FINN11B - Financial Markets
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
what are FINANCIAL MARKETS?
It refers to channels or places where funds and financial instruments such as stocks, bonds and other securities are exchanged between willing individuals and/or entities.
what are FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS?
These are organizations that provide financial services to customers. They include banks, credit unions, insurance companies, investment firms, and more. They facilitate financial transactions, lending, investments, and risk management.
what is the FINANCIAL SYSTEM?
It permits an efficient method to move funds between entities that have funds and entities that need funds and is a regular, time-efficient, and cost-effective link between fund providers and fund demanders
what is FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT?
It is an important process to ensure that profit and wealth is maximized.
what is the LIFE-BLOOD of the company?
Finance
what are the SOURCES OF WEALTH?
Labor (Salary or Wage)
Capital (Interest)
Land (Rent)
Entrepreneurship (Profit)
what is LABOR (salary or wage)? (As a source of wealth)
It refers to the compensation paid to employees for their work. It is either a fixed amount paid regularly or is typically paid hourly or daily.
what is Capital (Interest)? (As a source of wealth)
It can either be financial or industrial. The person who invests is called an investor. As the venture is realizing good returns, this will earn interest.
What is LAND (rent)? (As a source of wealth)
It is a payment made by a tenant to a landlord in exchange for the use of land or property.
what is ENTREPRENEURSHIP (profit)? (As a source of wealth)
It will eventually be accumulated, and investment will be diversified as it grows employing new breed of individuals and labor force and the cycle goes on.
what does the french word “Finer” mean? (Origin of Finance)
to end and settle a debt
what is the FINANCIAL SYSTEMS COMPOSED OF?
It is is composed of network of interrelated systems of financial markets, intermediaries and services.
who are the FUND PROVIDERS?
It is the households, companies, and government agencies who have available funds because they spend less than their income.
who are the FUND DEMANDERS?
It is the households, companies, and government agencies that have fund shortages because of deciding to spend more than their income.
what is DIRECT FINANCING?
It is when the borrower-spenders borrow and deal directly with lenders through selling financial instruments (or securities).
what is INDIRECT FINANCING?
It is when the borrowing activity between both parties still happens indirectly through the intervention of a financial intermediary.
what is FINANCE?
It is the application of economic principles to decision-making that involves the allocation of money under conditions of uncertainty.
what does EFFICIENT CAPITAL ALLOCATION mean? (Importance of Financial System)
It occurs when funds are invested in productive investments that yield return for the fund providers and fund demanders.
what does ECONOMY GROWTH mean? (Importance of Financial System)
It is when fund providers can charge interest on the fund they are willing to loan while fund demanders can earn from their investment.
what does ENHANCES WELFARE OF INDIVIDUAL CONSUMERS mean? (Importance of Financial System)
It is the immediate access to funds allowing them to purchase things as they prefer.
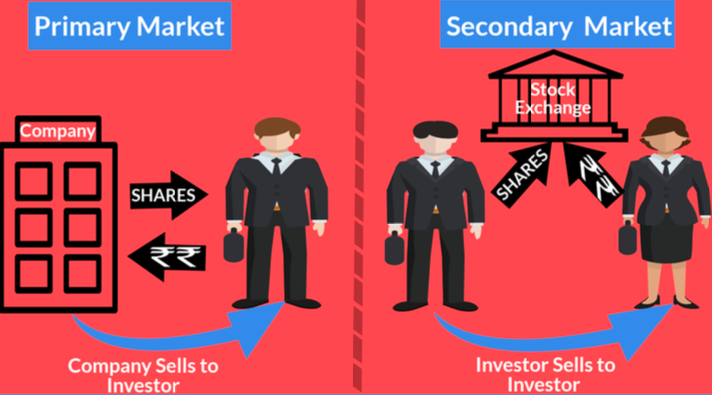
what is the difference between Primary Market & Secondary Market?
Primary Market: Company to Investor
Secondary Market: Investor to Investor
what are the ELEMENTS OF THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM?
Lenders & Borrowers
Financial Intermediaries
Financial Instruments
Financial Markets
Regulatory Environment
Money Creation
Price Discovery
who are the LENDERS & BORROWERS?
They are the most essential stakeholders that make up the foundation of a transaction in the financial system. Without these two parties, the financial system will not exist.
what are FINANCIAL INTERMEDIARIES?
It is a special type of financial entity that acts as a third part to facilitate the borrowing activity between lenders and borrowers.
what are FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS?
It is a medium of exchange of contractual obligation of a party, where such contract can be traded.
what are the TWO TYPES OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS?
Cash and Derivative Financial Instruments
where are CASH FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS exchanged?
Money Market
where are DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS traded?
Capital Market
what is REGULATORY ENVIRONMENT?
It is the governance body to ensure that the transactions that occur within the financial systems complies with the laws and regulations.
what did the financial system create?
It is used to either be reinvested or earned out from the system flows - Money
what is PRICE DISCOVERY?
It is the process of determining or valuing the financial instrument in the market.
what are DERIVATIVES?
They are financial contracts wherein they have conditions (i.e. the price and the date products will be sold). It can also be considered a gamble due to price fluctuations.
what are the THREE MAJOR ECONOMIC FUNCTIONS OF FINANCIAL MARKETS?
Price Discovery
Liquidity
Reduction in Transaction Costs
what is LIQUIDITY?
It refers to the ease of converting assets into cash without affecting their price. It measures how quickly an asset can be bought or sold in the market.
what are TRANSACTION COSTS?
These are the costs incurred of parties' transaction to trade a financial instrument.
what are the TWO TYPES OF TRANSACTION COSTS?
Search Costs and Information Costs
what are SEARCH COSTS?
These are costs incurred to look for financial instruments that can be purchased or sold by a party.
what are EXPLICIT SEARCH COSTS?
These are expenses needed to advertise intent to purchase or sell a financial instrument.
what are IMPLICIT SEARCH COSTS?
These include value of time consumed to look for a counterparty for the transaction.
what are INFORMATION COSTS?
These are costs related in evaluating investment characteristics of a financial instrument.
what are the TWO TYPES OF FINANCIAL MARKETS based on INSTRUMENTS TRADED?
Money Market and Capital Market
what are MONEY MARKETS?
It is the sector of the financial system where financial instruments that will mature or be redeemed in one year or less from the issuance date are traded.
what are CAPITAL MARKETS?
is the sector of the financial markets where financial instruments issued by governments and corporations that will mature beyond one year from issuance date (long-term) are traded.
what are the TWO TYPES OF FINANCIAL MARKET based on MARKET TYPE?
Primary Market and Secondary Market
what are PRIMARY MARKETS?
It is a type of financial market wherein fund demanders such as corporation or a government agency raise funds through new issuances of financial instruments e.g. bonds and stocks
what are SECONDARY MARKETS?
It refers to the market wherein the securities issued in primary market are subsequently traded i.e. resold and repurchased (secondhand).
what are the FOUR TYPES OF ISSUE METHODS?
Public Offering
Auction
Private Placement (Limited Public Offer)
Tap Issue
what is PUBLIC OFFERING?
It occurs when securities are offered for sale to the general public.
what is AUCTION?
It is a public sale in which goods or property are sold to the highest bidder.
what is PRIVATE PLACEMENT (LIMITED PUBLIC OFFER)?
It occurs when the issuer looks for a single investor, an institutional buyer or group of buyers to purchase the whole securities issuance instead of offering it to the general public .
what is TAP ISSUE?
It occurs when issuers are open to receive bids for their securities at all times.