The Multiplier Model and Business Cycles in Economics
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Multiplier Model
Determines income changes from spending decisions.
Aggregate Demand
Total demand in the economy, AD = C + I.
Co
Autonomous consumption
C1
Marginal Propensity to consume (MPC)
Consumption Function
C = c0 + c1Y; relationship between consumption and income.
Equilibrium Determination Formula
1/1-C1 X (Co + I)
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
Change in consumption from change in income.
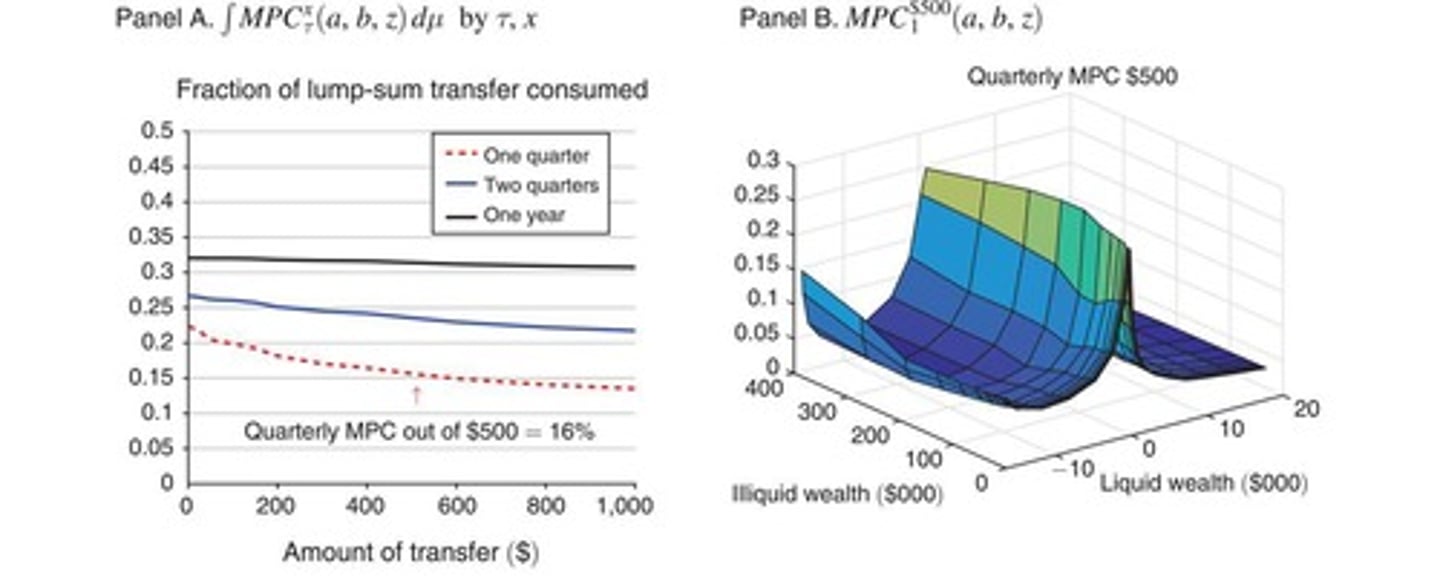
Autonomous Consumption
Consumption independent of current income levels.
Equilibrium Income
Income level where AD equals output.
45-Degree Line
Graphical representation where output equals AD.
Multiplier Effect
The multiplier effect refers to the process by which an initial change in aggregate demand (AD) leads to a larger overall change in national income (GDP) due to repeated rounds of spending and re-spending in the economy.
Investment (I)
Expenditure on capital goods, assumed constant for now.
Temporary Income Shock
Short-term income change affecting consumption patterns.
Business Cycles
Fluctuations in economic activity over time.
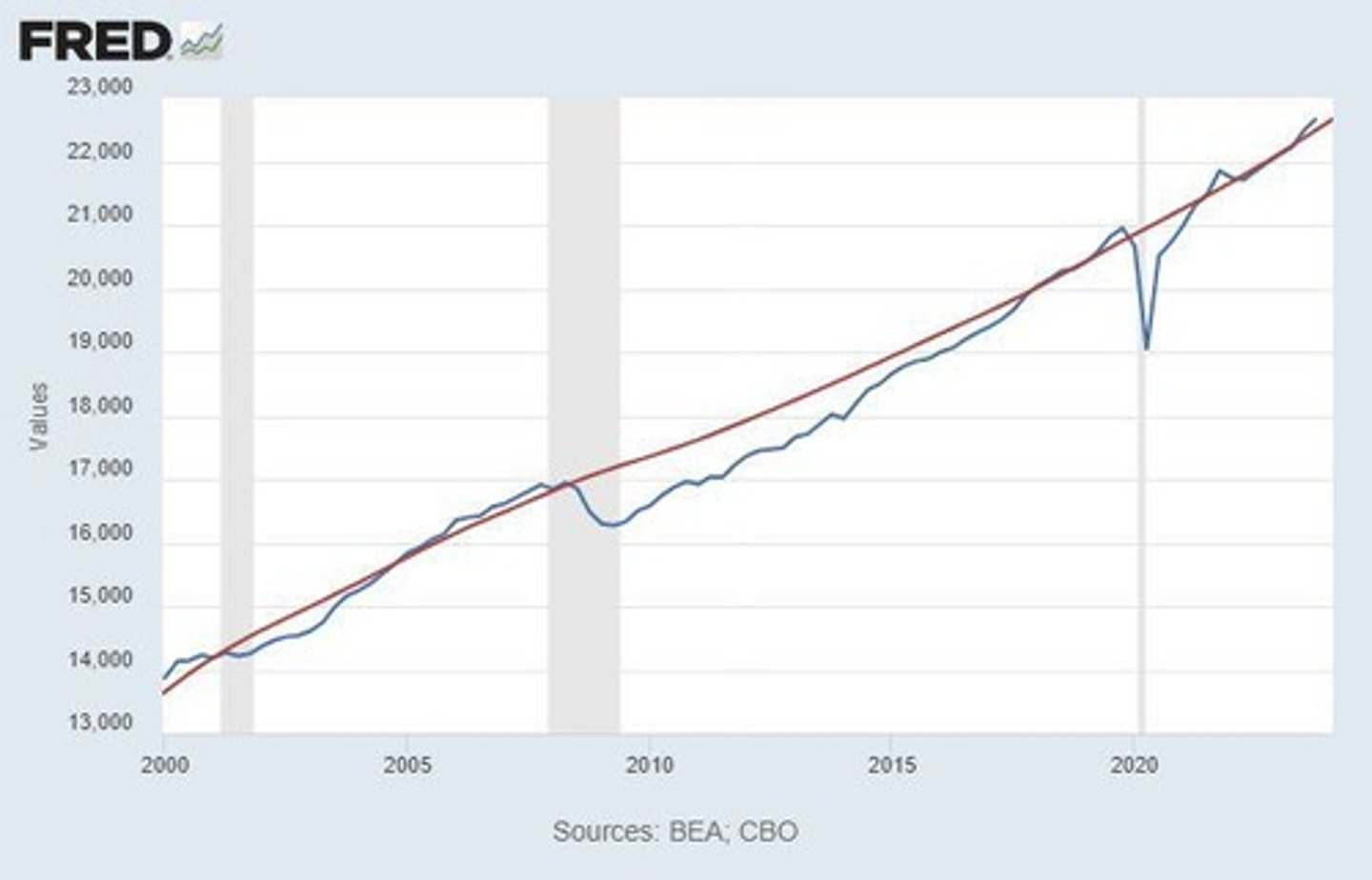
Recession
Negative GDP growth below average trend.
Recovery
Positive GDP growth following a recession.
Expansion
Positive GDP growth above average trend.
Contraction
Negative GDP growth after an expansion.
Factors of Production
Inputs used to produce goods and services.
Income (Y)
Total earnings from production in the economy.
Consumption (C)
Total spending by households on goods and services.
Investment Demand
Firms' desire to purchase capital goods.
Fiscal Stimulus
Government spending to boost economic activity.
Adjustment Mechanisms
Processes returning economy to trend after shocks.
Consumer Confidence
Expectations affecting autonomous consumption levels.
Income Determination
Process of establishing income levels in the economy.
Aggregate Labor/Product Model
Framework for understanding medium-run income determination.
Negative Income Shock
Sudden drop in income affecting consumption negatively.
Expected Income
Anticipated income influencing consumption behavior.
Equilibrium in Diagrams
Graphical representation of income and AD balance.
Changes in MPC
Variations in consumer behavior affecting overall consumption.