add maths things to remember
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
f(2x)
horizontal shrink by 1/2
2f(x)
vertical stretch by 2
y=-f(x)
reflection in x axis
y=f(-x)
reflection in y axis
f(x)+b
change in y by b
f(x+a)
change in x by -a
factor theorem
if (x-a) is a factor of the polynomial f(x), then x=a is a root/solution of the equation f(x)=0
remainder theorem
If a polynomial f(x) is divided by (x-a), the remainder is f(a)
quadratic formula
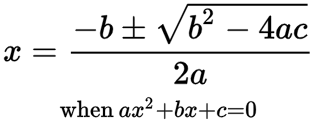
binomial expansion
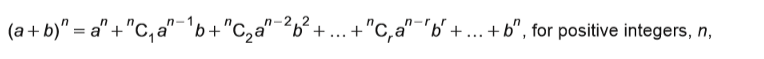
nCr =
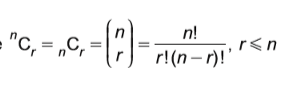
midpoint =
(x1+x2/2, y1+y2/2)
distance between 2 points
√((x2 - x1)² + (y2 - y1)²)
equation of straight line with gradient m through point (x0, y0)
y-y0=m(x-x0)
tanθ =
sinθ/cosθ
sin^2θ + cos^2θ =
1
cosine rule
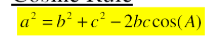
gradient of turning points =
0
if d2y/dx2 > 0, turning point is
minimum
if d2y/dx2 < 0, turning point is
maximum
are under curve between x=a and x=b is
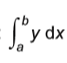
trapezium rule
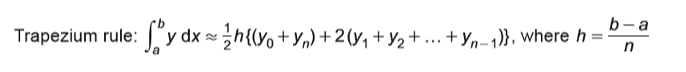
SUVAT IF ACCELERATION IS CONSTANT
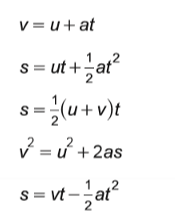
kinematics if acceleration is not constant
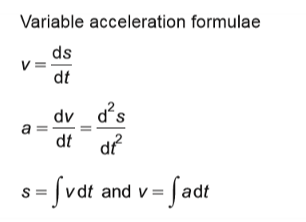
x=a^n
loga(x) = n
loga xy =
logax + logay
loga x/y =
logax - logay
loga x^m =
m logax
nPr
n!//(n-r)!
nCr
n!/r!(n-r)!