Honors Chemistry - Unit 5: Gas Laws
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
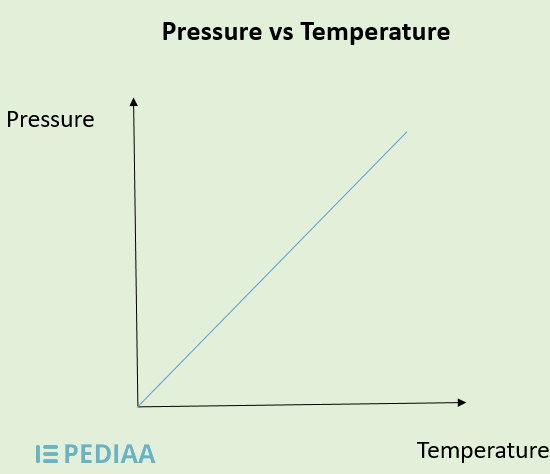
Relationship of pressure and temperature
Direct - Higher T = higher P because higher T = more kinetic energy, more particle velocity, more # and F of particle collisions, then more P.
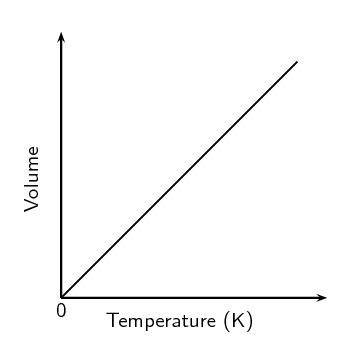
Relationship of temperature and volume
Direct - More temperature = more volume because of more kinetic energy, more particle velocity, more particle spacing, and more volume.
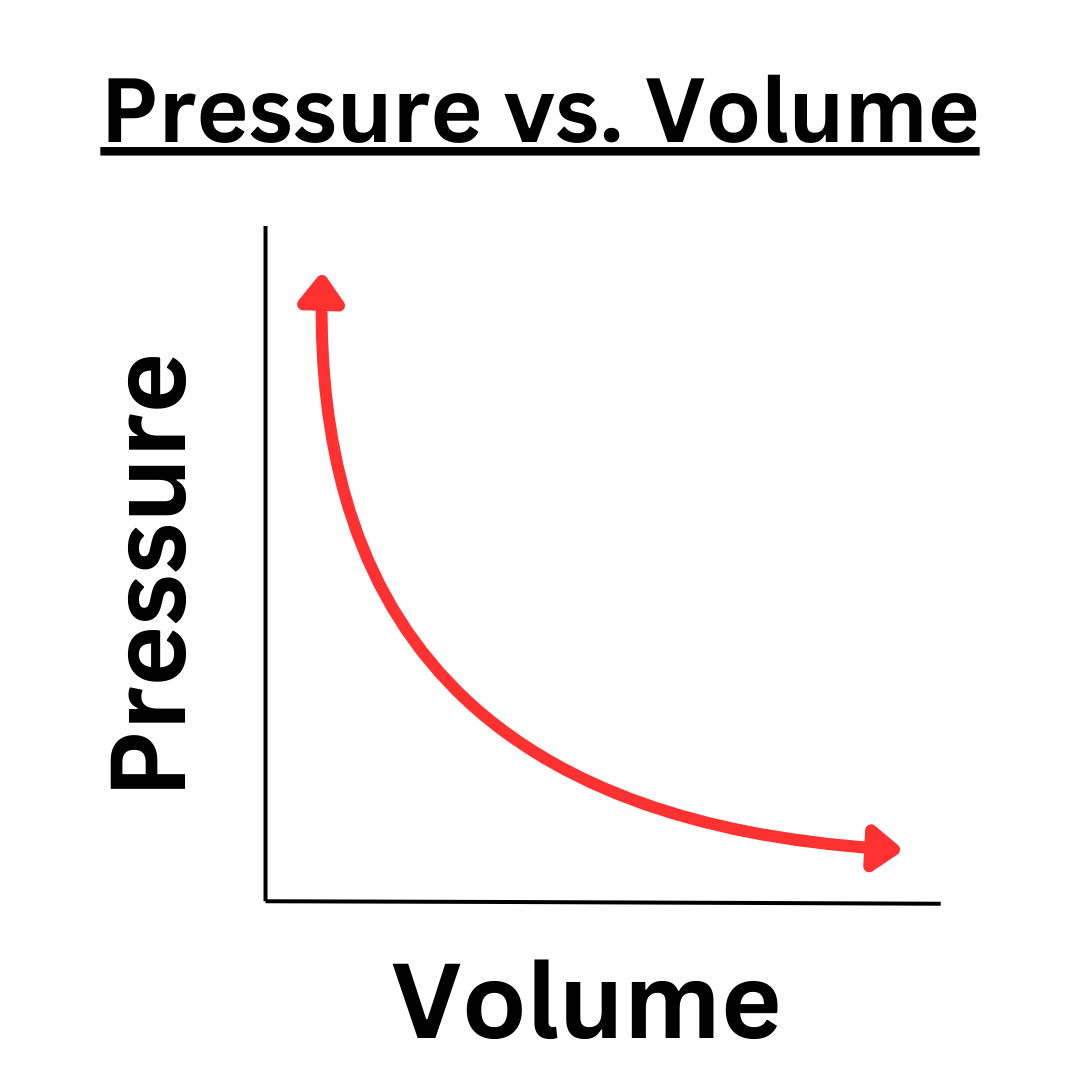
Relationship between volume and pressure
Inverse - higher volume = less pressure because of more particle spacing, less # and F of particle collisions, less particle velocity, and less pressure.
Relationship between volume and number of particles
Direct - more n = more volume (in a nonrigid system) because more particles = more # and F of particle collisions, = more particle spacing = more V.
Relationship between pressure and number of particles
Direct - more n = more P because more n has = V, less particle spacing, more # and F of particle collisions, so more P.
Relationship between number of particles and temperature
Inverse - More T = less n because more T = more kinetic energy, more particle velocity, more # and F of particle collisions, and more particle spacing. Bigger P means particles can push out of nonrigid system.
Definition of pressure (P)
Force/particle collisions in a certain area - measured in psi/atm/kPa - shown in particle diagrams by bent arrows (shows particle collisions).
Definition of volume (V)
Space that particles take up - measured by mL/cm*3 - shown in particle diagrams by by the size of the box/system.
Definition of temperature (T)
Average kinetic energy of a substance - measured in °C or K - shown in particle diagrams by the length of the arrows.
Definition of number of particles (n)
Number of particles in a system - measured in g - shown in particle diagrams by the little circles/symbols (mass DOES NOT = n anymore)
What sucks particles out of a system?
A vacuum
What adds particles into a system?
A pump
Does particle mass affect gas behavior?
NO, lighter particles move faster but have the same temperature as heavier particles.
Particle level definition for higher T = higher P in a syringe
Nonrigid system - higher T = higher kinetic energy, higher particle velocity, more # and F of particle collisions, more particle spacing, more V, less density, higher P. OR F/a = more F with more particle collisions and more area with more volume. This is a proportionate ratio.
Explanation of how a straw works at the particle level
Mouth - Higher T in mouth = higher kinetic energy, higher particle velocity, more particle spacing, more # and F of particle collisions, and more P in mouth. Straw - more volume, more particle spacing, less # and F of particle collisions, and less P in straw. So, the air pushes the drink into the straw because the P of air > P of straw and to equalize P of air and drink.

Can you do gas ratios while using a temperature in °C?
NO, you have to convert to kelvin. You take your T in °C and add 273.15 to attain your T value in kelvin.
Particle level explanation of boiling
When P of liquid > P of air - Liquid to gas, more particle spacing, and more potential energy. P of water > P of air because higher T of water = higher kinetic energy, more # and F of particle collisions, more P of water. For P of air, higher V, more particle spacing, less # and F of particle collisions, and less P of air.
Particle level explanation of how a vacuum works
The fan inside the vacuum pushes particles outside. Less n means less particle spacing, less # and F of particle collisions, so P in < P out. More n outside means less particle spacing, more # and F of particle collisions, so equal P inside and outside.