2. Molecules to metabolism
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
* major component of cell membranes (phospholipids and cholesterol)
* long-term energy storage molecule (fats and oils)
* Also may function as a signalling molecule (steroids)
* DNA codes for protiens while RNA has an active role in the manufacturing of proteins
* Major regulatory molecules involved in catalysis (all enzymes are proteins)
* May also function as structural molecules or play a role in cellular signalling (transduction pathways)
* **Compound lipids** – Esters of fatty acids, alcohol *and* additional groups (e.g. phospholipids and glycolipids)
* **Derived lipids** – Substances derived from simple or compound lipids (e.g. steroids and carotenoids)
how are polynucleotide chains formed
bonds between the pentose sugar and phosphate group
phosphodiester bond
What was vitalism theory
organic molecules cannot be produced from inorganic molecules
organic molecules can only be synthesised by living systems As they posses a certain “vital force” needed
* The artificial synthesis of urea demonstrates that organic molecules are not fundamentally different to inorganic molecules
* They enable the synthesis and assimilation of new materials for use within the cell
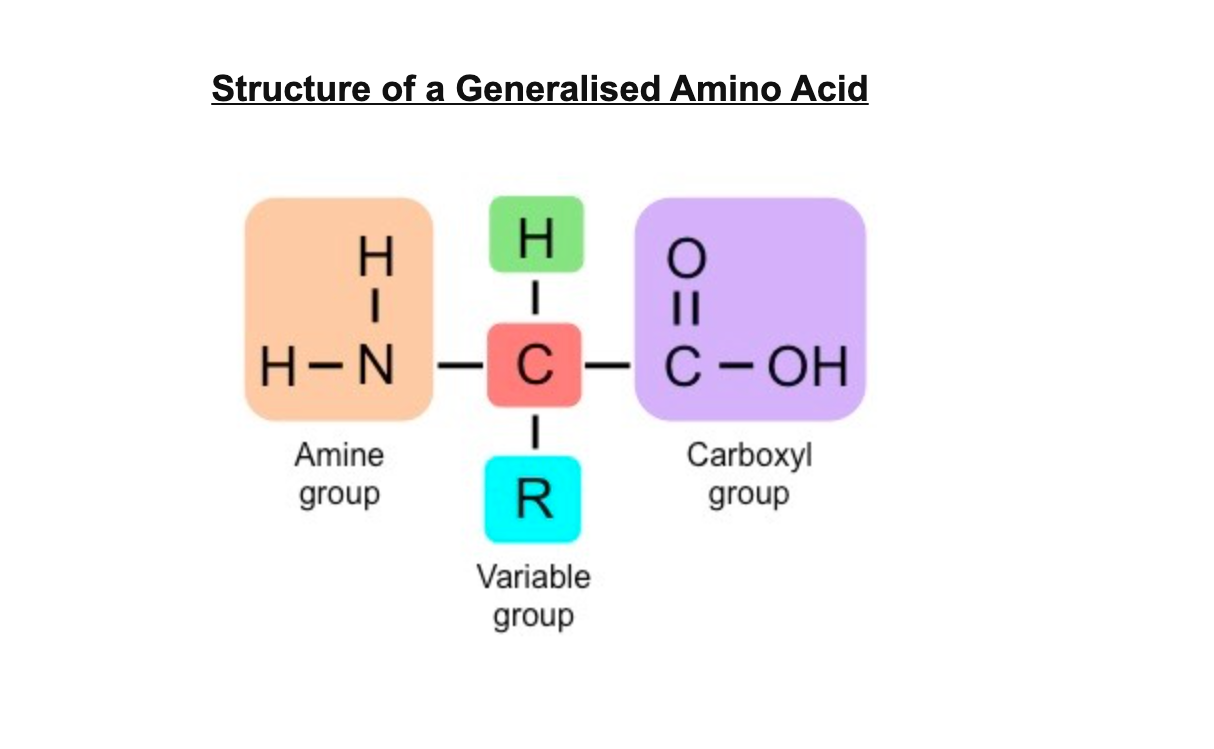
peptide bonds
ester linkage
phosphodiester bonds (phosphate of one to a sugar of another)
\
c+glycolysis
same row is same number of orbitals
Fe iron
Na sodium
P hospherus
S ulfer
Compare and contrast carbohydrates, lipids and proteins
all macromolecules
all contain C, H, O
carbohydrates and lipids are composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen WHILE proteins are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sometimes sulphur[1]
→ the monomers for carbohydrates are monosaccharides WHILE the monomer for proteins are amino acids, and for lipids they are fatty acids and glycerol[1]
→ carbohydrates are mainly used for energy in cells WHILE proteins are used as building blocks and lipids are for energy storage