Anatomy and Physiology Lab Practical
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
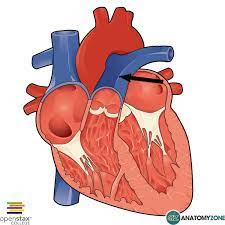
pulmonary trunk
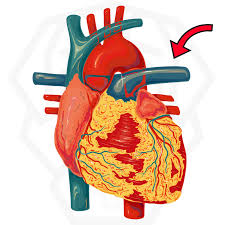
pulmonary artery
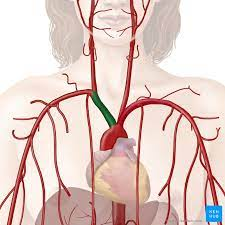
brachiocephalic artery
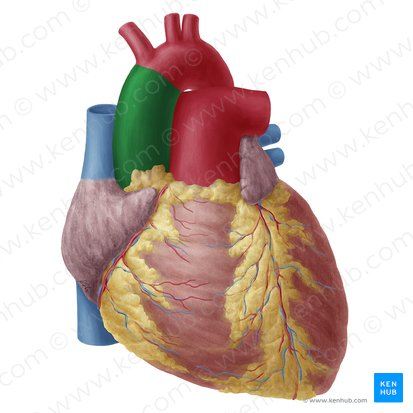
ascending aorta
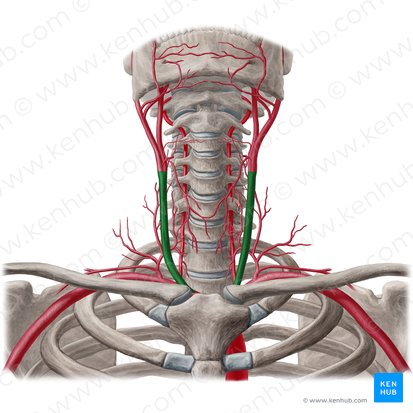
common carotid
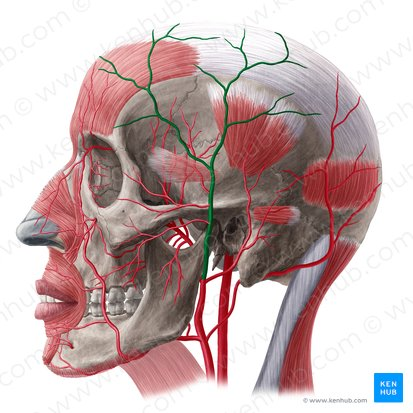
external carotid
internal carotid
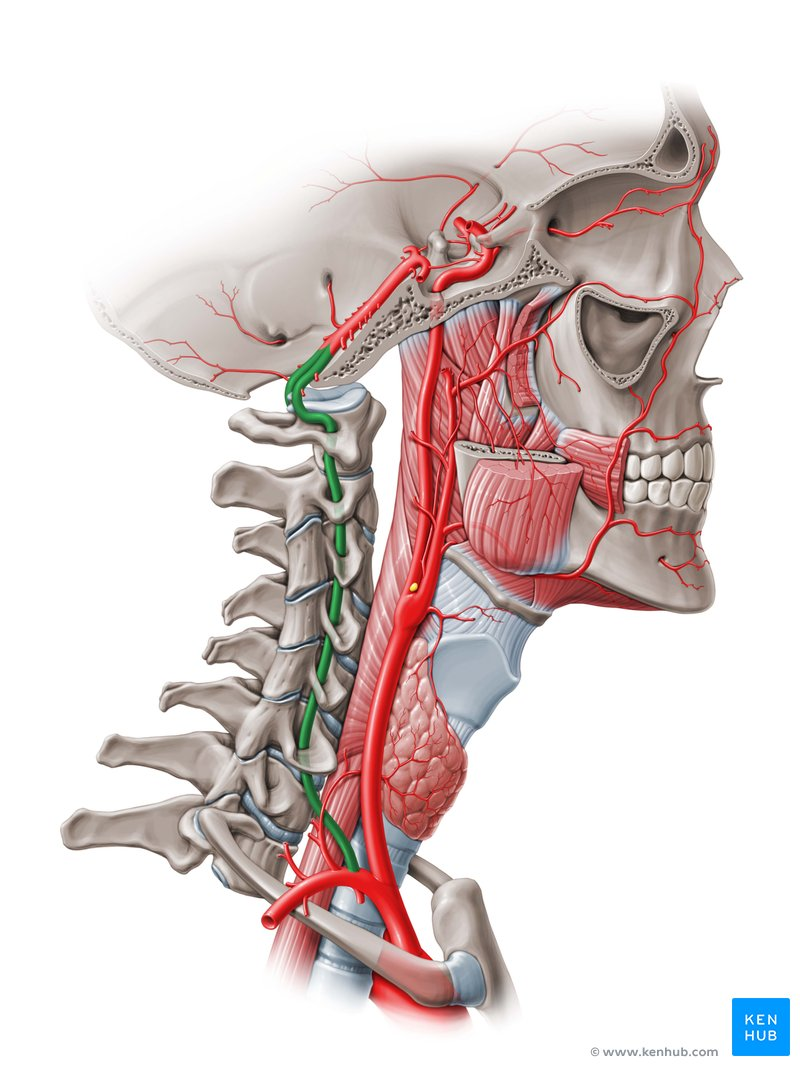
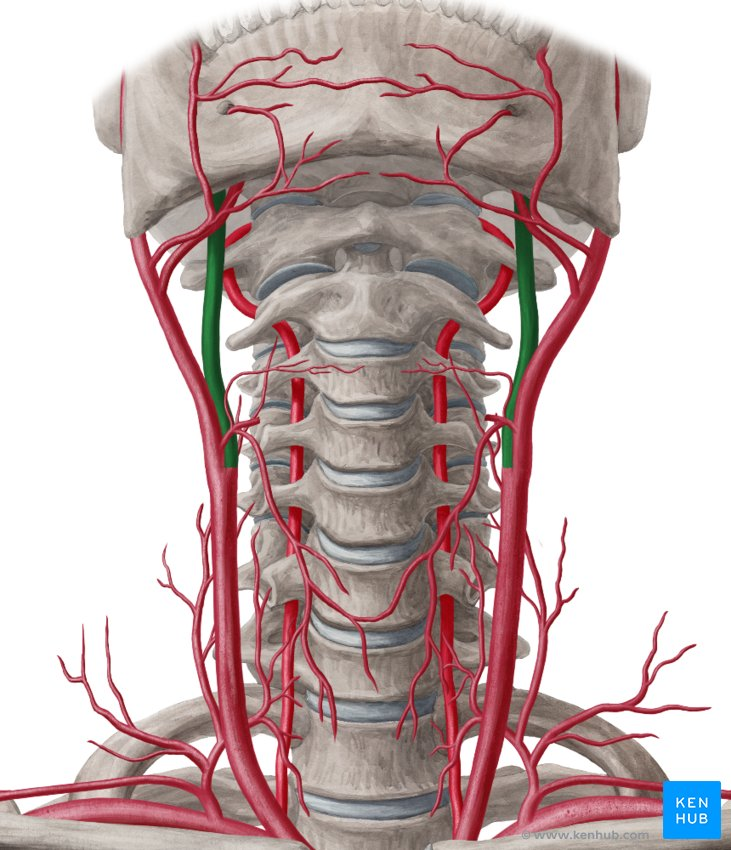
vertebral artery
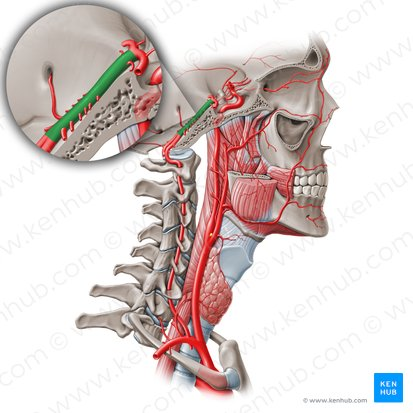
basilar artery
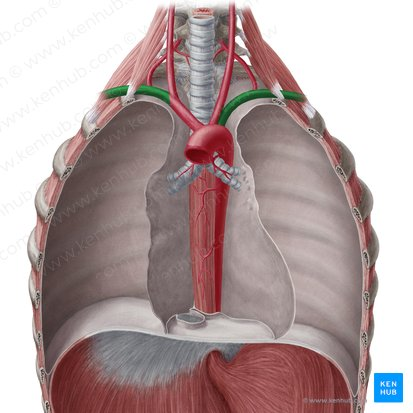
subclavian artery
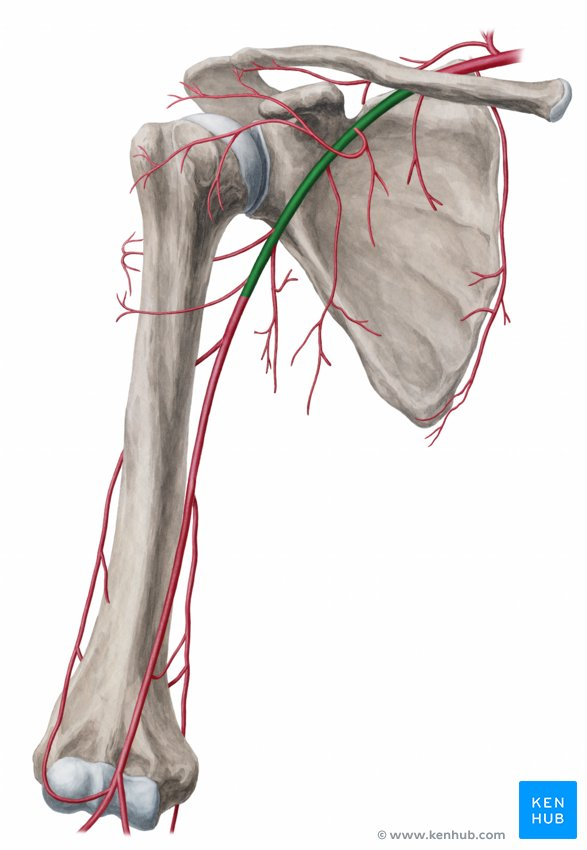
axillary artery
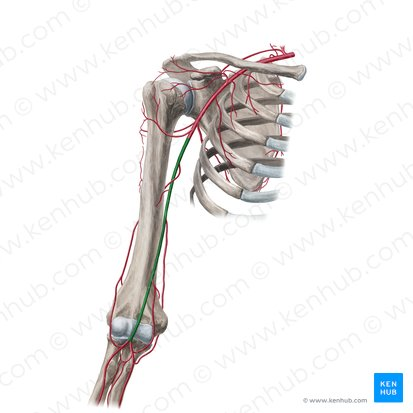
brachial artery
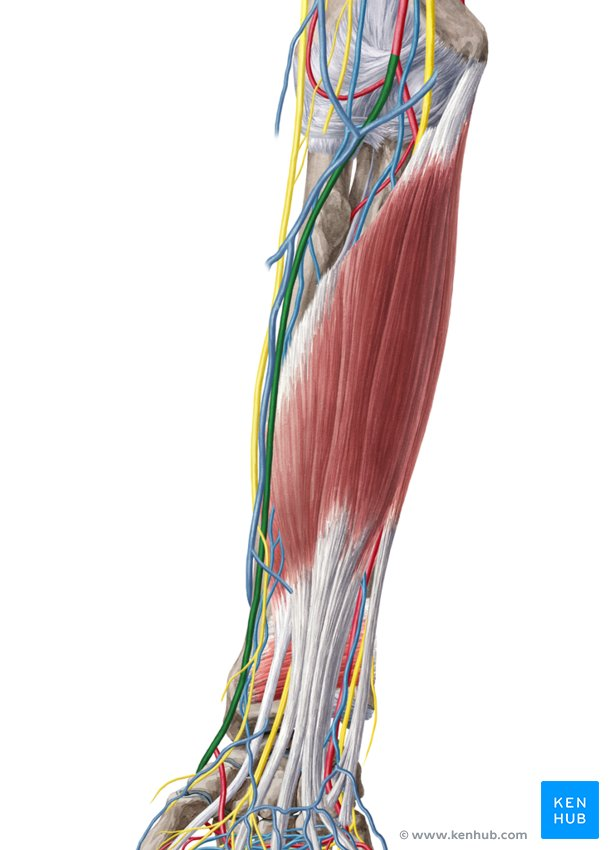
radial artery
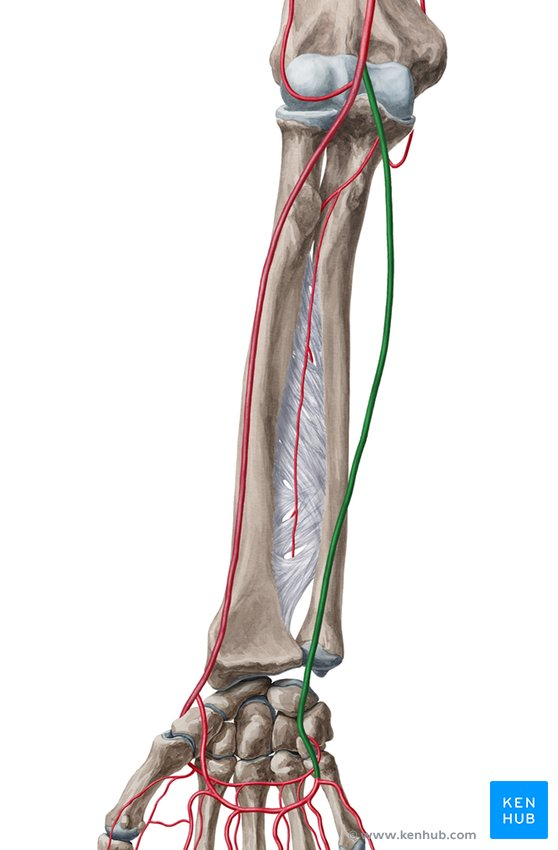
ulnar artery
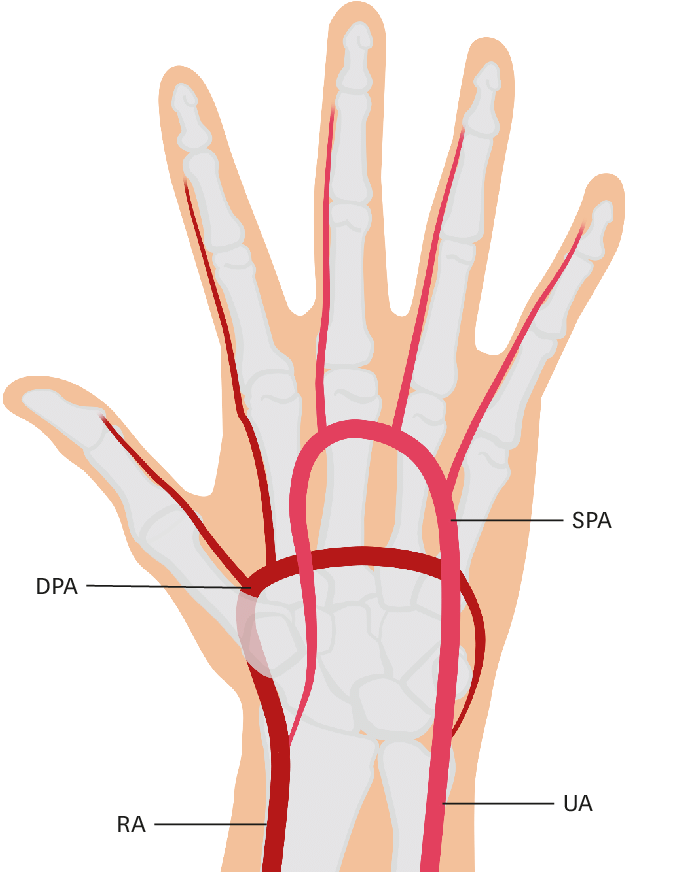
palmar arch artery
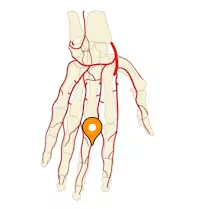
digital artery
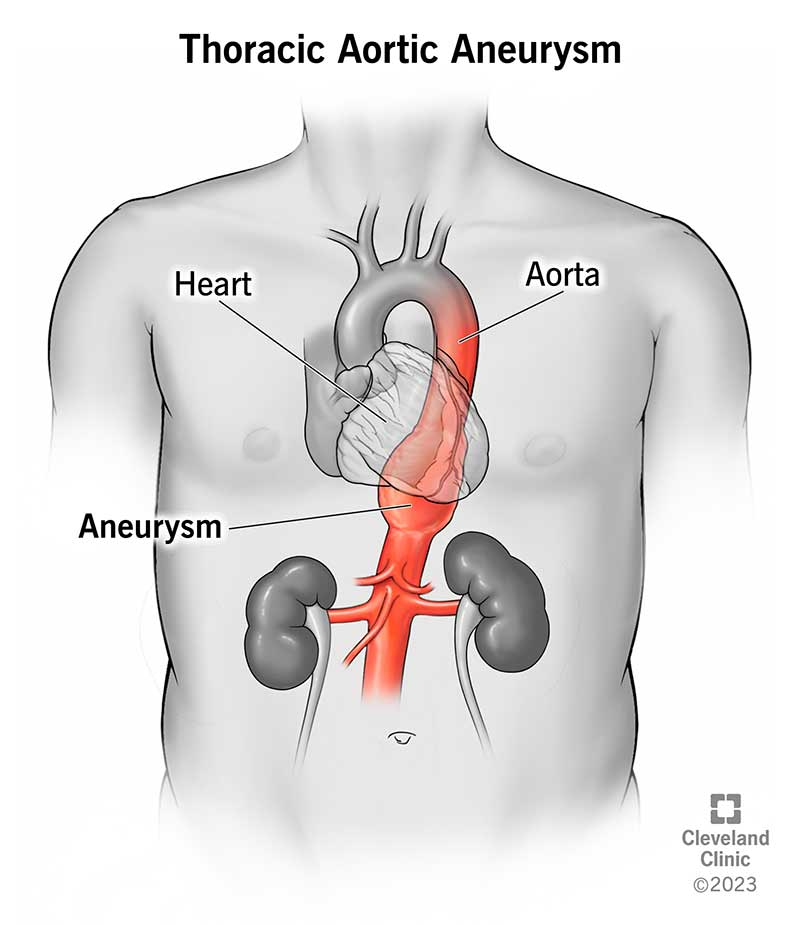
descending aorta
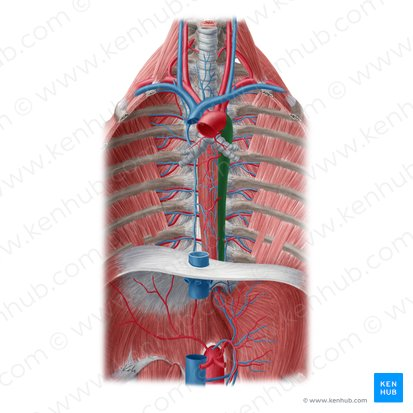
thoracic aorta
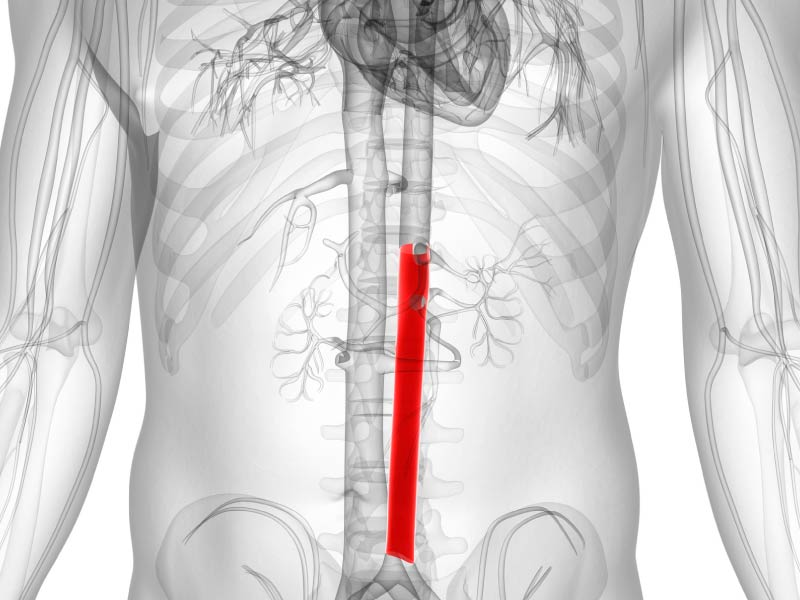
abdominal aorta
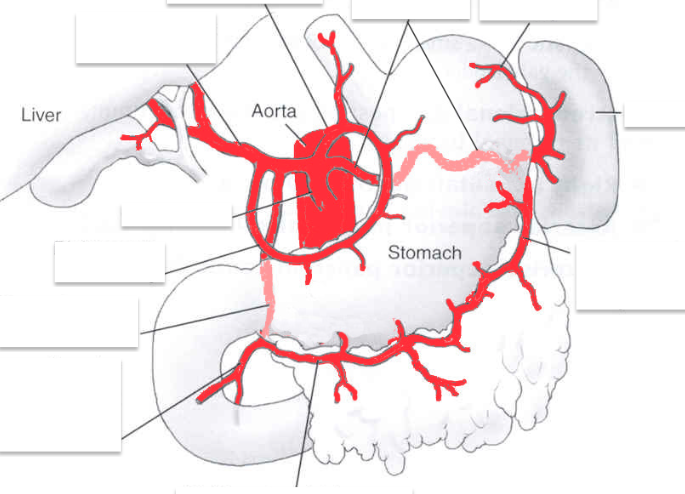
celiac trunk
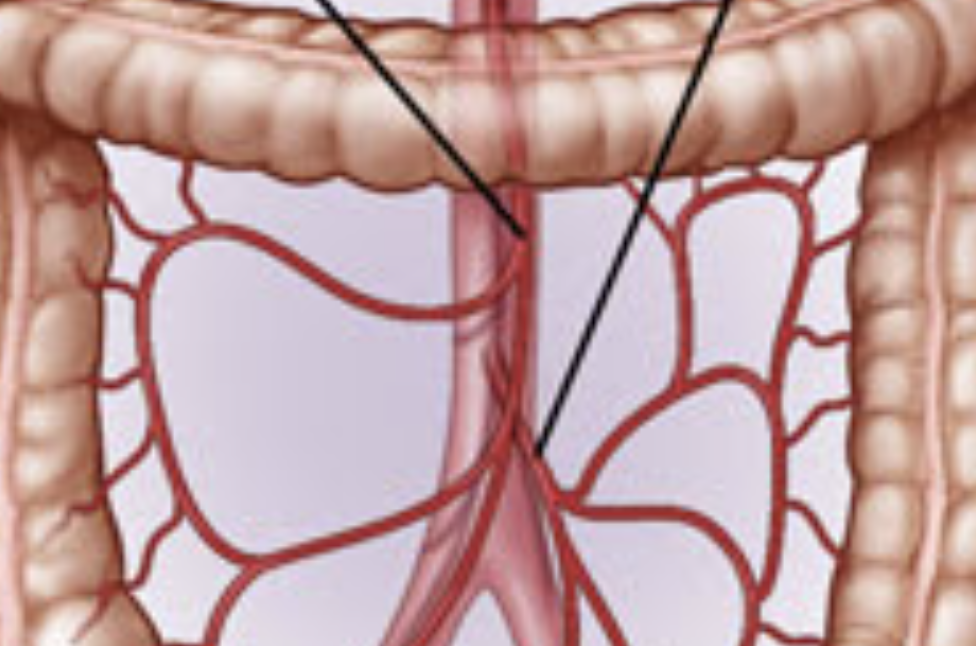
superior and inferior mesenteric artery
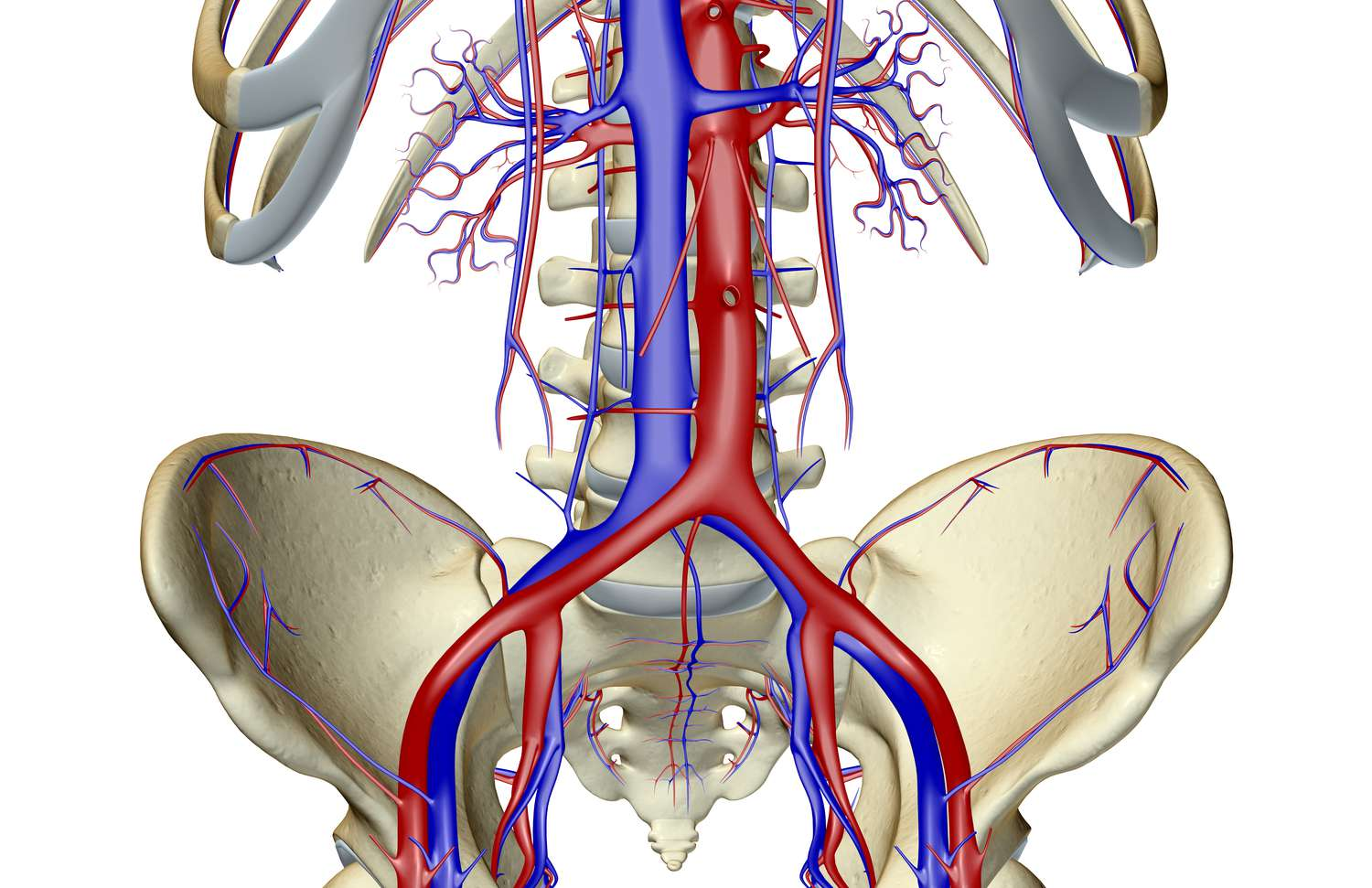
what is the red artery?
common iliac artery
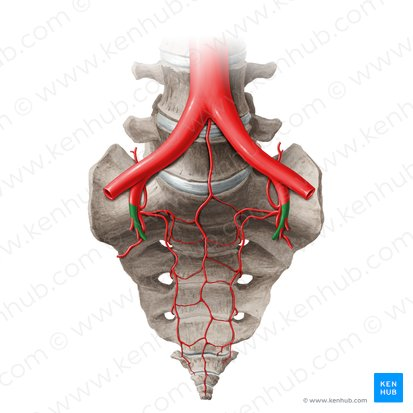
internal iliac artery
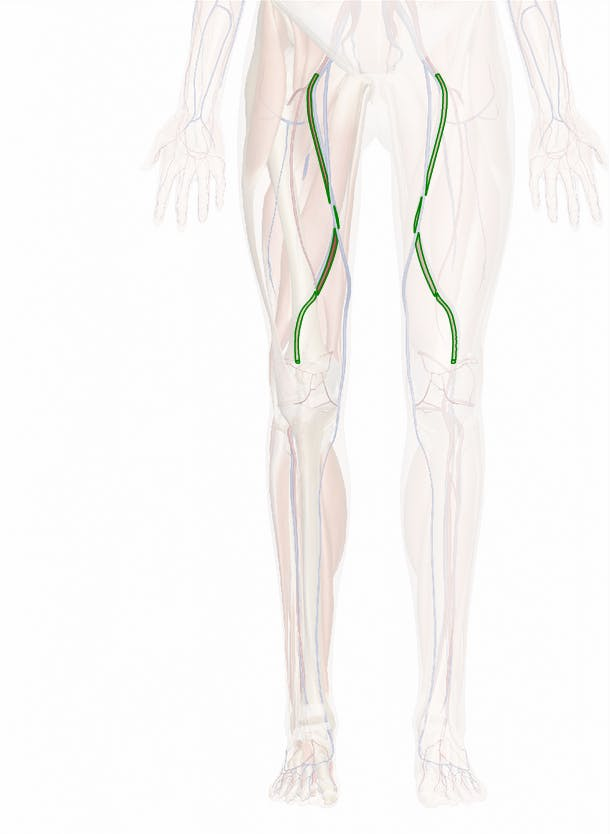
femoral artery
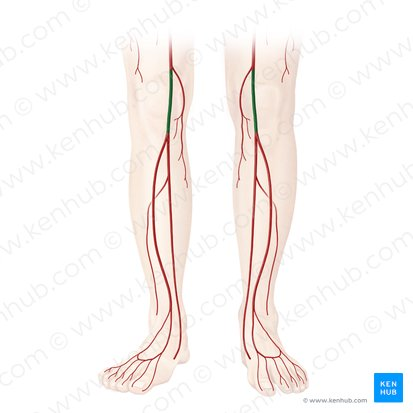
popliteal artery
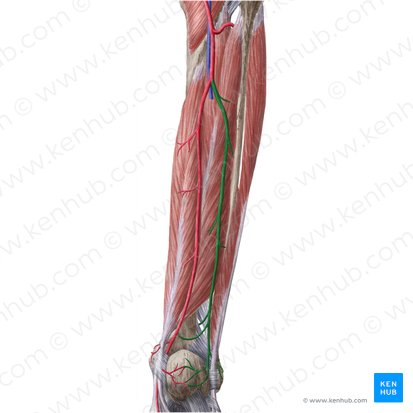
what is the artery?
fibular artery
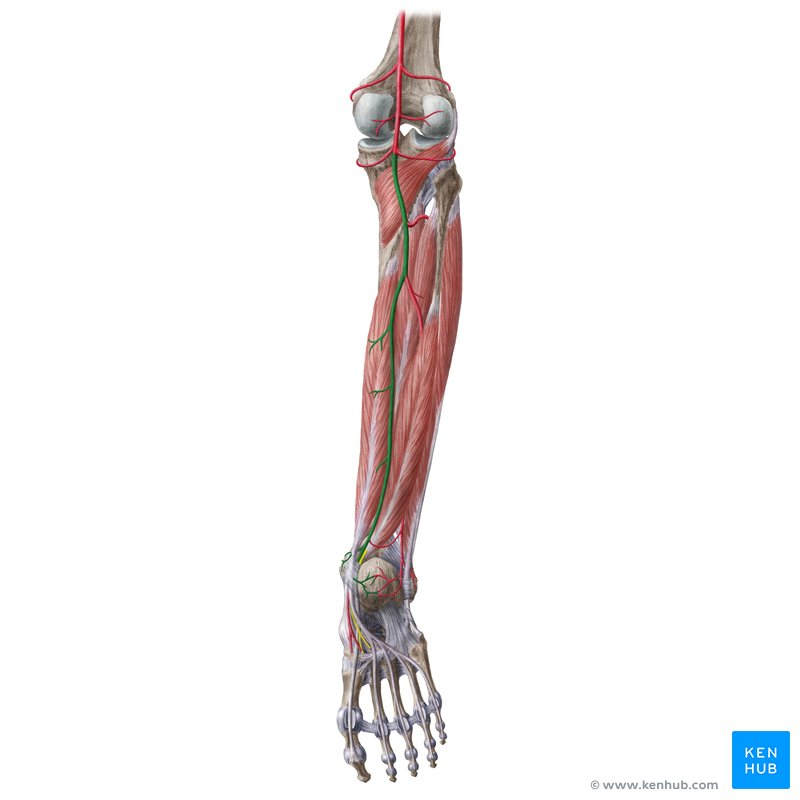
tibial artery
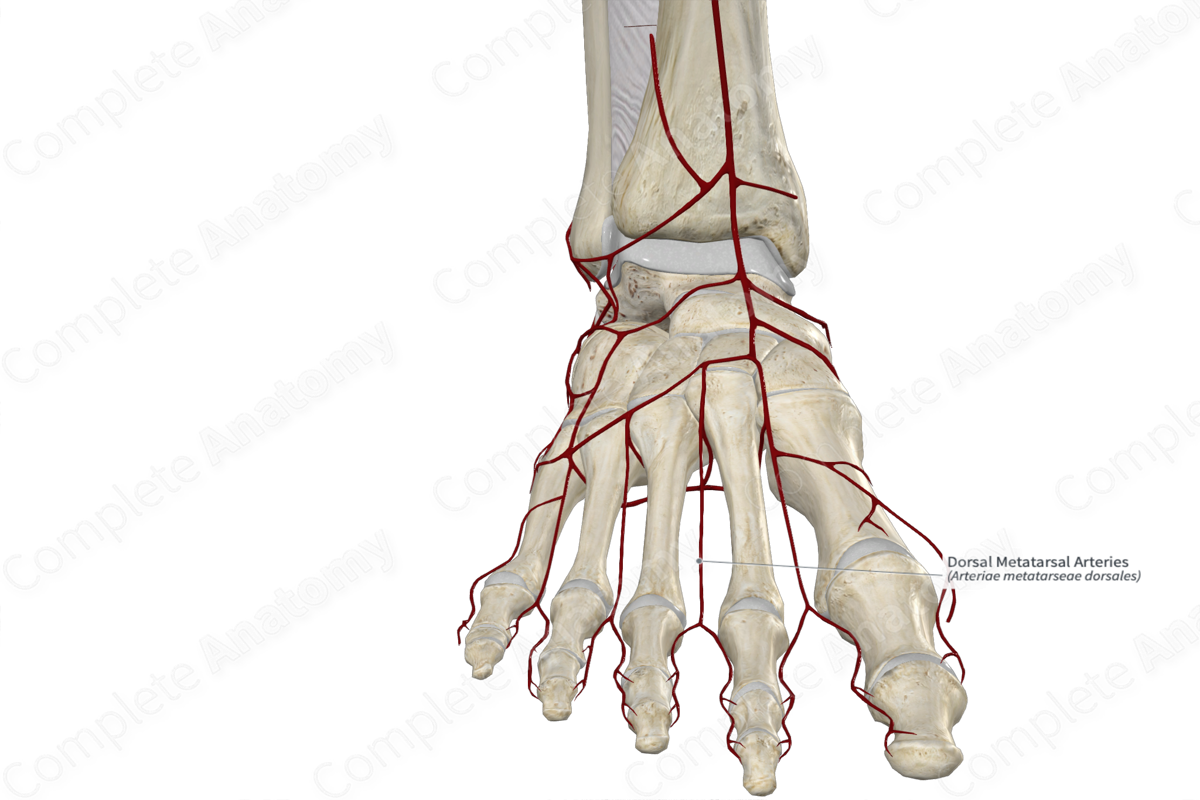
dorsal arch artery
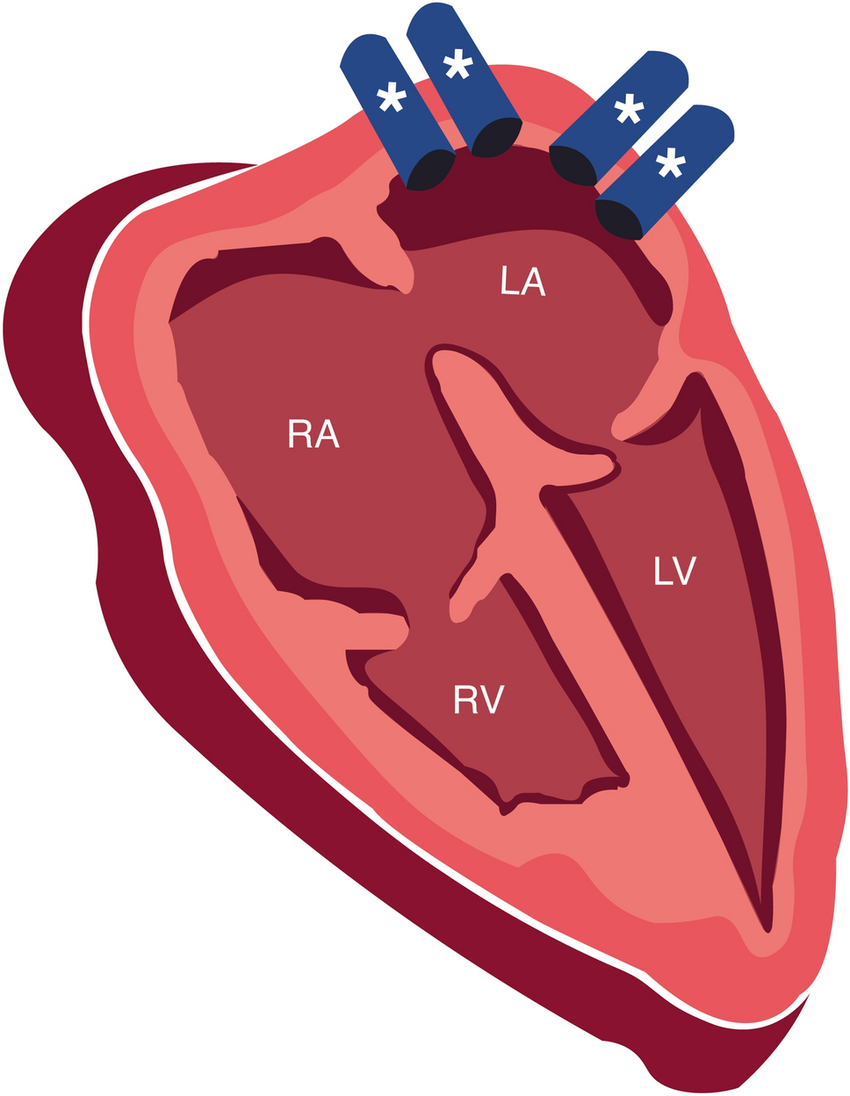
pulmonary veins
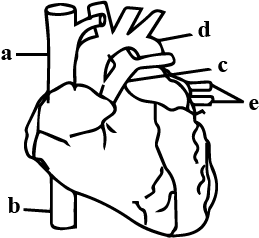
what are a and b?
superior and inferior vena cava
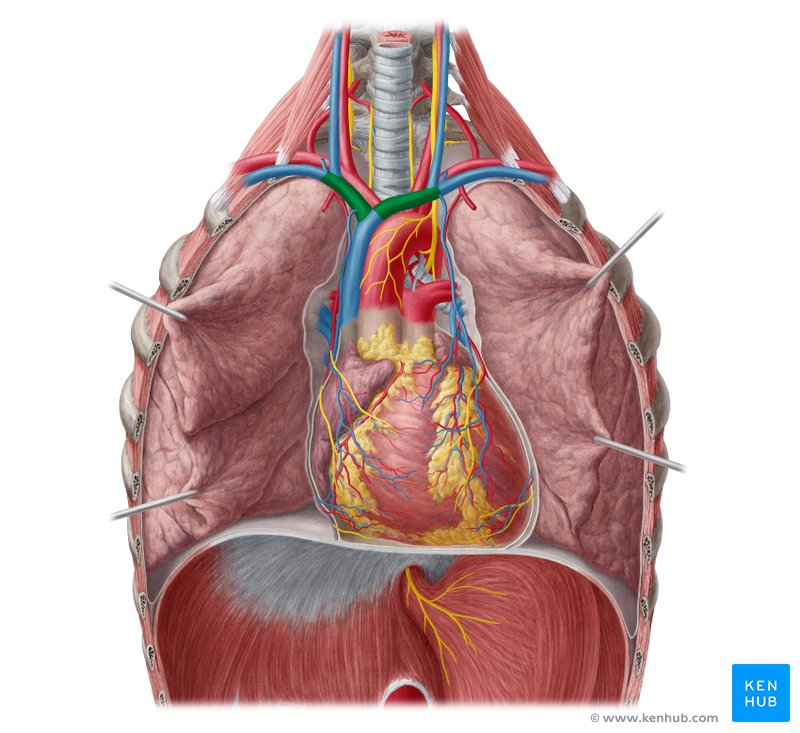
brachiocephalic vein
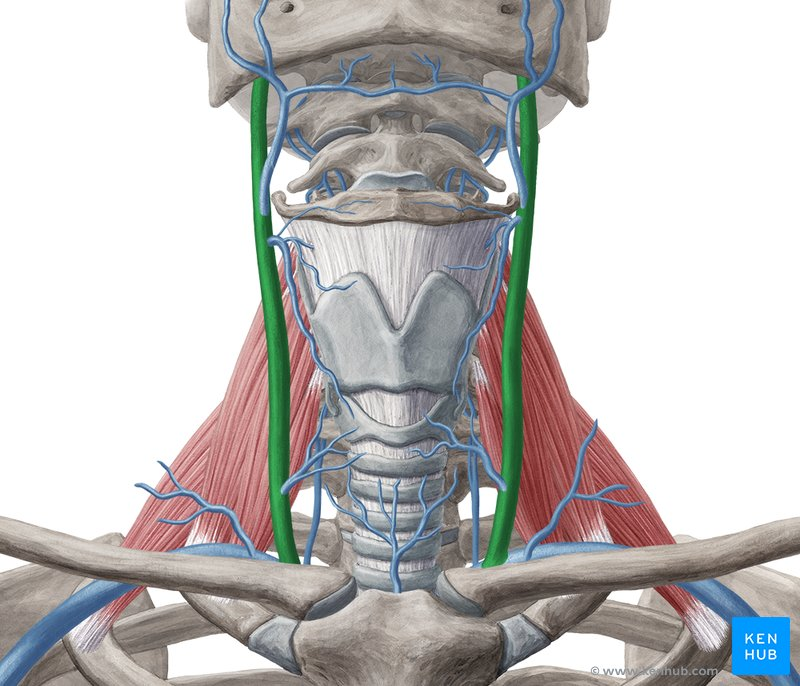
internal jugular vein
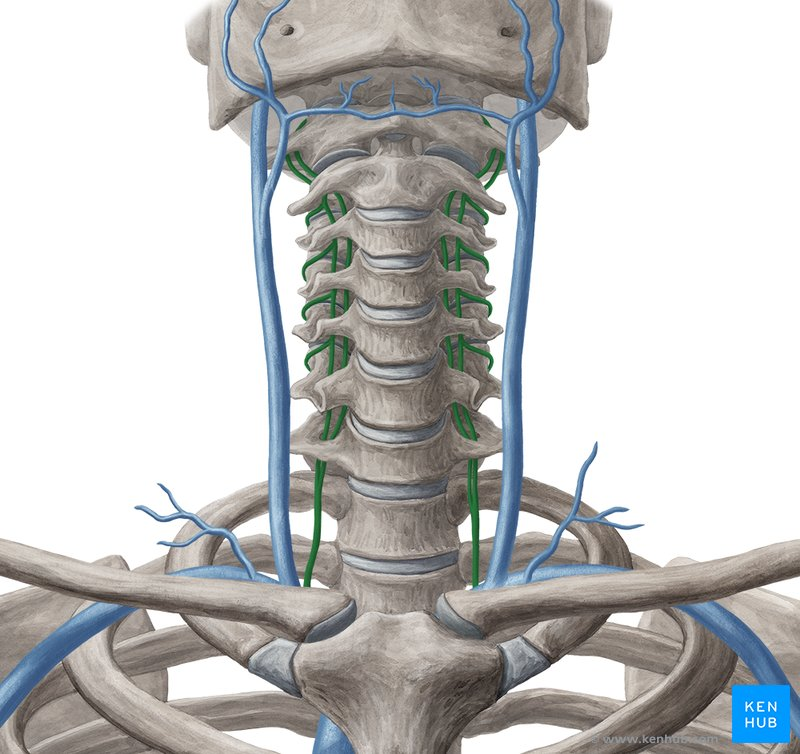
vertebral vein
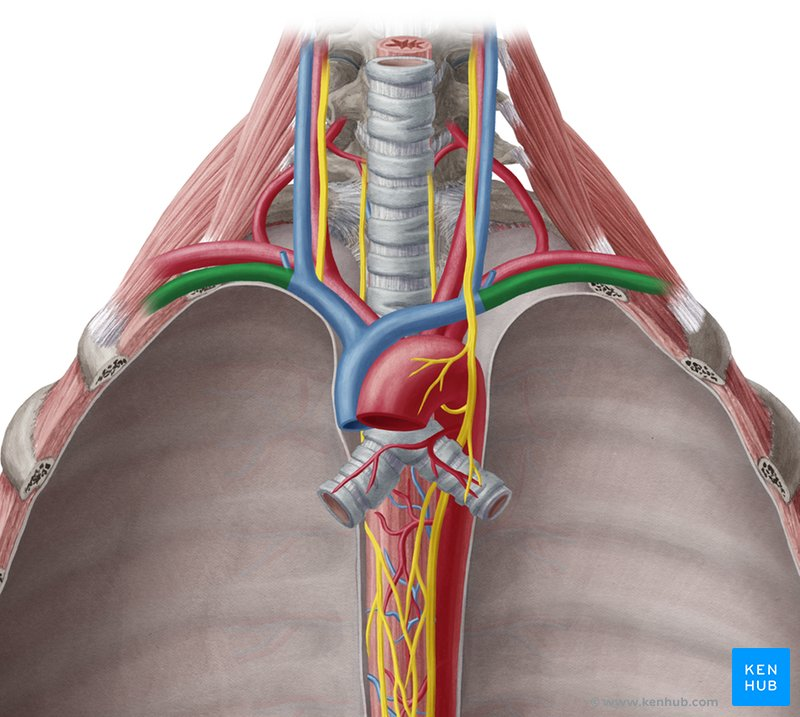
subclavian vein
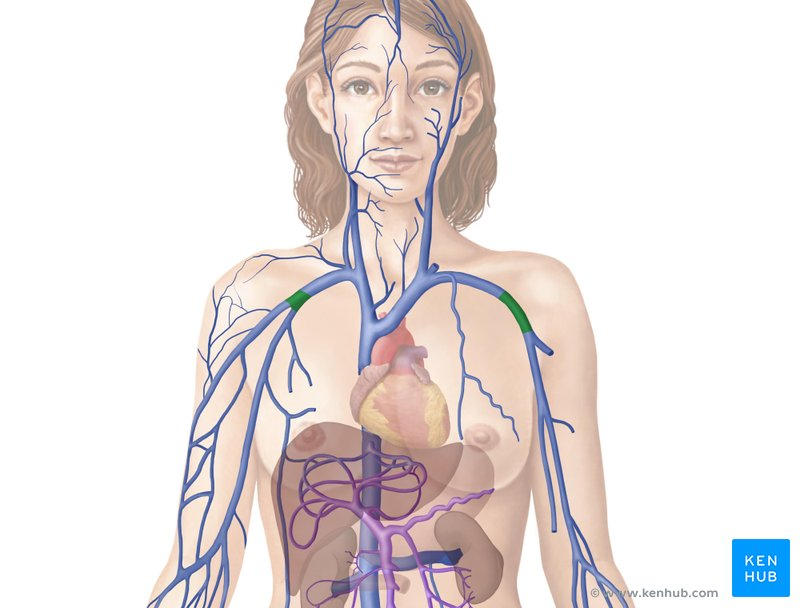
axillary vein
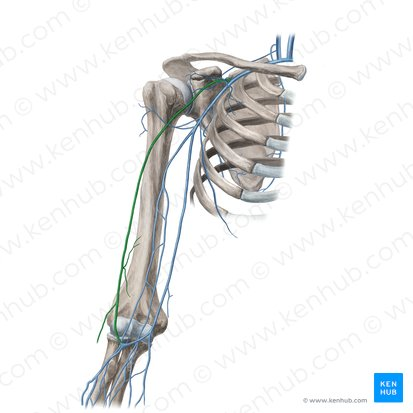
cephalic vein
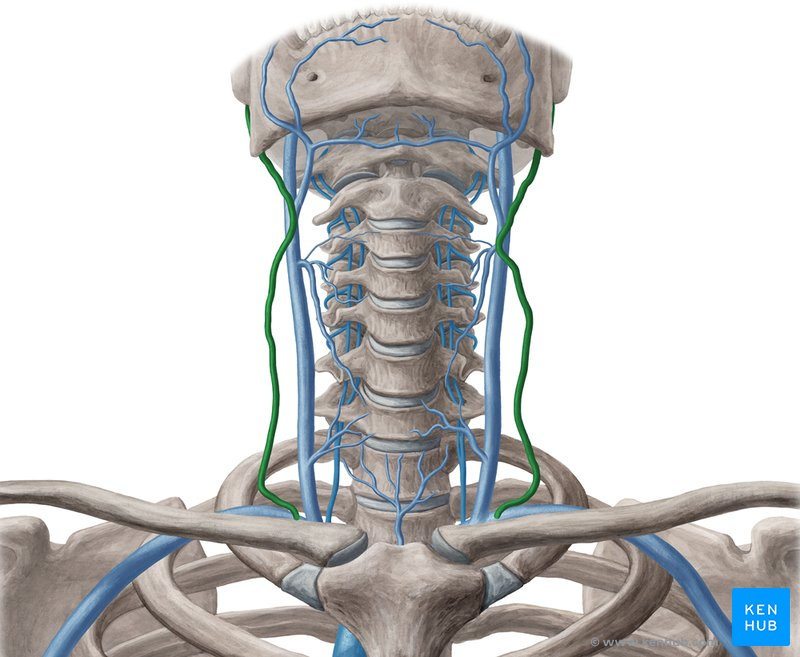
external jugular vein
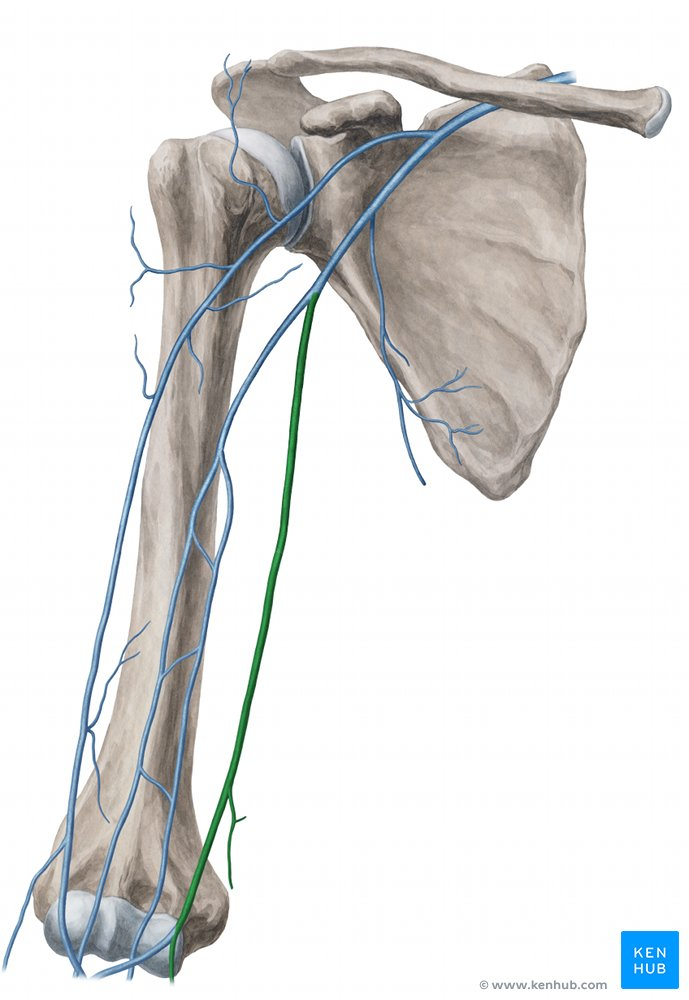
brachial vein
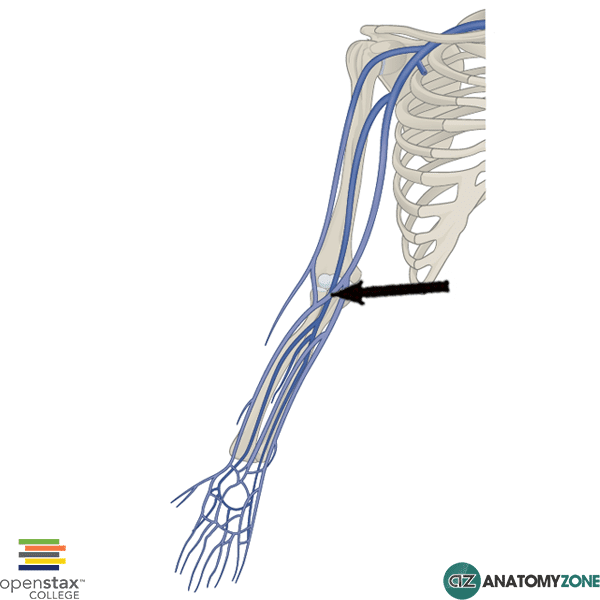
median cubital vein
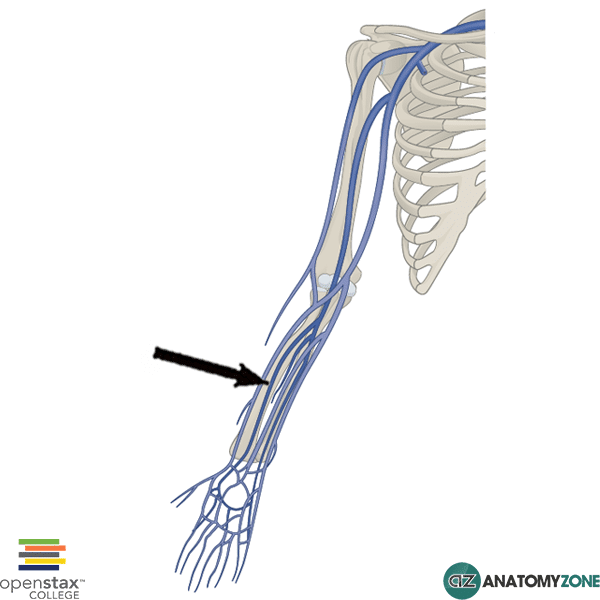
radial vein
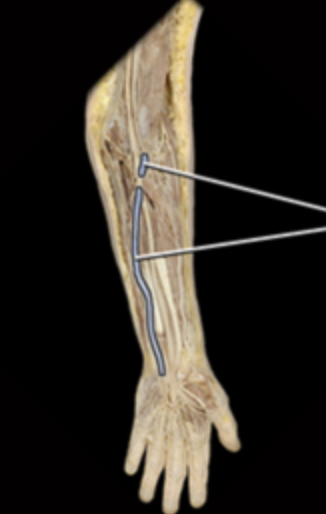
ulnar vein
palmar arch veins
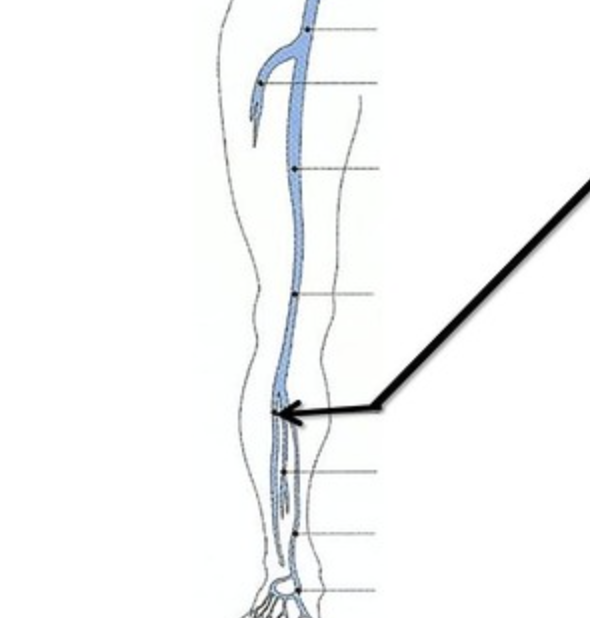
what is the blue vein?
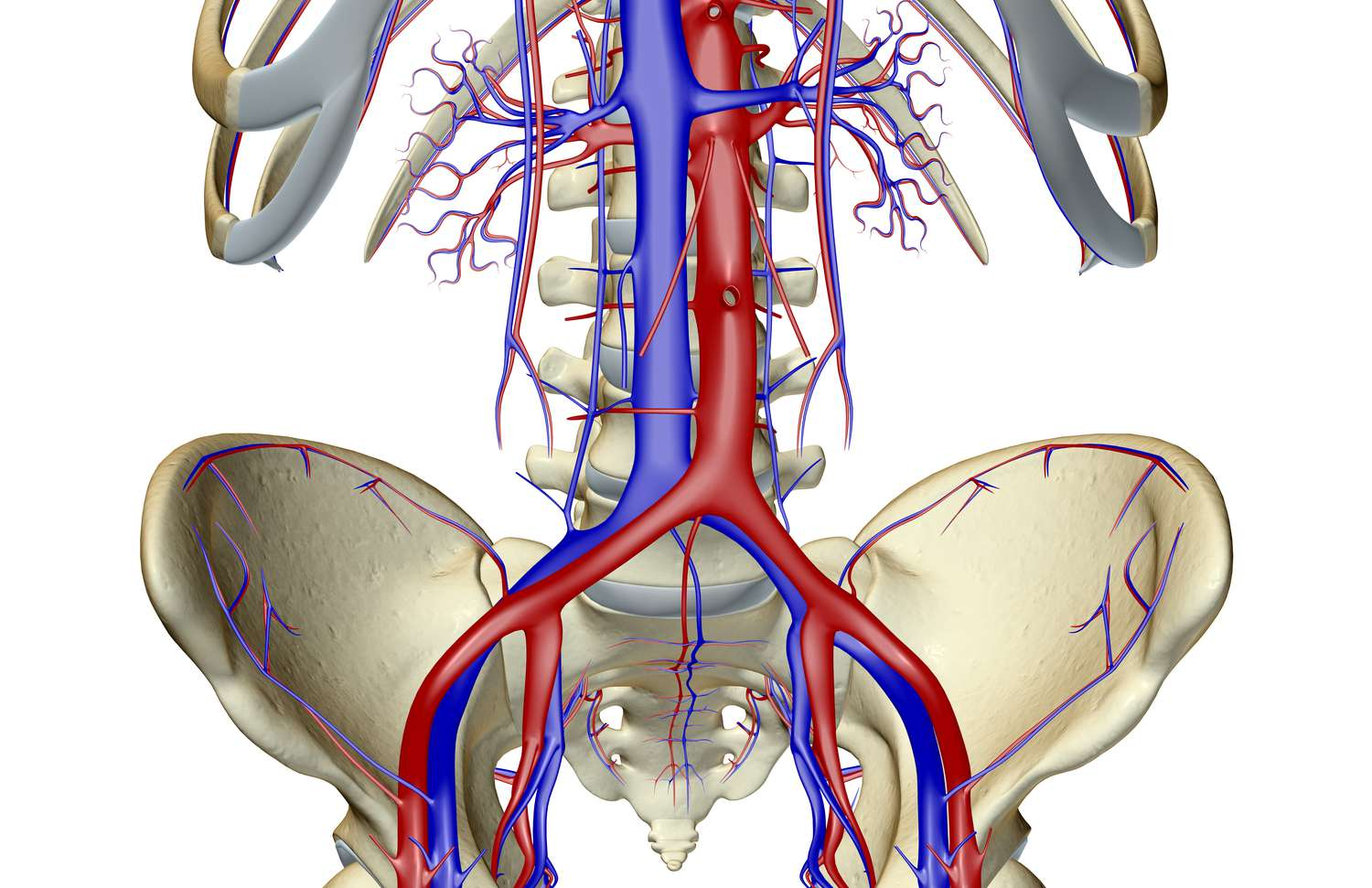
common iliac vein
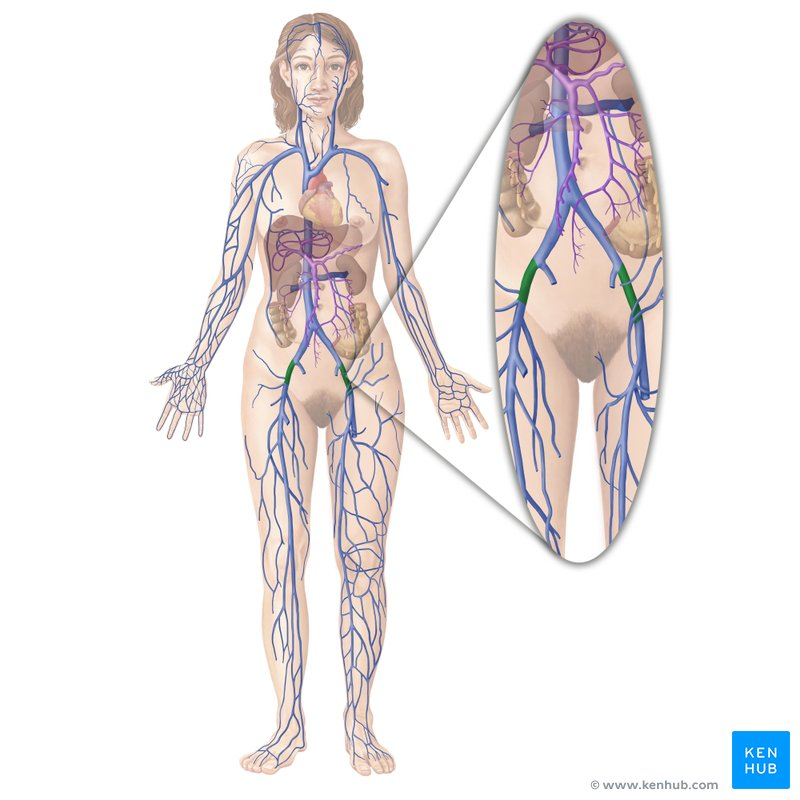
external iliac vein
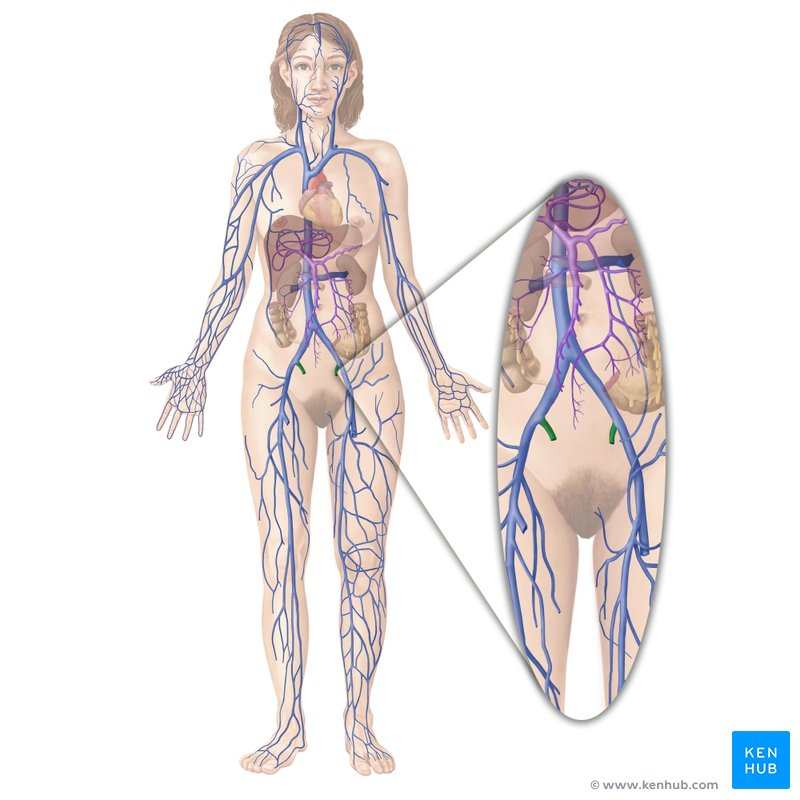
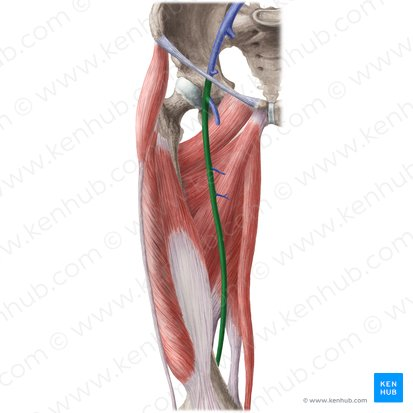
internal iliac vein
femoral vein
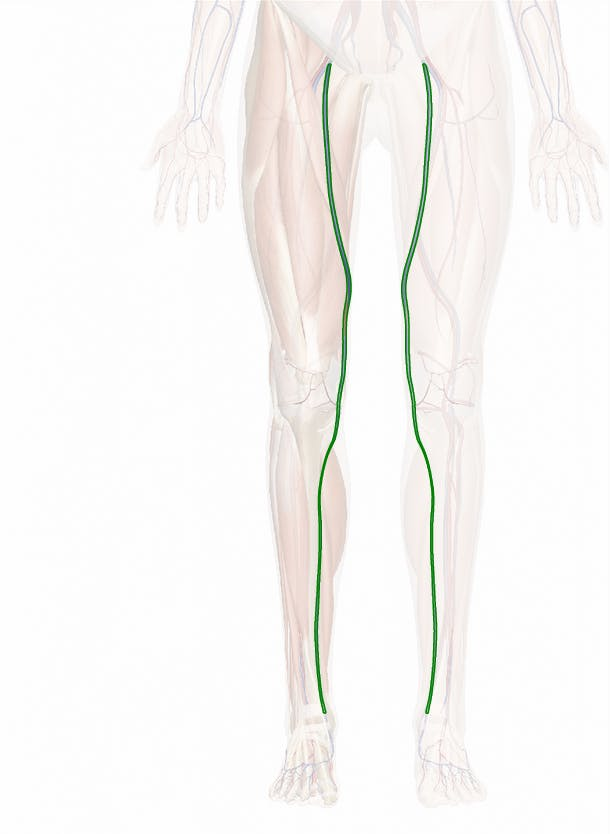
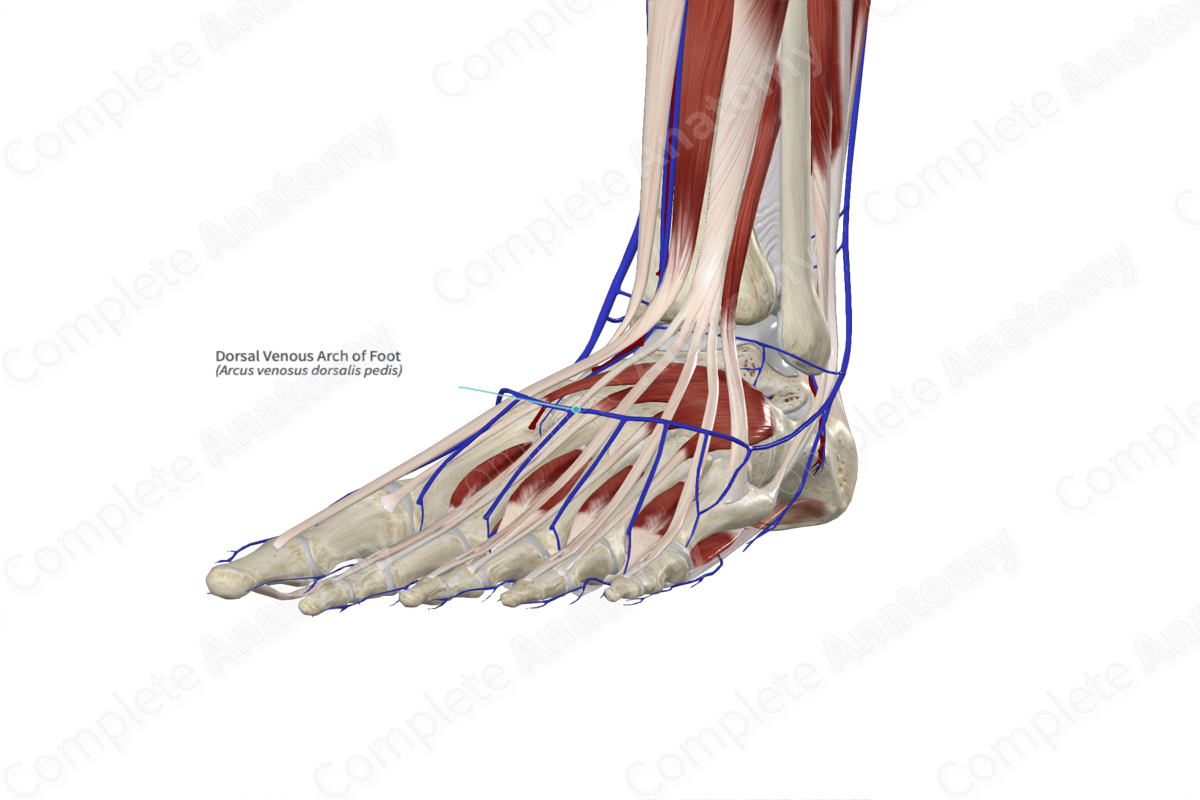
saphenous vein
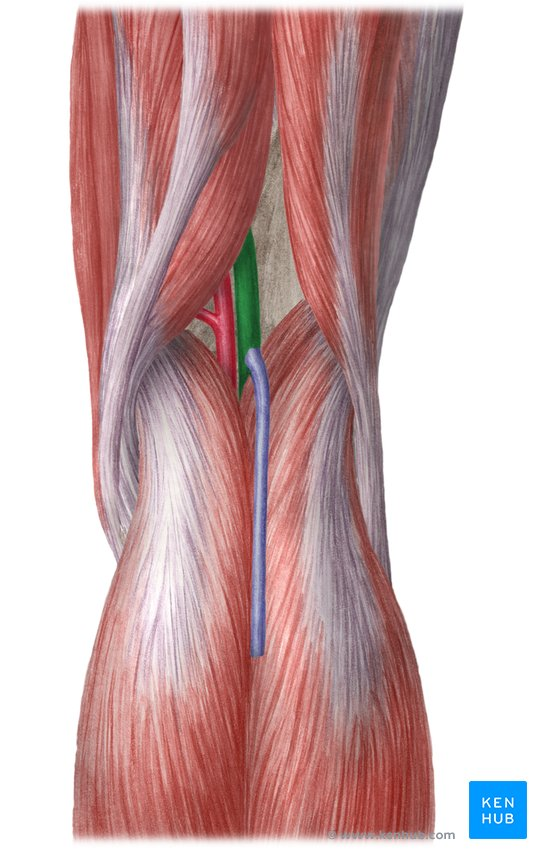
popliteal vein
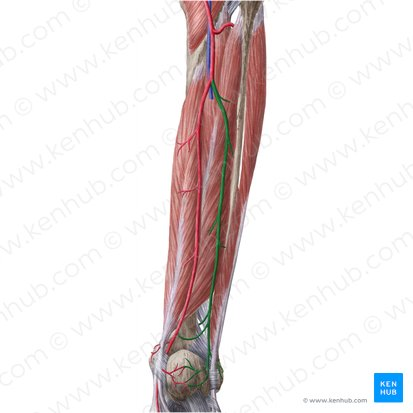
fibular vein
tibial vein
dorsal arch vein
which chambers contain oxygenated blood?
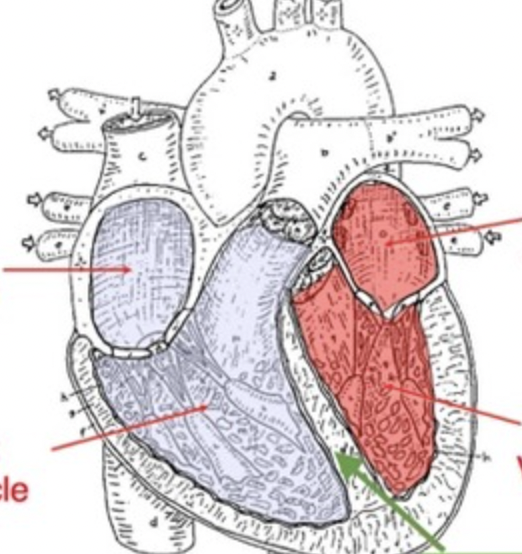
left atrium
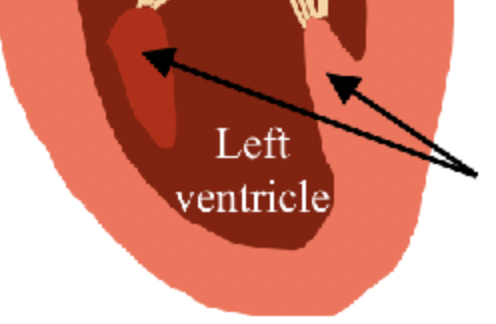
left ventricle
which chambers contain deoxygenated blood?
right atrium
right ventricle
what is the “systemic circulation”?
oxygenated blood goes from the left ventricle into the aorta
then goes to the rest of the body
deoxygenated blood then enters the superior and inferior vena cava to go to the right atrium
What is the “pulmonary circulation”?
deoxygenated blood goes from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery
then goes to the lungs
oxygenated blood enters the pulmonary veins and goes to the left atrium
What is the difference between arteries and veins?
arteries carry blood away from the heart
veins carry blood towards the heart
Do all arteries contain oxygenated blood and do all veins contain deoxygenated blood?
no
most arteries do contain oxygenated blood and most veins do contain deoxygenated blood
but there are some exceptions
right atrium
left atrium
right ventricle
left ventricle
right auricle
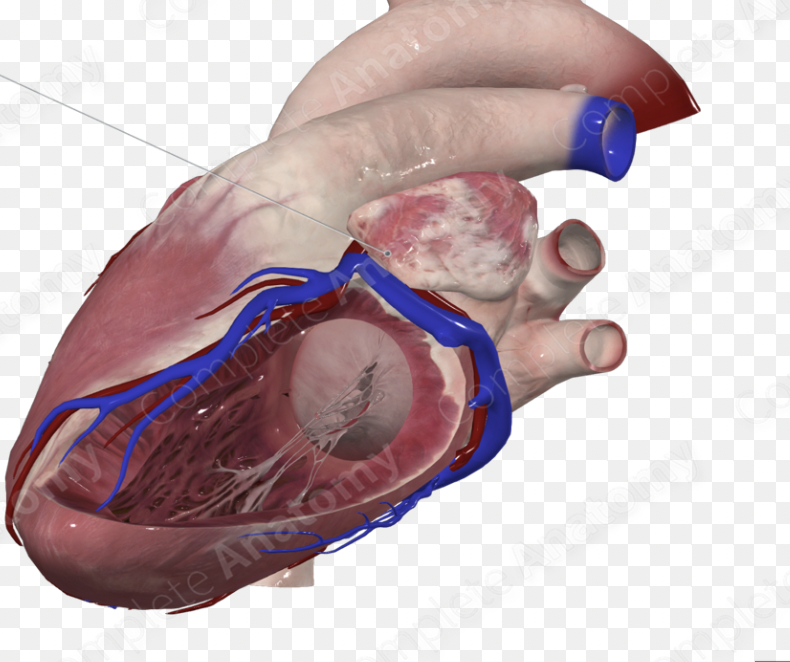
left auricle
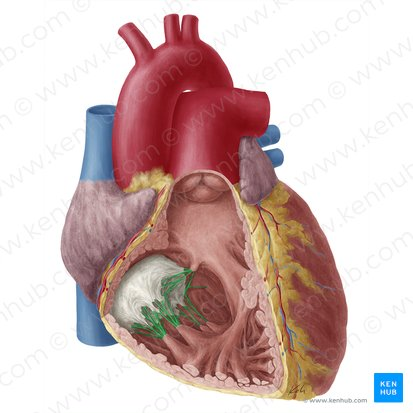
chordae tendineae
papillary muscles
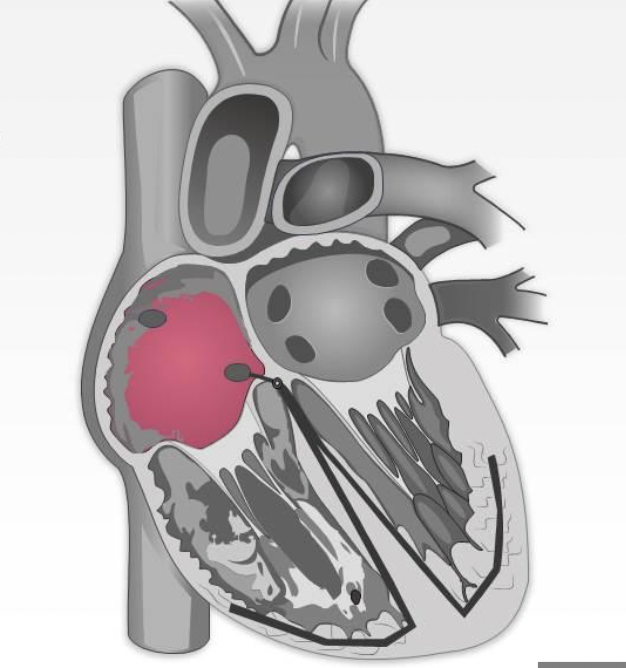
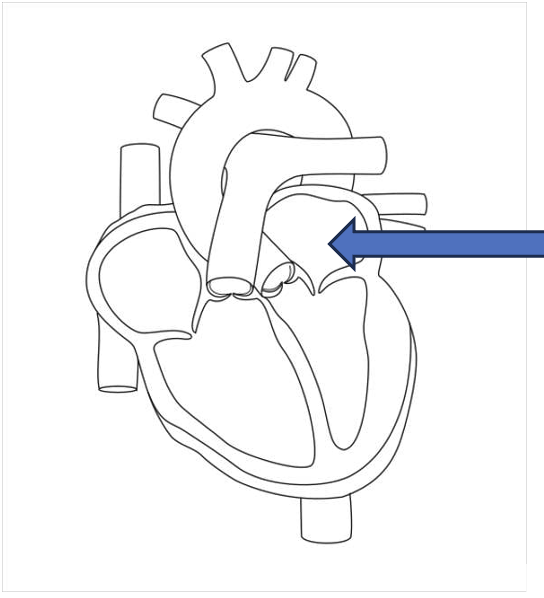
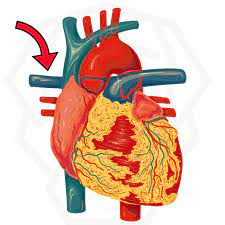
what is the green arrow pointing to?
interventricular septum
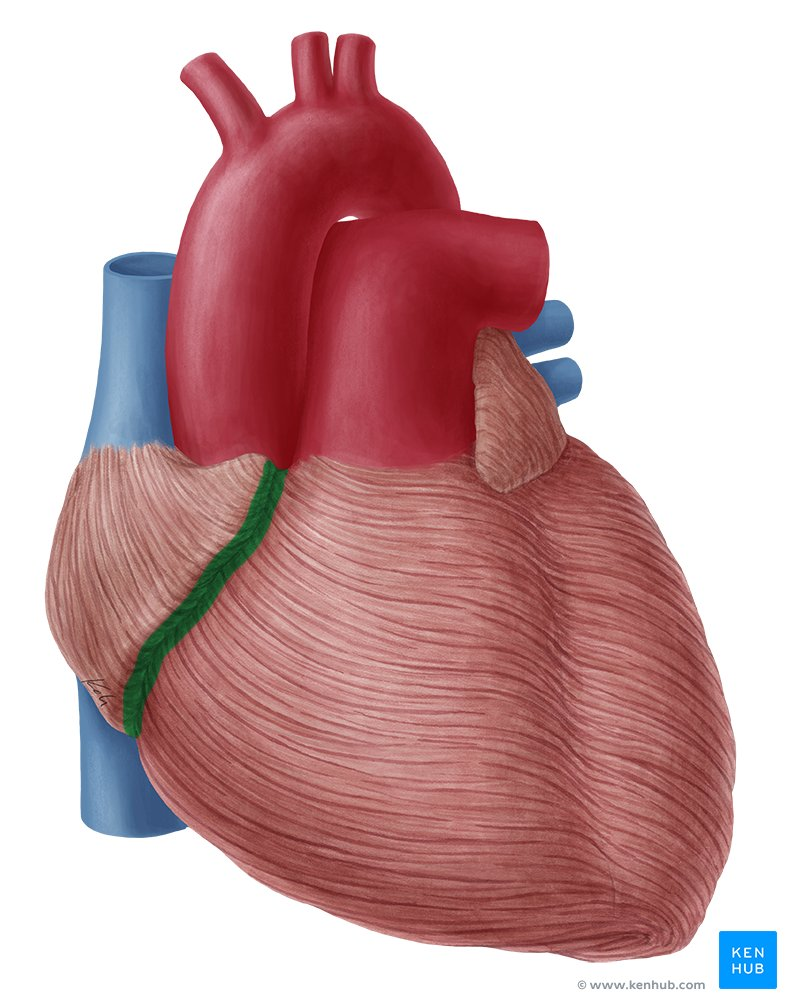
right coronary sulcus
interventricular sulcus
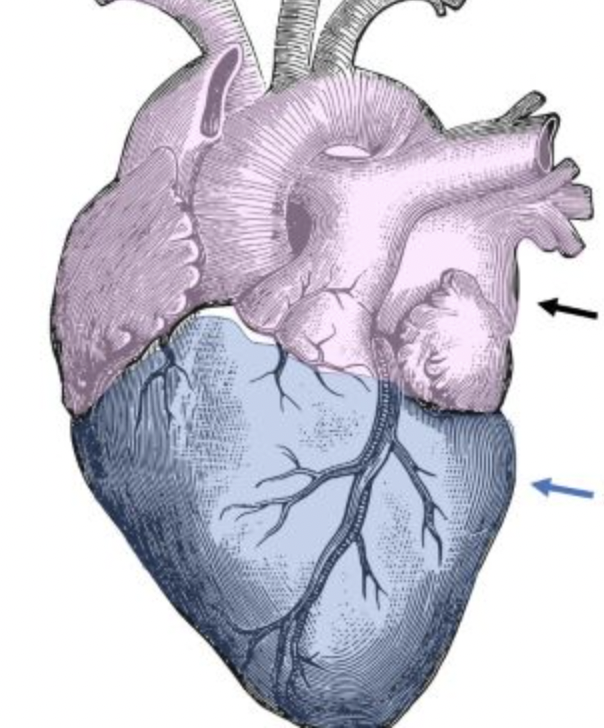
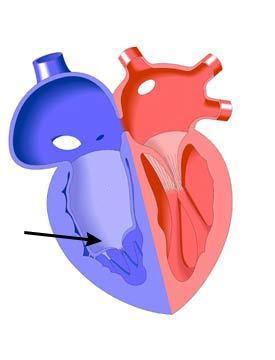
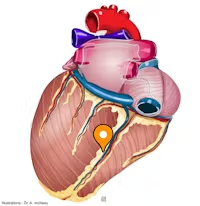
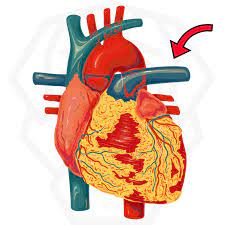
what is the black arrow pointing to?
base
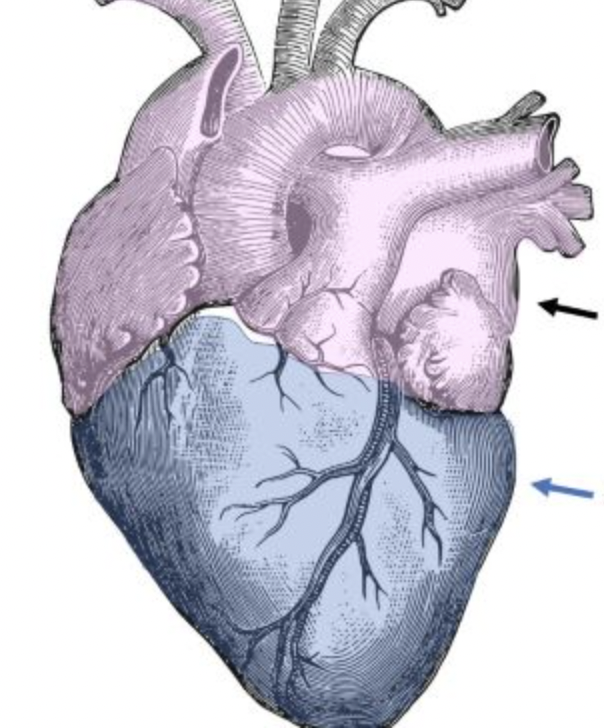
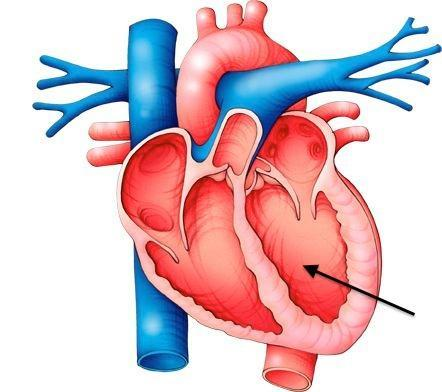
what is the blue arrow pointing to?
apex
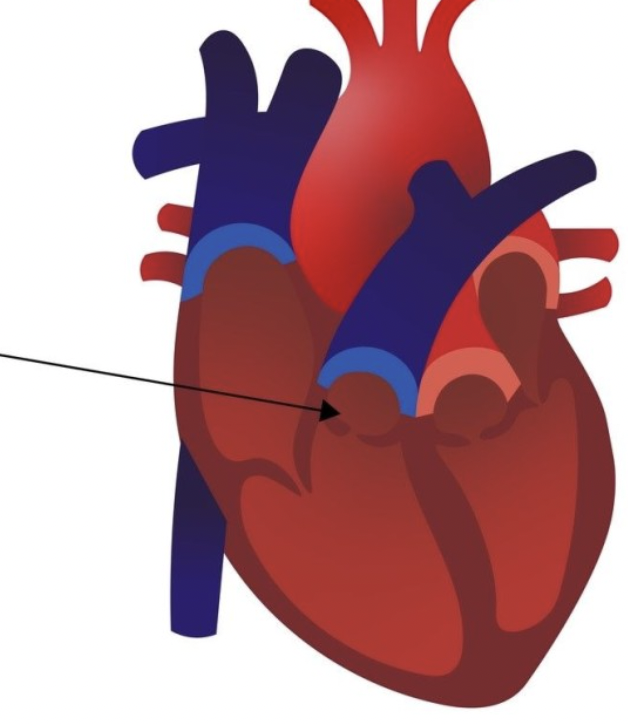
pulmonary valve
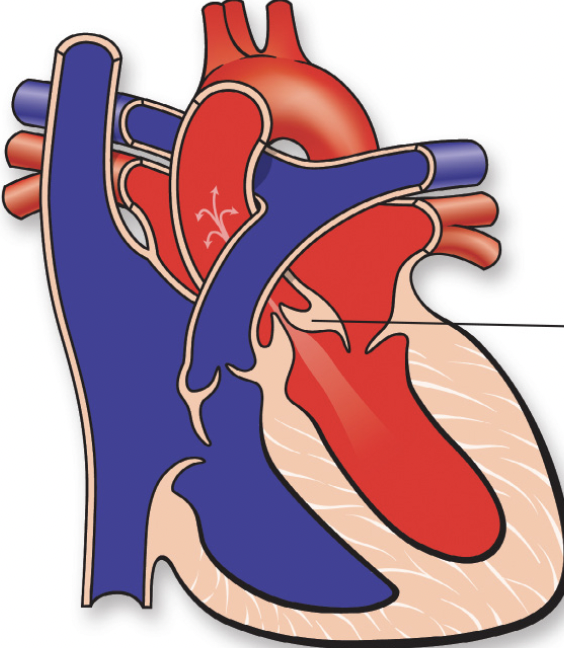
aortic valve
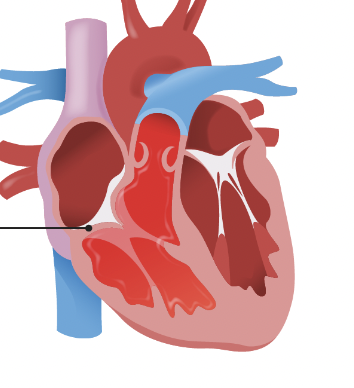
tricuspid valve
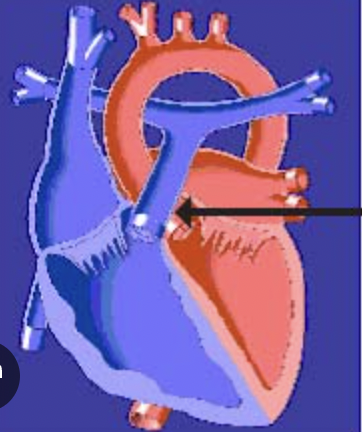
bicuspid valve
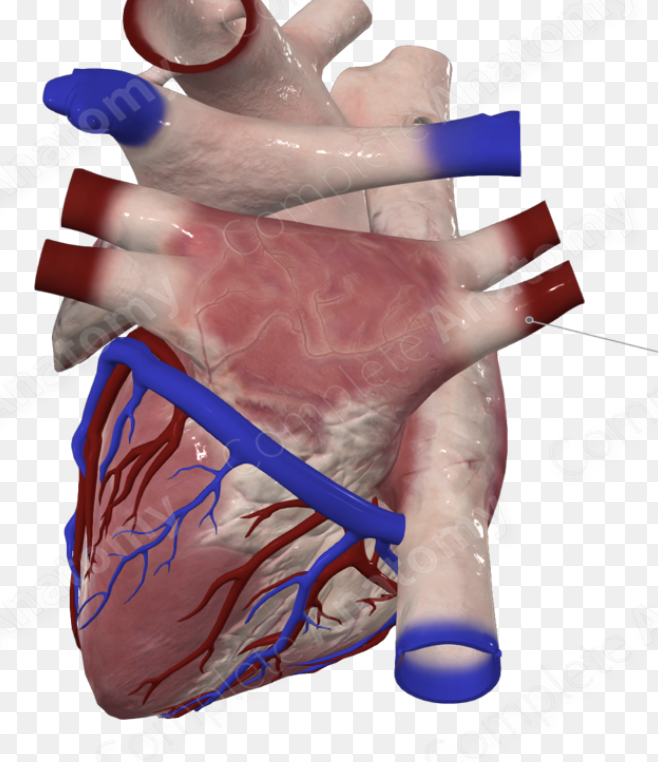
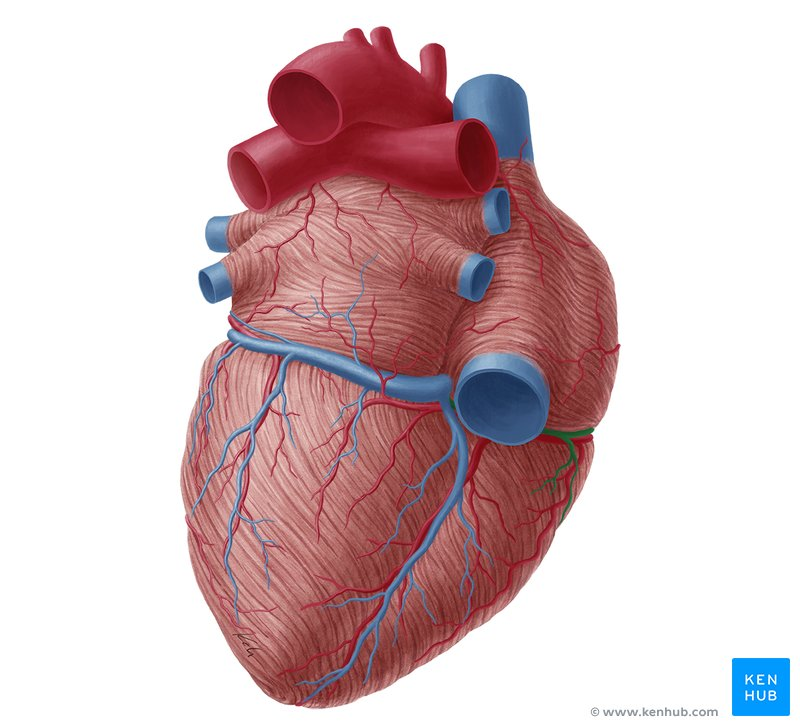
right pulmonary artery
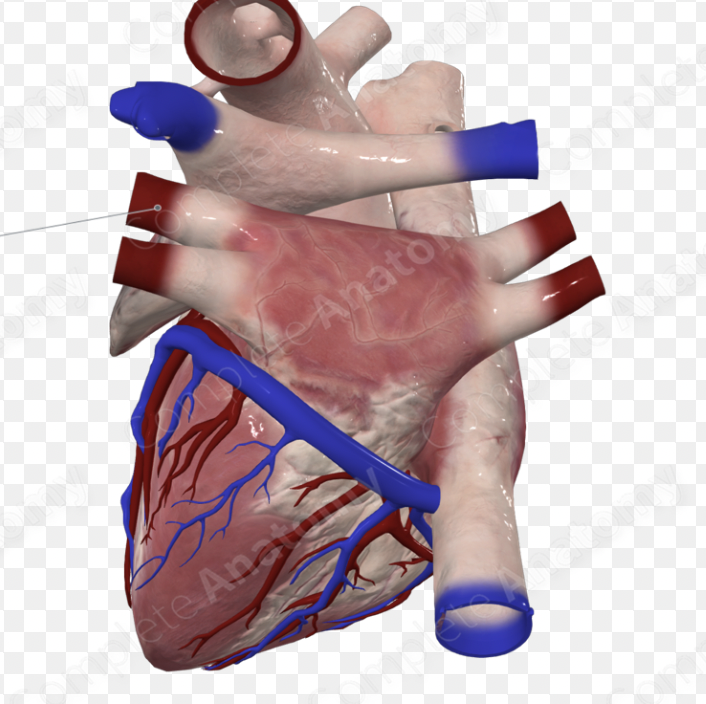
left pulmonary artery
right pulmonary vein
left pulmonary vein
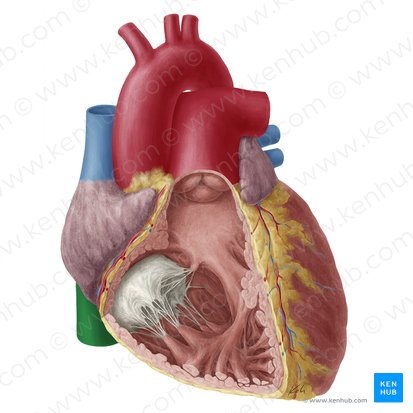
inferior vena cava
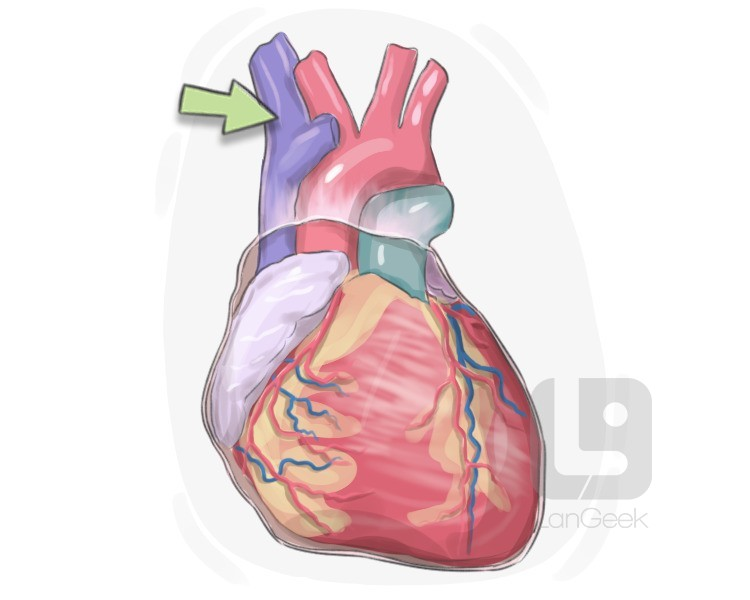
superior vena cava
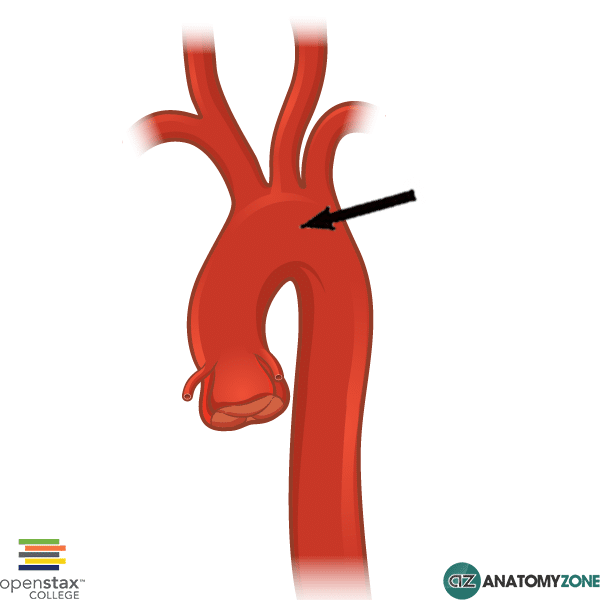
aortic arch
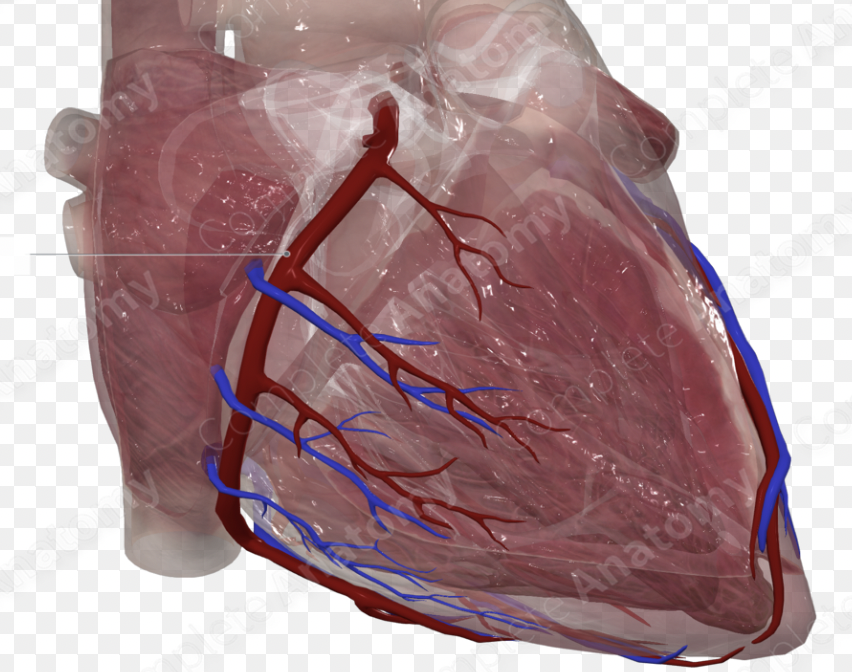
right coronary artery
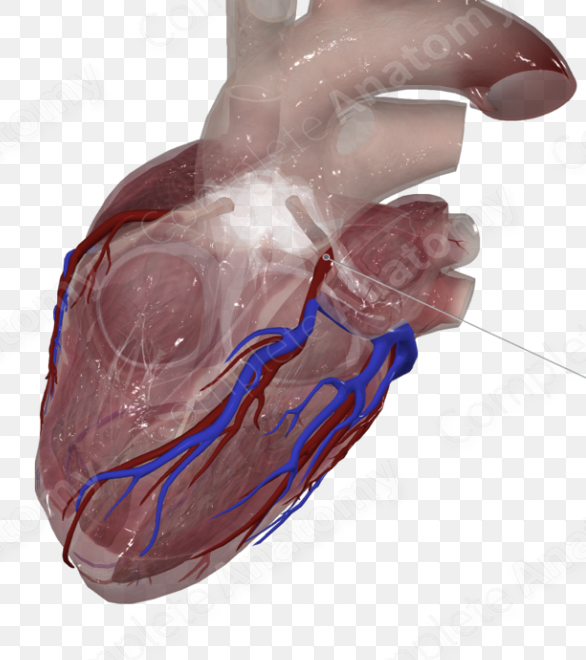
left coronary artery
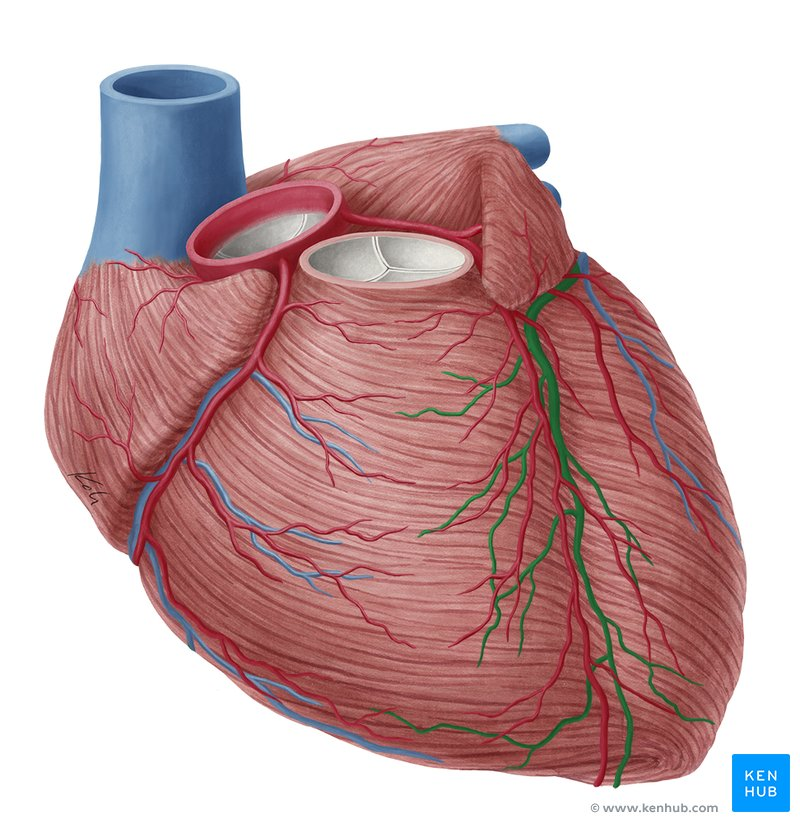
great cardiac vein
middle cardiac vein
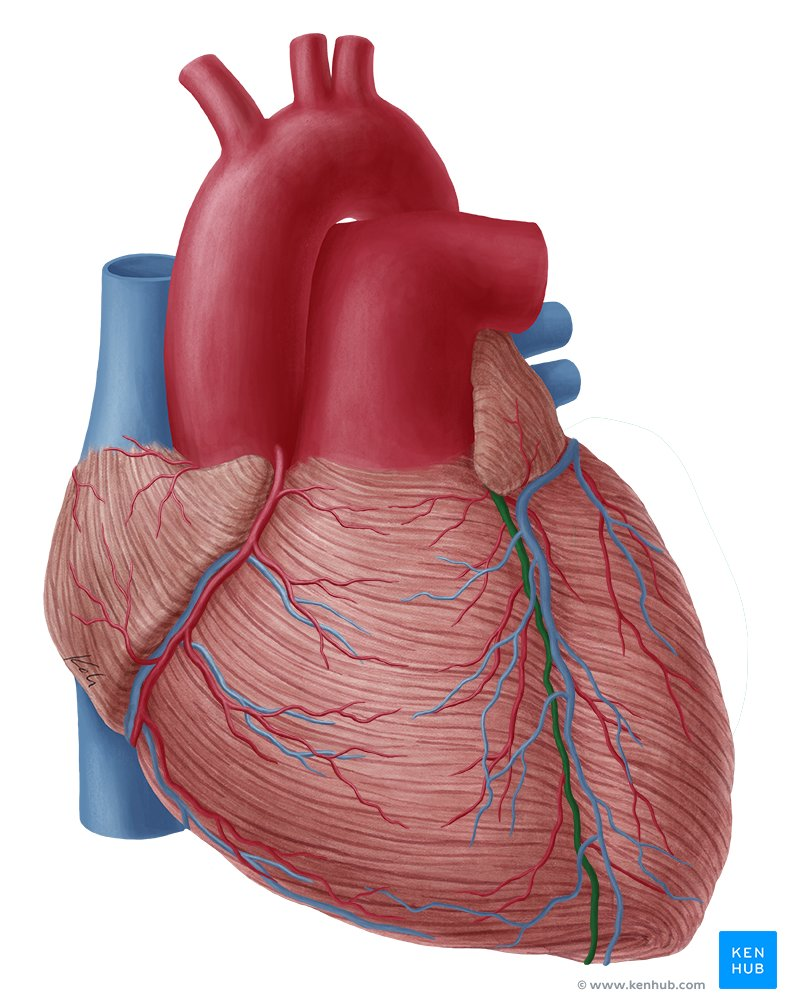
anterior interventricular artery
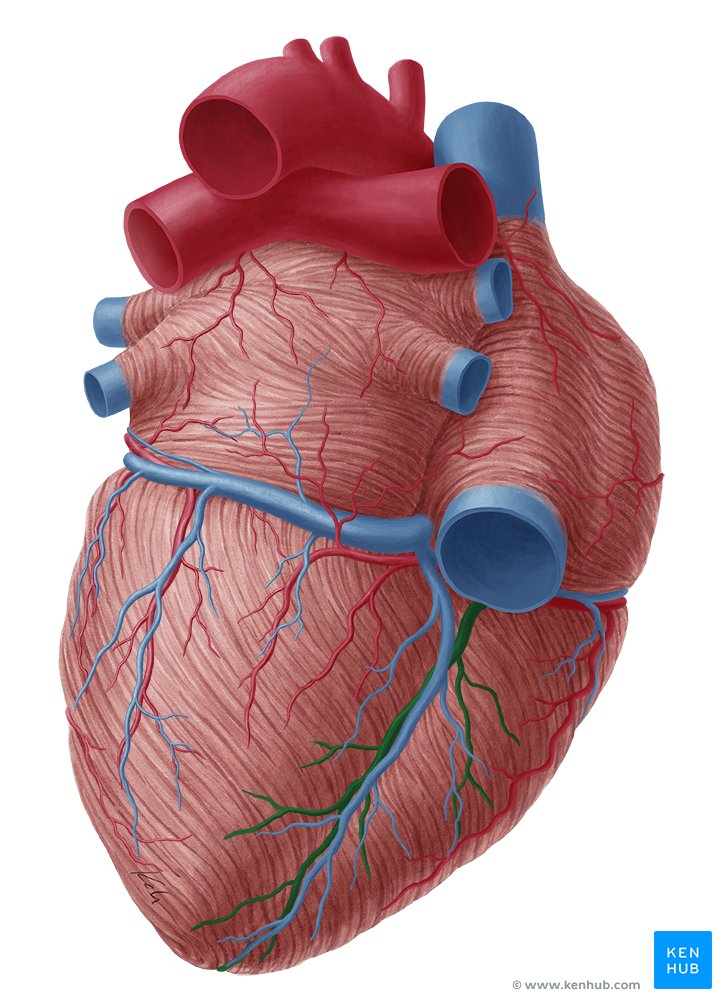
posterior interventricular artery
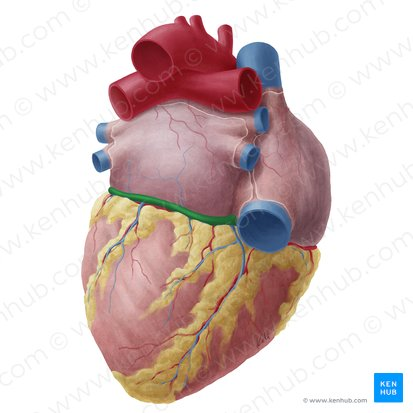
left coronary sulcus
what is the difference between the lengths of the pre / postganglionic neurons for sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems?
sympathetic: short preganglionic and long postganglionic fibers
parasympathetic: long preganglionic fibers and short postganglionic fibers
Which neurons (pre / post) release ACh vs. NE / E for each division?
sympathetic: preganglionic - ACh and postganglionic - NE / E
parasympathetic: preganglionic - ACh and postganglionic - ACh
Sympathetic and parasympathetic effects on body
sympathetic
fight or flight
increases heart rate
dilation of pupils
increased sweating
bronchodilation
parasympathetic
rest and digest
increased GI movement
decreased heart rate
constriction of pupils
bronchoconstriction
Differences in sympathetic and parasympathetic anatomy
sympathetic
thoracic and lumbar regions of spine
parasympathetic
cranial and sacral regions of spine
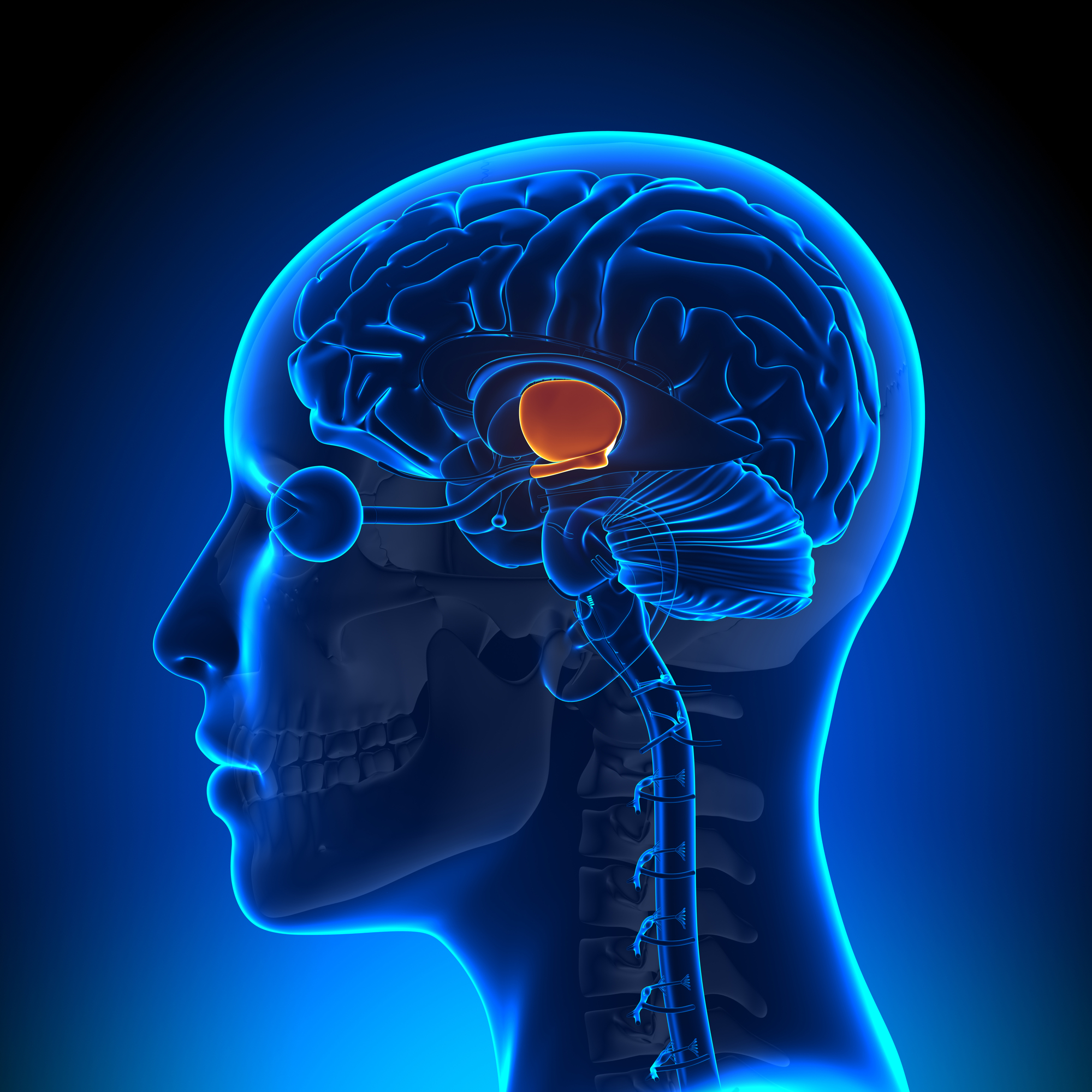
hypothalamus
TRH : Thyroid Releasing Hormone
GHRH : Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone
GHIH : Growth Hormone Inhibiting Hormone
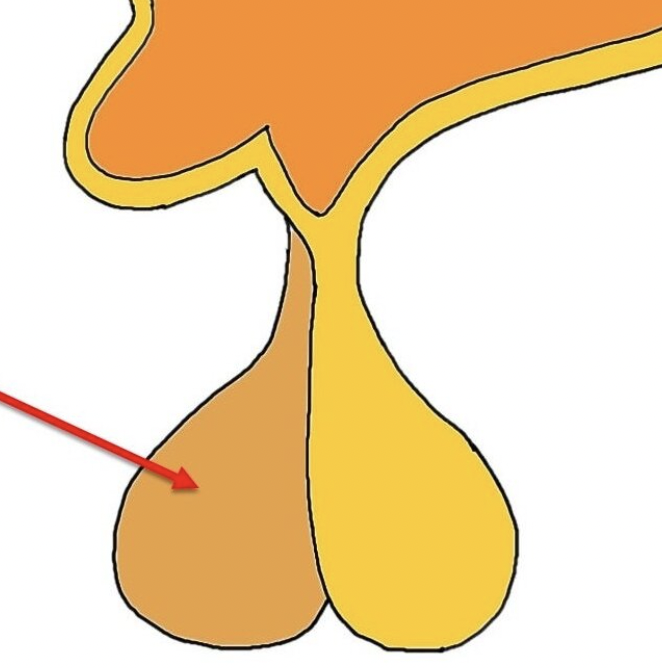
anterior pituitary
GH : Growth Hormone
TSH : Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
ACTH : Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
FSH: Follicle Stimulating Hormone
LH : Luteinizing Hormone
PRL : Prolactin
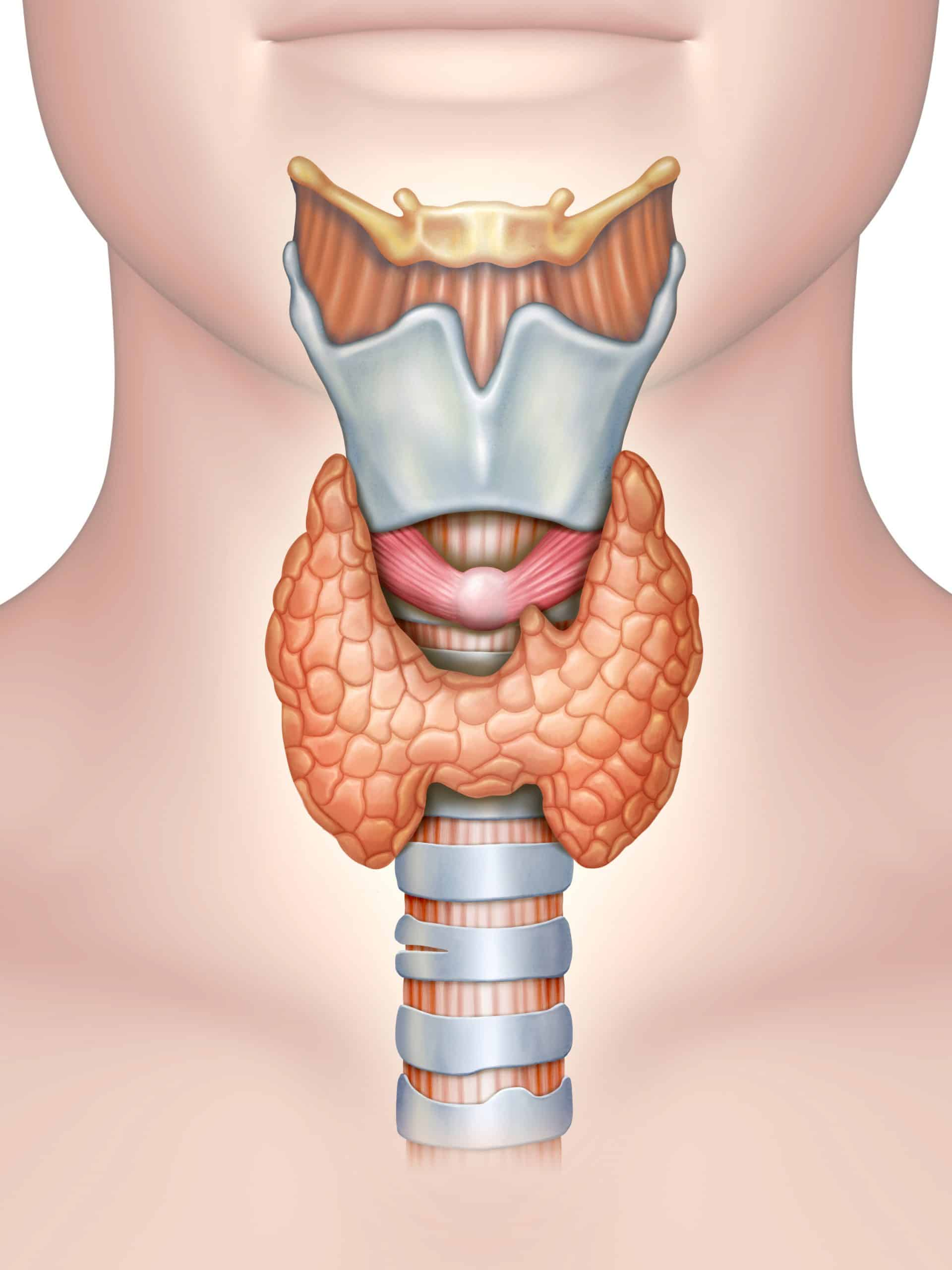
posterior pituitary
OXT : Oxytocin
ADH : Antidiuretic Hormone
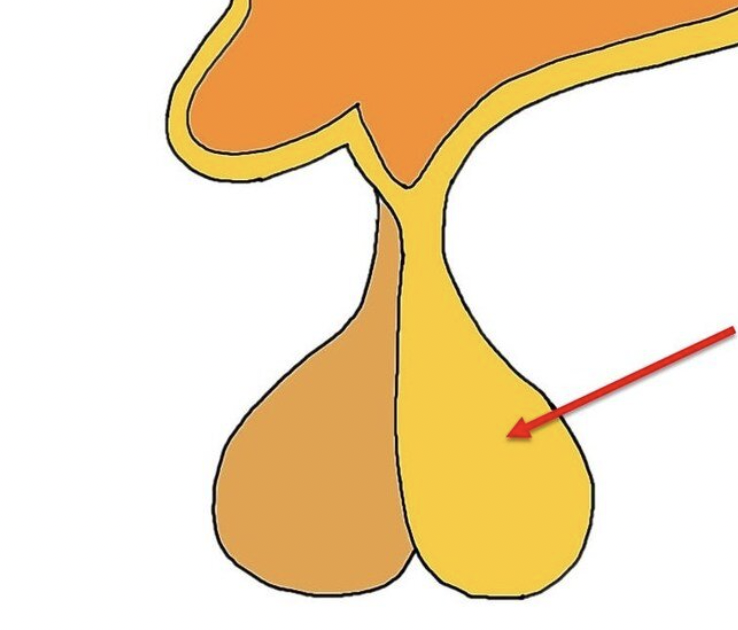
thyroid
T3
T4
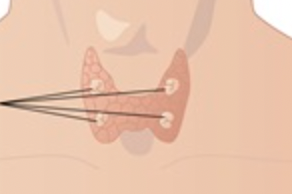
parathyroid
PTH : Parathyroid Hormone
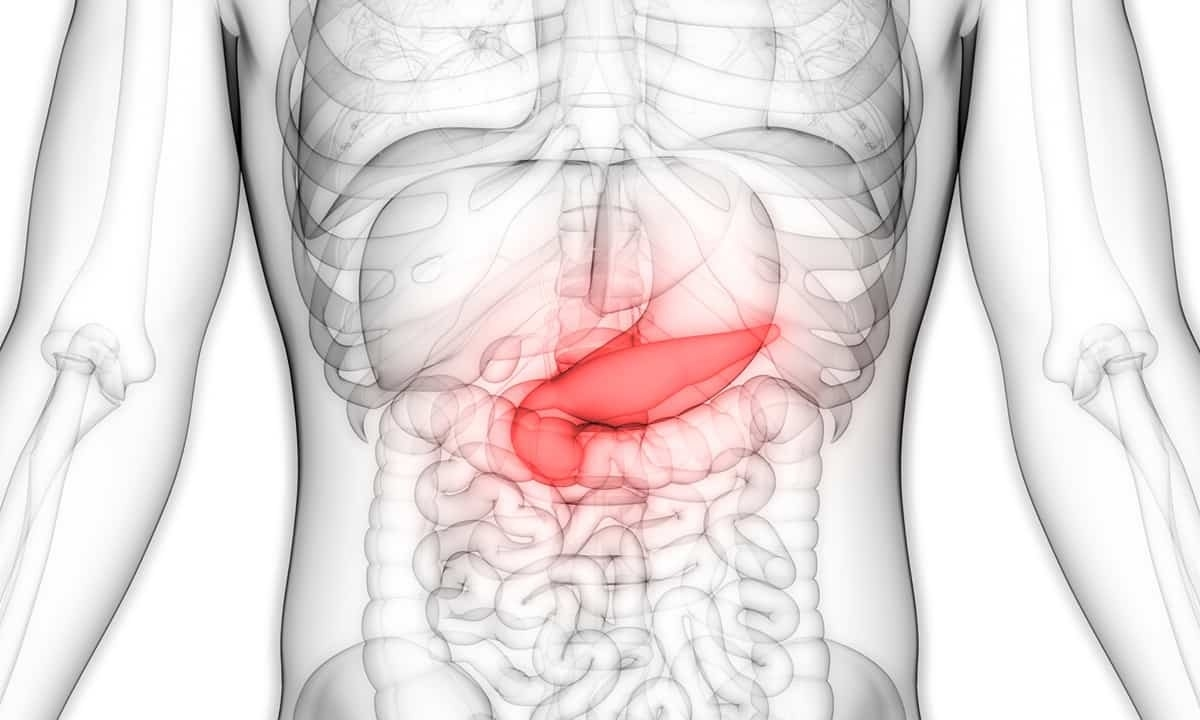
pancreas
insulin
glucagon
adrenal gland
Adrenal Cortex
cortisol
aldosterone
androgens
Adrenal Medulla
epinephrine
norepinephrine
ovaries
estrogen
progesterone