parasitology
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
parasite
smaller organism that lives on or in and at the expense of a larger organism called the host
endoparasites
parasites within the bodies of hosts
ectoparasites
live on the external surface of host or in the skin
obligate parasites
parasites that always require a host
facultative parasites
organisms that are parasites only if given the opportunity
definitive host
host in whic the adult or sexually reproductive processes of the parasite occur
intermediate host
host in which there is required development of intermediate or larval stages
paratenic host / transport host
host infected by a parasite that does not undergo any required development, though in may grow in size, the parasite should be transferable from paratenic host until it makes it’s way into the final host.
reservoir host
parasites may cycle other than the host we consider to be interest
vector
organism that transmits parasites directly from host to host
mechanical vector
transmits parasites without the need for the parasite to develop in the vector, syringes for ex.
biological vector
a vector that is required in the life cycle of the parasite
direct life cycle
infective stage is reached in the environment, no intermediate host
indirect life cycle
infective stage is reached in an intermediate host
prepatent period
period (days/months) form infection production of parasite offspring
zoonosis
a disease of animals transmitted to people
helminths
worms
3 groups of helminths
roundworms = nematodes
flukes = trematodes
tapeworms = cestodes
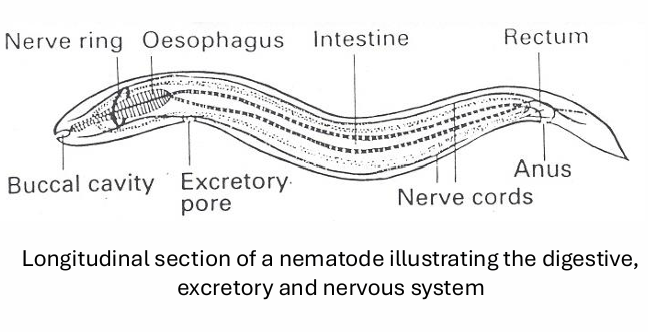
nematodes
elongated and tubular
have cuticle secreted by living cellular tegument
digestive tract like a tube
excretory/secretory products-released from specialized excretory or secretory organs through the cuticle or via oral and anal openings = host/parasite interactions
nervous and muscular tissues to allow for serpentine movement
males and females have specialized organs and structures to produce offspring, facilitating mating = genetic recombination
direct/indirect lifec cycles
example of direct nematodes
no intermediate host, egg to adult in one host
trichostrongyloid
example if indirect nematode
intermediate host, molluscan or annelid as intermediate host
metastrongyloid
superfamilies of nematodes are grouped based on what characteristics
morphology
life cycle
predilection site in host
nematodes / 4 superfamilies of the order stronglylida
strongyloidea
trichostrongyloidwa
ancylostomatoidea
metastrongyloidea
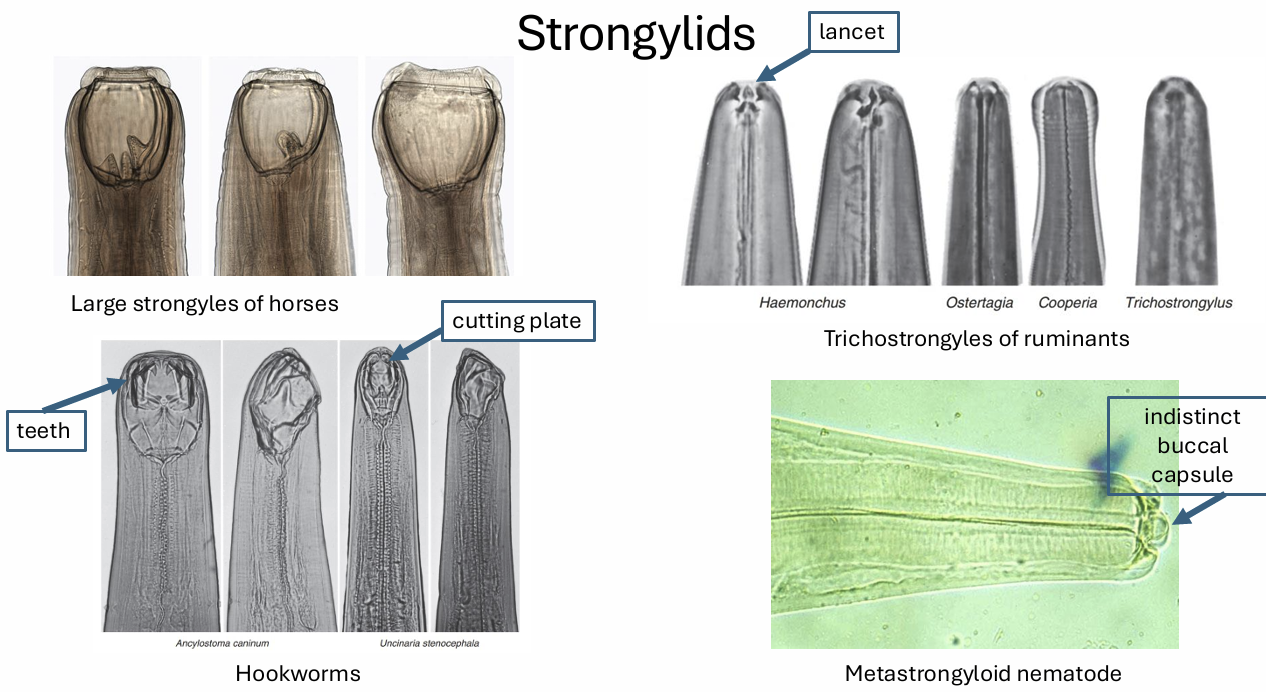
family strongyloidea
part of nematodes
large bowels strongylees of horses. nodular worms of ruminants, swine and primates
family trichostronglyloidea
abomasal and small intestinal hairworms of ruminants
family ancylostomatoidea
intestinal hookworms of diverse mammal
family metastrongyloidea
lungworms
families of nematodes that have direct life cycles
strongyloidea
trichostrongyloidea
ancylostomatoidea
families of nematodes that have indirect life cycles
metastrongyloidea
strongyloids
well developed, often have teeth
buccal cavity with plug of mucosa, blood suckling
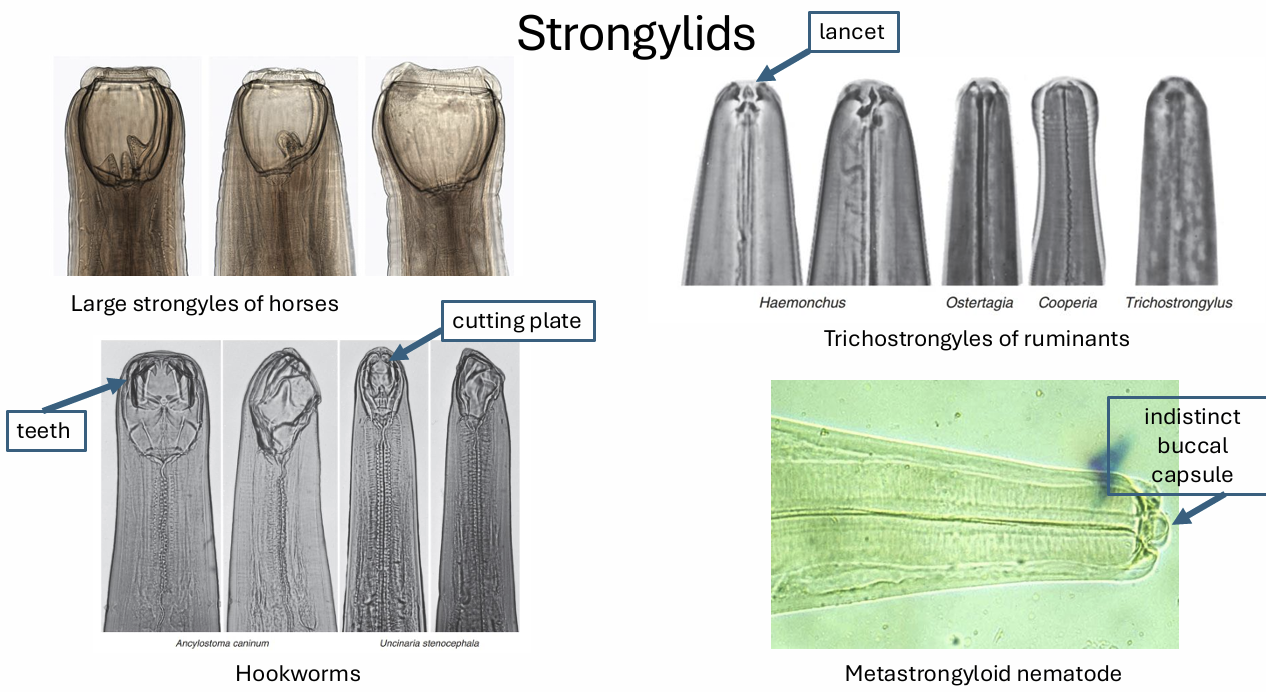
trichostrongyloids
have a tooth or lancet
may be blood suckling and damage mucosa
hook worms
have teeth or cutting plates on ventral
blood suckling mat cause anemia
metastrongyloid
no teeth
occupy space in respiratory tract
which family of strogylids are seen as larvae and not eggs on feces?
metastrongyloid
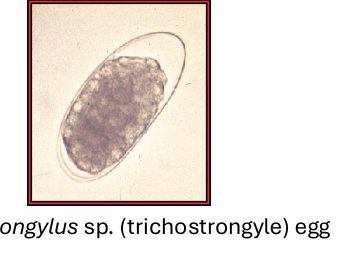
characteristics of strongyloid eggs
ellipsoidal
smooth surface
thin-shelled
contain an embryo in morula stage
cannot determine species or even genus, based on appearance of eggs
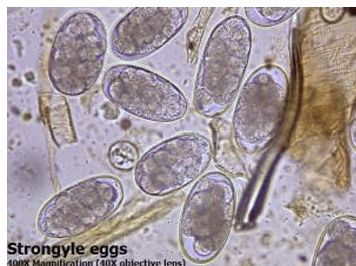
what type of strongylids eggs we see in horses?
strongyle type eggs
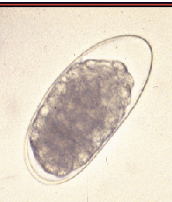
what type of strongylids eggs we see in ruminants?
trichostrongyle type eggs
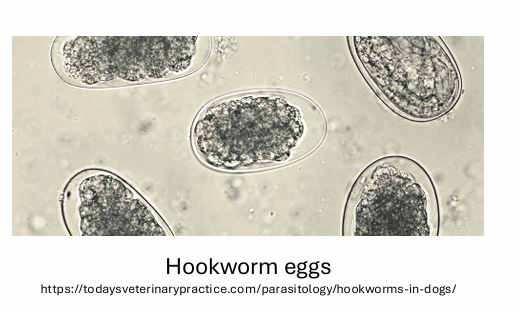
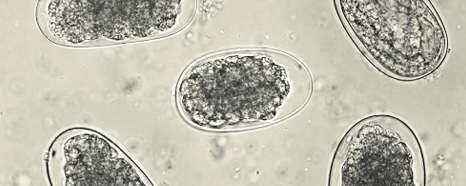
what type of strongylids eggs we see in dogs?
hookworms
strongyloides spp. /Order Rhabditoidea of nematodes contains the superfamily
rhabditoidea
order rhabditoidea/ superfamily rhabditoidea are found where in the host
small and delicate nematodes of the small intestine
free living and parasitic lifestyles
only females are parasitic
strongyloidess females reproduce via
asexual repro. via parthenogenesis
life cycle is direct
strongyloidess. spp (order rhabditoidea) infect hosts via
percutaneous
oral
tansmammary
transplacental
larval stages may migrate through lungs
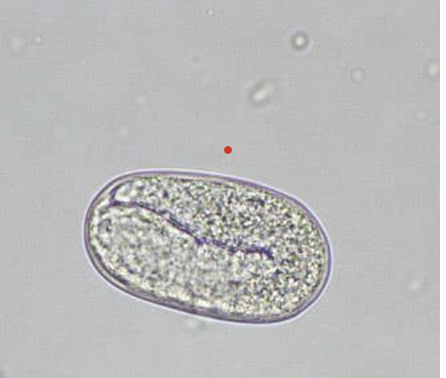
characteristics of strongyloides spp.
ellipsoidal
smooth surface
thin shelled
contain fully formed larva when pased in feces
order ascaridida of nematodes contain the superfamily
ascaridoidea (roundworms)

t/f ascarids are some of the largest nematodes parasites
true
ascarids are mainly found in the
small intestine
ascarids have wht type of cycle
direct
hepatotracheal migration
by ascarids
migrate through the liver and are carried through the bloodstream to the lungs
characteristics of ascarids eggs
round to slightly oval
surface may be pitted
thick walled
contain single cell\
whistanding of extreme temperatures, chemical and physical insults and remain inefective for years
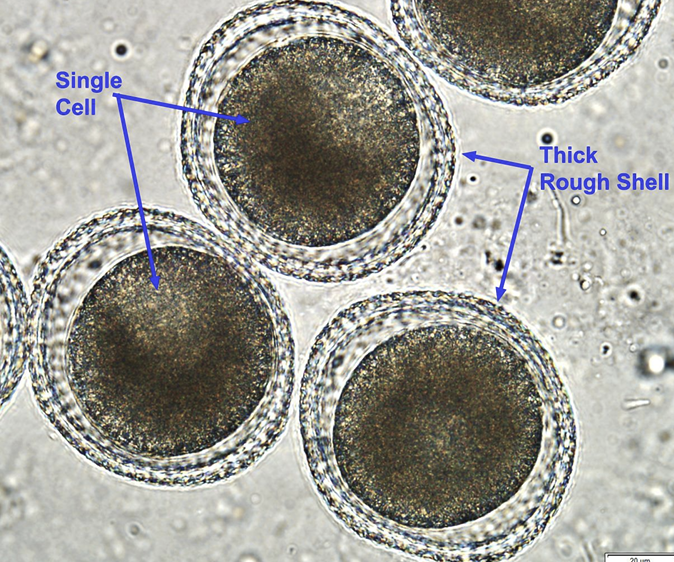
t/f ascarids eggs can remain inefective for years
true
females like to lay a lot of eggs and are a problem to erradicate
ascarids
order enoplida contains the superfamily
trichinelloidea
2 groups of Trichuris spp (order enoplida)
whipworms
capillarids
whipworms (trichuris spp) characteristics
resemble a fine hair like anterior region with a stout posterior region
whipworms are usually found in ____ and will cause____
wall of large intestine or cecum, blood flecked feces
capillarids characteristics
not whip like, but hardly ever seen
capillarids are usually found in
airways, intestinal tract, bladder
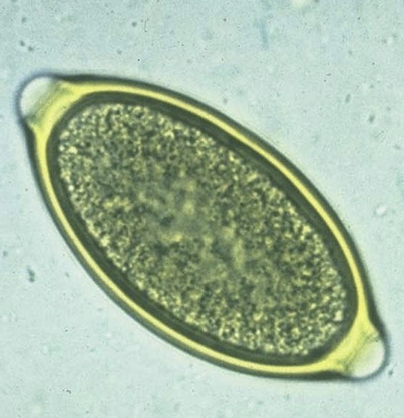
characteristics of whipworm eggs
football shaped
thick walled
symmetrical bipolar plugs
remain inefective for years
characteristics of capillarid eggs
similar to trichuris but bipolar plugs are assymetrical
can determine genus based on appearance of surface of shell wall
Order Oxyurida contains the superfamily
Oxyuroidea (pinworms)
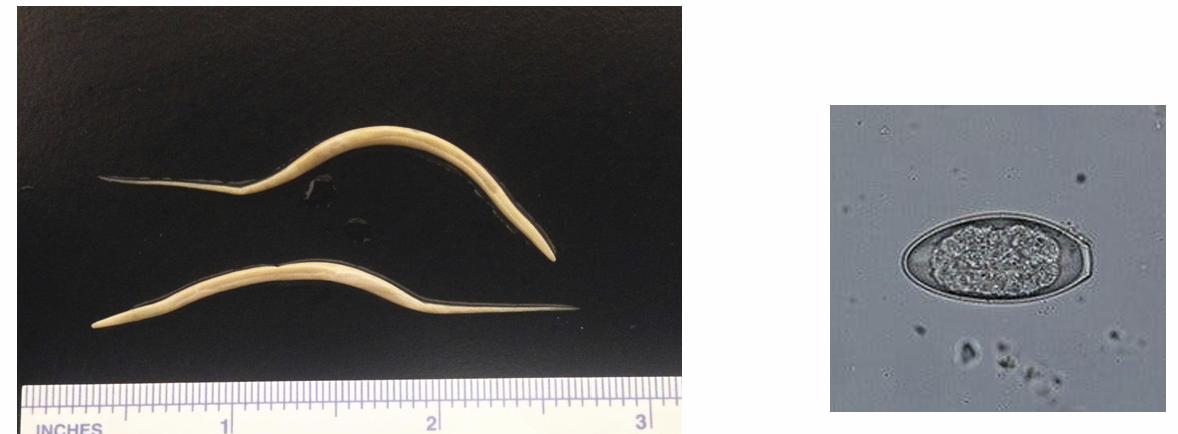
pinworm that infects horses_____ and where do they infect
oxyuris equi
large intestine
pinworms have what type of cycle?
direct life cycle
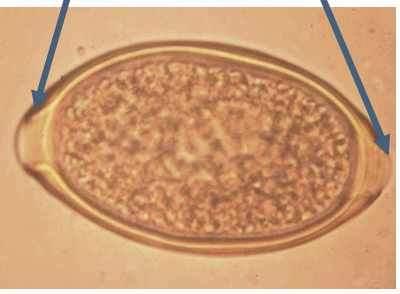
characteristics of pinworm eggs
flattened on one side, convex on the other
operculum on one end
may be embryonated
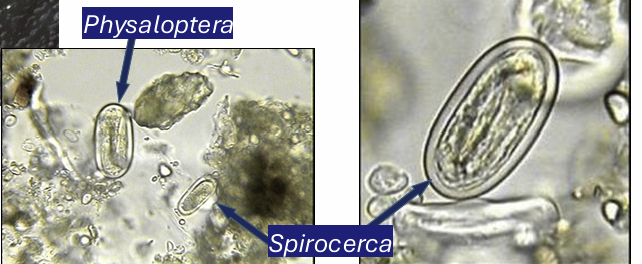
The order spirurida (spirurids) contains the superfamilies
physalopteroidea
spiruidea
habronematoidea
filaroi
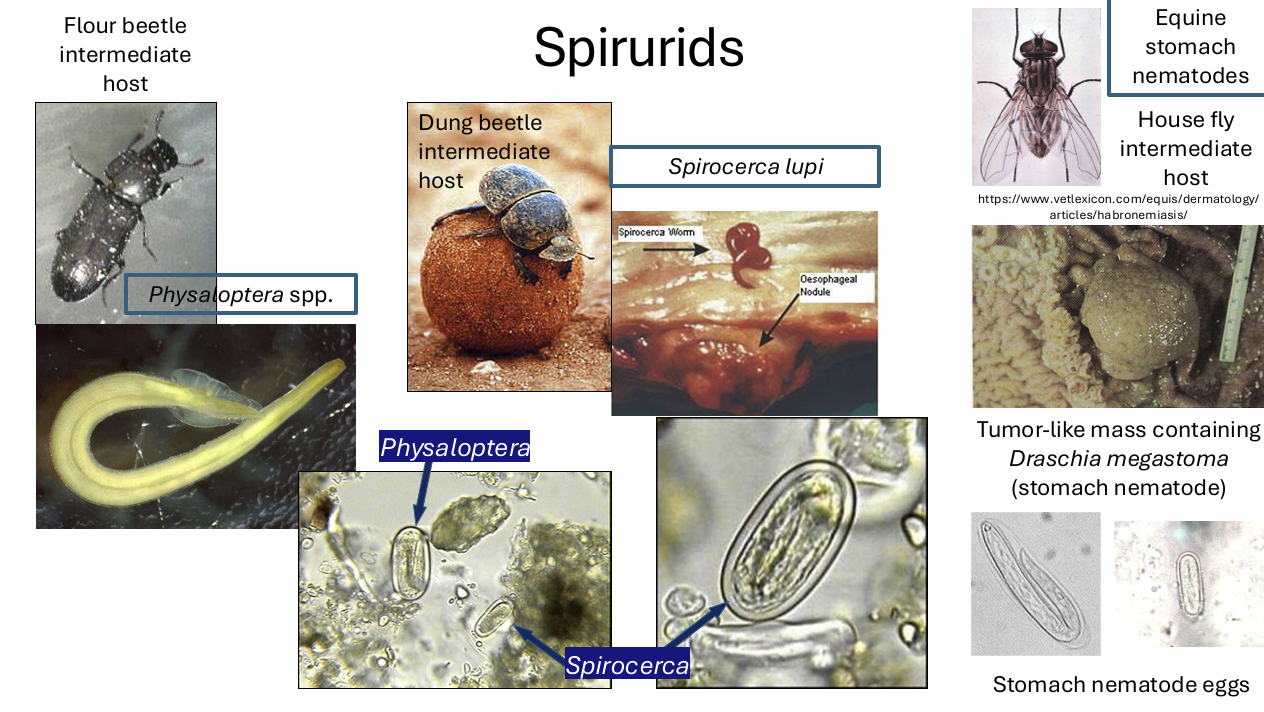
ex. of nematode of the family physalopteroidea from spirurids
physaloptera
ex. of nematode from the family spiruroidea
spirocerca lupi
ex. of nematode from the family habronematoidea
stomach nematodes of horses
the canine heartworm is part of the spirurids, which family?
filaroidea (dirofilaria immitis)
filarial nematodes such as canine heartworm release
microfilariae
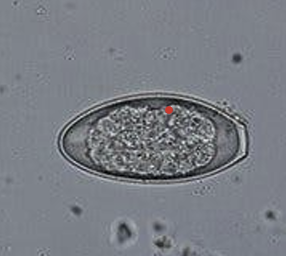
characteristics of spirurid egss
ellipsoidal
thick walled
embryonated
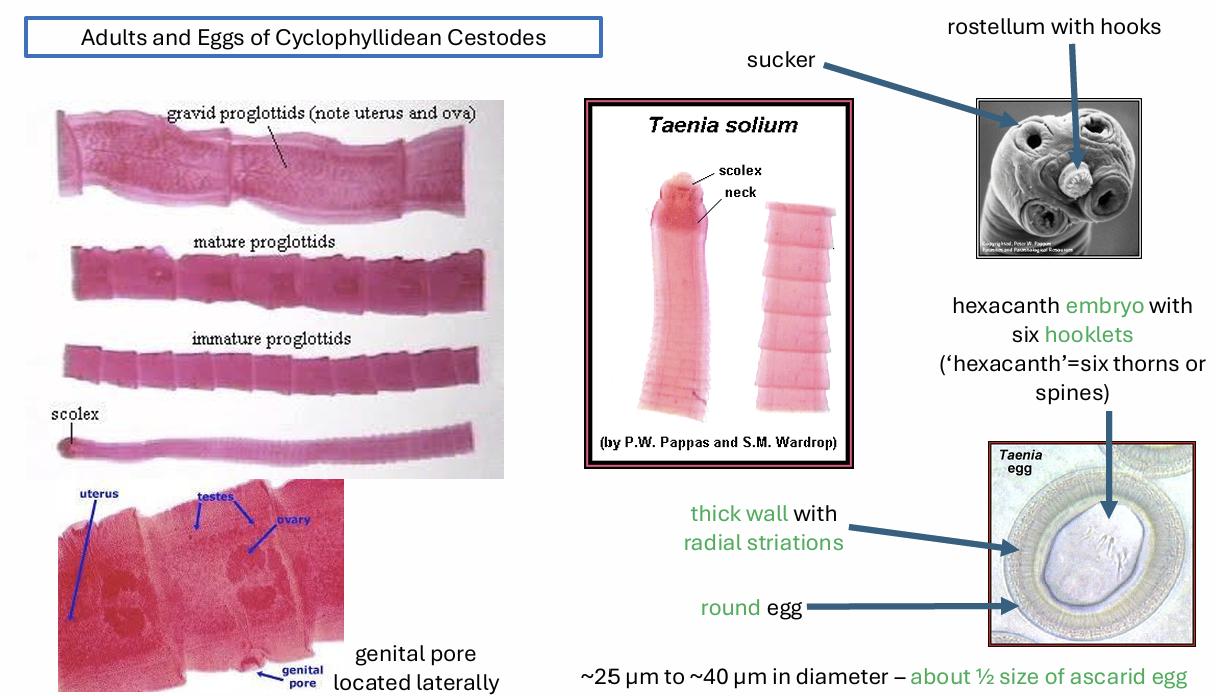
characteristics of cestodes (tapeworms)
flattened
no body cavity
strobila-chain of independent, progessively maturing reproductive units
scolex- immature segments
proglottids-more mature segments
tapeworms live in the
digestive tract
strobila
independent, progessively maturing reproductive units
tapeworms absorb nutrient via the
integument
t/f cestodes are hemaphroditic
true
cestodes have what type of life cycles?
indirect
2 groups of cestodes
cyclophyllidea
diphyllobothriidea
characteristics of cyclophyllidea
one intermediate host
non-motile egg, ingested by intermediate host
metacestode stages
the intermediate phase, called metacestode, of the group cyclophyllidea occurs in which animals
vertebrates
cysticercus
coenurus
strobilocercus
hydatid cyst
multilocular cyst
invertebrates, cysticercoid
diphyllobothriidea have how many intermediate hots?
2 intermediate hosts
eggs hatches in aquatics conditions
ciliated coracidium
the egg of the diphyllobothriidea is called coracidium
1 intermidiate host = copepod in crustraceans
2 intermediate host = mammal, amphibian, reptile, fish
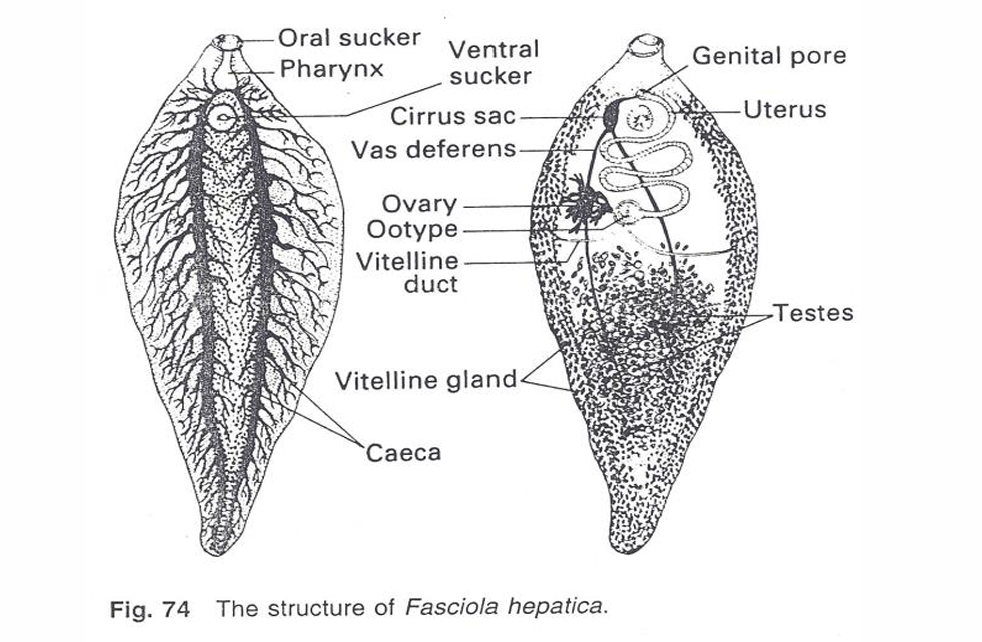
characteristics of trematodes (flukes)
falttened
no body cavity
external cuticle
excretory system = exretory pore
only opening to digestive tract is mouth = eat anbd excrete
nervous + muscles system
hermaphroditic
trematodes live mostly in
digestive tracts
bile ducts
lungs
arteries
oviducts
what lifecycles do trematodes have
indirect-asexual repro.
trematodes eggs
similar to diphylloborthriidean eggs
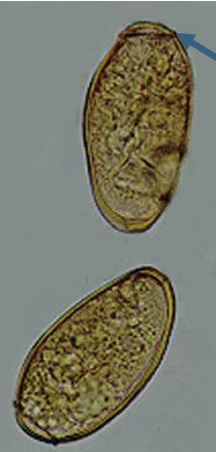
t/f trematodes can have 1 intermediate host or 2 intermdiated hosts
true