5.3 Slides Explaining and Classifying Psychological Disorders
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Eclectic approach
Combines multiple psychological perspectives for treatment.
Behavioral perspective
Focuses on learned behaviors causing mental disorders.
Level of Dysfunction
Interference with daily functioning due to disorder.
Maladaptive learned associations
Unhealthy responses learned from past experiences.
Perception of Distress
Individual's experience of suffering from symptoms.
Psychodynamic perspective
Focuses on unconscious thoughts from childhood.
Deviation from social norm
Behavior that significantly differs from societal expectations.
Humanistic perspective
Emphasizes personal growth and social support.
Cultural/societal norms
Standards that define acceptable behavior in society.
Cognitive perspective
Focuses on maladaptive thoughts and beliefs.
Stigma
Negative social attitudes towards mental health conditions.
Evolutionary perspective
Examines behaviors affecting survival and reproduction.
Racism
Discrimination based on race affecting mental health.
Sociocultural perspective
Influence of society and culture on disorders.
Sexism
Discrimination based on gender impacting mental health.
Ageism
Discrimination against individuals based on age.
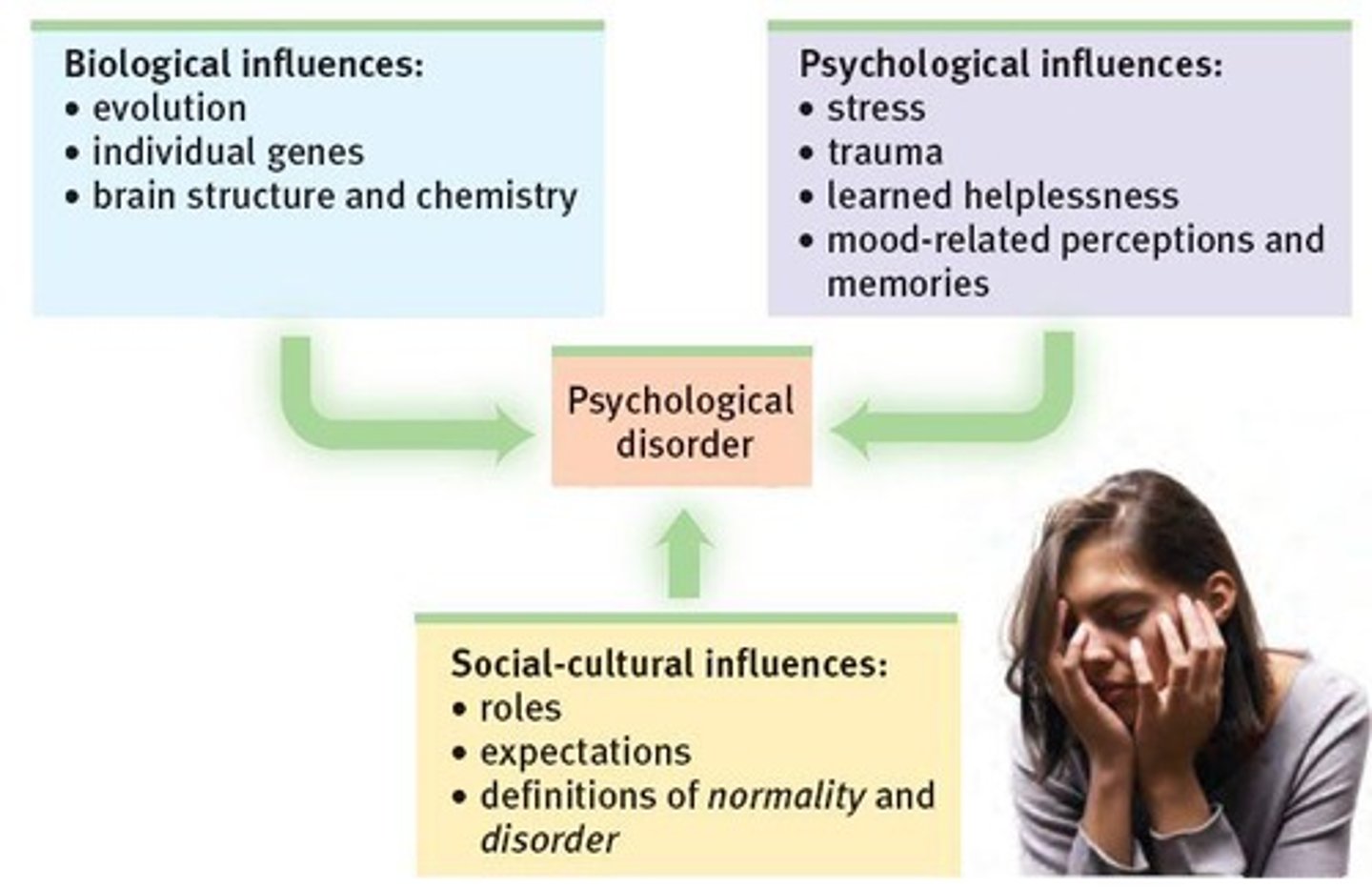
Biopsychosocial model
Integrates biological, psychological, and social factors.
Discrimination
Unjust treatment based on group characteristics.
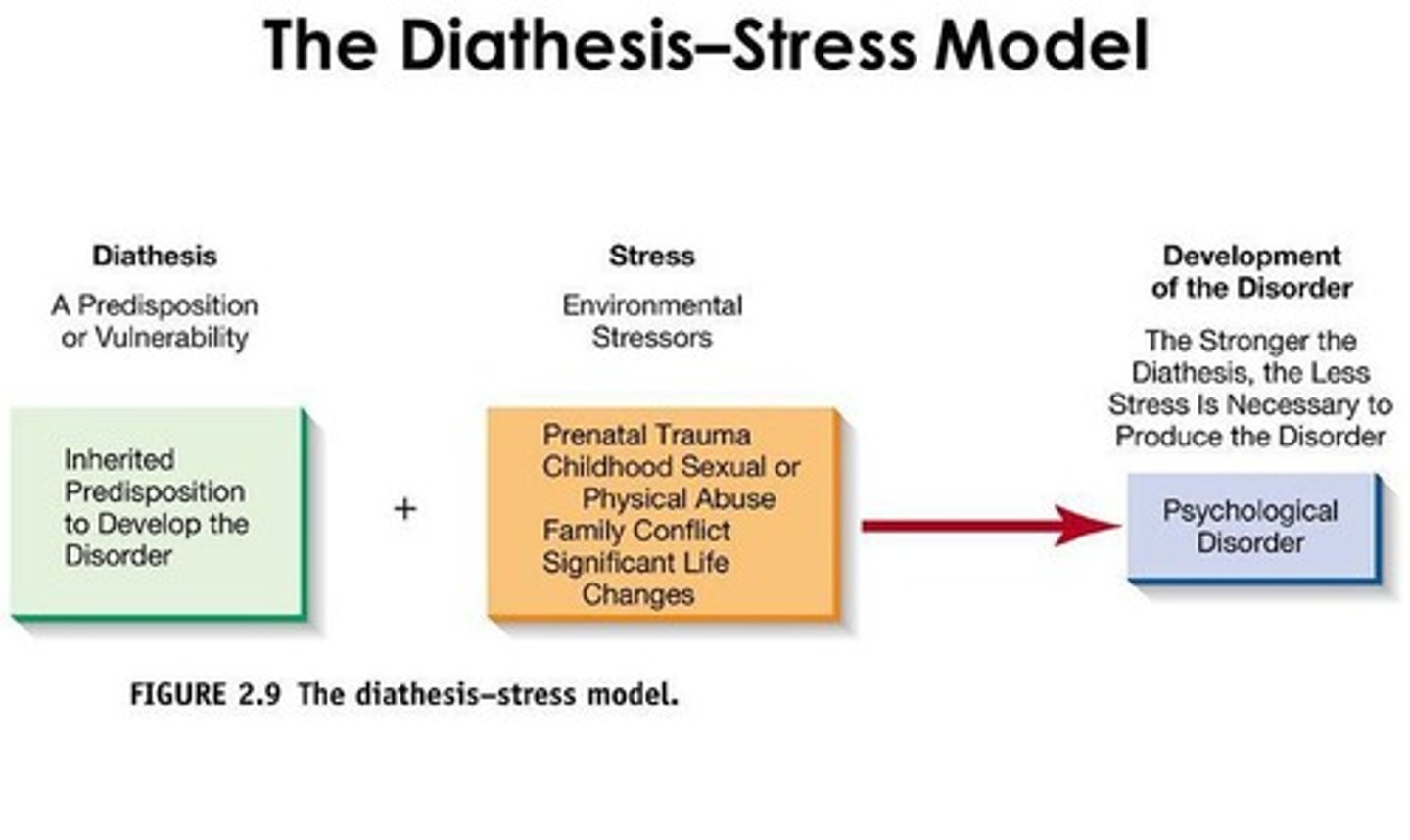
Diathesis-stress model
Disorders arise from genetic vulnerability and stress.
DSM
Manual for diagnosing mental disorders, latest DSM-5-TR.
ICD
International classification of mental disorders, latest ICD-11.
Operational Definitions
Criteria for distinguishing normal from abnormal behavior.
4 D's of psychopathology
Dysfunction, distress, deviation, danger in disorders.
Dysfunctional behavior
Behavior disrupting normal daily life activities.
Danger to self or others
Risk posed by individual due to disorder.
Diagnostic labels
Terms used to categorize mental health conditions.
Preconceptions/stereotypes
Assumptions affecting perceptions of diagnosed individuals.
Rosenhan study
Research illustrating issues with diagnostic labels.
Causation
Study of origins and causes of disorders.
Etiology
Scientific study of the causes of diseases.
Maladaptive thoughts
Negative thinking patterns contributing to disorders.
Social cognitive explanations
Focus on learned behaviors from social interactions.
Culture-bound disorders
Disorders specific to certain cultural contexts.
Susto
Latin American anxiety disorder linked to black magic.
Tajin-kyofusho
Japanese social anxiety about appearance and social withdrawal.
Antisocial personality disorder
Characterized by disregard for others' rights.
Major depression
Severe mood disorder affecting daily functioning.
Bipolar disorder
Mood disorder with extreme highs and lows.
Schizophrenia
Severe disorder affecting thought processes and perception.
OCD
Disorder marked by obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors.
Alcohol use disorder
Problematic drinking leading to significant impairment.
Phobias
Intense fears of specific objects or situations.
Childhood trauma
Early life stress impacting mental health later.
Learned helplessness
Condition where individuals feel powerless to change.
Epigenetics
Study of how environment affects gene expression.
Mental disorder incidence
Rate of occurrence of mental disorders in populations.
US children incidence rate
13% of US children diagnosed with mental disorders.
Poverty and disorders
Higher disorder rates among those below poverty line.
Developmental trends
Patterns of disorder symptoms appearing over lifespan.
Psychological disorders
Clinically significant disturbances in cognition or behavior.