General Histology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
levels of histology
atoms → molecules → cells + extracellular material and fluids → tissues → organs → organ systems
4 types of tissues
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
characteristics of epithelial tissue
- cellularity (little ECF)
- polarity (2 distinct sides)
- attachment
- avascularity (diffusion to aquire nutrients)
- regeneration (quickly, skin cells)
- sheets/layers (organized)
epithelial tissue function
- provide physical protection (abrasions, viruses)
- control permeability (water resistant ex)
- provide sensation
- secrete (stomach acid, saliva, etc)
simple epithelium
single layer of cells
stratified epithelium
more than one layer of cells
squamos epithelia
irregular shape of cells
cuboid epithelia
contain cells that are hexagonal with a height equal to their width & the nuclei are near the center of the cell
transitional epithelia
epithelia that can transition for appearing multilayered to simple; also called uroepithelial (change shape with no damage)
columnar epithelia
epithelia made of cells taller than they are wide, specialized in absorption
simple squamous epithelium
- function: reduces friction, controls vessel permeability, performs absorption and secretion
- delicate (easily damaged)
- found where fast exchange needed (alveoli)
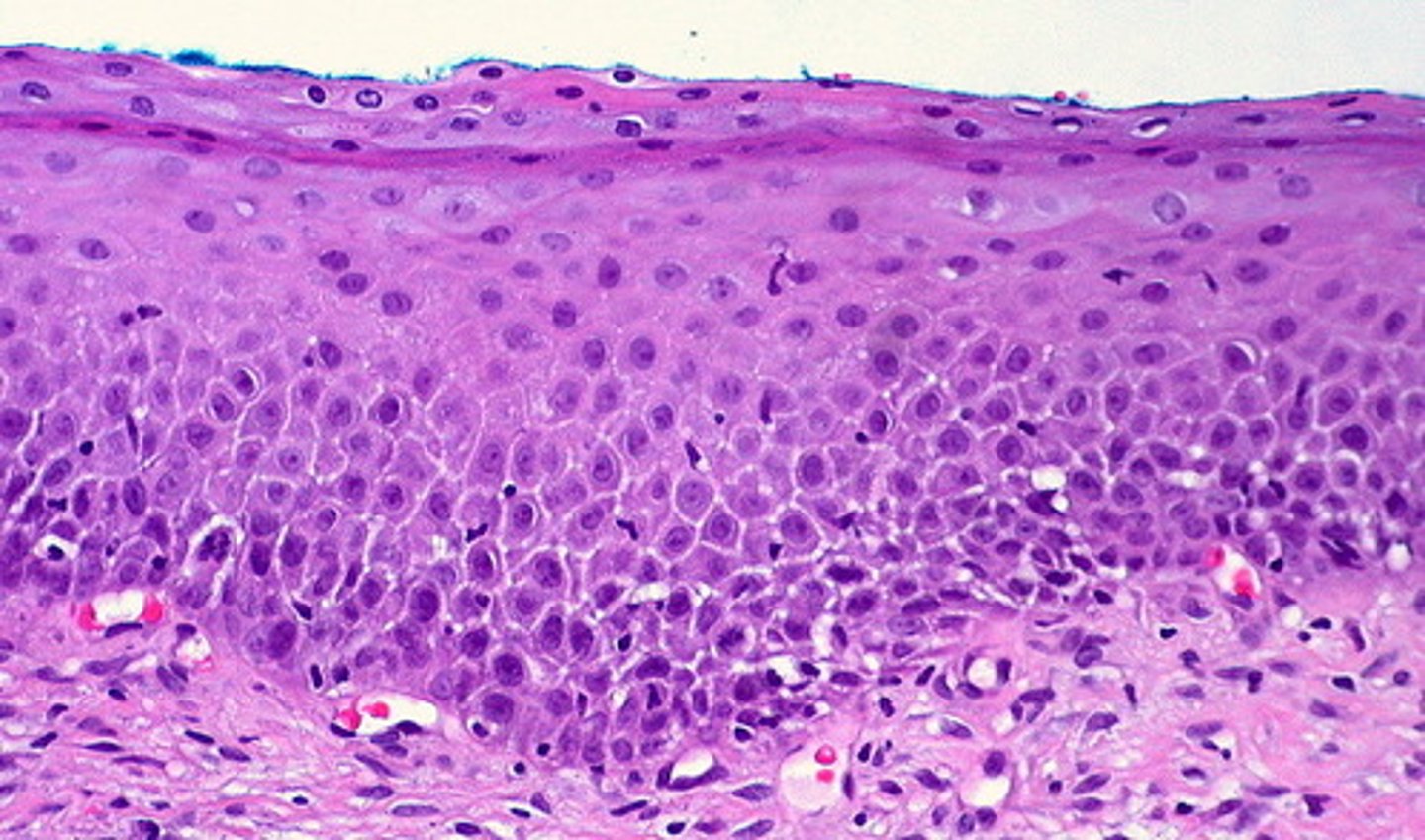
stratified squamous epithelium
- function: provides physical protection against abrasion, pathogens, and chemical attack
- thick/robust
- surface of skin; lining of oral cavity, throat, esophagus, etc
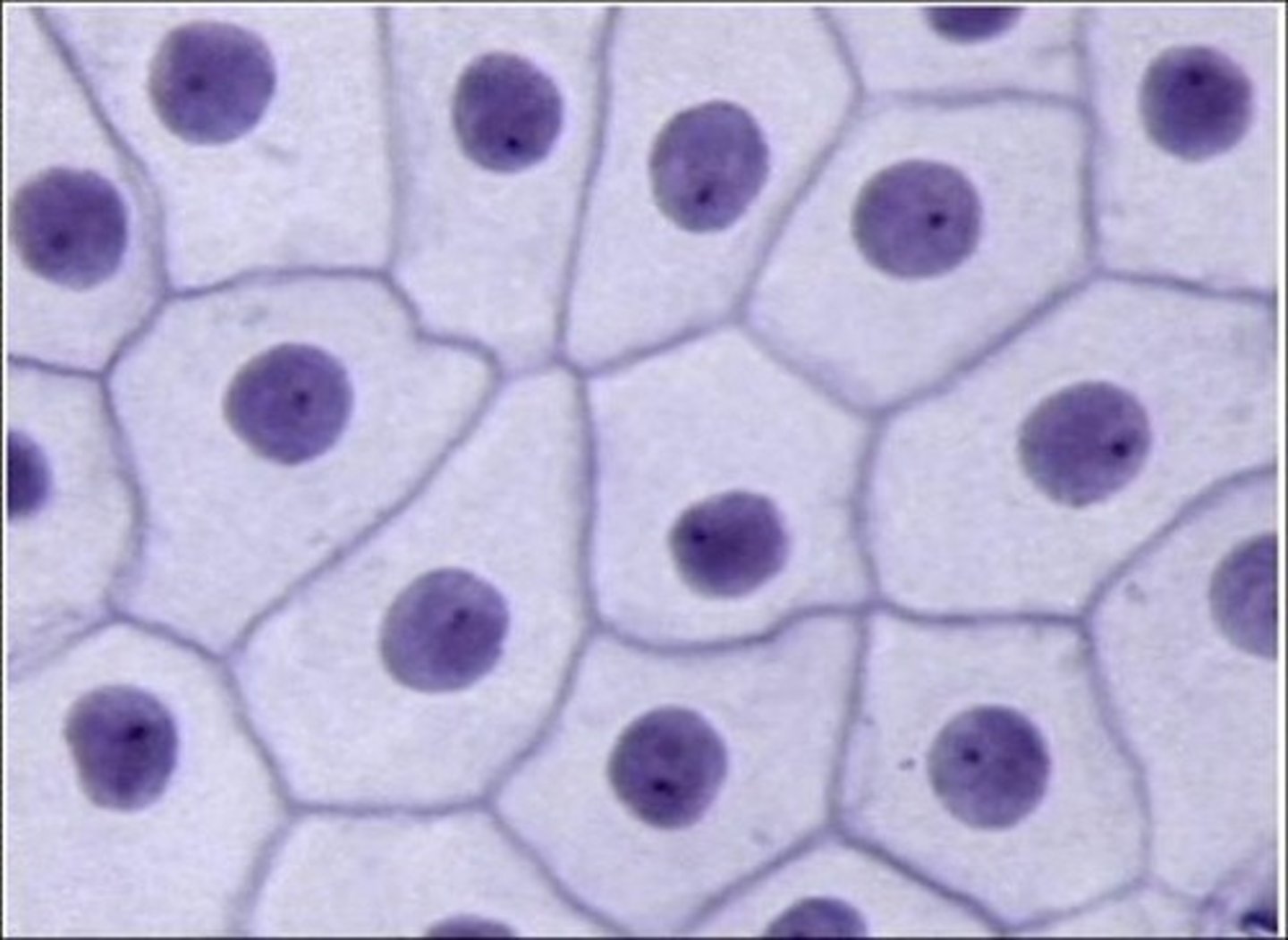
simple cuboidal epithelium
- function: secretion, absorption, limited protection
- location: glands, ducts, portions of kidney tubercles, thyroid gland

stratified cuboidal epithelium
- function: protection, secretion, absorption
- location: lining of some ducts (rare)
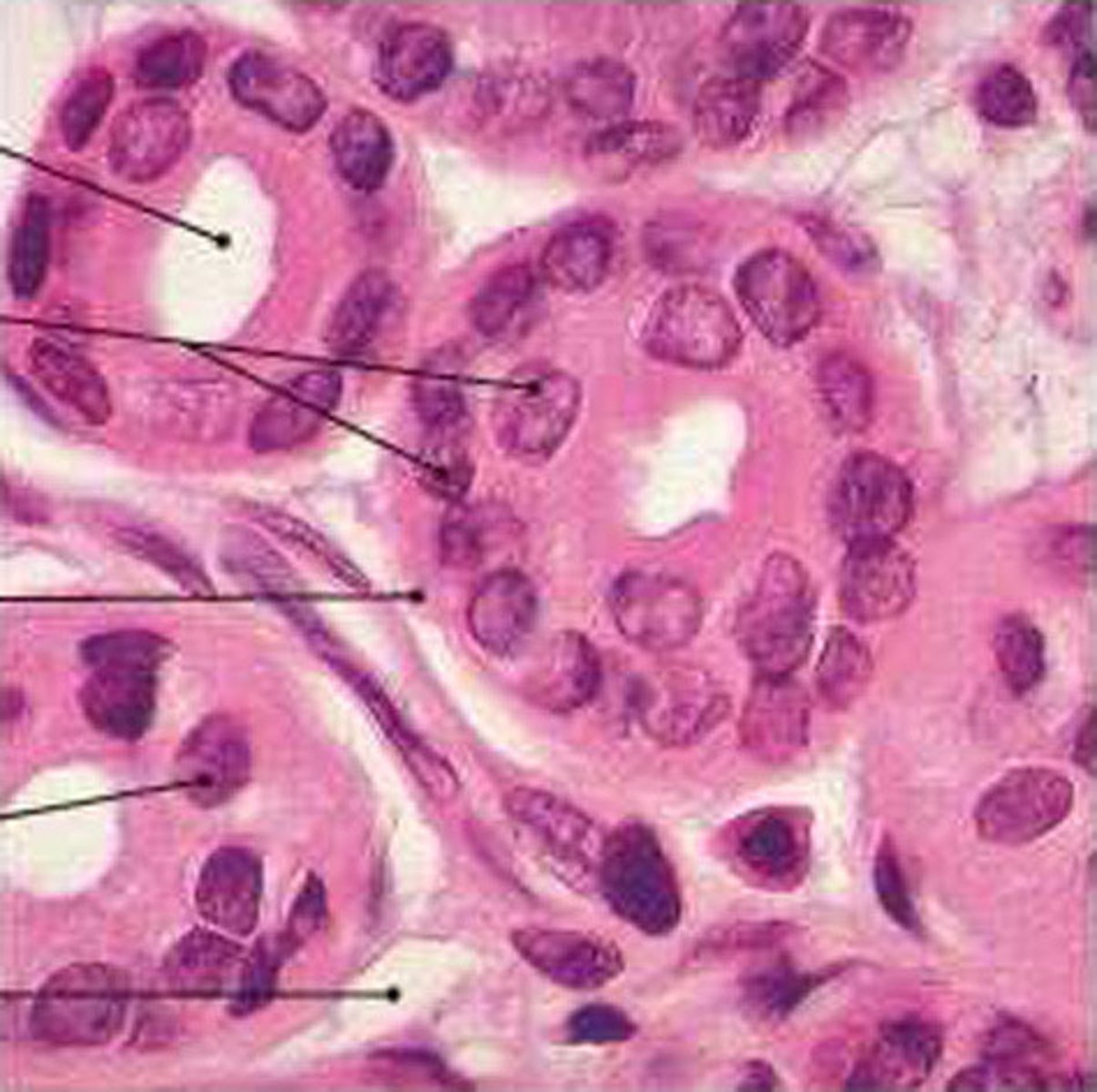
simple columnar epithelium
- function: protection, secretion, absorption
- locations: lining of stomach, intestine, collecting ducts, etc

stratified columnar epithelium
- function: protection
- locations: small areas of the pharynx, salivary gland ducts
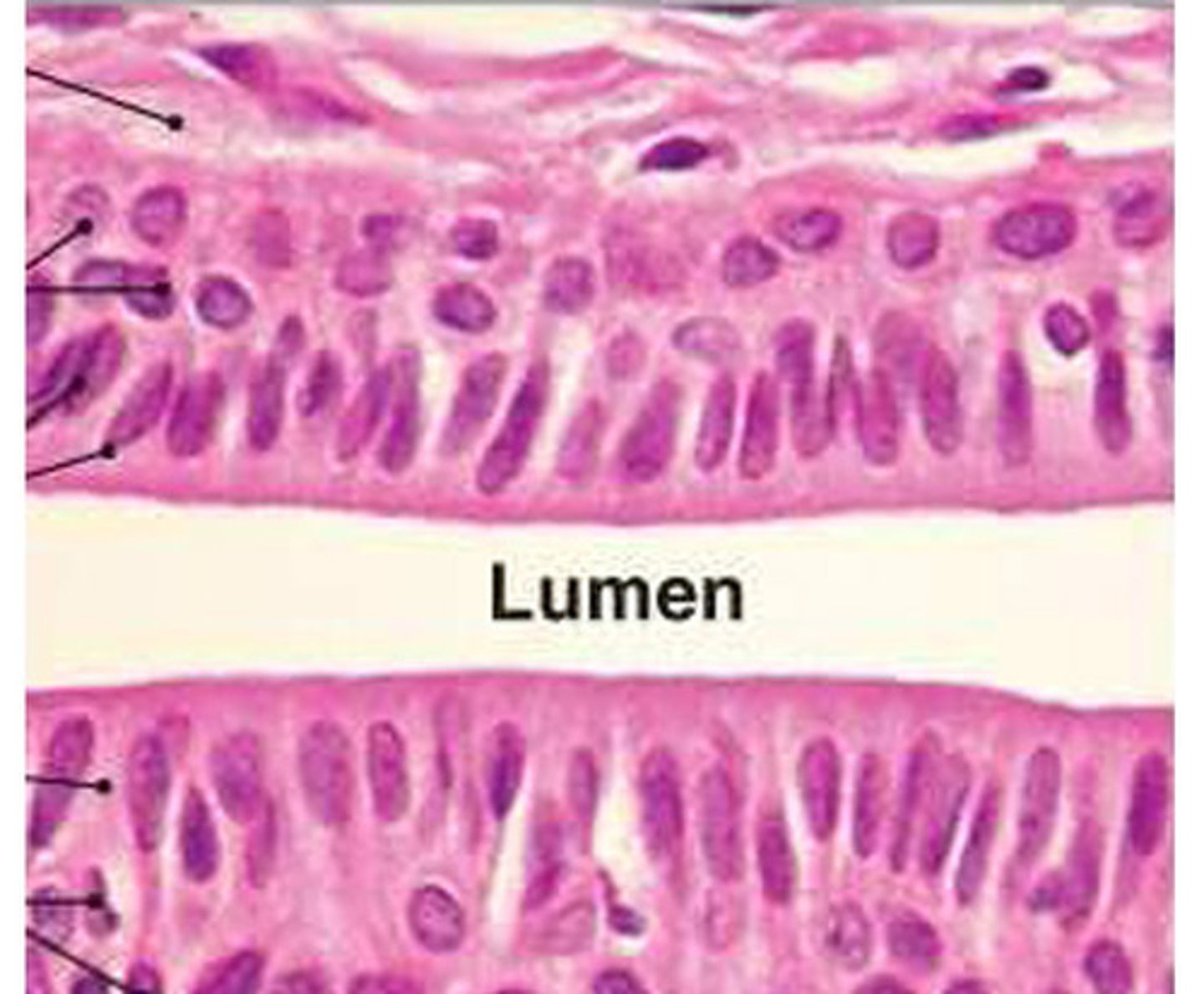
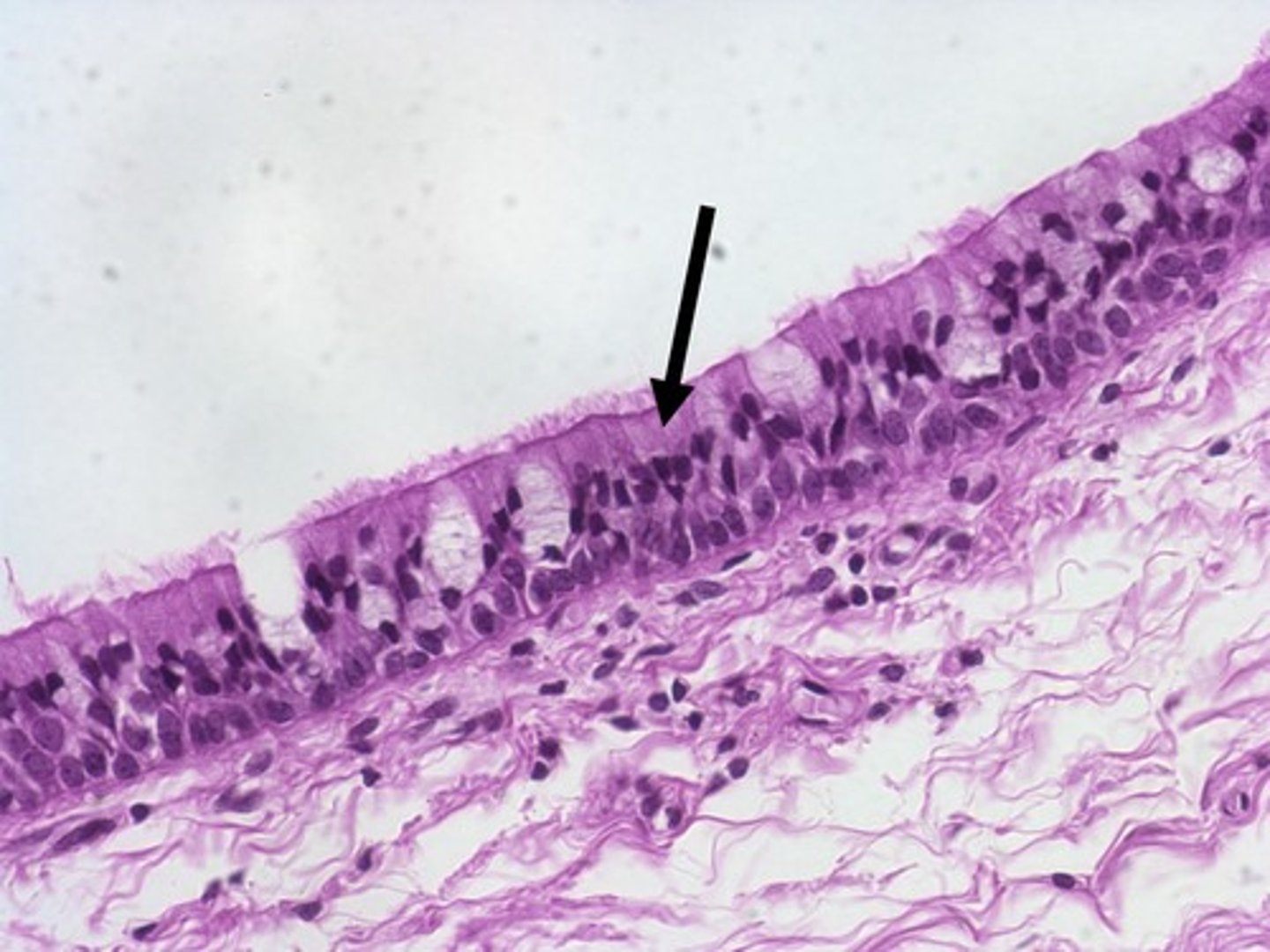
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
- function: protection, secretion
- locations: lining of nasal cavity, trachea, and bronchi
- nuclei all different directions
- all tissues connect to basement layer
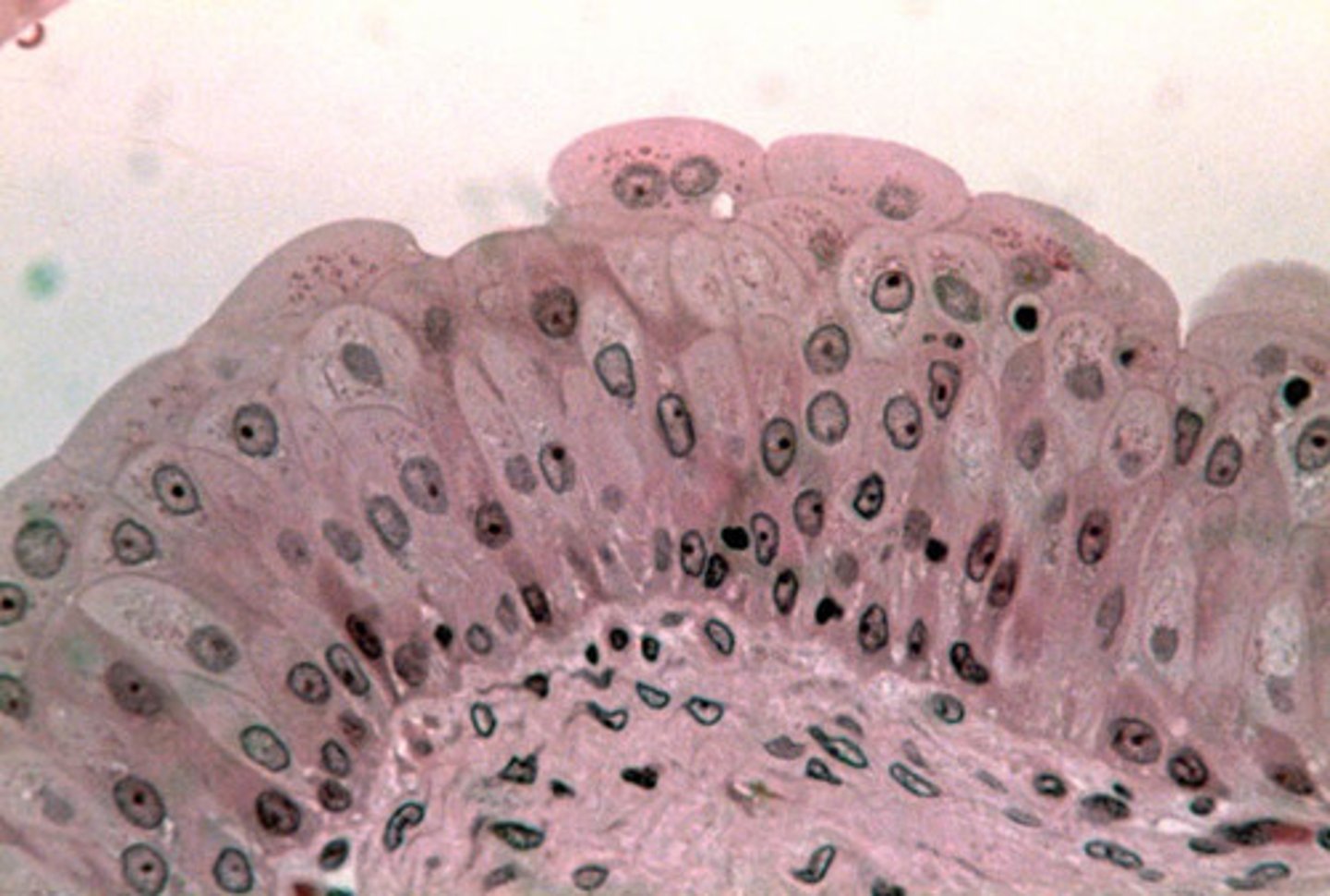
transitional epithelium
- function: permits expansion and recoil after stretching
- locations: urinary bladder, renal pelvis, ureters
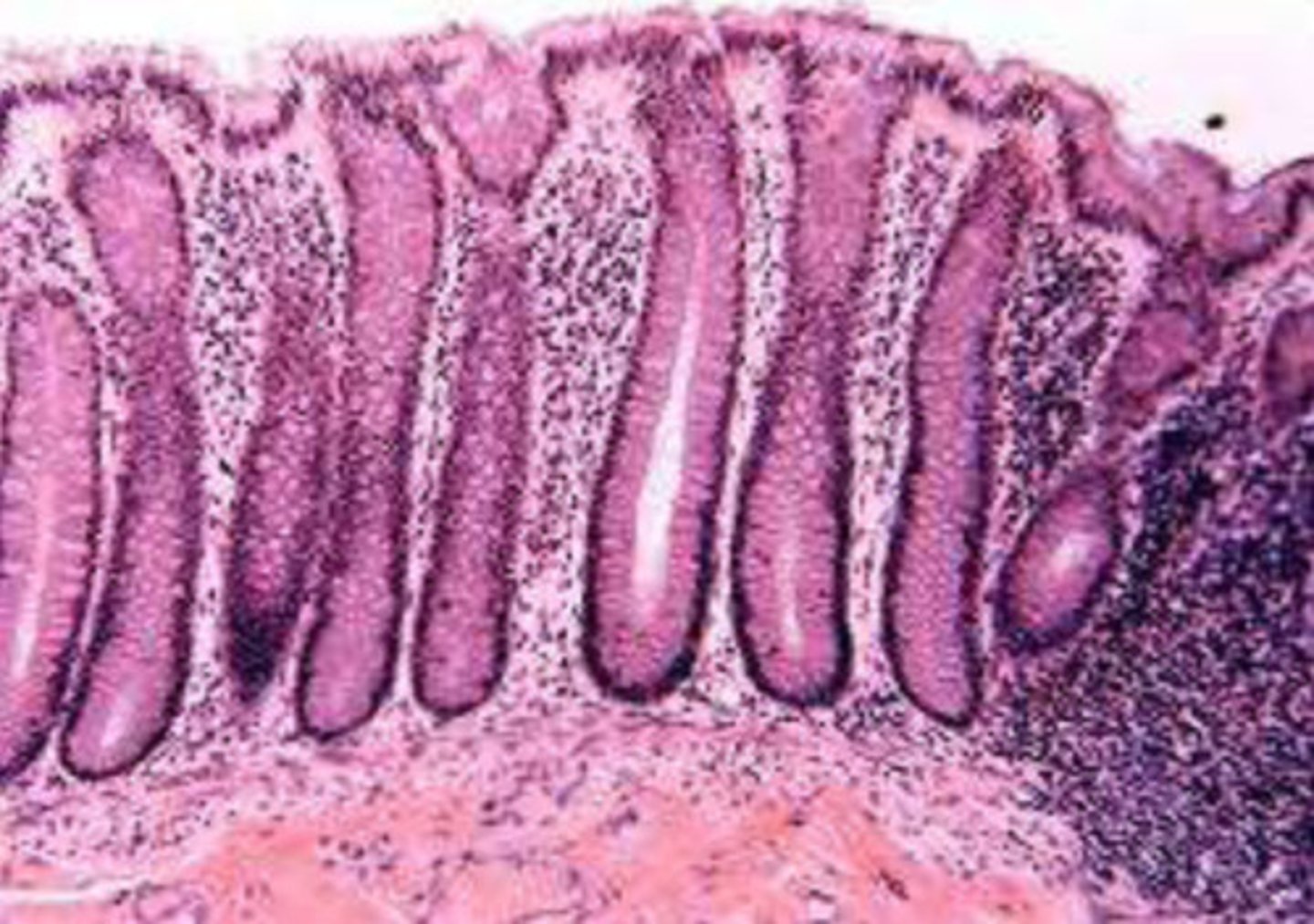
glandular epithelia
Exocrine:
- serous glands secrete enzymes
- mucous glands secrete mucins
- mixed exocrine glands
Endocrine:
- secretes hormones (through CV system)
connective tissue - 3 main components
- specialized cells
- extracellular protein fibers
- ground substance (water/gel fluid of connective tissue)
extracellular protein fibers + ground substance =
matrix (collective term for the extra cellular component of connective tissue)
connective tissue - function
- establish structural framework (bones ex)
- transport fluid and dissolved material (blood ex)
- protect organs (bones to fat tissue)
- support, surround, and connect other tissues
- store energy
- defend body from microorganisms
3 types of connective tissue
connective tissue proper, fluid connective tissue, supporting connective tissue
connective tissue proper
Loose
- fibers create loose open framework
- areolar, adipose, and reticular tissue
- bubble wrap!
Dense
- fibers densely packed
- dense regular, dense irregular, elastic
- glue!
fluid connective tissue
Blood
- contained in cardiovascular system
- plasma
Lymph
- contained in lymphatic system
- formed as interstitial fluid
- collected into lymphatic vessels
- drained in blood vessels
supporting connective tissue
Cartilage
- solid, rubbery matrix
- hyaline, elastic, and fibrous cartilage
Bone
- solid, crystalline matrix
supporting connective tissue qualities
- few cells
- high amounts of fiber
- ground substance that may contain inorganic calcium salts
cells in connective tissue proper
FIXED CELLS:
Fibroblasts
Fibrocytes
Fixed macrophages
Adipocytes
Mesenchymal cells
Melanocytes
WANDERING CELLS:
Free macrophages
Mast cells
Lymphocytes
Neutrophils and eosinophils
fibroblasts (fixed cells)
produce connective tissue fibers
fibrocytes (fixed cells)
maintain connective tissue fibers and matrix
mixed macrophages (fixed cells)
phagocytize pathogens and damaged cells
adipocytes (fixed cells)
store lipid reserves
mesenchymal cells (fixed cells)
connective tissue stem cells that can differentiate into other cell types
melanocytes (fixed cells)
synthesize melanin
free macrophages (wandering cells)
mobile/traveling phagocytic cells (derived from monocytes of the blood)
mast cells (wandering cells)
stimulate local inflammation
lymphocytes (wandering cells)
participate in immune response
neutrophils and eosinophils (wandering cells)
small, phagocytic blood cells that mobilize during infection or tissue injury
fibers in connective tissue
collagen
- long and cylindrical fibers
- three subunits coiled
- most common and strongest filament
reticular
- single unit of protein fibers
- thin, help hold organs in place, forms scar tissue
elastic
- contain elastin, lots of stretch (150%)
loose connective tissue
- packing material
- binding material
- forms fascia and sheaths
- arrangements of fibers give strength and flexibilty
3 loose connective tissues
areolar
- all different directions
- under skin (shock absorption)
- highly vascularized
adipose
- like packing material
- fat tissue
reticular
- form network
- holds in place
dense connective tissue
- densely packed collagen fibers
- parallel to the direction of force
- strong and flexible
- forms tendons, ligaments, and aponeuroses
- silvery, white appearance
3 dense connective tissues
dense regular, dense irregular, elastic
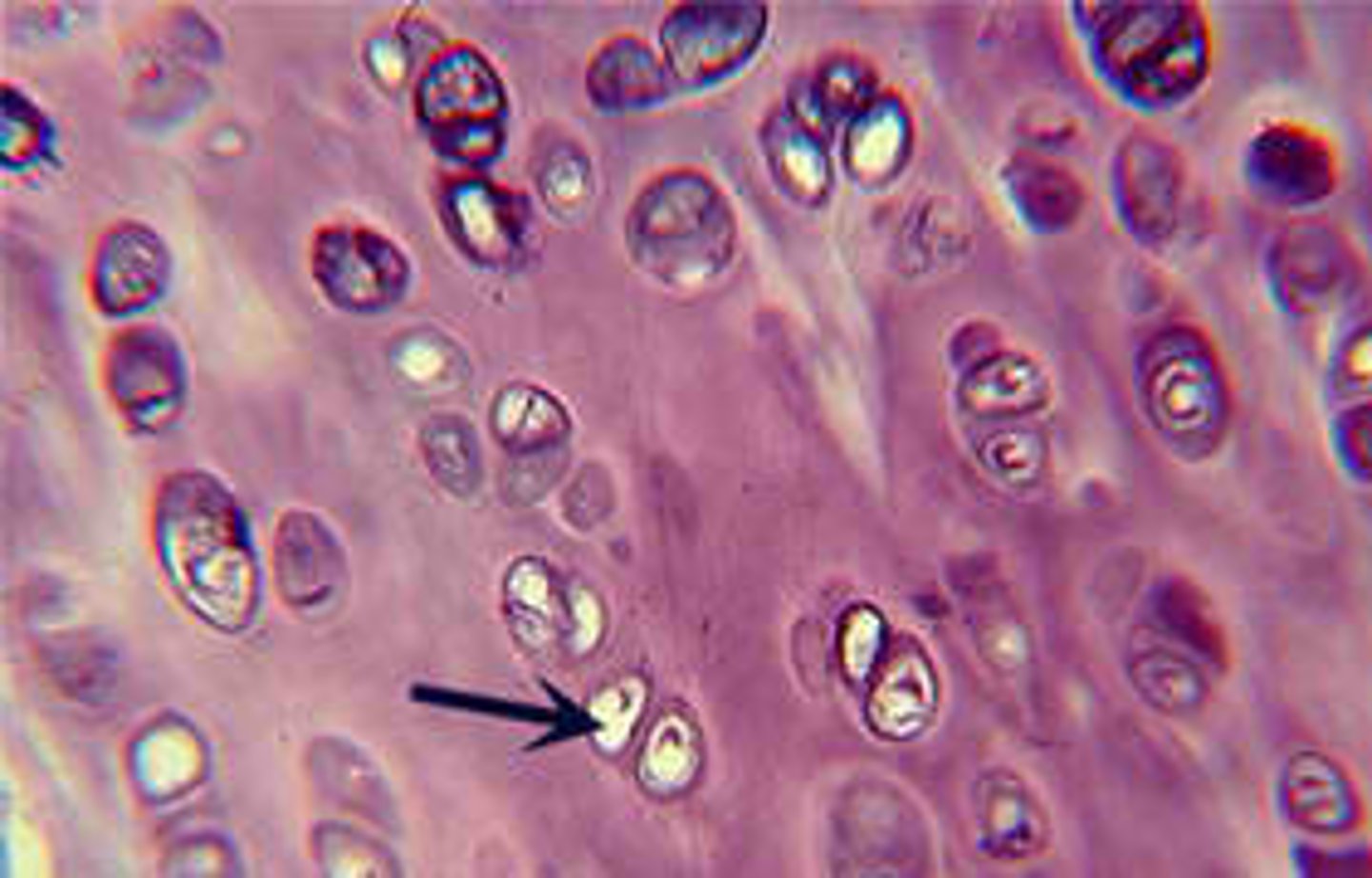
hyaline cartilage
- function: provides stiff but somewhat flexible support, reduces friction between bony surfaces
- locations: between tips of ribs and bones of sternum, covering bones at synovial joints
- avascular and aneural (wont heal or slowly)
fibrous cartilage
- function: resists compression, prevents bone-to-bone contact, limits relative movement
- locations: pads within knee joints, between pubic bones, intervertebral discs
- can be compressed and not damaged
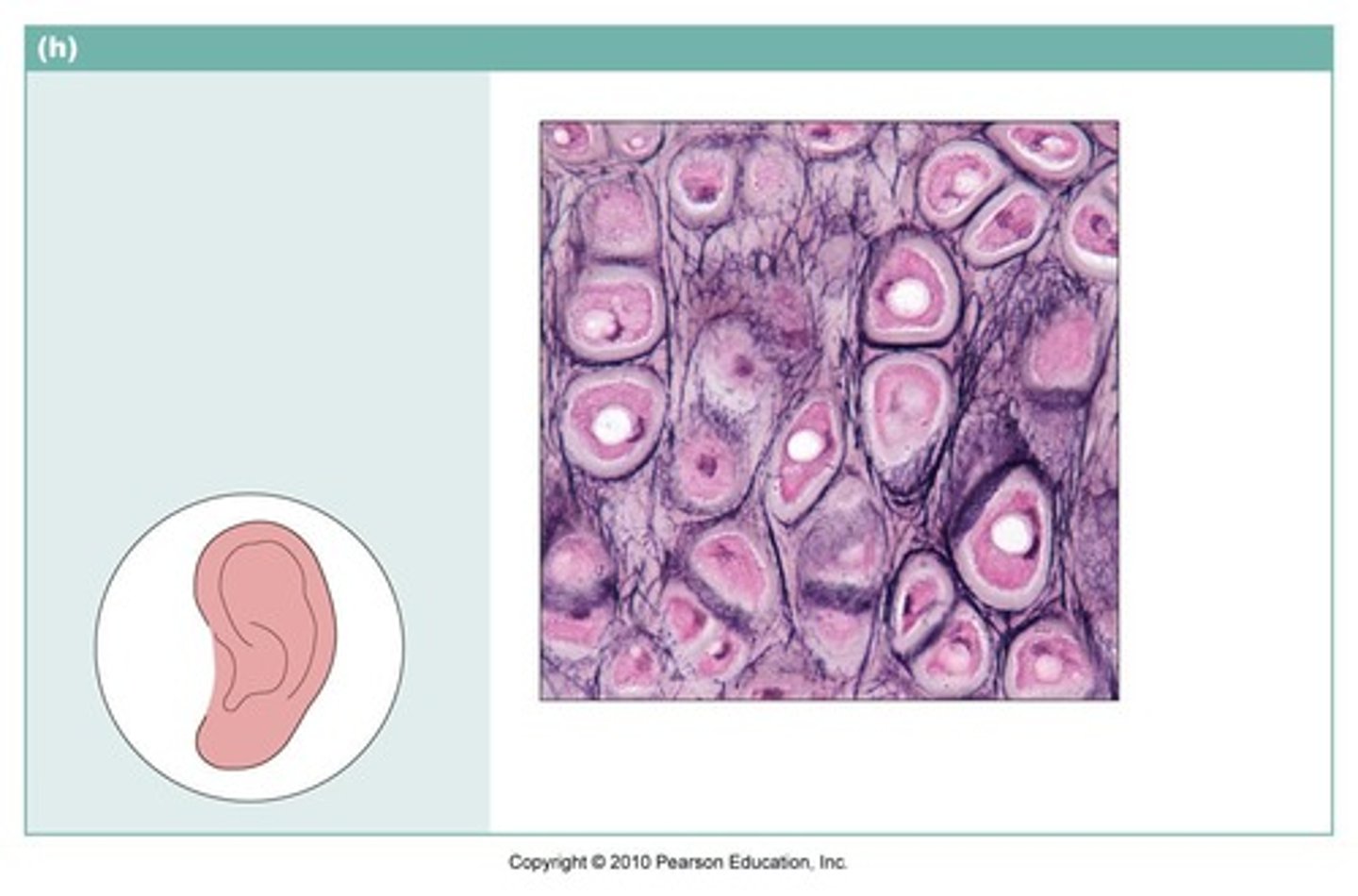
elastic cartilage
- function: provides support, but tolerates distortion without damage and returns to original shape
- locations: external and internal ear
4 membranes (epithelial + connective tissue)
1. mucous ('wet', exchange with exterior)
2. serous (lines ventral body cavities)
3. cutaneous (thick, dry, and water resistant)
4. synovial (areolar tissue with incomplete layer of epithelium)
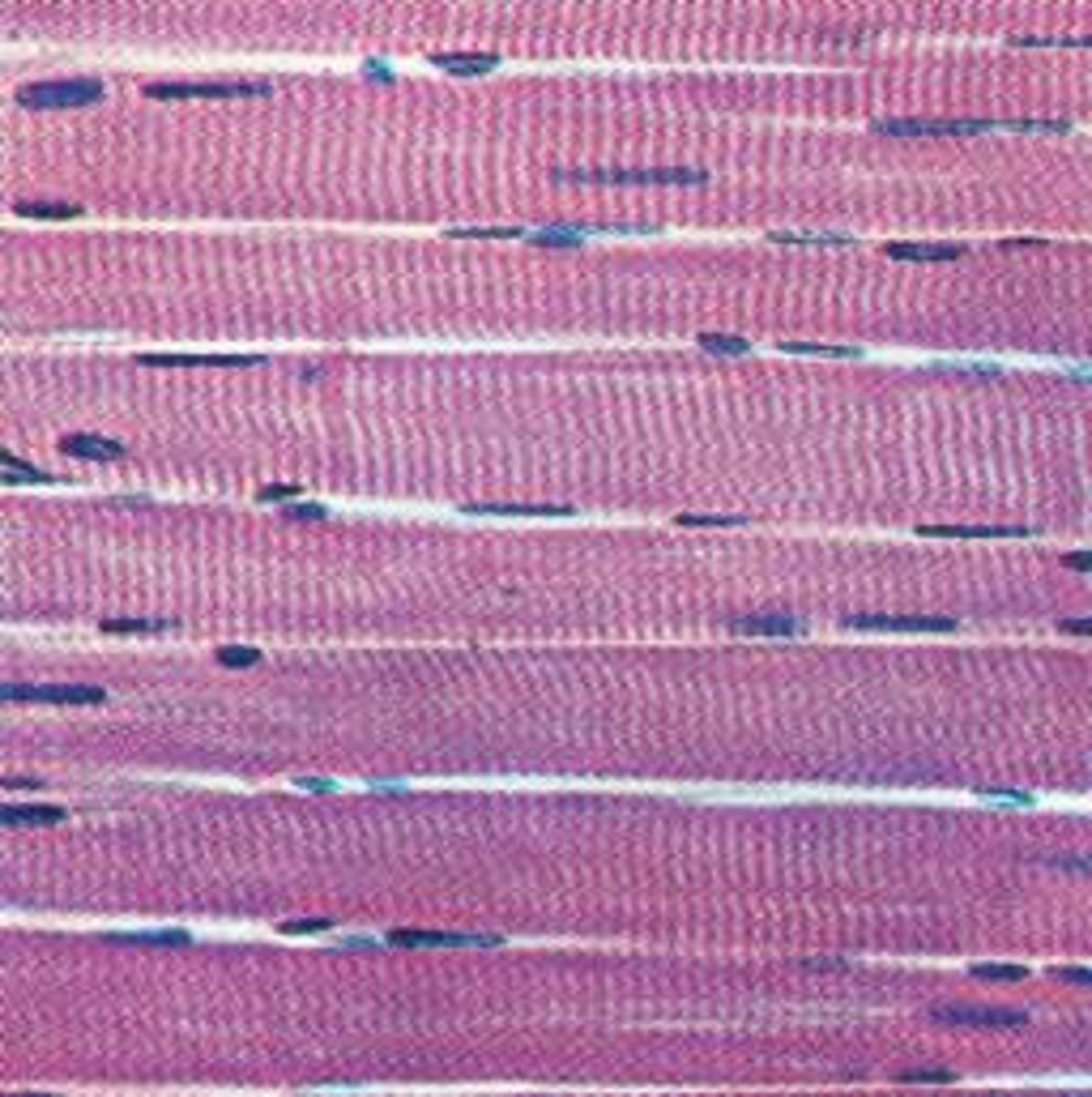
skeletal muscle tissue
- function: moves or stabilizes the position of the skeleton, guards entrances and exits to the digestive/respiratory/urinary tracts, generates heat, protects internal organs
- locations: combined with connective tissues and neural tissues in skeletal muscles
- striated, multi-nucleated, voluntary control
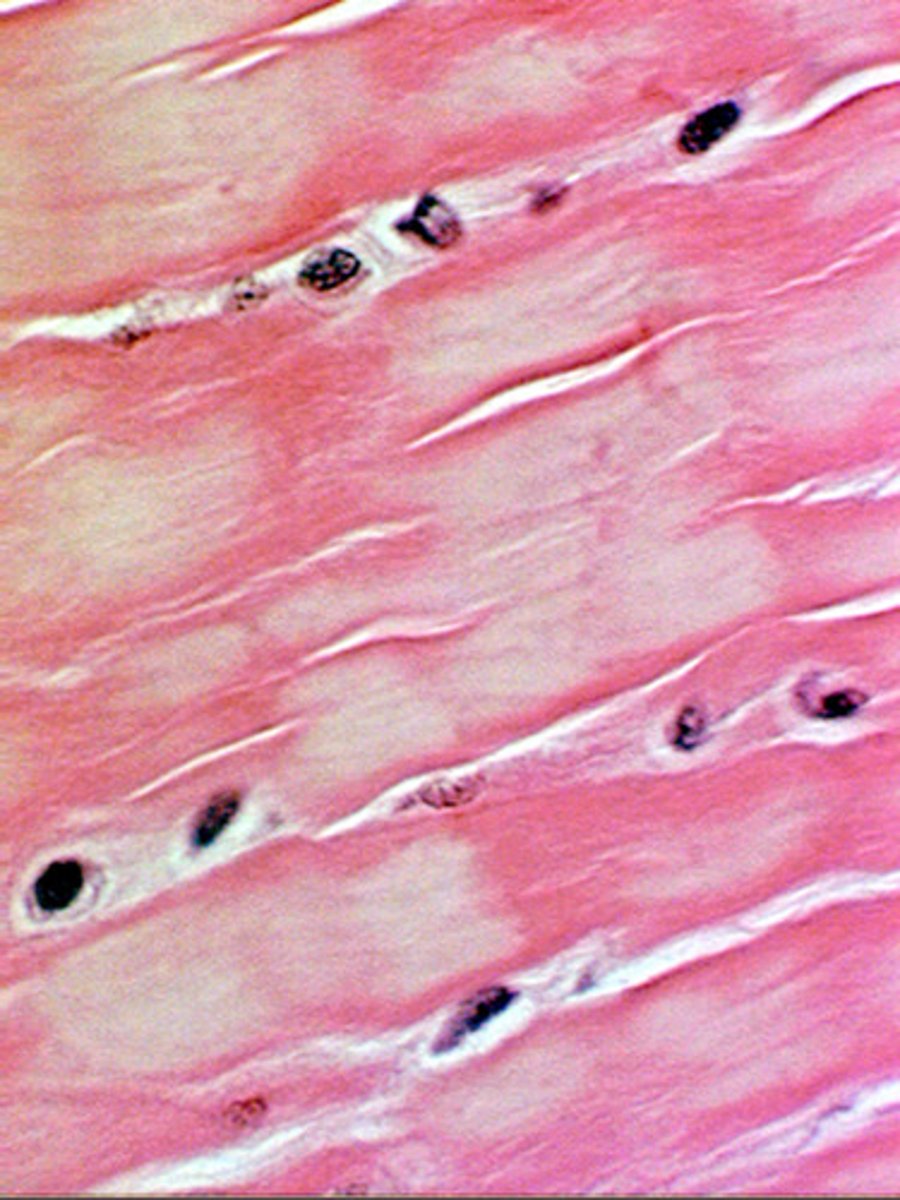
cardiac muscle tissue
- function: circulates blood, maintains BP
- locations: heart
- striated, one nucleus, short
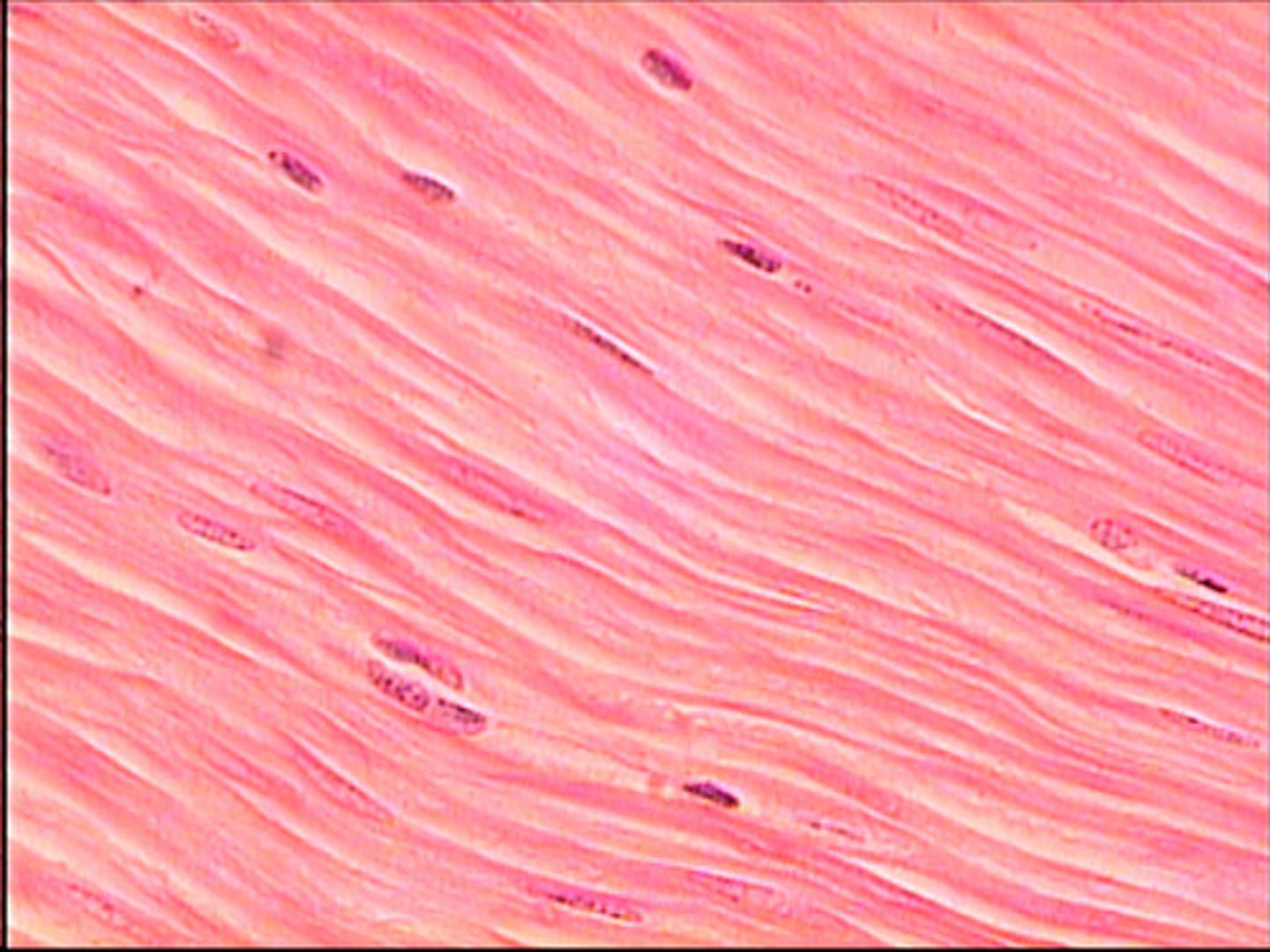
smooth muscle tissue
- function: moves food, urine, and reproductive tract secretions, controls diameter of respiratory passageways, regulates diameter of blood vessels
- locations: walls of blood vessels and in digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive organs
- one nucleus, not under voluntary control
neural tissue
- specialized to conduct electrical signals
- neurons: cells that conduct electrical signals
- neuroglia: supporting cells in neural tissue

tissues, nutrients, and aging
- repair and maintenance become less efficient with age
- hormonal and lifestyle changes affect tissues
- epithelia becomes thin and connective tissue fragile
- cardiac and neural tissue does not regenerate (minor damage adds up over time, can cause severe health issues)