Chapter 11 Microbiology Smartbook
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
Which term refers to the sum total of all microbes found on and within a normal human?
Microbiome
We may or may not be aware that a(n) ______ is taking place, but when the effects cause damage or disrupt tissues and organs, we have entered the pathologic state called a(n) ______.
infection; disease
Some microbes associated with the body that can be rapidly lost, for example when hand washing, are termed _____
transients
A condition in which microbes get past the host defenses, enter the tissues, and multiply is called a(n)
infection
What best defines an infectious disease?
A pathologic state resulting from the disruption and destruction of tissues by microbes
The human _____ is the sum total of all microbes found on and in a normal human.
microbiome
The goals of the Human Microbiome Project are to characterize ______
the microbes living on healthy human bodies
the microbes living on diseased human bodies
______ can be characterized as any deviation from the healthy state.
Disease
Laboratory cultivation _____-estimates the number and variety of microbes in the normal microbiota.
under
Microbes that are part of the normal microbiota are termed _____,
colonist
Which of the following statements regarding the human microbiome are correct?
Viruses are found in healthy humans in large numbers.
Our resident microbes produce enzymes that help us digest food.
The invasion and multiplication of a pathogen in the human host is referred to as a(n)
infection
How different are the microbes on the two hands of a normal, healthy adult?
One hand has a significantly different set of microbes than the other.
An infectious disease is a pathologic state caused directly by _____ or their products.
microbes
Normal biota can cause infection and disease in which of the following cases?
The person is immunocompromised
The patient is elderly.
The host is physically or mentally stressed.
Which effort aims to characterize the microbes living on healthy human bodies as well as to determine the changes in microbe composition in various diseases?
Human Microbiome Project (HMP)
Which of the following are sources of the microbiota that colonize a newborn?
Food
Family members
How do the actual number and variety of microorganisms considered as normal microbiota described by the Human Microbiome Project compare to the number and variety of microorganisms considered normal microbiota by laboratory cultivation?
Laboratory cultivation underestimates the number and variety of microbes.
Identify correct statements regarding the human microbiome.
Healthy people also have dangerous pathogens, but in small numbers.
The composition of the gut microbiome has an influence on the development of obesity.
Any biological agent whose relationship with its host is parasitic and results in infection is called a ________.
Pathogen
While the ______ found on one body site may differ from that found in another location, the ______ profile was similar between body locations and stable across human subjects.
microbiota; protein
Organ transplant patients or cancer sufferers receiving chemotherapeutic drugs may have compromised _____ systems, allowing them to easily experience disease caused by their normal biota.
immune
An infection in which the disease symptoms are influenced by more than one microbe is termed a(n) _____ infection.
polymicrobial (mixed)
A(n) ________ infection is characterized as an infection with a member of the normal biota.
endogenous
Laboratory cultivation _____-estimates the number and variety of microbes in the normal microbiota.
under
Endogenous
Already existing on or in the body
Exogenous
Originating from a source outside the body
Any biological agent whose relationship with its host is parasitic and results in infection is called a(n)
pathogen
Which of the following is not a common site of entry through the skin?
Intact skin
Pathogens enter the ______ tract when people eat contaminated foods or drink contaminated fluids.
gastrointestinal
An infection in which the disease symptoms are influenced by more than one colonizer is termed a(n) ______ infection.
polymicrobial
Which process depends on binding between specific molecules on both the host and pathogen, so that the pathogen can gain a stable foothold on host tissues?
Adhesion
Infection with a member of the normal biota, rather than an agent from the outside environment, is an example of an _____ infection.
endogenous
White blood cells capable of engulfing other cells and particles are generally referred to as
phagocytes
A pathogen can indirectly damage its host by inducing excessive _____ responses.
immune
Microbes gain access through areas of _______ skin including areas with nicks, abrasions, and punctures.
broken
A pathogen can directly damage its host by secreting ______ or _______
enzymes
exotoxin
The gastrointestinal tract is the portal of entry for pathogens contained in ______ substances
ingested
Which of the following is NOT a main role for exoenzymes in the disease process?
Increase the amount of systemic inflammation
Which of the following substances is NOT an example of an exoenzyme?
Hemolysin
Many pathogenic bacteria, fungi, protozoa and worms secrete ______
that break down and inflict damage on tissues.
exoenzymes
A pathogen can indirectly damage its host by ______.
inducing excessive immune responses
Pathogenic staphylococci produce an enzyme that causes clotting of blood or plasma that is called
coagulase
pathogen can directly damage its host by ______
secretion of toxins
secretion of exoenzymes
Exoenzymes play which of the following main roles in the disease process?
Inflict damage on tissue
Dissolve the host defensive barriers
Which type of toxin acts on the nervous system?
Neurotoxin
Which of the following are examples of exoenzymes?
Streptokinase
Mucinase
Hyaluronidase
What is an exoenzyme?
An extracellular enzyme that may damage host tissues
Which type of toxin acts on the intestines?
Enterotoxin
Which of the following exoenzymes is responsible for clotting the blood or plasma?
Coagulase
exotoxins
have effects on a specific cell type
endotoxins
have systemic effects such as fever, inflammation, diarrhea, and shock
Which term refers to a toxin that is secreted and acts upon a specific cellular target?
Multiple choice question
Exotoxin
Toxins that act on the nervous system are called
neurotoxins
A specific chemical product of an organism that is poisonous to other organisms is called a(n)
toxin
A(n) ______ is a type of bacterial exotoxin that is capable of destroying red blood cells and causing the release of hemoglobin.
hemolysin
A toxin that acts on the intestines is called a(n)
enterotoxin
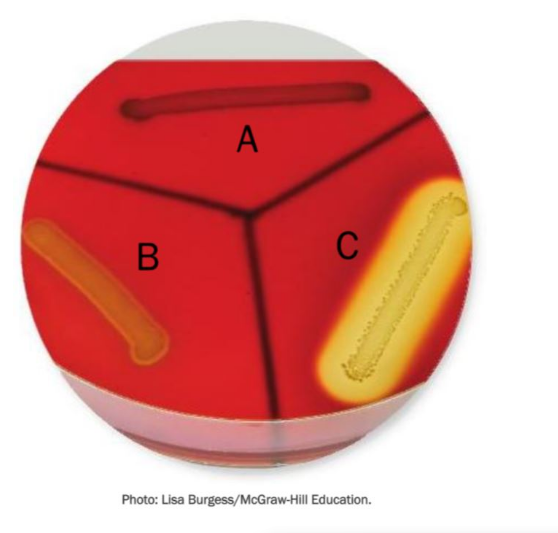
Which strain of bacteria is producing the most severe hemolysis?
C
Which type of toxins have effects on a specific cell type?
Exotoxins
A bacterial toxin that is not ordinarily released but instead is an integral part of gram-negative cell walls is called a(n) ______
endotoxin
A toxin that is secreted and acts upon a specific cellular target is called a(n)
exotoxin
Which of the following is the substance referred to as endotoxin?
Lipopolysaccharide
In what ways do exotoxins usually affect host cells?
Disrupting intracellular function
Damaging the cell membrane
Causing lysis of cell
The outer membrane of ______ bacteria contains lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
gram-negative
Which of the following is a bacterial exotoxin that disrupts the cell membrane of red blood cells, causing them to burst?
Hemolysin
Where is lipopolysaccharide (LPS) located in bacterial cells?
Outer membrane
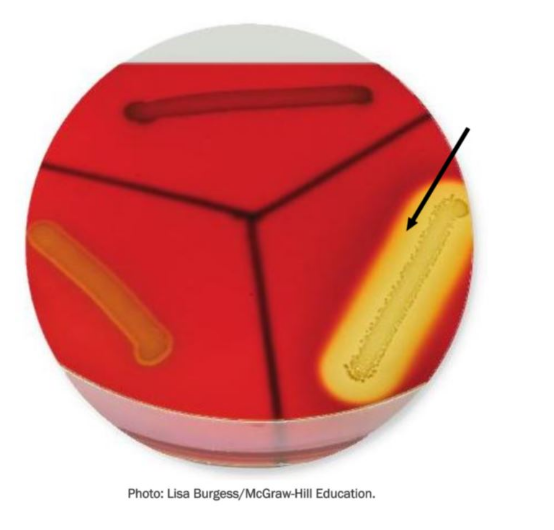
In this image, the arrow points to a region of the medium where bacterial cells have secreted _____.
hemolysin
With a decrease in a host's ability to mount an immune defense against an infection, the host is said to be _____.
immunocompromised
A bacterial toxin that is an integral part of gram-negative cell walls is referred to as
endotoxin
In cases like tuberculosis and streptococcal pharyngitis, the infectious agent breaks loose from a local infection and is carried to other tissues, resulting in a ____ infection.
focal
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a(n) ______ which is part of the outer membrane of gram negative cell walls.
endotoxin
An infection that spreads to several sites and tissue fluids usually via the bloodstream is called a(n) ______ infection.
Gram-negative
After entering the body, microbes remain confined to a specific tissue in a(n) ______ infection.
localized
Lipopolysaccharide is located in the _________ _________ of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria.
outer membrane
An infection that occurs as a complication of a pre-existing one is called a(n) _______
secondary
An immunocompromised host is one who shows a decrease in ______.
the ability to mount an immune defense to infection
An infection that persists over a long duration is referred to as a _______ infection
chronic
When an infectious agent spreads from a local site and is carried to other tissues, the infection is called a(n) ______ infection.
focal
A(n) ______ infection invades many compartments and organs via the bloodstream.
systemic
n infection that occurs when a microbe enters a specific tissue, infects it, and remains confined there is called a(n)______ infection.
localized
In a sequence of infections, the first infection that predisposes the patient to further infection is called the _______ infection.
primary
A(n) ______ infection is caused by a different microbe than the one that initiated the primary infection and is often a result of lowered host immune defenses.
secondary
Diseases caused by more than one infectious agent at the same time are referred to as ______ diseases or as _______ infections.
polymicrobial, mixed
A(n) ______ infection is characterized as an infection that progresses and persists over a long period of time.
chronic
Subjective evidence of infection and disease as perceived by the patient is called a(n)
symptom
In cases like tuberculosis and streptococcal pharyngitis, the infectious agent breaks loose from a local infection and is carried to other tissues, resulting in a _____ infection.
focal
An infection that is characterized by rapid onset and short duration is called a(n) ______ infection.
acute
Any abnormality uncovered upon physical examination or diagnosis that indicates the presence of disease is referred to as a(n)
sign
Which type of infection is caused by several microbial agents that establish themselves at the infection site at the same time?
Polymicrobial infection
If a patient reports pain in his throat, this is considered to be a ______ of a possible infection.
symptom
A nonspecific response to tissue injury or infection that protects the host from further damage is called
Inflammation
An infection that occurs when a microbe breaks loose from a localized infection and is carried by the circulation to another tissue is called a(n) ______ infection.
focal
Which of the following represent collections of microbes and inflammatory cells that have been walled-off within the tissues?
abscesses and granulomas
Any characteristic that can be objectively observed, such as the appearance of a skin rash, is called a(n) ______ of a disease.
sign
The collection of signs and symptoms that when seen together indicate a particular disease is referred to as a(n) ______.
syndrome
______ is the swelling of one or more lymph nodes.
Lymphadenitis
Diseases caused by more than one infectious agent at the same time are referred to as ________ diseases or as _________ infections.
polymicrobial, mixed
_____ is a decrease in the number of circulating white blood cells.
Leukopenia
The formation of ______ or _______ occurs when inflammatory cells and microbes become walled-off by the immune system.
abscesses
granulomas
______ is an increase in the number of circulating white blood cells.
Leukocytosis