Echinoderms and Tetrapods
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover basic terms and definitions relevant to the study of Echinoderms and Tetrapods.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Echinodermata
A phylum of marine animals that includes starfish, sea urchins, and sand dollars, characterized by a calciferous endoskeleton and water vascular system.
Tetrapods
A group of animals that include amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals; they have four limbs and are adapted to life on land.
Amphibians
A class of tetrapods that includes frogs, salamanders, and caecilians, characterized by a life cycle that includes both aquatic and terrestrial stages.
Amniotic Egg
An egg that contains an amnion, allowing the embryo to develop in a terrestrial environment, found in reptiles, birds, and mammals.
Viviparity
The reproductive strategy in which animals give birth to live young rather than laying eggs.
Poikilothermy
The ability of an organism to have a variable body temperature that fluctuates with the environment.
Homeothermy
The ability of an organism to maintain a stable internal body temperature regardless of external conditions.
Counter-current heat exchange
A mechanism that helps to retain body heat by allowing warm arterial blood to heat cool venous blood.
Metamorphosis
A developmental process through which animals, especially amphibians, undergo a significant change in form and function, typically from larval to adult stages.
Amniotes
A clade that includes all tetrapods except amphibians, characterized by the presence of an amniotic egg.
What are mammals known for?
Mammals are warm-blooded vertebrates with hair or fur and mammary glands that produce milk for their young.
What is thermoregulation?
Thermoregulation is the process by which an organism maintains its internal temperature within a tolerable range.
What are the main ways mammals thermoregulate?
Mammals thermoregulate through behaviors, physiological adaptations like shivering, sweating, and altering blood flow, and insulative structures like fur.
What are reptiles?
Reptiles are cold-blooded vertebrates that have scales and lay eggs, typically requiring external heat sources for metabolic processes.
What is Allen's Rule?
Allen's Rule states that endothermic animals in colder climates tend to have shorter appendages (like limbs and ears) compared to those in warmer climates.
What is Bergmann's Rule?
Bergmann's Rule states that within a species, individuals in colder climates tend to be larger than those in warmer climates to conserve body heat.
What is temporal heterothermy?
Temporal heterothermy refers to organisms that can vary their body temperature at different times, such as during day and night. (ex. torpor → hibernation)
What is regional heterothermy?
Regional heterothermy is when different parts of the body of an organism maintain different temperatures.
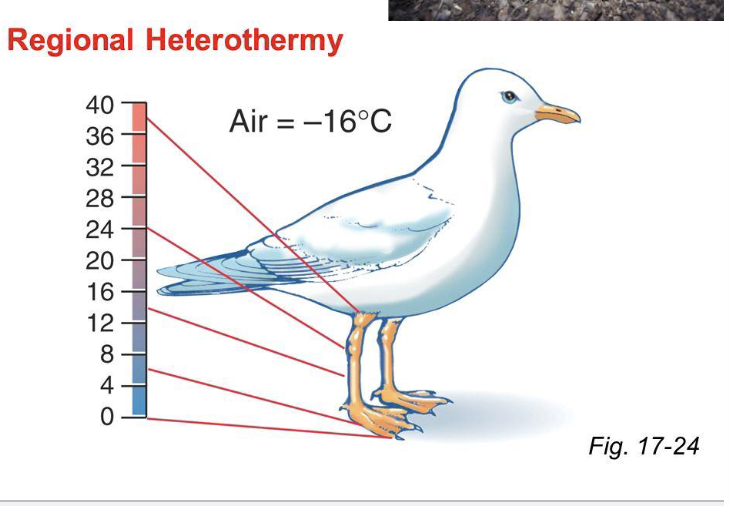
What is ectothermy?
Ectothermy is the biological trait of relying primarily on external environmental heat sources to regulate body temperature.
What is endothermy?
Endothermy is the ability of an organism to generate and maintain its own body temperature through metabolic activity.
What is vasoconstriction?
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of blood vessels, which decreases blood flow and raises blood pressure, often occurs in response to cold to conserve heat.
What is vasodilation?
Vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels, which increases blood flow and lowers blood pressure, often occurs in response to heat to release excess body heat.
How does vasoconstriction help in thermoregulation?
Vasoconstriction helps in thermoregulation by reducing blood flow to the skin, minimizing heat loss in cold environments.
How does vasodilation aid in thermoregulation?
Vasodilation aids in thermoregulation by increasing blood flow to the skin, promoting heat loss in hot conditions.
What are amphibians?
Amphibians are a class of ectothermic vertebrates that include frogs, salamanders, and caecilians.
Complete Metamorphisis - amphibians
Complete metamorphosis in amphibians involves distinct life stages: egg, larva (tadpole), and adult
Decline of Amphibia
rapid decline because of chytrid fungus, habitat loss, climate change, and pollution
Gas Exchange - Amphibia
through their skin, lungs, gills, and mouth (tadpoles are water breathers and metamorphize into frogs that breathe air)
waste exchange - amphibia
excrete waste across their skin, urine, and gills and excrete ammonia as a primary waste product, allowing for efficient osmoregulation.
Amniotes
all tetrapods except for amphibia. They are characterized by having an amniotic egg that protects the embryo and allows for reproduction in dry environments.
Mammals and reptiles amniotic egg
reptiles and mammals that lay eggs produce amniotic eggs and lay them outside of water. other mammals don’t lay eggs but have amniotic sacs.
Amphibia Reproduction
Amphibians typically reproduce through external fertilization, lots of eggs, but little protection from parents
Vocalization - Amphibians
use vocalization primarily for social interactions, such as attracting mates or establishing territory.
Semiterrestrial - Amphibian
amphibians live both in aquatic environments (like water for breeding) and on land.
Mammals
Egg-laying monotremes, pouch-bearing marsupials, and placental (eutherians)
Mammary glands
produce milk for offspring
Warm-blooded mammals
are mammals that can regulate their body temperature internally, allowing them to thrive in a variety of environments.
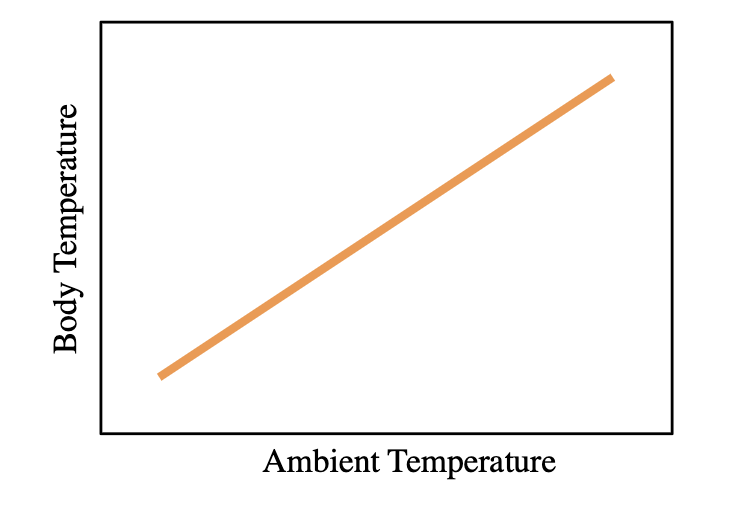
Dependent Variable in the figure is : a) body temperature. b) ambient temperature
a) body temperature

Poikilotherm or Homeotherm?
Poikilotherm - body temp is strongly affected by environmental temp
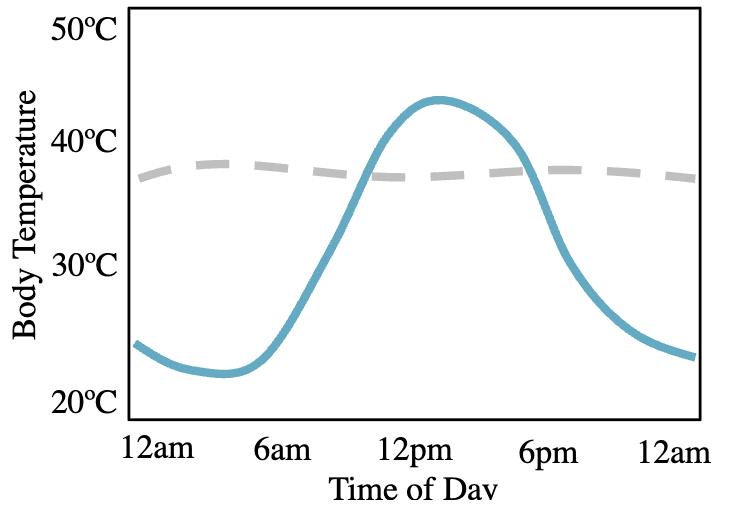
What organism does the gray, dashed line describe best: poikilotherm or homeotherm?
Homeotherm - its hotter at noon than midday but body temp remains steady all day long.
What is/are the independent variables in this figure?
a) time of day
b) body temp
c) poikilotherm vs homeotherm
d) two of the above
e) all of the above
d) two of the above (time of day and poikilotherm vs homeotherm)
Cost and benefits of homeothermy
Homeothermy provides stable body temperatures, allowing for consistent metabolic functions, but it requires more energy to maintain compared to poikilothermy.
Thermoregulatory Adaptations
Insulation - fat, fur, feathers (reduce heat exchange with environment)
Surface area to volume ratio - shorter appendages and bigger body size reduce heat loss, and vice versa
Counter current heat exchange
Counter current heat exchange
helps retain body heat in efficient manner, in which warm arterial blood warms the cooler venous blood returning to the body.
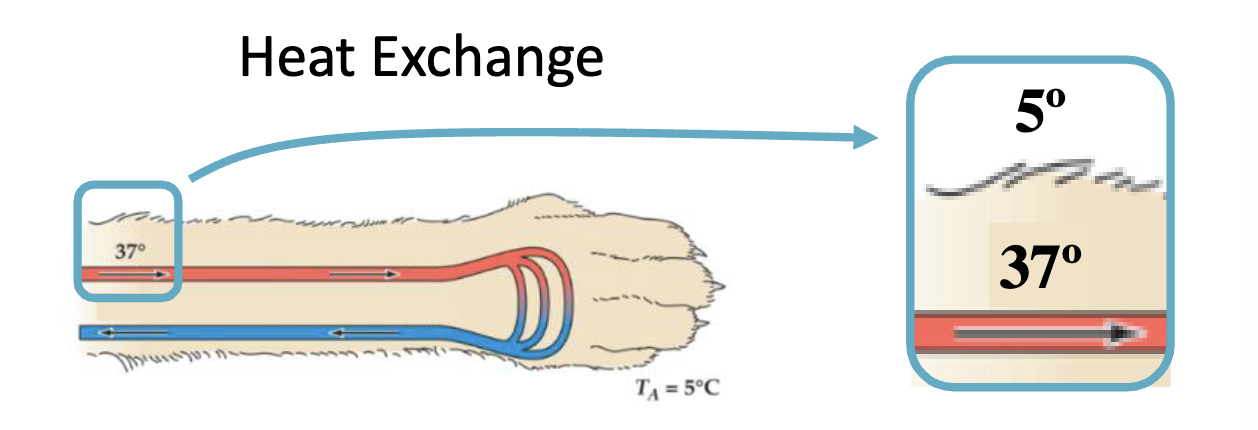
Will the animal lose or gain heat from the environment?
Lose
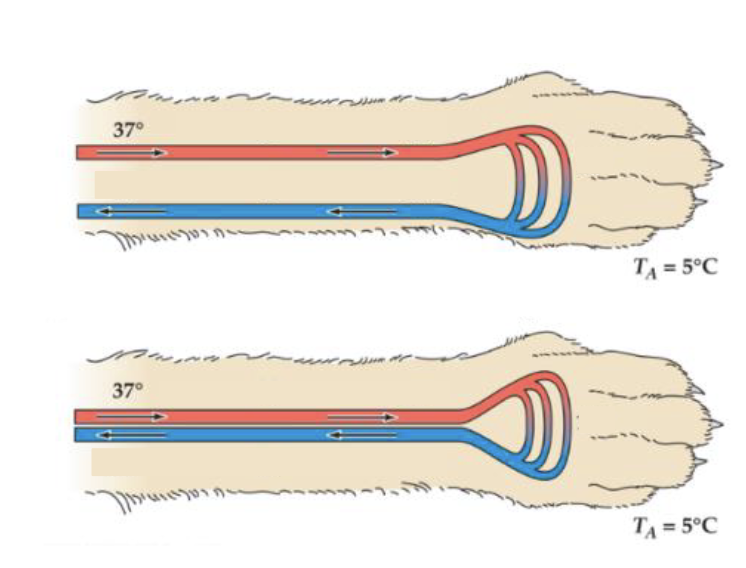
Which animal will lose the most heat to the environment
The top one → the veins are closer to surface of skin so more heat goes to environment
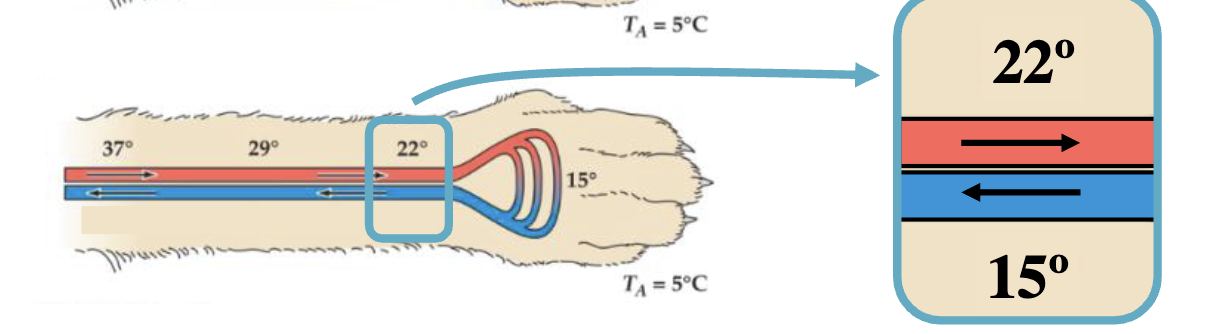
How will heat transfer between these blood vessels?
a) red to blue
b) blue to red
c) no net change
d) not enough info to tell
a) red to blue → heat will flow from warm to cool
waste exchange for mammals
trough kidneys and urine - in the form of urea
differentiated teeth
in mammals - different teeth for different fuctions
monotremes
lay eggs, have hair, produce milk, and lack nipples (ex. platypus and echidnas)
marsupials
live young (no eggs), nipples provide milk, placenta provides nutrients in utero, born early→develop in marsupiam/pouch (ex. opposumns, kangaroos, koalas)
eutherian
complete embryonic development attached to placenta
placenta
organ combining maternal and embryonic tissues
After gestation…
embyro emerges from mothers body (ex. 9 months for human)
Advantages of viviparity and placenta?
Offspring develop at more constant, favorable temp
they are physically protected
they are portable → mothers aren’t tied to nest
tradeoffs of placenta and viviparity
placenta is energetically expensive to produce and bearing live young is energetically costly (need enough food!)
Reptiles
lizards & snakes, turtles, crocodiles & alligators, and birds
reptile adaptations for life on land
watertight skin make by layer of keratin
breathe air through well developed lungs
excrete uric acid
amniotic eggs
ectotherms → bask in sunlight, seek shade, etc to keep body temp regulated
Birds
descended from dinosaurs that had feathers → outgrowths of skin made from keratin, providing insulation and used for display (ENDOTHERMIC)
Reptiles in flight
wings/flight evolved indp in pterosaurs, birds, and bats (tetrapod amniotes)