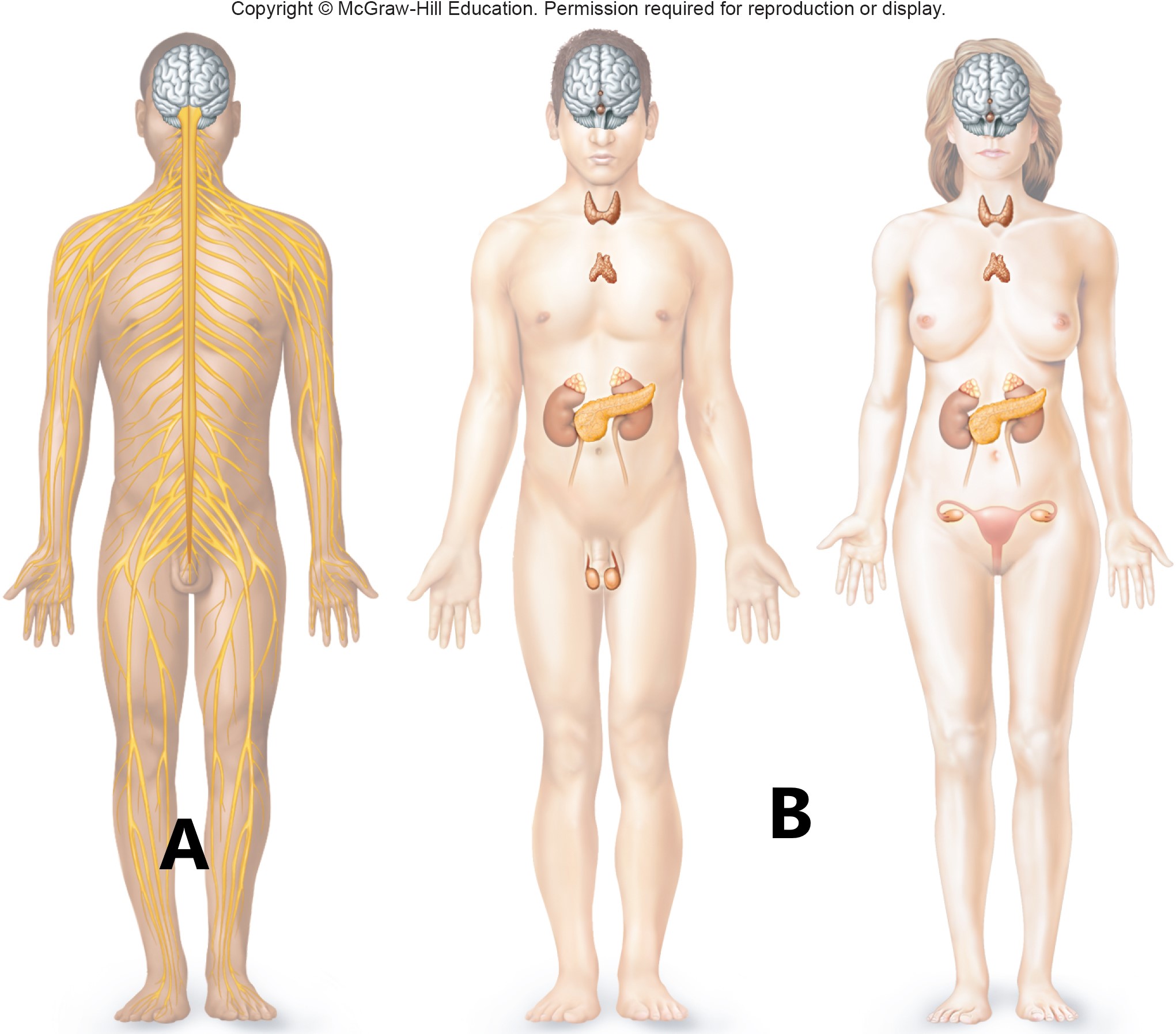
A B
nervous system
endocrine system
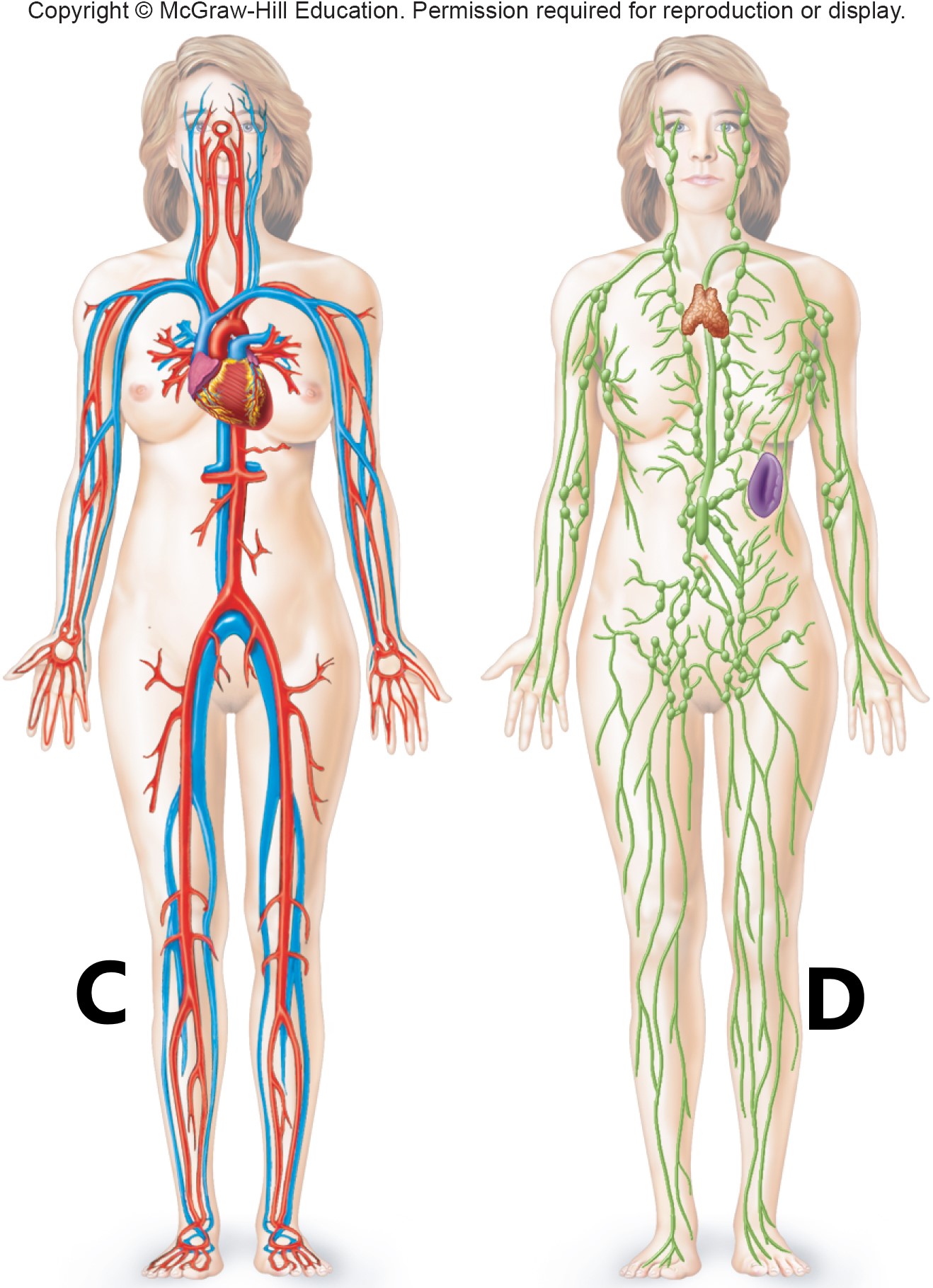
C D
cardiovascular system
lymphatic system
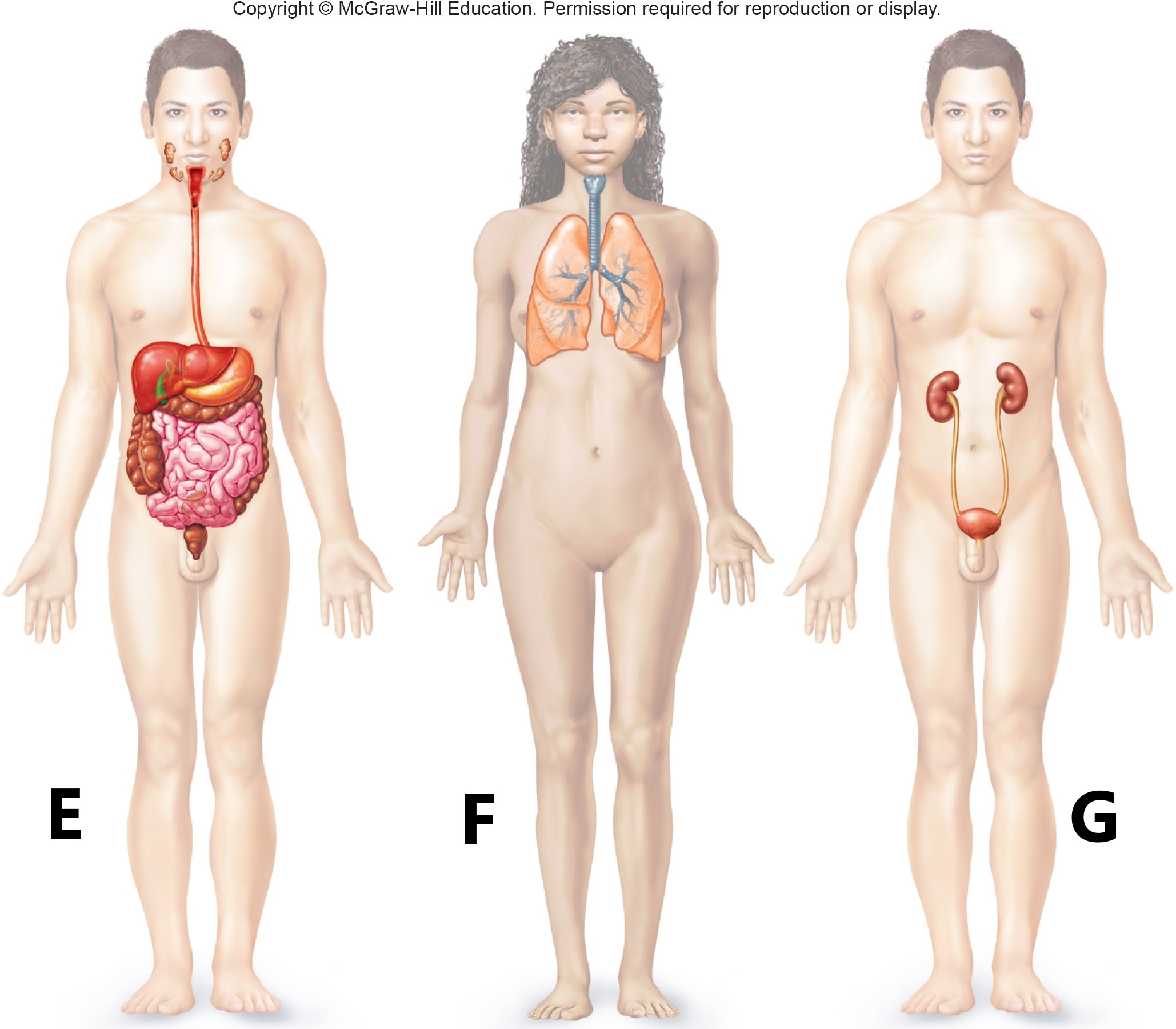
E F G
digestive system
respiratory system
urinary system
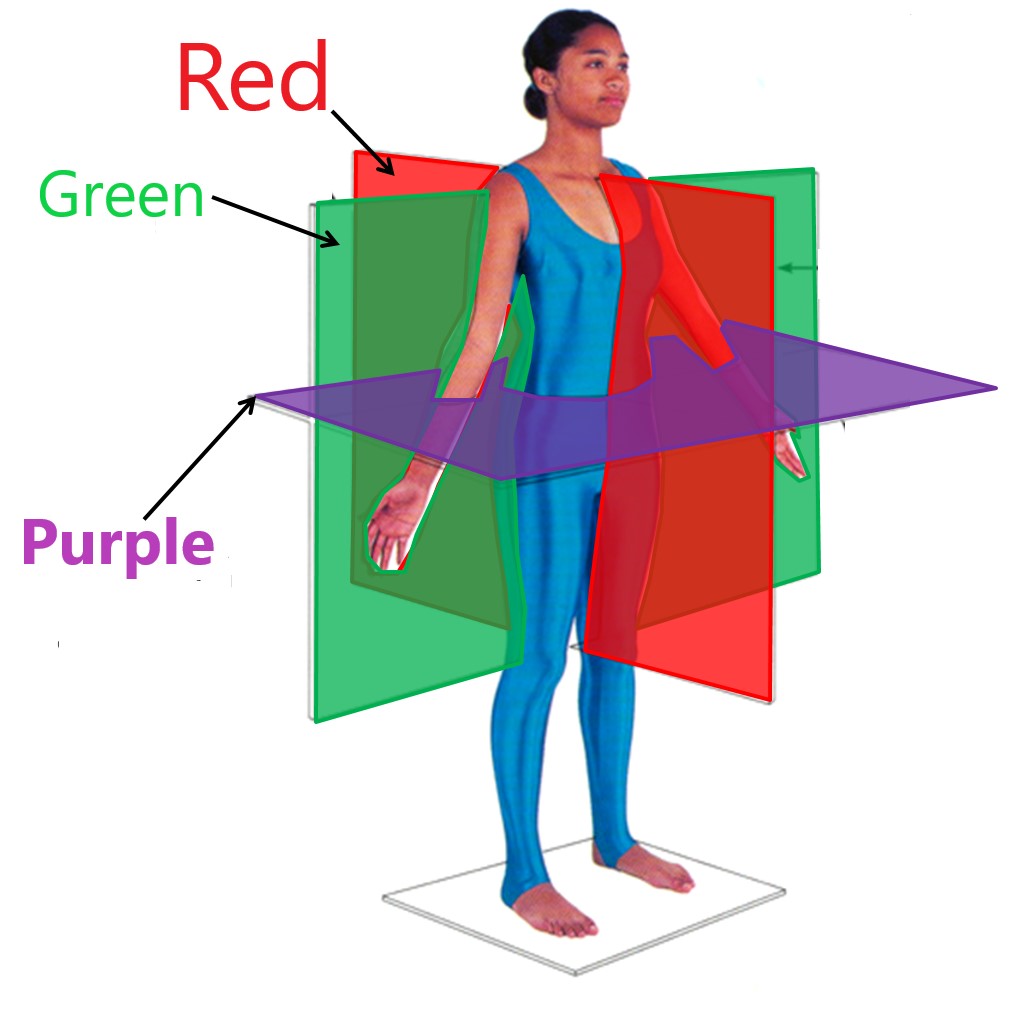
coronal plane
green
transverse plane
purple
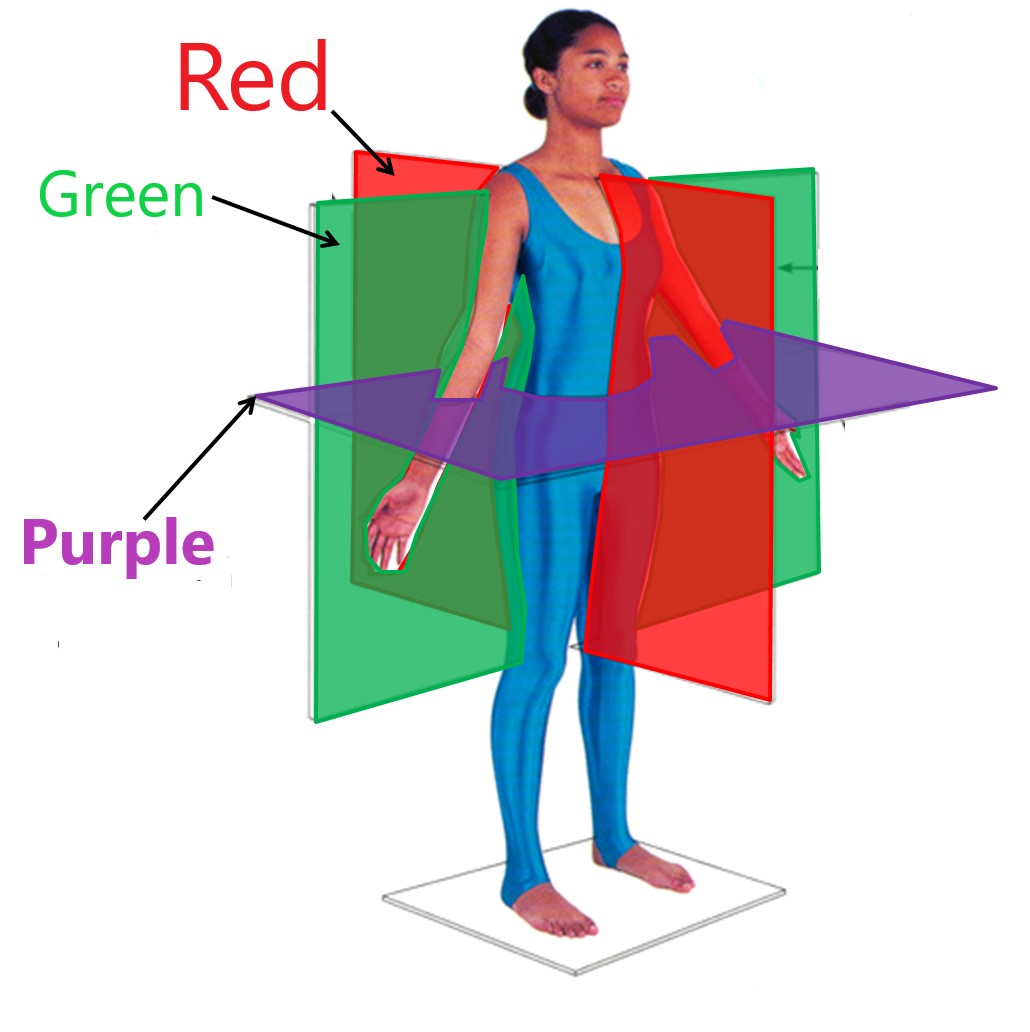
sagittal plane
red
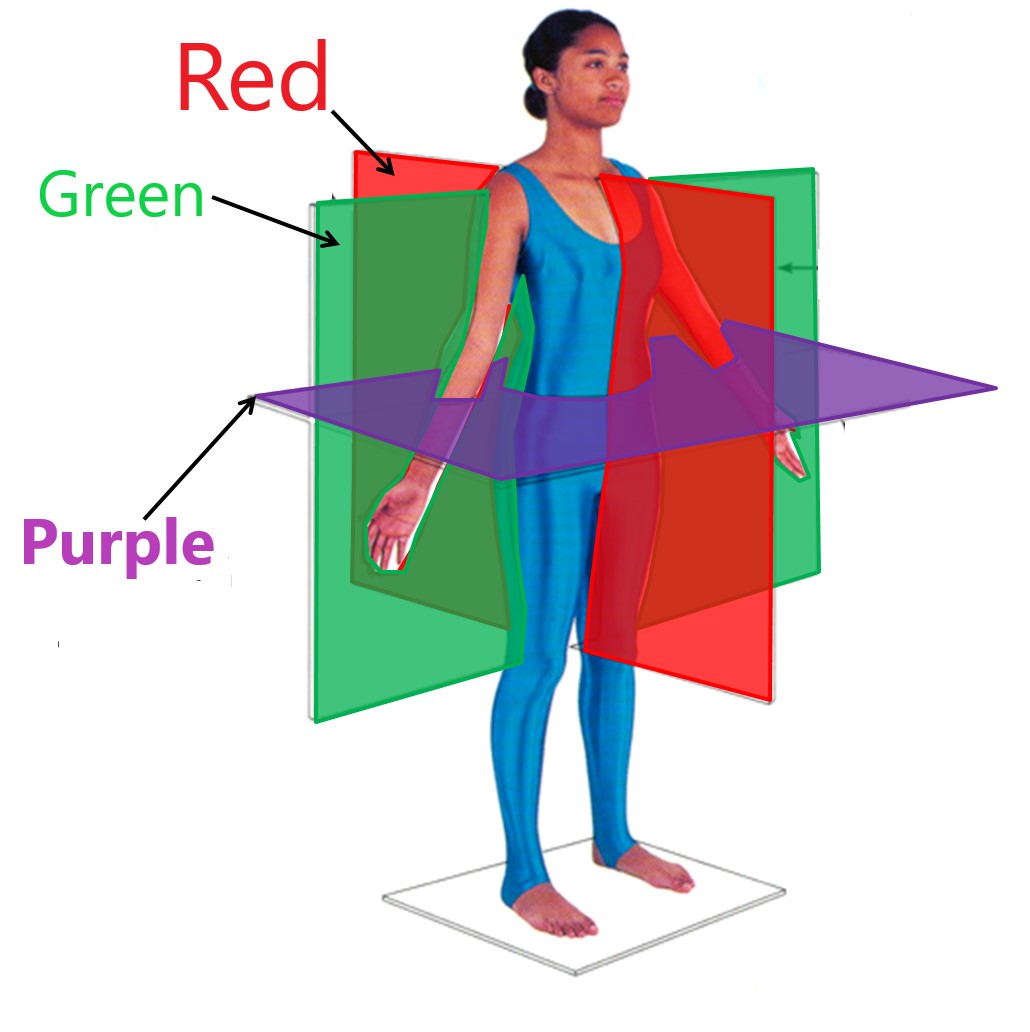
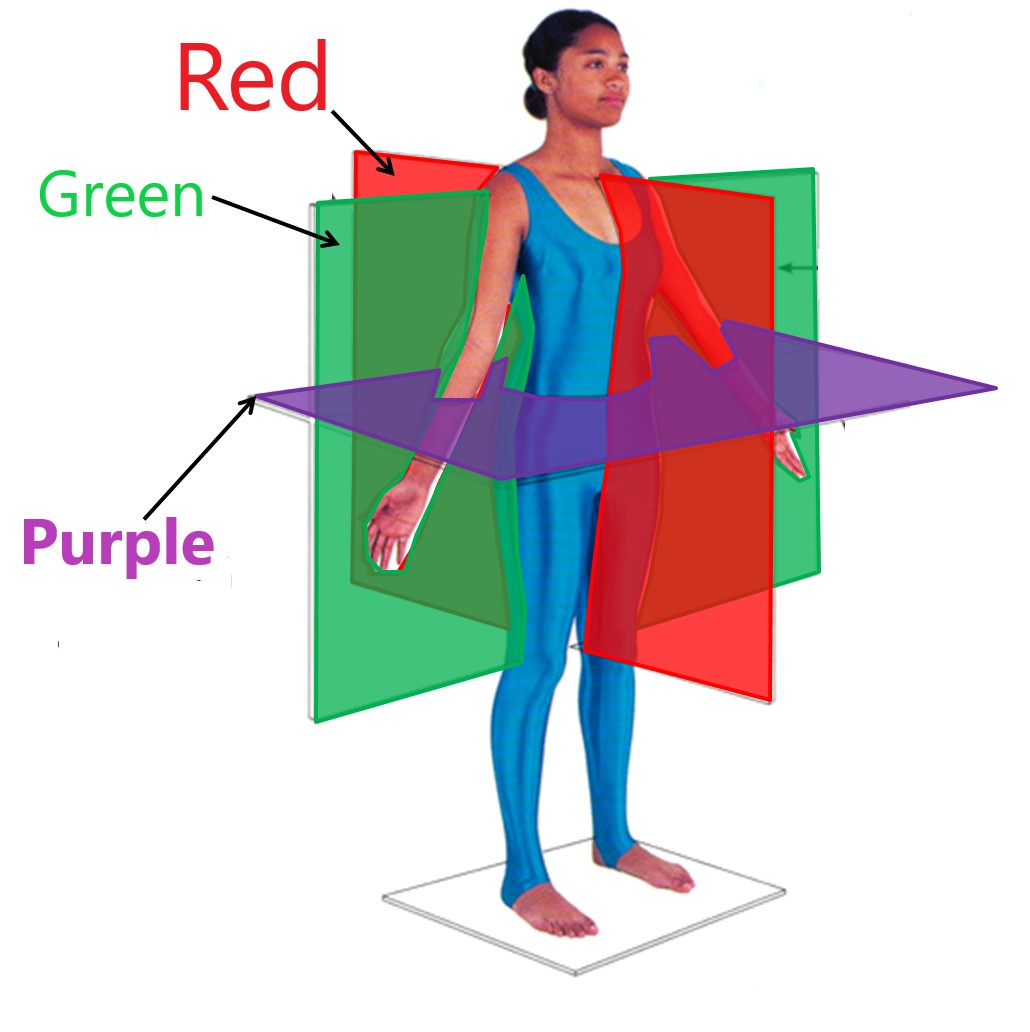
horizontal plane
purple
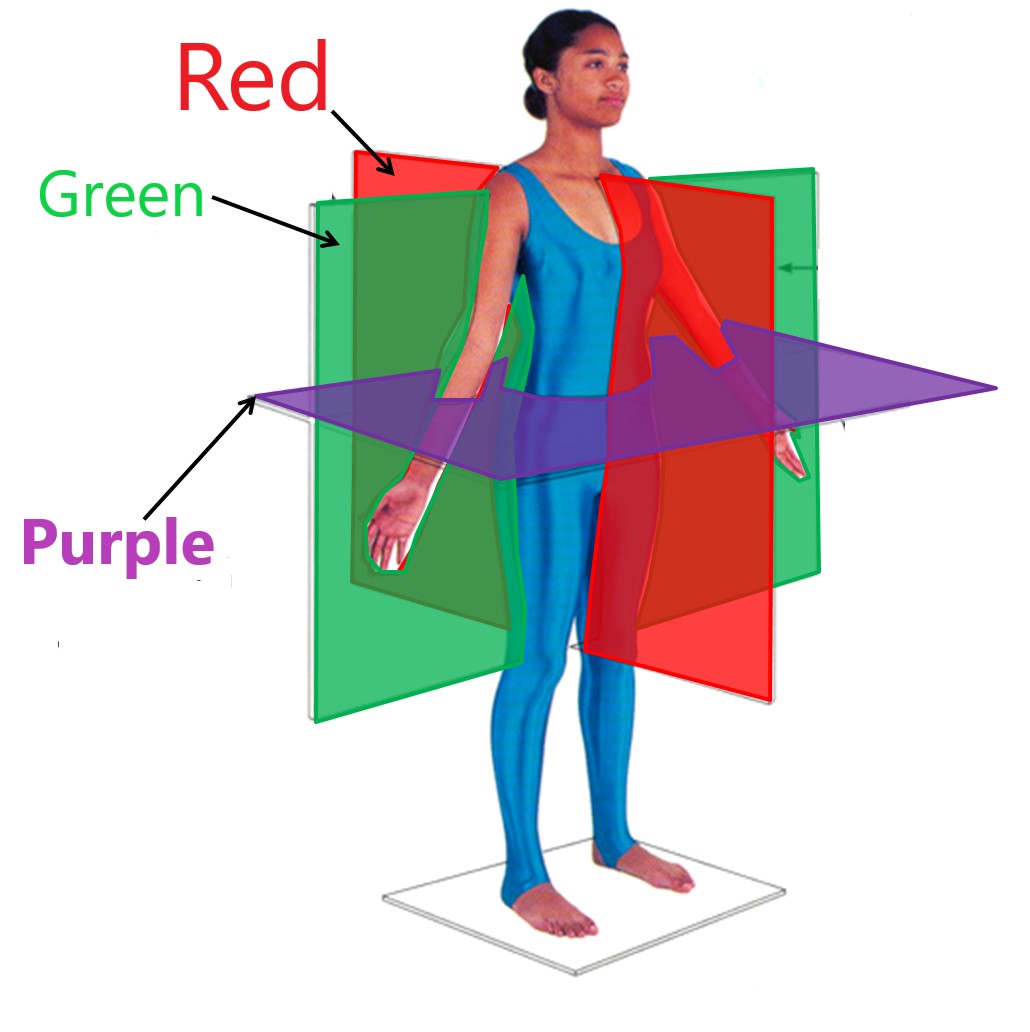
frontal plane
green
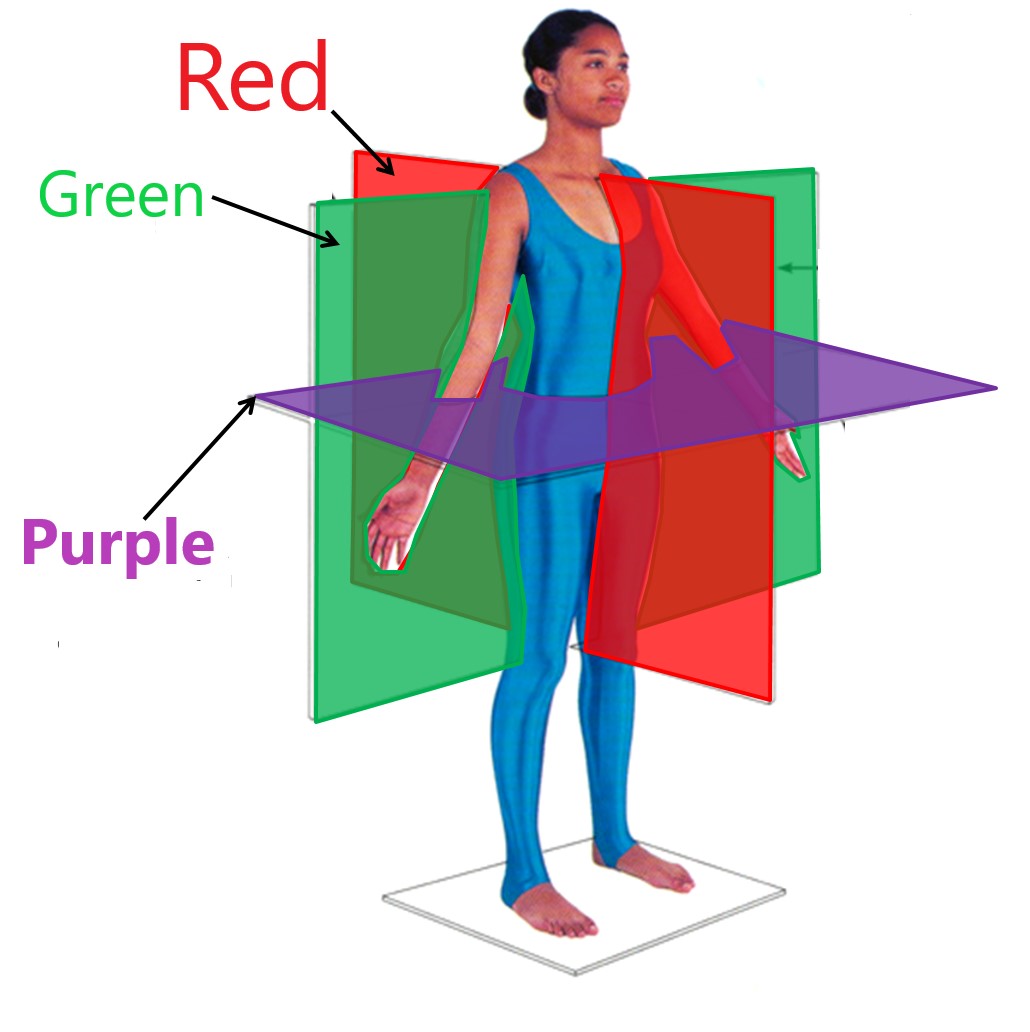
midsagittal plane
red