Chapter 26 Compounds with the carbonyl group
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
what is the carbonyl group
C=O bond
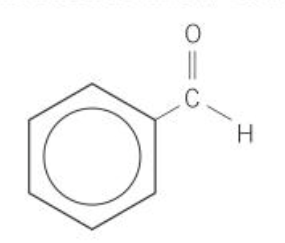
what is the iupac name of this
benzenecarbaldehyde
how do the boiling points of carbonyl compounds compare with alkanes and alcohols of similar chain length
C=O bond is strongly polar so dipole dipole forces can form
carbonyl compounds have higher boiling points than similar length alkanes but lower than alcohols because there is no hydrogen bonding
what is the solubility of carbonyl compounds
hydrogen bonds form between the O in C=O and water
solubility decreases as chain length increases
what forms when aldehydes are oxidised
carboxylic acid
why can’t ketones be oxidised
because a C - C bond has to be broken
what is the general equation for oxidation of aldehydes
RCHO + [O] → RCOOH
what happens when aldehydes and ketones are added to Fehling’s solution
Aldehyde reduces Cu2+ ions to Cu+ ions, forming a brick red precipitate of Cu2O
Ketone shows no visible change
what happens when aldehydes and ketones are added to Tollen’s reagent
Aldehyde forms a silver mirror
Ketone shows no visible change
what is the reducing agent used to reduce aldehydes and ketones
NaBH4
Tetrahydridoborate (III)
what is the general equation for reduction of aldehydes
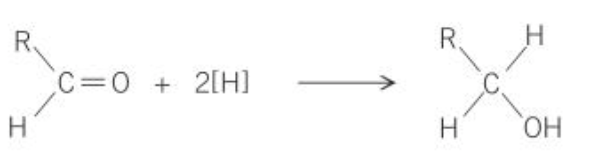
what is the general equation for reduction of ketones
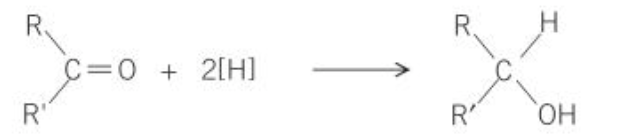
what is the symbol for a reducing agent
[H]
what are aldehydes and ketones reduced to
aldehydes → primary alcohols
ketones → secondary alcohols
what type of reactions are the reductions of aldehydes and ketones
nucleophillic addition
what is the mechanism for the reduction of an aldehyde
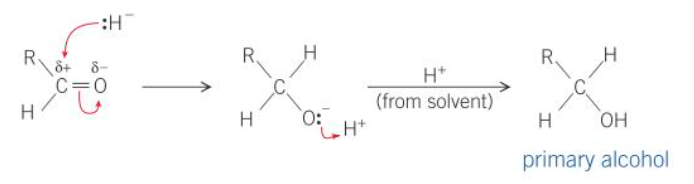
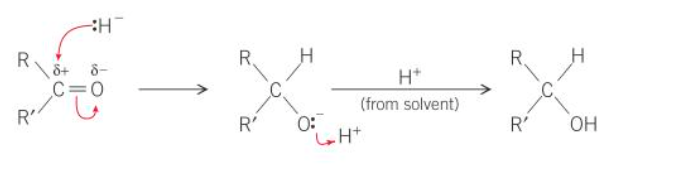
what is the mechanism for the reduction of a ketone
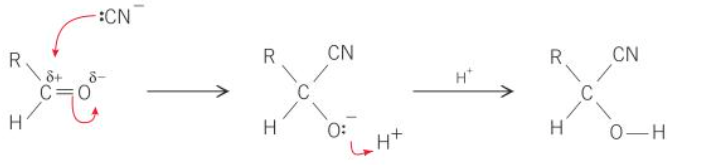
how are hydroxynitriles formed
add KCN followed by dilute acid to aldehydes or ketones
what is the general equation for the formation of a hydroxynitrile from an aldehyde
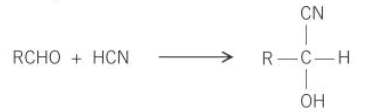
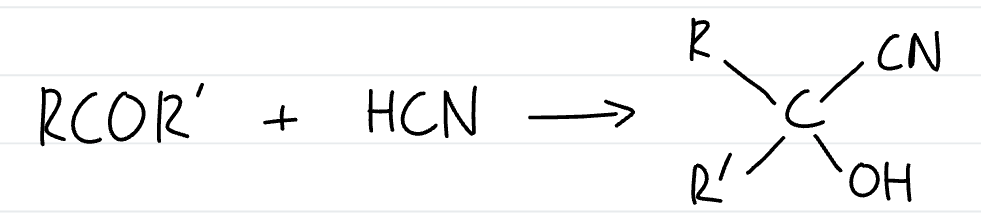
what is the general equation for the formation of a hydroxynitrile from a ketone
what type of reaction is the formation of hydroxynitriles from aldehydes and ketones
nucleophillic addition
what is the mechanism of aldehyde + KCN
what is the mechanism of ketone + KCN
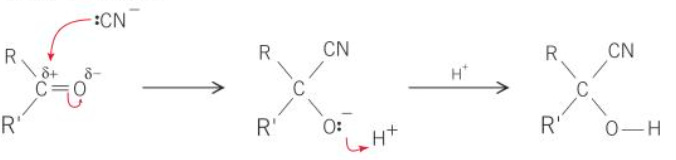
what type of ketones can make a racemic mixture when reacted with KCN
unsymmetrical ketones
why can the addition of KCN to aldehydes and unsymmetrical ketones form a racemic mixture
the CN- ion can attack the partially positive C from the top or bottom
what are the dangers of using KCN
CN- ions are toxic
why can the H- nucleophile not reduce the C=C bond
H- is repelled by the high electron density in the C=C bond
why is KCN used instead of HCN to form hydroxynitriles
HCN is hard to store as a gas and can react to produce dangerous byproducts
what are the conditions for the reduction of aldehydes and ketones
aqueous conditions
uses of esters
food flavourings
perfumes
solvents
plasticisers
how is an ester made
carboxylic acid and alcohol react in presence of concentrated sulfuric acid catalyst
what is the solubility of carboxylic acids
up to and including butanoic acid are soluble
due to formation of hydrogen bonds
what type of molecules are vegetabl and animal oils
triglycerides
esters of propane-1,2,3-triol (glycerol)
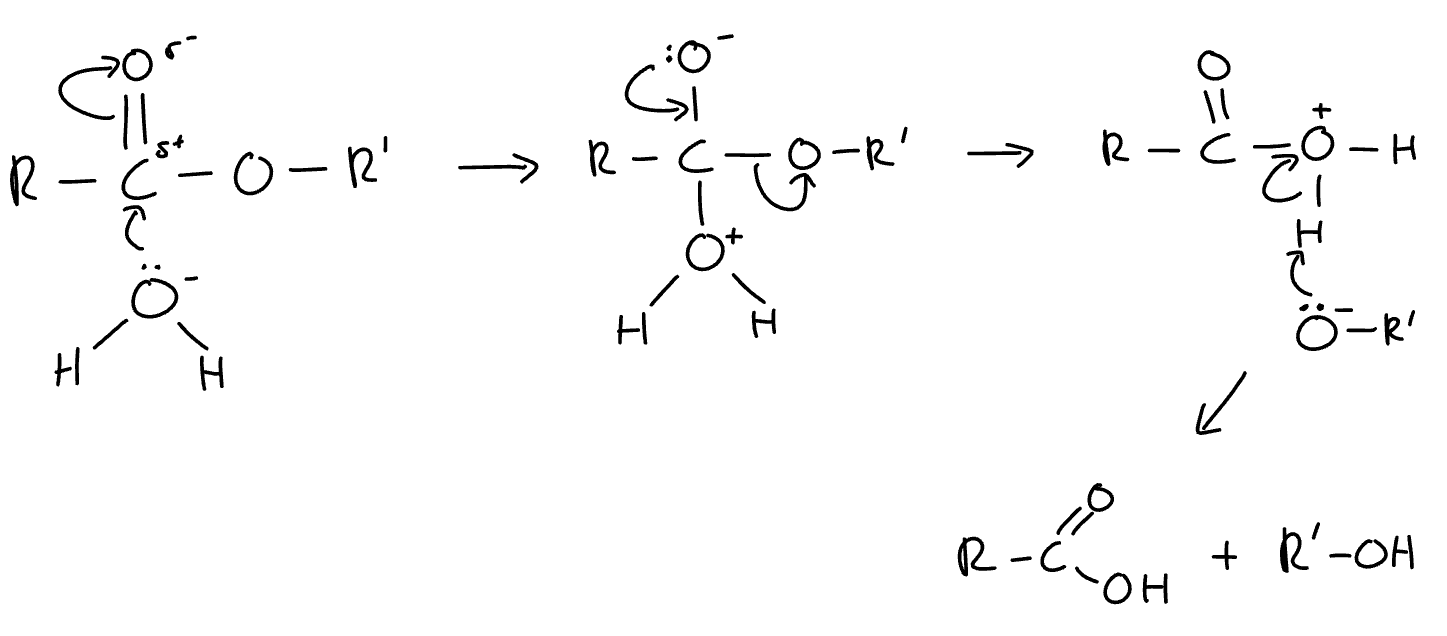
what are the products when an ester is hydrolysed in acidic conditions
alcohol + carboxylic acid
what type of reaction is the hydrolysis of esters
nucleophillic addition
mechanism for hydrolysis of esters
what are the products when esters are hydrolysed in alkaline conditions
alcohol + salt of the carboxylic acid
how is soap made
hydrolise vegetable and animal oils in alkaline conditions
produces soap and glycerol
what are biodiesels
mixture of methyl esters of long chain carboxylic acids
e.g. CH3OOC(CH2)14CH3
how to produce biodiesels
vegetable oils reacted with methanol
in presence of a strong alkali catalyst
what vegetable oil is typically used to make biodiesel
rapeseed oil
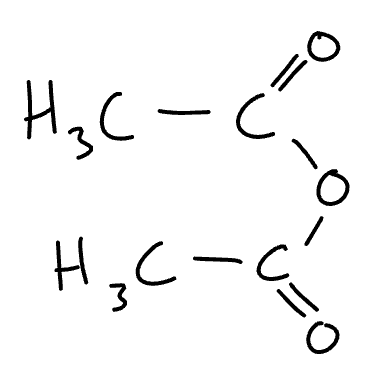
structure of ethanoic anhydride
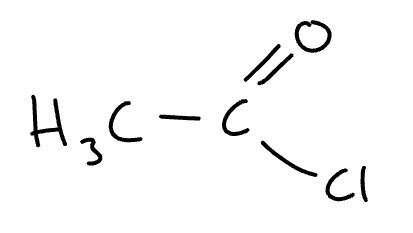
structure of ethanoyl chloride
structure of ethyl amine
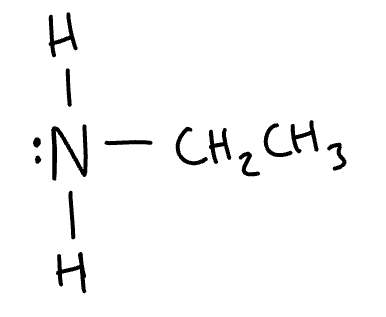
order of reactivity of nucleophiles for acylation
primary amines
ammonia
alcohols
water
order of reactivity of acid derivatives
acyl chlorides
acid anhydrides
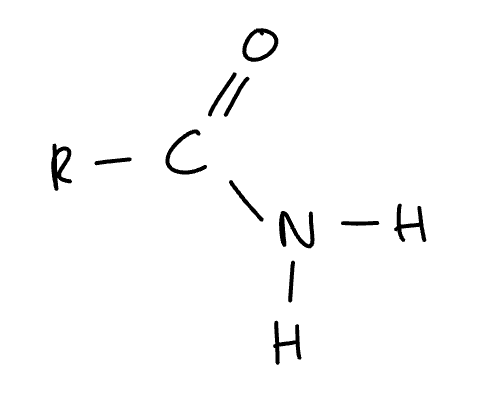
product formed when acyl chloride/acid anhydride reacts with ammonia
amide
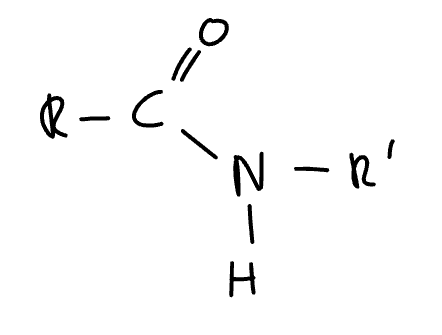
product formed when acyl chloride/acid anhydride reacts with a primary amine
N-substituted amide
product formed when acyl chloride/acid anhydride reacts with a alcohol
ester
product formed when acyl chloride/acid anhydride reacts with a water molecule
carboxylic acid
what is the reaction of acyl chloride/acid anhydrides with nucleophiles
addition-elimination reaction
what is the advantage of using ethanoic anydride over ethanoyl chloride in the manufacture of aspirin
ethanoyl chloride produces HCl gas
but by product for ethanoic anhydride is ethanoic acid
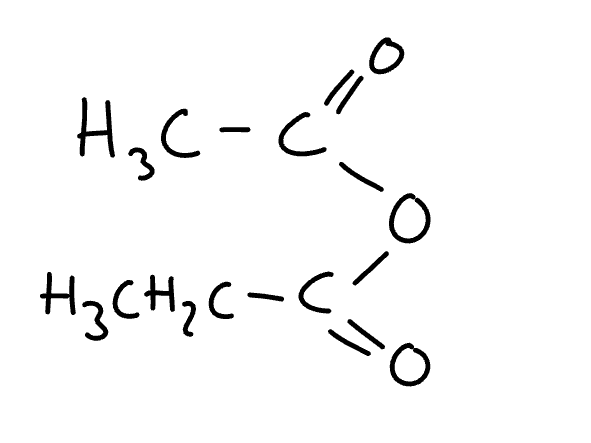
name the molecule
ethanoic propanoic anhydride
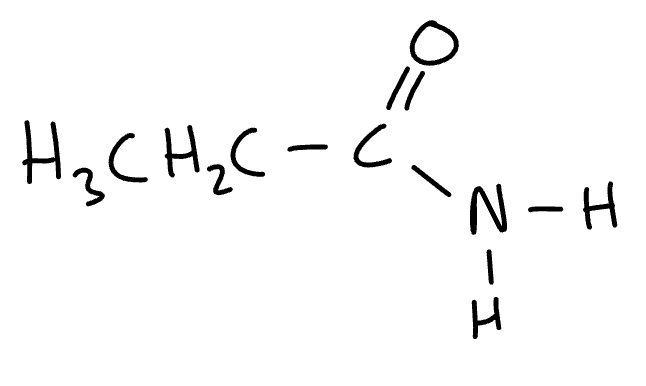
name the molecule
propanamide
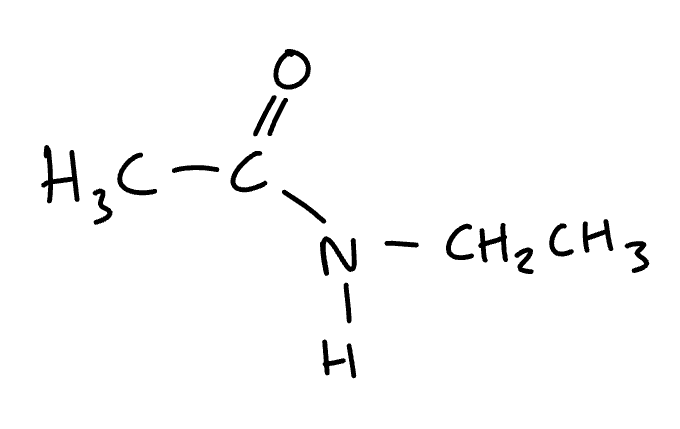
name the molecule
N-ethyl ethanamide
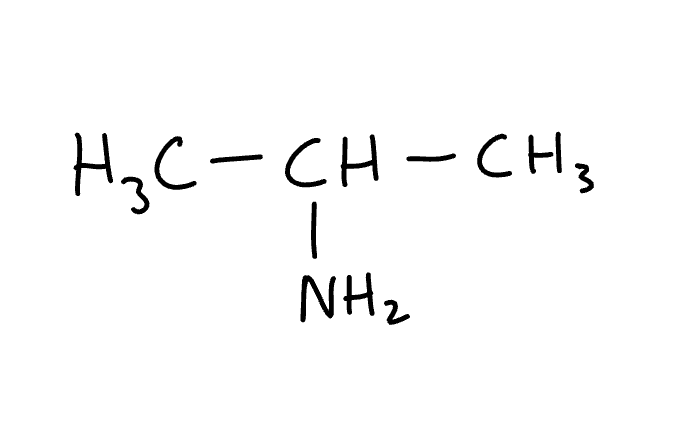
name the molecule
2-aminopropane