1.1 Model of The Atom, Symbols, Relative Atomic Mass, Electronic Charge & Isotopes
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards are for Topic 1 - Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table in AQA GCSE Chemistry (Triple Higher). They cover specification points 4.1.1.1 - 4.1.1.7
Chemistry
GCSE Chemistry
AQA
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
4.1.1.1 Atoms, Elements & Compounds
4.1.1.2 Mixtures
4.1.1.3 The Development of the Model of the Atom
4.1.1.4 Relative Electrical Charges of Subatomic Particles
4.1.1.5 Size & Mass of Atoms
4.1.1.6 Relative Atomic Mass
4.1.1.7 Electronic Structure
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What is the smallest part of an element that can exist?
Who first proposed in 1803 that all matter was made of tiny, indivisible spheres called atoms?
What subatomic particle did J. J. Thomson discover through his experiments?
The ____ __________ model of the atom, suggested by J.J. Thomson, describes the atom as a ball of positive charge with negative electrons embedded in it.
What experiment, designed by Ernest Rutherford in 1909, was used to test the plum pudding model?
In the alpha scattering experiment, what were the positively charged alpha particles fired at?
All alpha particles were expected to pass straight through the foil.
What did the observation that most alpha particles passed straight through the gold foil indicate about the structure of an atom?
That an atom is mostly empty space.
What did the deflection of some alpha particles in Rutherford's experiment suggest about the atom's nucleus?
The nucleus must have a positive charge, as it repelled the positive alpha particles.
What did the observation that a small number of alpha particles bounced straight back from the gold foil imply?
That the mass of the atom is concentrated in a tiny central nucleus.
Rutherford's experiment led to the ________ model, which states the atom's mass is concentrated in a positively charged nucleus.
Who adapted Rutherford's nuclear model by suggesting that electrons orbit the nucleus in specific shells or energy levels?
Niels Bohr
Further experiments by Rutherford led to the idea that the nucleus contained small, positively charged particles called what?
Protons
James Chadwick
Protons and neutrons
Why does an atom have no overall electrical charge?
It contains an equal number of positive protons and negative electrons, so their charges cancel out.
Atomic number
Mass number
mass number - atomic number
11
11
Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
Isotopes of a given element have the same atomic number but different _____ numbers.
Because they have the same number of electrons, which determines chemical properties.
An electrically charged particle formed when an atom or molecule gains or loses electrons.
By losing electrons
Why does losing electrons cause an atom to become a positively charged ion?
Because it has more positively charged protons than negatively charged electrons, so it has an overall positive charge.
By gaining electrons
Why does gaining electrons cause an atom to become a negatively charged ion?
Because it has more negatively charged electrons than positively charged protons, so it has an overall negative charge.
Electronic structure
2
8
8
2,8,1
2,8,8
2,8,8,2
Why are the elements in Group 0 (the noble gases) chemically inert or unreactive?
Because they have a stable arrangement of electrons with a full outer shell.
Atoms react to achieve a stable electronic structure, which usually means having a _____ outer shell.
A weighted average mass of the atoms of an element, taking into account the abundance of its isotopes.
Because they are a weighted average of the masses of an element's different isotopes.
Ar = ((abundance1 × mass1) + (abundance2 × mass2)) / total abundance (100)
A substance made up of only one type of atom is called an ________.
A substance formed from two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions is called a ____________.
The central part of an atom containing protons and neutrons is the __________.
Electron shells
The number of electrons in the outermost shell of an atom determines its __________ properties.
A magnesium ion (Mg2+) is formed when a magnesium atom loses two electrons. If a Mg atom has 12 protons, how many electrons does the ion have?
10

This question is about elements, compounds and mixtures.
Substance A contains only one type of atom.
Substance A does not conduct electricity.
Which type of substance is A?
Non-metallic element

This question is about elements, compounds and mixtures.
Substance B contains two types of atoms.
The atoms are chemically combined together in fixed proportions.
Which type of substance is B?
Compound

What is the name of the elements in Group 0 of the periodic table?
Noble gases

Which statement about the elements in Group 0 is correct?
The boiling points increase down the group.

Neon is in Group 0.
What type of particles are in a sample of neon?
Atoms
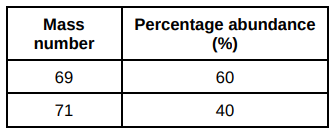
The table shows the mass numbers and percentage abundances of the isotopes of gallium.
Calculate the relative atomic mass (Ar) of gallium.
Give your answer to 1 decimal place.
69.8
Gallium (Ga) is in Group 3 of the modern periodic table.
Give the numbers of electrons and neutrons in an atom of the isotope 6931Ga.
31 electrons and 38 neutrons
Gallium (Ga) is in Group 3 of the modern periodic table.
What is the most likely formula of a gallium ion?
Ga3+
This question is about models of the atom.
Atoms were first thought to be tiny spheres that could not be divided.
Which particle was discovered to change this model of the atom?
Electron
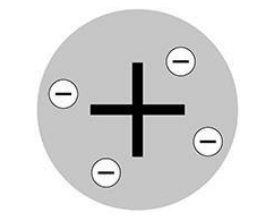
The diagram shows a model of the atom.
What is the name of this model of the atom?
Plum pudding mode
The model of the atom used today has three subatomic particles:
electrons
neutrons
protons
Complete the sentences.
Atoms of the same element have the same atomic number because they have the same number of _______________.
Atoms of the same element can have different mass numbers because they have different numbers of _______________.
Atoms have no overall charge because they have the same number of _______________ and _______________.
protons, neutrons, protons, electrons

The radius of a nucleus is approximately 1 × 10-14 m.
The radius of an atom is approximately 1 × 10-10 m.
A teacher uses a ball of radius 1 cm to represent the nucleus.
What could represent the atom on the same scale?
A sports arena of radius 100 m.