IB Computer Science HL Paper 1 Topic 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:08 PM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
1
New cards
Network
* A group of computers and other computing hardware devices linked together through communication channels to enable communication between users
2
New cards
Bus topology
Computer network in which a bus (cable) connects all devices together through a common cable
3
New cards
Check digit
Extra digit added to numerical data that is used to check data integrity after input, transmission, storage and processing
4
New cards
Data packet
* Portion of a message that is transmitted through a network
* Contains data such as check digits and destination address
* Contains data such as check digits and destination address
5
New cards
Handshaking
Exchange of predetermined signals to signify that a connection has been established between two systems
6
New cards
Protocol
* International rules that ensure the safe transfer of data between systems
7
New cards
Hub
* Network connection point for devices
* Data arriving at a hub is copied and sent to all the devices on the network
* Data arriving at a hub is copied and sent to all the devices on the network
8
New cards
What does TCP / IP stand for?
Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol
9
New cards
TCP / IP
* Standard communications protocol used to connect hosts on the Internet
10
New cards
Server
* A computer system that serves as a central repository of data and programs and is shared by clients
* Role is to await and fulfill requests from client programs
* Role is to await and fulfill requests from client programs
11
New cards
Client
* A piece of computer hardware or software that accesses a service made available by a server
12
New cards
Network Types
* Local Area Network (LAN)
* Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
* Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)
* Wide Area Network (WAN)
* Storage Area Network (SAN)
* Internet
* Extranet
* Virtual Private Network (VPN)
* Personal Area Network (PAN)
* Peer-To-Peer (P2P)
* Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
* Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)
* Wide Area Network (WAN)
* Storage Area Network (SAN)
* Internet
* Extranet
* Virtual Private Network (VPN)
* Personal Area Network (PAN)
* Peer-To-Peer (P2P)
13
New cards
Local Area Network (LAN)
* Computer network where all the connected computers are within a limited geographical area (e.g school, office, home)
* Connection may be through cables and / or microwave transmission
* Connection may be through cables and / or microwave transmission
14
New cards
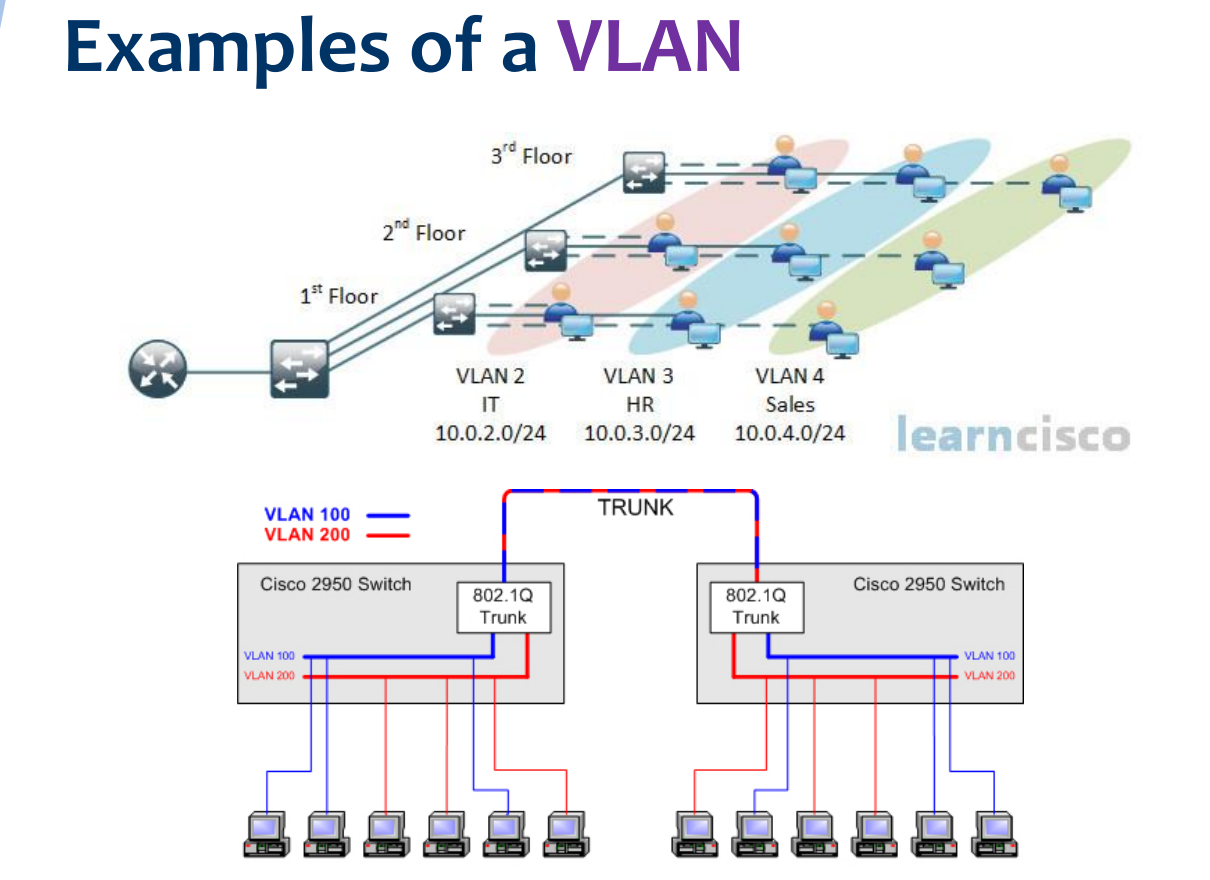
Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)
* A logical group of network devices that appear to be on the same LAN despite their geographical distribution
* Allows a group of network devices to communicate in a simulated environment as if they exist in a single LAN
* Allows a group of network devices to communicate in a simulated environment as if they exist in a single LAN
15
New cards
Pros of VLAN
* Scalability
* Security
* Ease of network management
* Can quickly adapt to changes in network requirements and relocation of workstations and server nodes
* Security
* Ease of network management
* Can quickly adapt to changes in network requirements and relocation of workstations and server nodes
16
New cards
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
* A wireless distribution method for two or more devices that use high-frequency radio waves, and often includes an Internet access point
* Allows users to move around the coverage area while maintaining an Internet connection
* Allows users to move around the coverage area while maintaining an Internet connection
17
New cards
Wide Area Network (WAN)
* Computer network where all the connected computers are in a larger geographic are than served by a LAN or MAN (metropolitan area network)
* Internet is a WAN
* Internet is a WAN
18
New cards
Peer-To-Peer (P2P)
* A network model in which some computers or hardware devices exchange files (e.g. BitTorrent)
* No central server - equal client system
* Supports file sharing or collaborative work
* No central server - equal client system
* Supports file sharing or collaborative work
19
New cards
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
* Uses the Internet to allow people to access the network remotely
* Provides a secure connection by encrypting the network (IPSEC protocol) - of hacked data will not be understood
* Uses tunneling protocols - allows the data to be hidden while travelling across the Internet
* Provides a secure connection by encrypting the network (IPSEC protocol) - of hacked data will not be understood
* Uses tunneling protocols - allows the data to be hidden while travelling across the Internet
20
New cards
Extranet
* A controlled private network
* Allows people to gain information about a specific company without granting access to the entire network
* The specific LAN or WAN is the extranet, and can only be accessed by people with the required credentials e.g usernames / passwords
* Allows people to gain information about a specific company without granting access to the entire network
* The specific LAN or WAN is the extranet, and can only be accessed by people with the required credentials e.g usernames / passwords
21
New cards
Personal Area Network (PAN)
* A network that interconnects devices centred around an individuals workspace - a LAN that only supports one person
* Covers a very short range
* Covers a very short range
22
New cards
Pros and cons of wireless networks
Proa
* Ease of use for mobile users, as they can work in many different locations
* Less time, space and cost due to lack of need for cables
Cons
* Security issues, as wireless transmissions are easily intercepted
* Ease of use for mobile users, as they can work in many different locations
* Less time, space and cost due to lack of need for cables
Cons
* Security issues, as wireless transmissions are easily intercepted
23
New cards
Voice Over IP (VoIP)
* Audio and video stream transmitted over the Internet, broadband internet connection needed
* Can be integrated in an office desk computer
* Can be integrated in an office desk computer
24
New cards
Layers in the seven layer Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model
* Application
* Presentation
* Session
* Transport
* Network
* Data Link
* Physical
* Presentation
* Session
* Transport
* Network
* Data Link
* Physical
25
New cards
Advantages of using layers in communication
* Easy to manage
* Greater understanding of each layer
* Common language for each layer
* Makes protocol design easier
* Greater understanding of each layer
* Common language for each layer
* Makes protocol design easier
26
New cards
Layers in TCP / IP protocol model
* Network access
* Internet
* Transport
* Application
* Internet
* Transport
* Application
27
New cards
Benefits that protocols provide
* Data integrity - information has not been changed / corrupted
* Source integrity - identity of the sender is validated
* Error checking / correction
* Source integrity - identity of the sender is validated
* Error checking / correction
28
New cards
Bandwidth
* The theoretical speed of data in a medium
* Depends on the signalling technique used and the physical properties of the medium
* Depends on the signalling technique used and the physical properties of the medium
29
New cards
Throughput
* The actual transfer rate of data
* Affected by:
* Bandwidth of the network
* Distance
* Amount of users
* Affected by:
* Bandwidth of the network
* Distance
* Amount of users