IB Biology 2025 SL Section C1 - Interaction & Interdependence
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Not finished as it doesn't include ATP, anaerobic and aerobic, photosynthesis, etc.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
carbon compounds
carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acid, proteins
Metabolism
the chemical processes (enzyme catalyzed) that occur within a living organism in order to maintain life.
Anabolism
the synthesis of complex molecules in living organisms from simpler ones, including ther formation of macrolmes from monomers by condensation reactions
Catabolism
the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules, including the hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers.
Subcomponent of carbohydrates
monosaccharides
subcomponent of lipids
Glycerol, fatty acids, phosphate groups
Subcomponent of proteins
amino acids
Protein examples
enzymes, antibodies, peptide hormones
Monosaccharide examples
glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose, deoxyribose
Disaccharide examples
sucrose, lactose, maltose
polysaccharide examples
starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin
phospholipid example
bilayer of cell membrane
Steroid examples
cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen
hydrogen bond
Attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative atom.
polar covalent bond
bond between the oxygen atom and the two hydrogen atoms of a signle water molecule; A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
Electrons
Negatively charged particles
covalent bond
A chemical bond formed when two atoms share electrons
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
high specific heat capacity
A property of water. Water can absorb lots of heat before changing temperature
Hydrophilic
water loving
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
monosachharides
monomer of carbohydrates; linked together by condensation reactions to form disaccharides
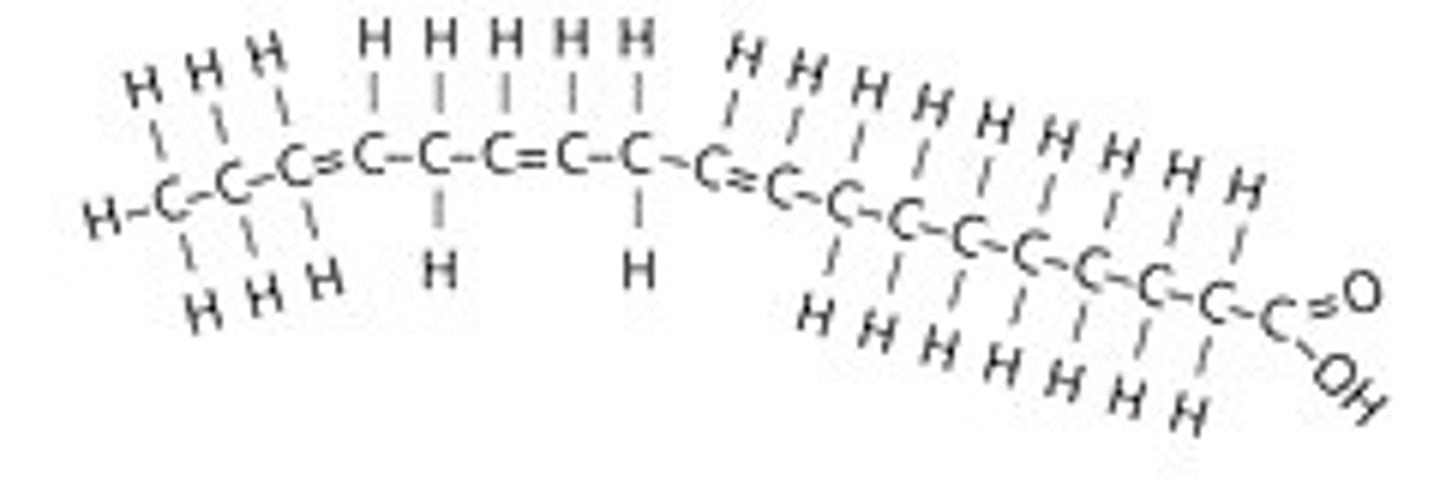
Types of fatty acids
saturated, monounsaturated, polyunsaturated
Triglycerides
formed by condensation from three fatty acids and one glycerol
condensation reaction
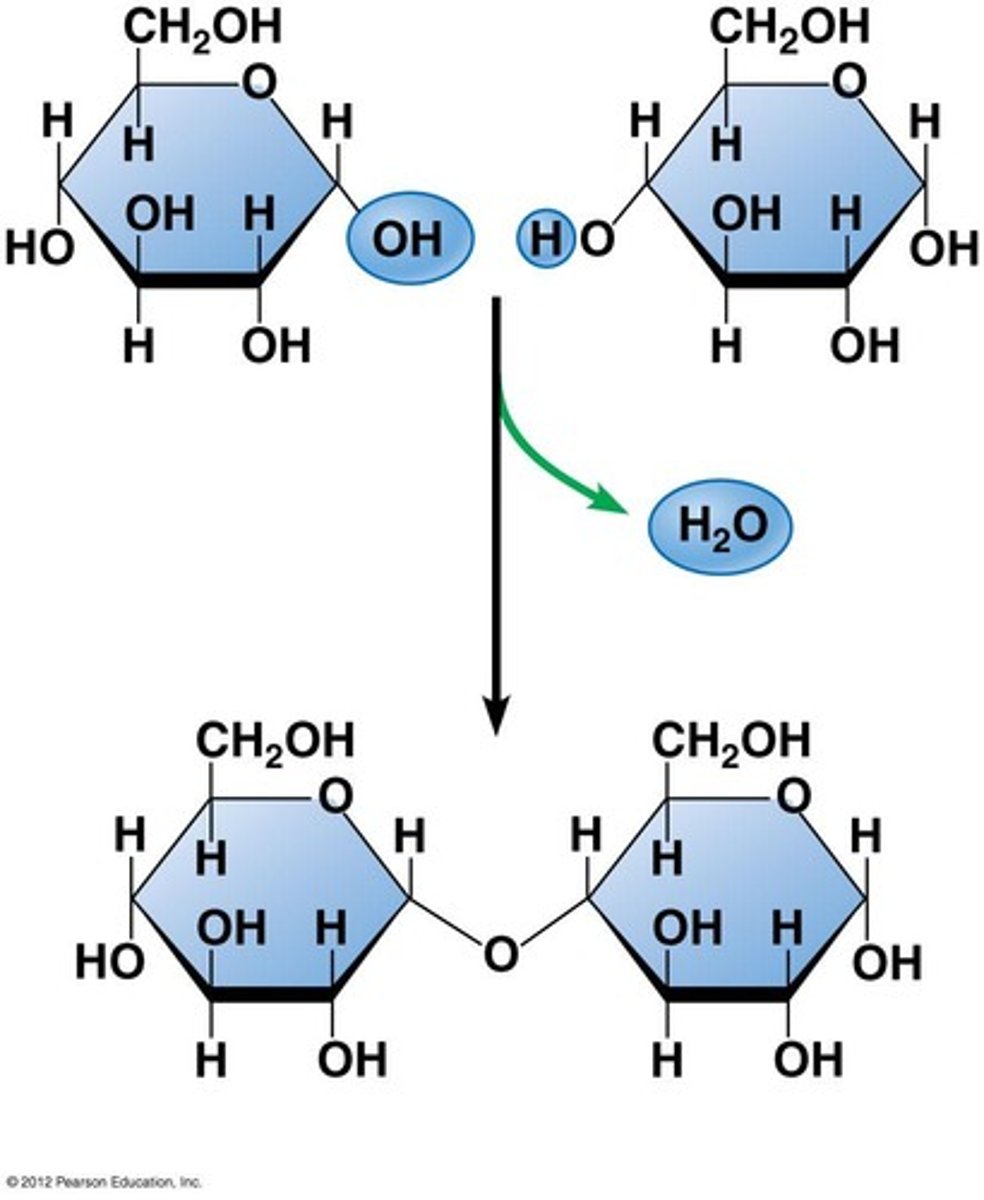
Cellulose
major component of cell walls, helps give rigidity support to roots, stems, and leaves
Starch
A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of glucose; usually located in roots
Glycogen
Storage form of glucose in animals; usually located in liver and muscle tissue
saturated fatty acid
carbons are saturated with hydrogen atoms; generally solid at room temperature; no double bonds
monounstaturated fatty acids
one double bond exists in the chain of a hydrocarbon; cause one "kink" or bend in the molecule
polyunsaturated fatty acid
two or more double bonds in the carbon chain; usually liquid at room temperature
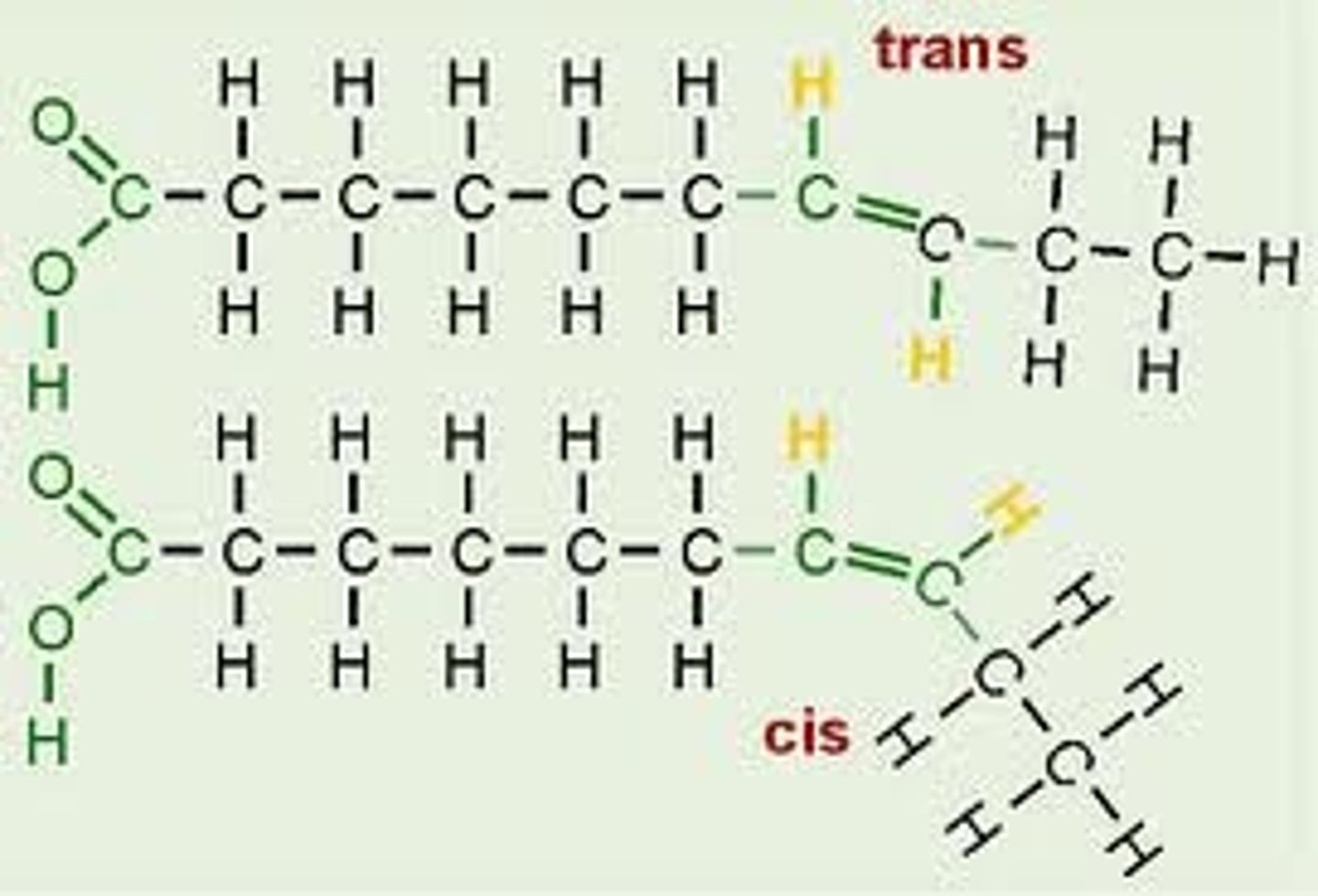
cis fatty acids
Two covalent single C-C bonds angle in the same direction adjacent to the C=C double bond
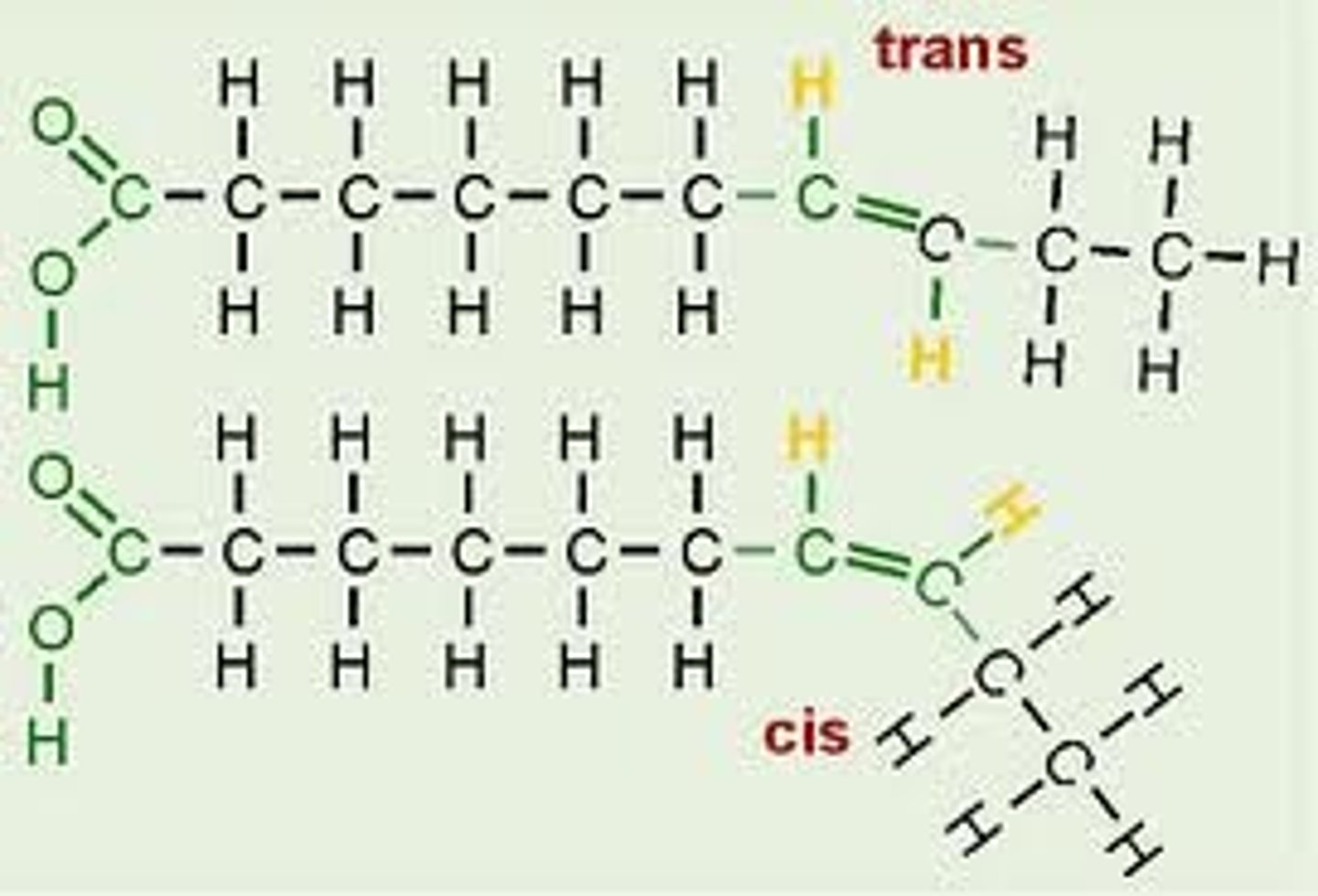
trans fatty acids
fatty acids with hydrogens on opposite sides of the double bond
amino acids
a simple organic compound containing both a carboxyl (—COOH) and an amino (—NH2) group; linked together by condensation to form polypeptides.
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis; amino acid linkage
peptide bond
The chemical bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid
Enzymes
proteins that act as biological catalysts; speed up chemical reactions that take place in cells by lowering the activation energy; act on specific substrates
Denature
destroy the characteristic properties of (a protein or other biological macromolecule) by heat, acidity, or other effects that disrupt its molecular conformation.
Organelle
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
Compartmentalization
Membrane-bound organelles allow different parts of the cell to perform different functions at the same time
stem cells
unspecialized cells that are able to renew themselves for long periods of time by cell division
Pluripotent
Cells that are capable of developing into most, but not all, of the body's cell types
totipotent
Stem cells with the potential to differentiate into any type of cell.
Multipotent
cell with limited potential to develop into many types of differentiated cells
stem cell niche
an area of a tissue that provides a specific microenvironment, in which stem cells are present in an undifferentiated and self-renewable state.
surface area to volume ratio
a variable that decreases as cells grow, so that it sets a limit to the size of cells.
Phopholipids
A glycerol linked to a phosphate group and to two fatty acids
amphipathic
having both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region
Differentiation
process in which cells become specialized in structure and function
Hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than another solution.
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
Isotonic
Having the same solute concentration as another solution.
Aquaporins
water channel proteins
Cholesterol
A steroid present in the plasma membranes of animal cells. It affects membrane fluidity.
Endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
Exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material
active transport
membrane transport in which the movement of solute molecules or ions across a membrane is coupled directly to an exergonic chemical reaction, most commonly the hydrolysis of ATP
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
integral proteins
Proteins that span the membrane.
peripheral proteins
The proteins of a membrane that are not embedded in the lipid bilayer; they are appendages loosely bound to the surface of the membrane.
Glycoproteins
Membrane carbohydrates that are covalently bonded to proteins.
Glycolipids
Membrane lipids with one or more covalently attached carbohydrates
turgor pressure
The pressure that water molecules exert against the cell wall
cell lysis
rupturing membranes of cells
Plasmolysis
Collapse of a walled cell's cytoplasm due to a lack of water
normal saline
A general phrase referring to a sterile solution of sodium chloride (NaCl, more commonly known as table salt) in water, but is only sterile when it is to be placed parenterally (such as intravenously); otherwise, a saline solution is a salt water solution.
contractile vacuole
The cell structure that collects extra water from the cytoplasm and then expels it from the cell
Solvation
The process of surrounding solute particles with solvent particles to form a solution
dilute
Less concentrated liquid
concentration gradient
A difference in the concentration of a substance across a distance.
dynamic equilibrium
Result of diffusion where there is continuous movement of particles but no overall change in concentration
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
Solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Solution
A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances
fluid mosaic model
model that describes the arrangement and movement of the molecules that make up a cell membrane