Lecture 14: Actin Cell Migration
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Actin
- determines cell shape
- cell contraction and motility (migration) in non-muscle cells
- muscle contraction (in muscle cells)
- participates in cell-cell and cell-matrix junctions
- participates in cytokinesis
Actin monomers
- Globular actin (G-actin) that bind to ATP/ADP, but can join a filament when bound to ATP.
Actin filaments
- F-actin - 2 parallel protofilaments of G-actin form a right-handed helix, G-actin bound to ATP assembles at the dynamic + end to form an actin microfilament
- Undergo dynamic remodeling:
-Plus "barbed" end - growth occurs at this end
- Minus "pointed" end - loss occurs at this end
Treadmilling of actin filaments
- Actin filaments can maintain a consistent length while actively being remolded.
- Occurs when G-actin- ATP is at the critical concentration
Kinetics of F-actin assembly in vitro
- 2-Actin monomers are added at the + end only.
- 3 - Action monomers are lost from the - end.
- 4-5- Equal numbers ofactin monomers areadded at the + end asare lost from - end(steady state =treadmilling)
Actin ability to assemble into different shapes
- Through interaction with actin binding proteins actin is able to assemble into different configurations in different cells and indifferent regions of the same cell
Actin Binding Proteins (ABPs)
- Regulate assembly of actin monomers.
- Nucleating proteins
- Monomer-sequestering proteins
- End-blocking (capping) proteins
- Monomer-polymerizing proteins.
- Actin filament depolymerizing proteins
- Cross-linking proteins
- Filament-serving proteins
- Membrane-binding proteins
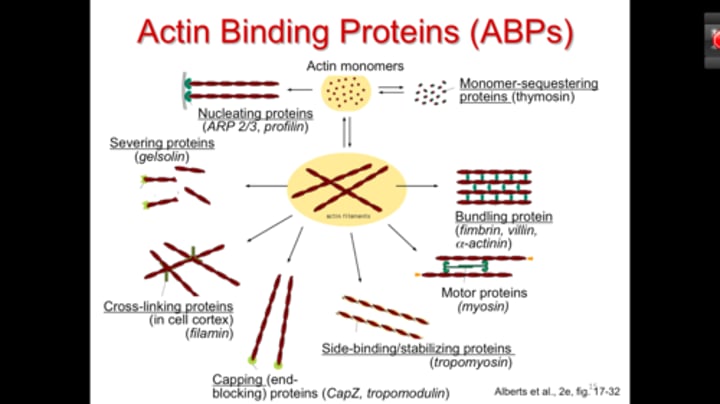
Nucleating Proteins (ABP)
- Provide a template for adding actin monomers
Monomer-sequestering proteins
- Bind to actin-ATP monomers and prevent them from polymerizing
End-blocking (capping) proteins
- Regulate the length of actin filaments
Monomer-polymerizing proteins
- Promote the growth of actin filaments
Actin filament depolymerizing proteins
- Bind actin-ADP subunits at the minus end promoting rapid turnover of actin filaments
Cross-linking proteins
- Alter the 3D organization of actin filaments
Filament-serving proteins
- Shorten filaments and decrease cytoplasmic viscosity
Membrane-binding proteins
- Link contractile proteins to plasma membrane
Myosin II motor protein
- The head binds to the actin
- The head is an ATP dependent motor that interacts with the actin filaments
- The tail binds to other myosin molecules (AKA the cargo)
- Myosin II heavy chains assemble into a bipolar myosin filament
- Actin filaments slide along myosin filaments to mediate cellular contraction in non-muscle cells
Cell migration
- The movement of cells from site of origin to final location
- AKA cell location
Steps in cell migration
- Step 0: Polarization
- Step 1: Protrusion
- Step 2: Adhesion
- Step 3: Contraction
- Step 4: Disassemble
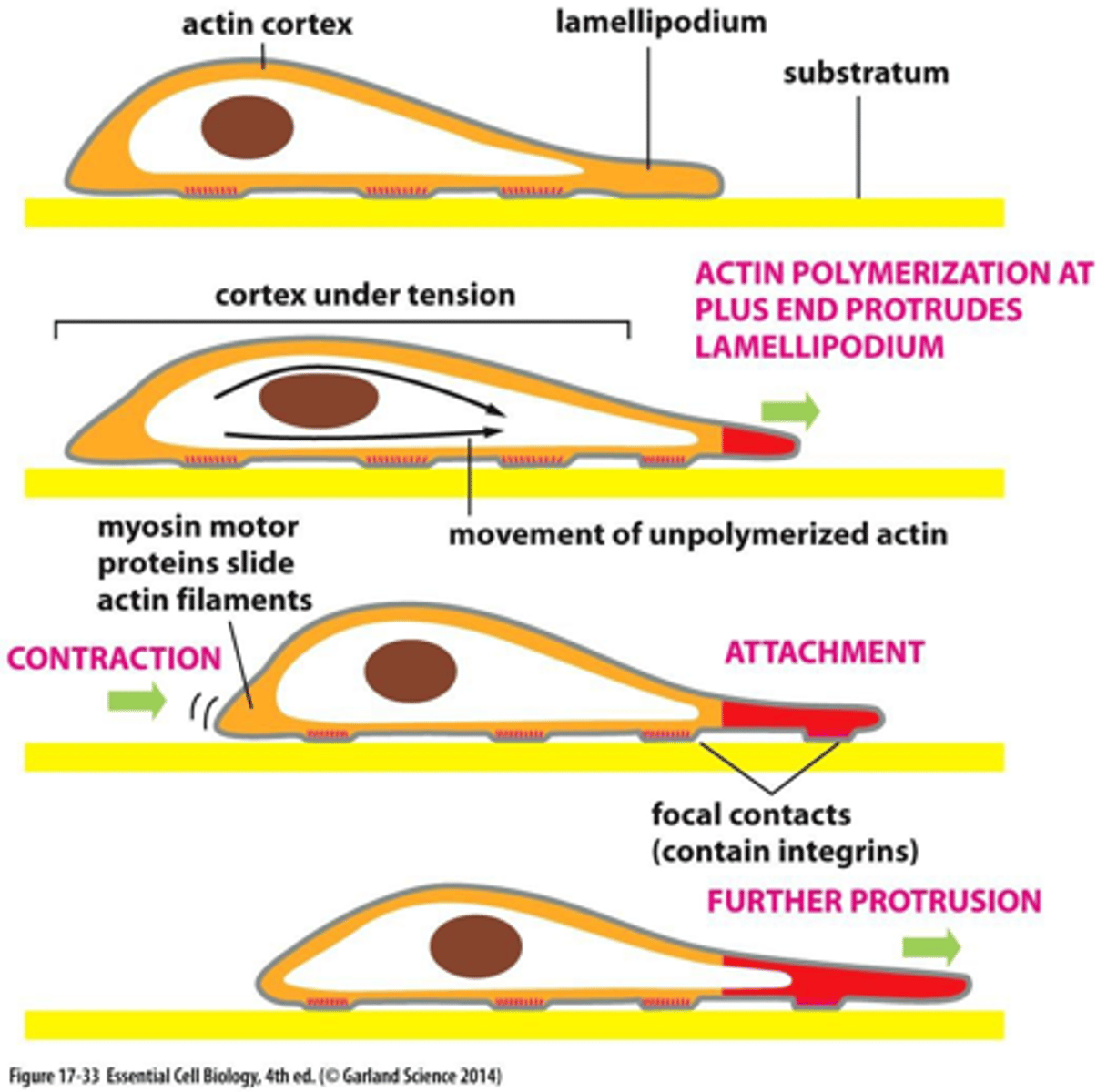
Step 0: Polarization
- A chemotactic (or other) initiating signal establishes direction of movement
Step 1: Protrusion
- Protrusion of a lamelipodium is actin-driven.
- Direction of cell movement
Step 2: Adhesion
- Cell forms new attachments with the substratum under the lamellipodia.
- Cells form adhesions with the substrate.
Step 3: Contraction
- The cell body is pulled forward by actin-myosin mediated contraction.
Step 4: Disassemble
- The force pulling on adhesions towards the rear of the cell causes them to disassemble.
Microtubules - Summary
- Subunits incorporated into polymer: GTP alpha-beta tubulin heterodimer.
- Preferred site of incorporation: + End (Beta tubulin)
- Polarity: Yes
- Enzymatic activity: GTPase
- Motor Proteins: Kinesins, Dynein
- Major group of associated proteins: MAPs
- Structure: Stiff, hollow tube
- Dimensions: 25 nm outer diam.
- Distribution: All Eukaryotes
- Primary Functions: Support, Intracellular Transport, Cell Organization
Intermediate Filaments - Summary
- Subunits incorporated into polymer: Various globular proteins
- Preferred site of incorporation: Internal
- Polarity: No
- Enzymatic activity: None
- Motor Proteins: None
- Major group of associated proteins: Plakins
- Structure: Tough, ropelike fibers
- Dimensions: 10 nm diam.
- Distribution: Animals
- Primary Functions: Structural Support
Actin Filaments - Summary
- Subunits incorporated into polymer: ATP - actin monomers
- Preferred site of incorporation: + End (Barbed)
- Polarity: Yes
- Enzymatic activity: ATPase
- Motor Proteins: Myosins
- Major group of associated proteins: Actin-binding proteins (ABPs)
- Structure:: Flexible, helical filament
- Dimensions: 8 nm diam.
- Distribution: All Eukaryotes
- Primary Functions: Motility, Contractility.