Gene expression
1/38
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Phenotype
The visible characteristics of an organism
What determines an individuals phenotype?
Genes (proteins)
What controls gene expression?
Transcription and translation
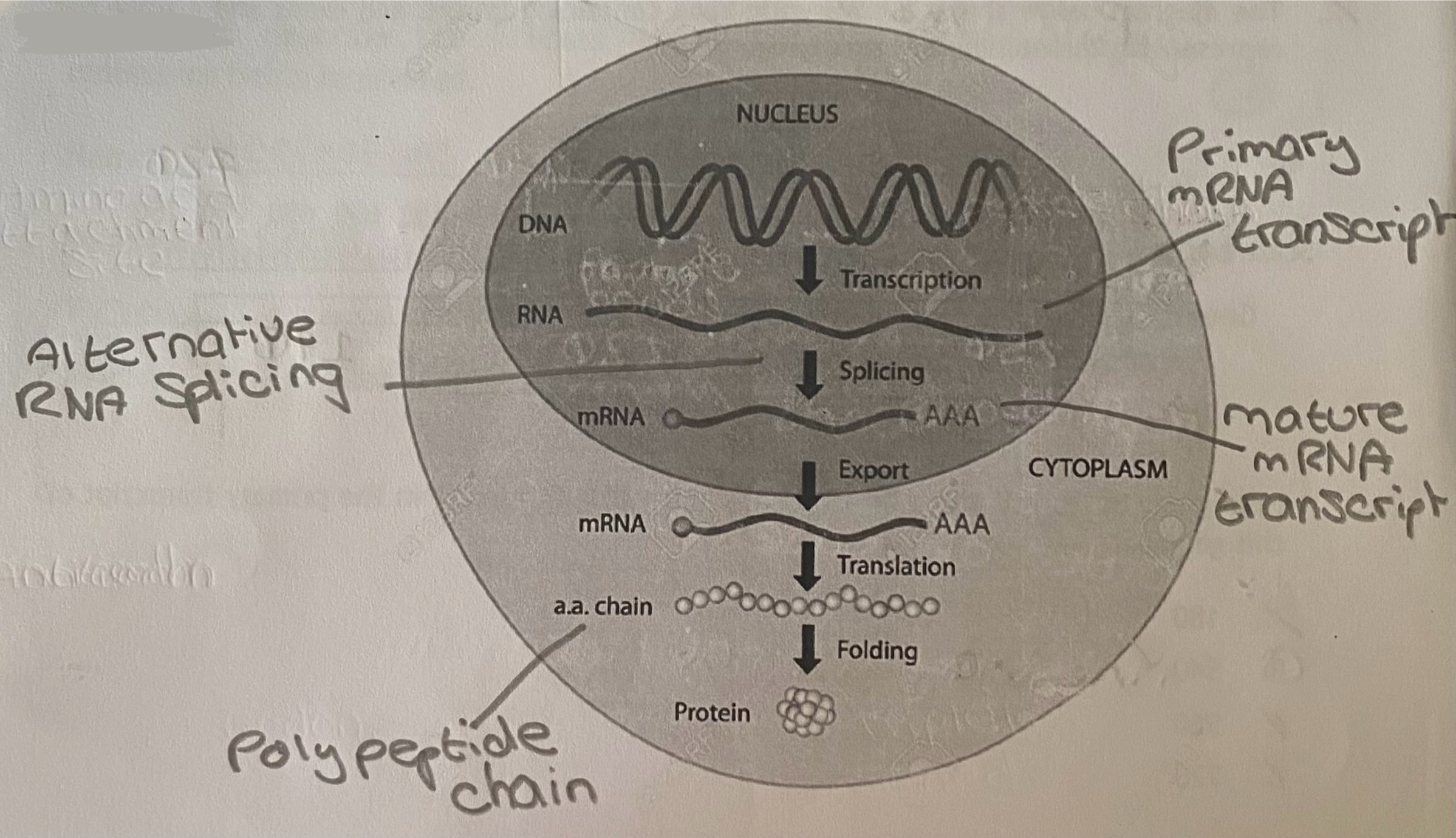
Diagram: gene expression
Protein synthesis
When a gene is expressed
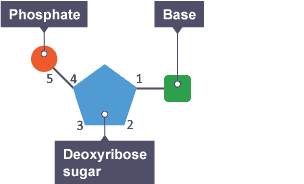
Diagram: DNA nucleotide
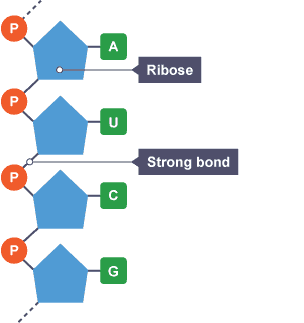
Diagram: RNA nucleotide
In what four ways does RNA differ from DNA?
RNA contains the base uracil whereas DNA contains the base thymine
RNA is found in the cytoplasm and the nucleus whereas DNA is only found in the nucleus
RNA is made of ribose sugar whereas DNA is made of deoxyribose sugar
RNA is single stranded whereas DNA is double stranded
mRNA
This carries a copy of the DNA code from the nucleus to the ribosome
tRNA
This takes a specific amino acid from the cytoplasm to the ribosome depending on the anti-codon
rRNA
This forms the ribosome and proteins
How does the genetic code from the DNA get to the ribosomes?
The mRNA strand takes the complementary code out of the nucleus and travels through the cytoplasm to get to the ribosomes
Transcription
The synthesis of the mRNA strand from a section of DNA, controlled by RNA polymerase
Where does transcription occur?
In the nucleus
What are the six stages of transcription?
RNA polymerase moves along the gene, unwinding and unzipping (breaking the hydrogen bonds between the bases) the DNA double helix
Free mRNA nucleotides join with the complementary nucleotides on the DNA template strand, this is controlled by RNA polymerase
Weak hydrogen bonds form between base pairs
Strong chemical bonds form between the sugar of one RNA nucleotide and the phosphate of another
Weak hydrogen bonds break between the complementary base pairs, allowing mRNA to peel off the DNA
This molecule is called a primary mRNA transcript
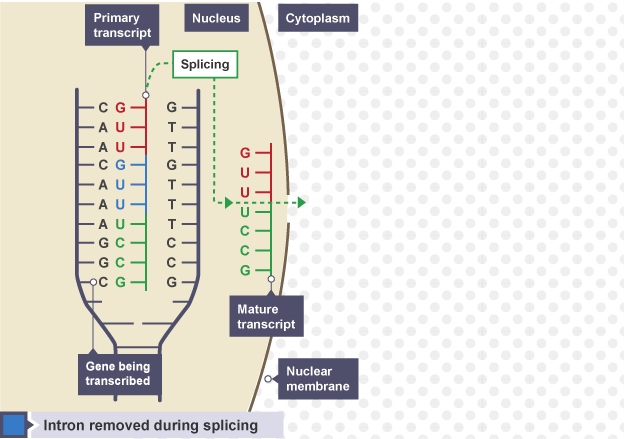
Diagram: transcription
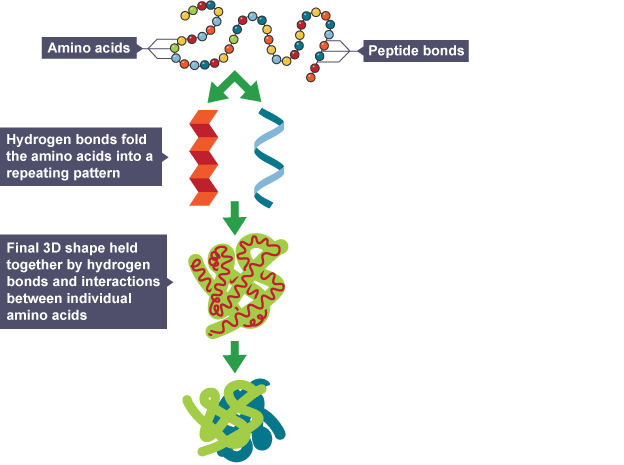
Diagram: protein structure
RNA splicing (this is apart of transcription)
When the introns of the primary mRNA transcript are removed and the exons are retained in order to form the mature mRNA transcript
What are the four stages of RNA splicing? (this is apart of transcription)
Introns (non-coding regions) are removed from the primary mRNA transcript
Exons (coding regions) are retained
Exons are spliced together to form the mature mRNA transcript
The mature mRNA transcript passes out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm, where it joins to a ribosome
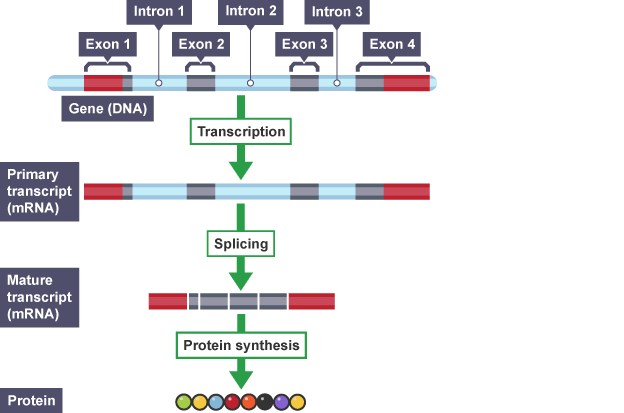
Diagram: RNA splicing
Introns
Non-coding regions of a gene that are cut out and removed from the primary mRNA transcript
Exons
Coding regions of a gene that are retained and joined together to form the mature mRNA transcript
Translation
The synthesis of a protein under the control of mRNA in the cytoplasm
Where does translation occur?
In the cytoplasm
What are the eight stages of translation?
A ribosome binds to the 5’ end of the mature mRNA transcript at a start codon
tRNA molecules have an anti-codon and an amino acid attachment site
tRNA molecules collect a specific amino acid
tRNA molecules carry the amino acid to the ribosome (where mRNA is attached)
The anti-codon of the tRNA molecules pairs up with a codon on the mRNA strand
This is repeated for many tRNA molecules and amino acids are brought adjacent to each other in the correct sequence
Peptide bonds form between adjacent amino acids to produce a polypeptide chain
A stop codon is reached which stops translation
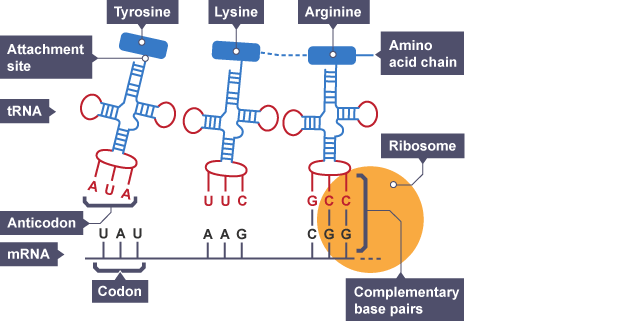
Diagram: translation
Codon
Every three bases (triplets) on the mature mRNA transcript
Anti-codon
Every three bases (triplets) on the tRNA molecule that correspond to a particular amino acid
What is the mRNA and tRNA code for the DNA code of: AGCT
mRNA: UCGA
tRNA: AGCU
Alternative RNA splicing
The same primary mRNA transcript can make several different mature mRNA transcripts as different exons are retained within the transcript (this changes the combination of exons but not the order)
Where does (alternative) RNA splicing occur?
In the nucleus
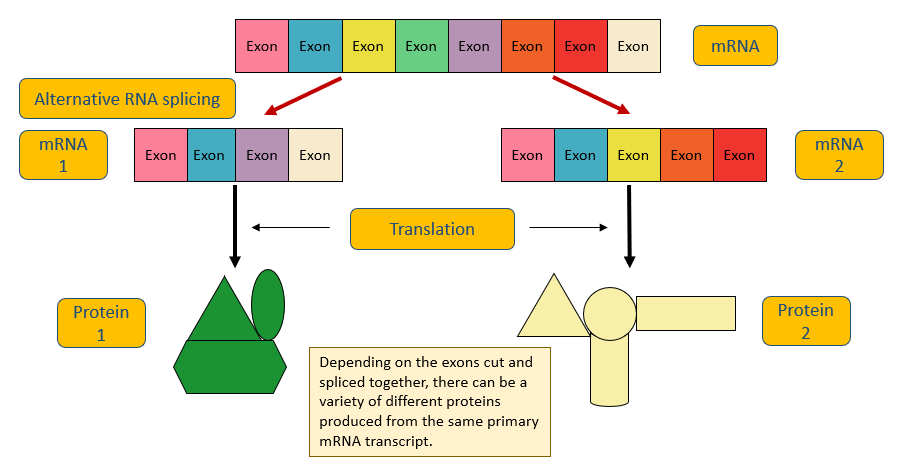
Diagram: alternative RNA splicing
How many genes are required to make a variety of proteins?
Just one
What are the four elements that all proteins contain?
Carbon
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
Oxygen
What bonds hold adjacent amino acids together?
Peptide bonds
What bonds hold different amino acids together in order to create a fold?
Hydrogen bonds
What determines the function of a protein?
The shape of the protein
How does DNA determine the shape and function of a protein?
Sequence of bases on the DNA strand > sequence of bases on the mRNA strand > sequence of bases on the tRNA molecule > sequence of amino acids > function of a protein
A gene
A section of DNA that codes for a protein