Bio Unit 2
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Homeostasis
The process by which organisms maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in external conditions
Stimulus-Response Model
Stimulus —> Receptor —> Control Centre —> Effector —> Response
Two types of effectors
Muscles and Glands
What does a muscle effector do
Contract to produce movement or generate heat
What does a gland effector do
Secrete substances such as hormones or enzymes
Negative feedback
A mechanism that reduces the effect of the initial change to bring the system back to normal
Characteristics of the nervous system
Neurons, messenger is electrical signal, carried by neurons, message is released close to the cell of influence, message is sent to specific cell/tissue, very quick and short
Characteristics of the endocrine system
Gland cells, messenger is hormones, carried by blood stream, message is released distant to the cell of influence, message is sent to the entire body, is slow and long
Chemoreceptors
Detects changes in chemical composition
Thermoreceptors
Detects changes in temperature
Mechanoreceptors
Detects physical pressure, stretch, vibration, or movement
Photoreceptors
Detects light
Nociceptors
Detects tissue damage or potentially harmful stimuli
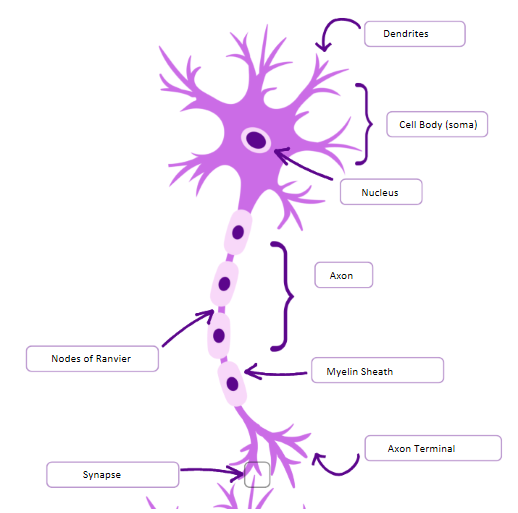
Description and Function of Dendrites
Short branching extensions from soma, receives signals from other neurons/sensory receptors
Description and Function of Cell Body (Soma)
Contains nucleus and organelles, integrates incoming signals, supports cell metabolism
Description and Function of Axon
A long, slender projection extending from soma, transmits electrical impulses from cell body to effectors
Description and Function of Myelin Sheath
Fatty insulating layer surrounding axon (made up of Schwann cells), increases speed of impulse conduction by insulating axon
Description and Function of Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps between myelin sheath segments along axon, allow impulses to jump from node to node (speed transmittion)
Description and Function of Axon Terminal
Distant end of axon (often branched), transmits the impulse to next neuron or effector
Description and Function of Synapse
Junction between two neurons/neuron and an effector, allows communication via neurotransmitters across small synaptic gap
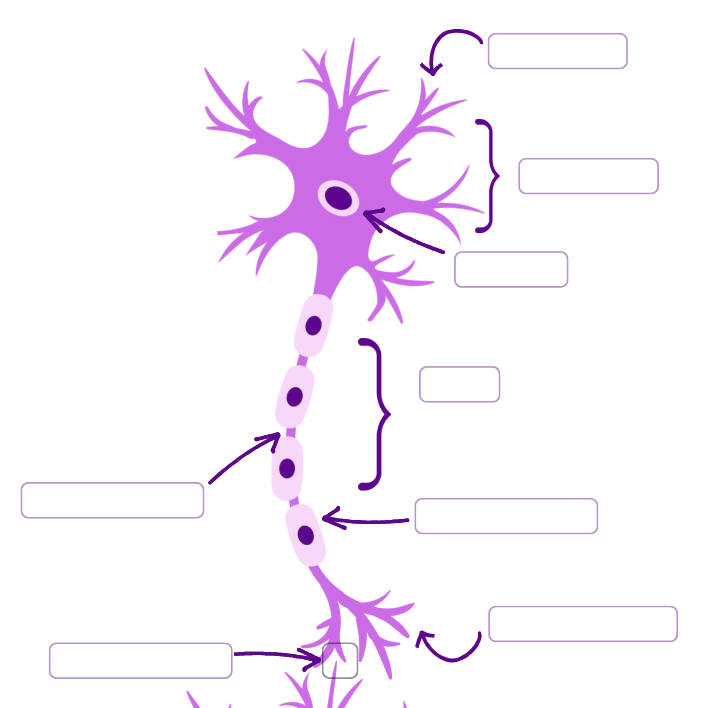
Label the neuron:
Three types of neurons
Sensory Neuron, Interneuron, Motor Neuron
Sensory Neuron
Transmits information from sensory receptors to central nervous system
Interneuron
Processes information and relays signals between sensory and motor neurons within the CNS
Motor Neuron
Sends signals from the CNS to effectors
Central Nervous System
Only brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
All nerves other than brain and spinal cord

Sensory Neuron

Interneuron
Motor Neuron