The Endocrine System
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
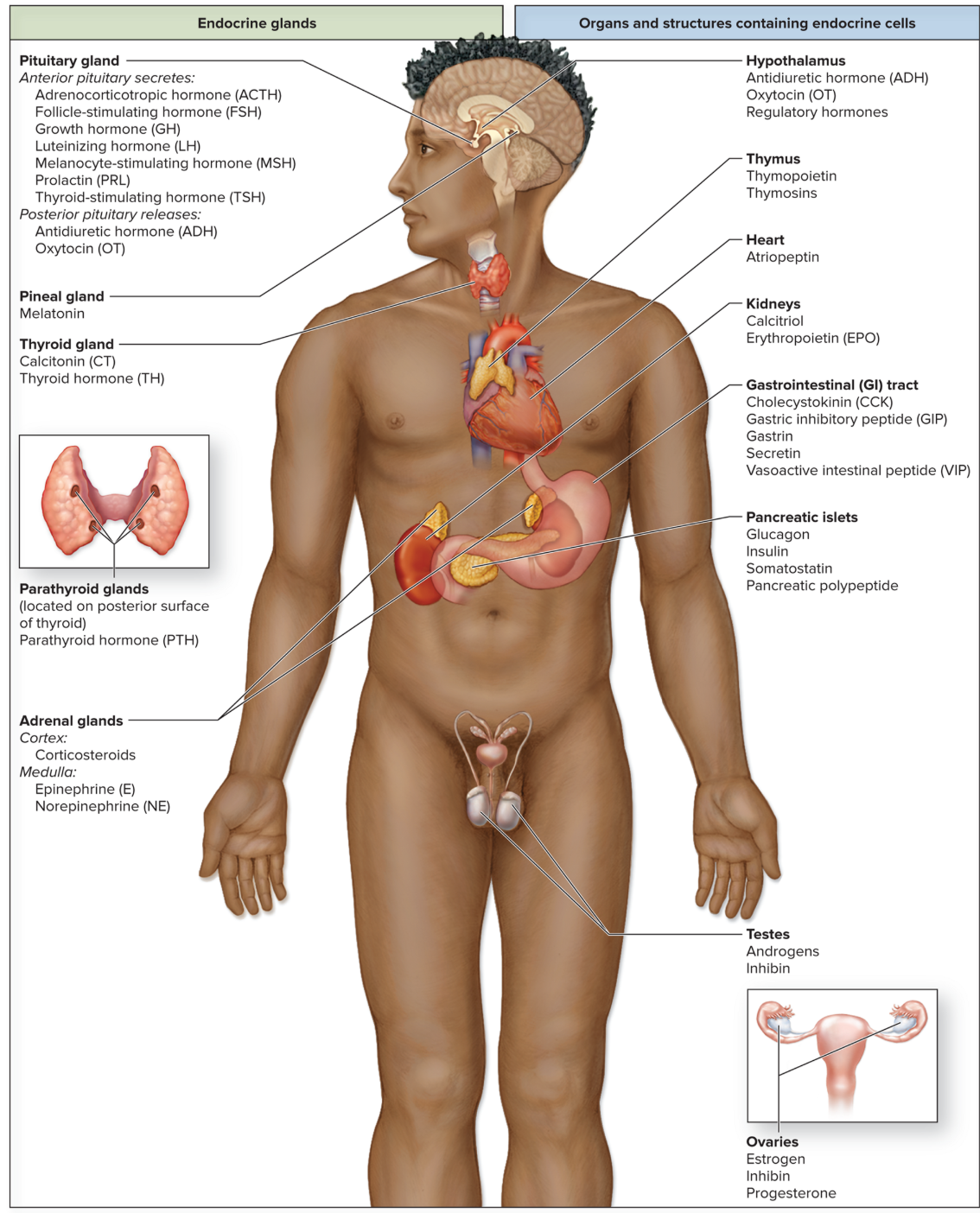
The Endocrine System
ductless glands
secrete directly into blood stream
produce hormones
action on other tissues/and or organs
→ target cells or target organs
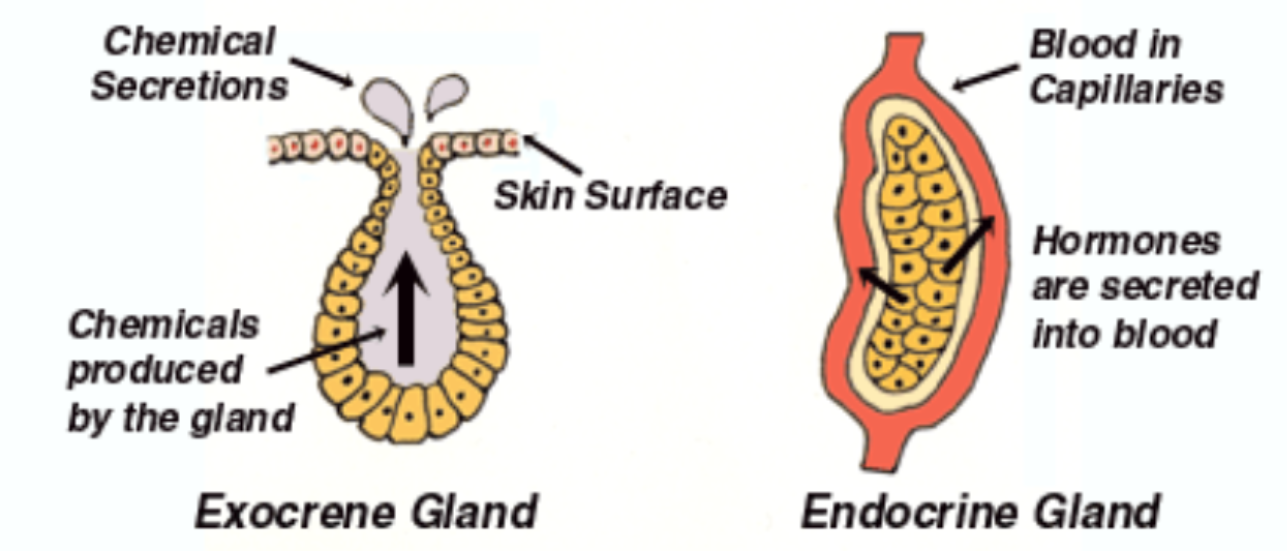
Difference between exocrine and endocrine glands
Exocrine Glands
release secretions into ducts (tubes) that carry their contents to other organs or outside the body
→ sweat glands (make sweat to cool body temp), salivary glands (produce saliva with enzymes for digestion), the pancreas (produces enzymes for digestion)
Endocrine Glands
secrete their products directly into the bloodstream
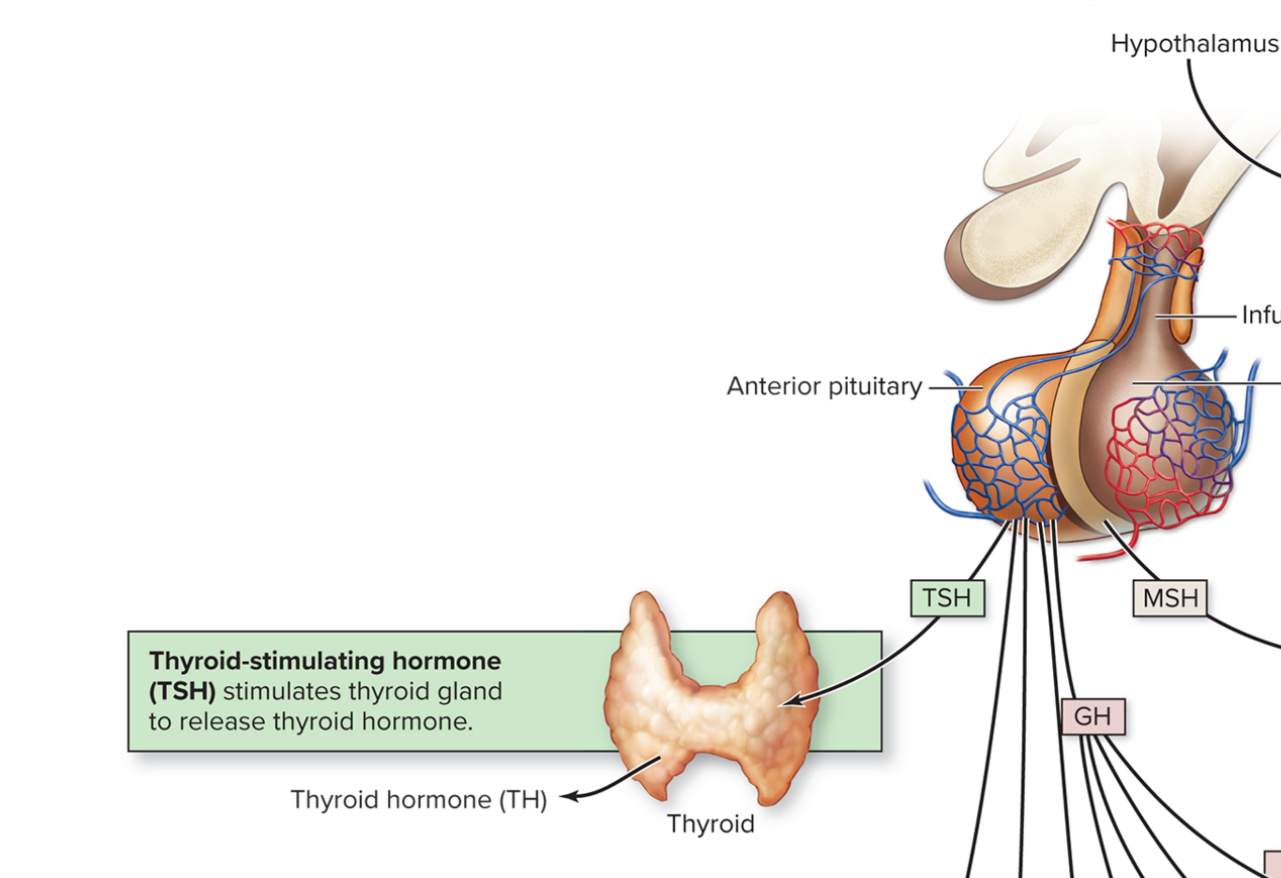
For example…What is TSH?
thyroid stimulating hormone (tropic hormone)
→ 1 endocrine gland stimulates another endocrine gland
comes from the anterior pituitary gland and stimulates the thyroid gland to release additional hormones
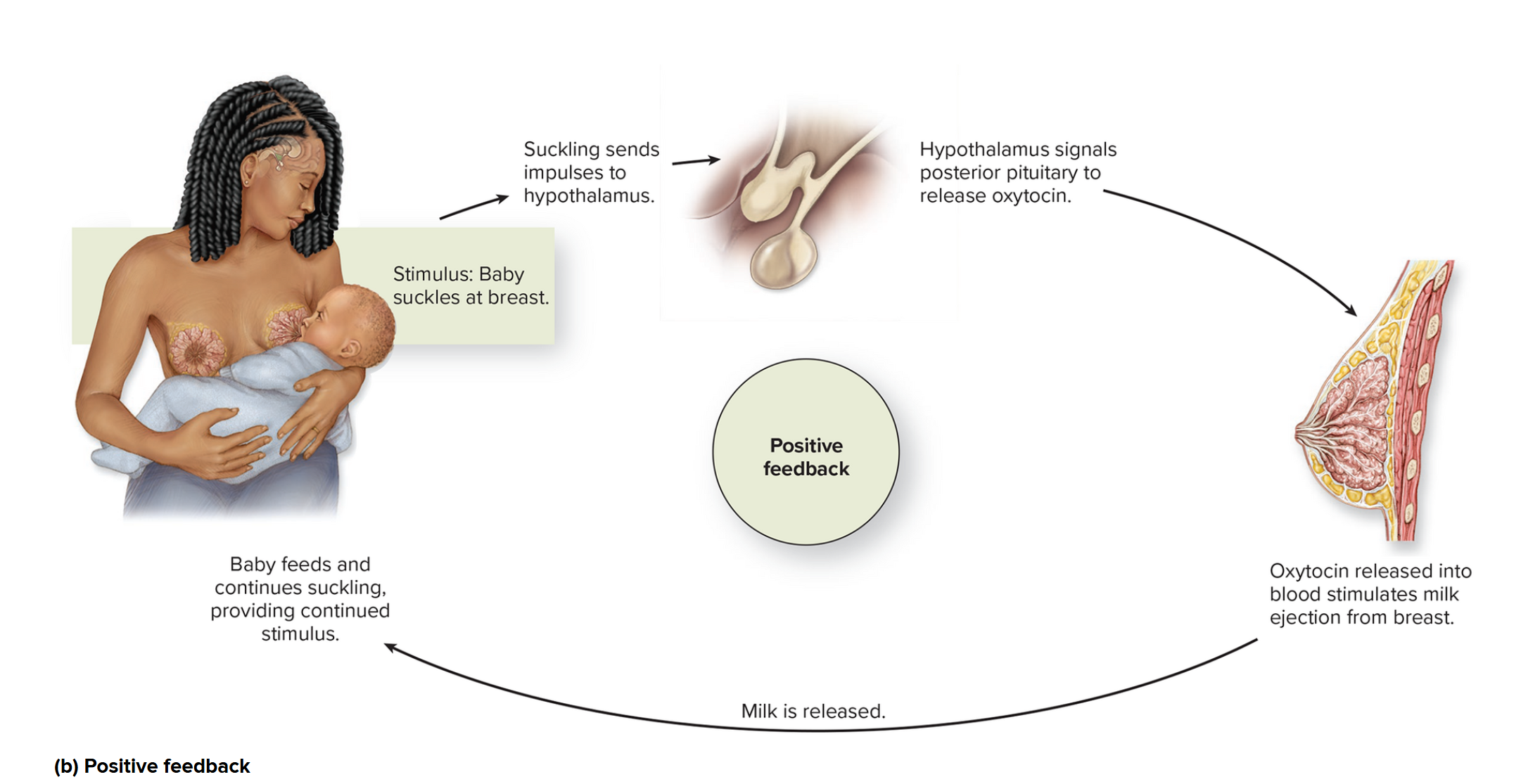
Positive Feedback
Hormone production results in increased hormone production → increased activity
suckling on mammary
oxytocin produced (released by posterior pituitary gland)
milk ejection
more suckling
more oxytocin
more milk ejection
stops when baby stops
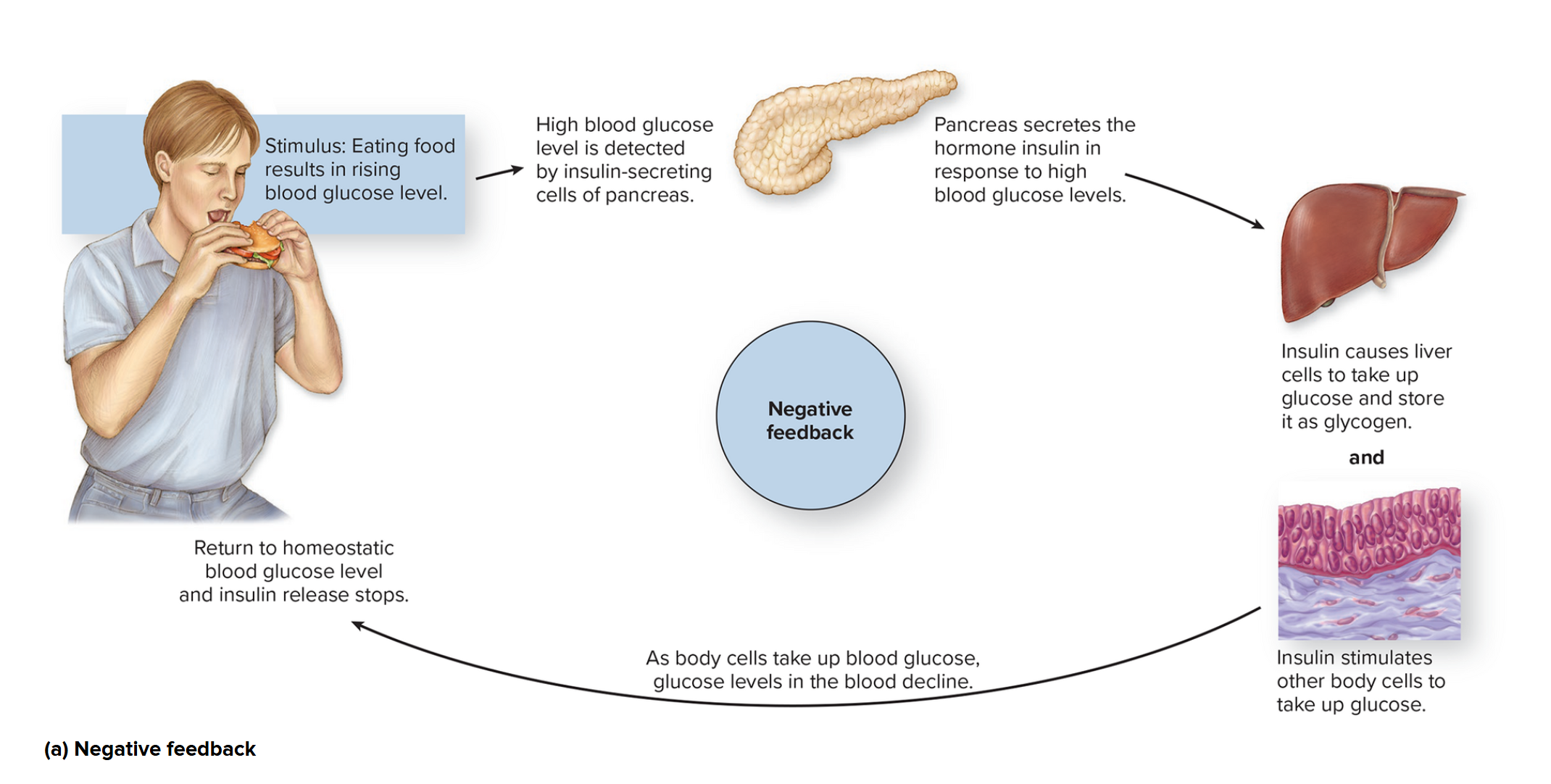
Negative Feedback
Hormone production results in decreased hormone production → decreased activity
glucose rises in blood
insulin produced (produced by pancreas)
glucose levels fall
insulin production falls
glucose level rises
→ lead to homeostasis
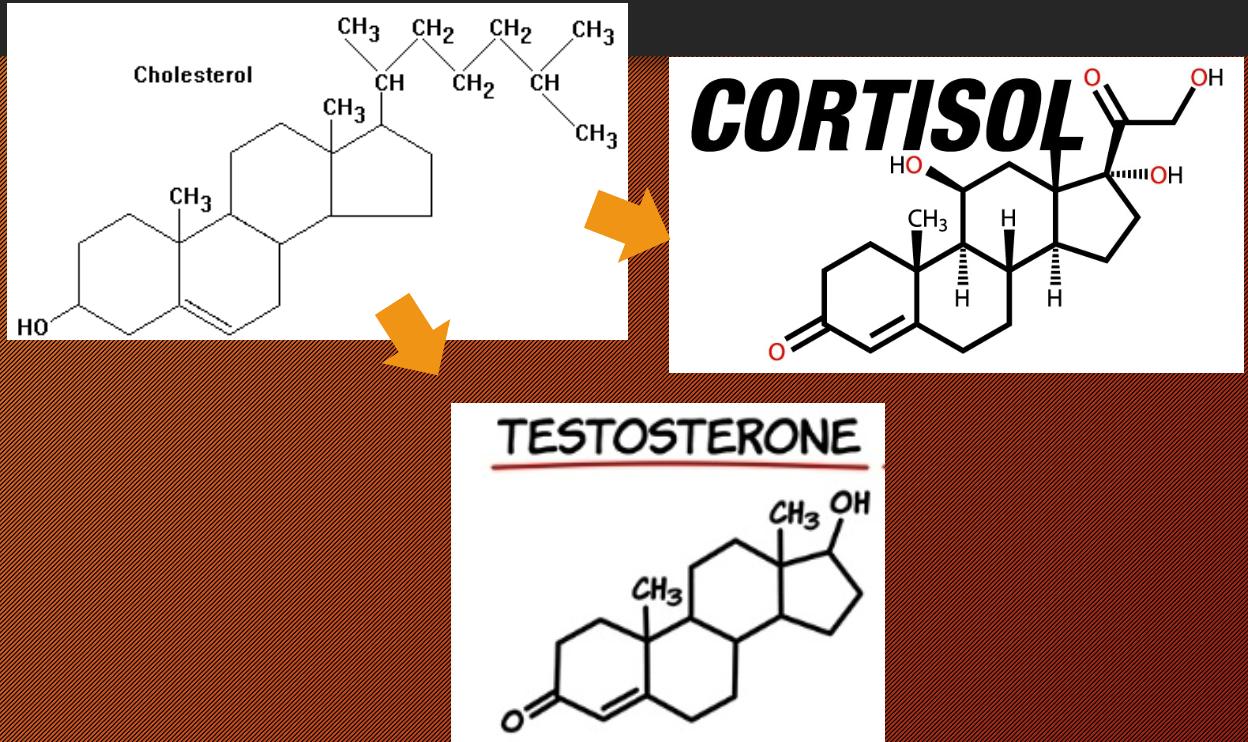
Hormone: Steroids
derived from cholesterol; secreted mostly by reproductive organs and adrenal cortex
Cholesterol → turn it into Testosterone
Cholesterol → turn it into Cortisol
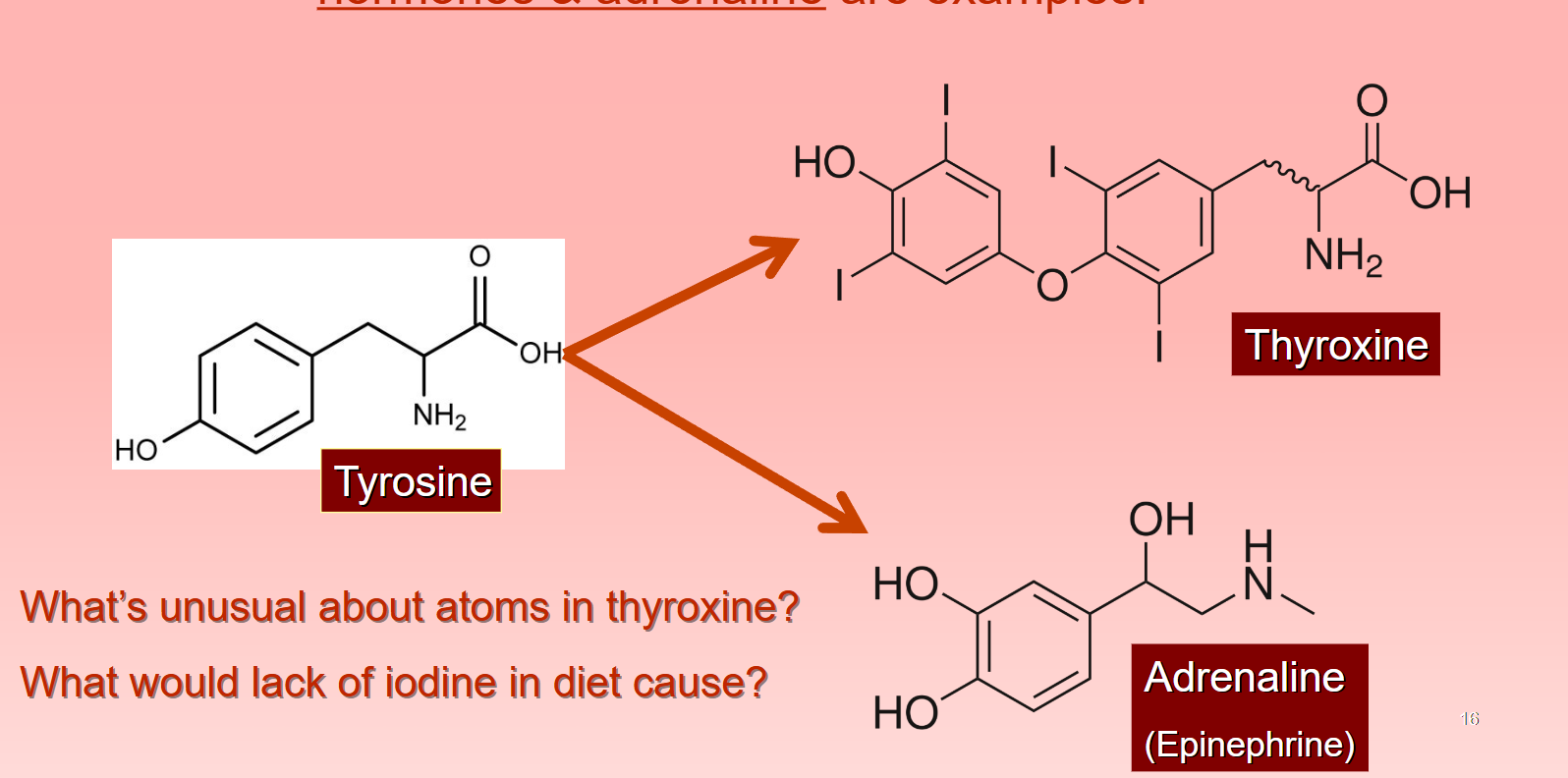
Hormone: Amines
amino acid derivatives (which are small)
thyroid hormones
→ Tyrosine → turn it into Thyroxine (produced by thyroid gland)
→ iodine is a part of thyroxine, which is necessary and natural (can’t make thyroxine without iodine)
→ lack of iodine: causes goiter (lump in ur throat bc thyroid gland size increases)
adrenaline
Hormone: Polypeptides (bonds) and Proteins (strings of amino acids) → Peptides
too large to pass through cell membranes
most hormones are “peptide hormones”
→ ALL pituitary hormones
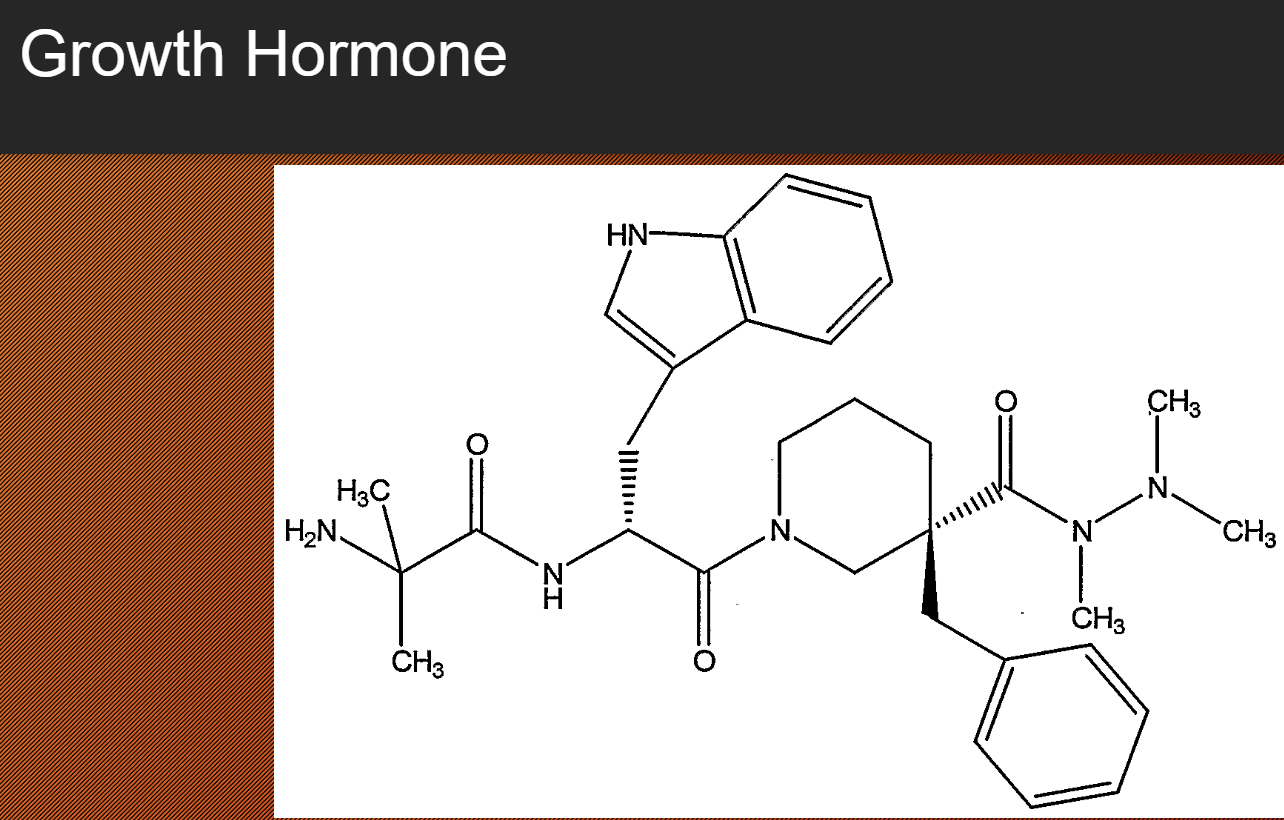
How does a peptide hormone act on a cell if its too large to enter?
most hormones bind to receptors on the surface of cells
this triggers a chain of reactions that causes the final result: “Cascade effect”
membrane proteins are involved
The Endocrine glands!
Hypothalamus
Pituitary-Anterior and Posterior
Pineal
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Thymus
Adrenal Glands
Pancreas
Gonads
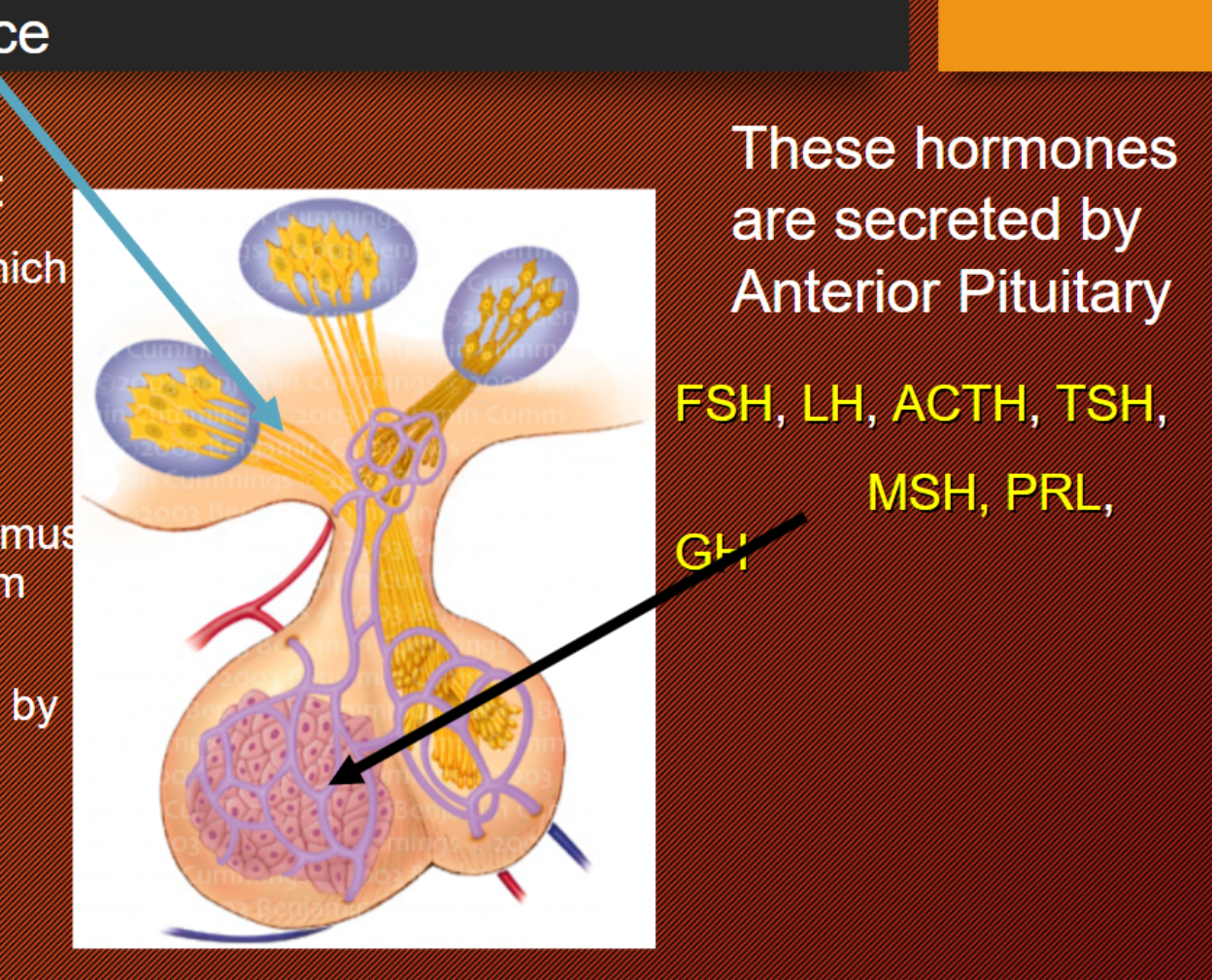
Hypothalamus: “control center”
Hypothalamus controls in 3 ways…
hormones from hypothalamus stimulate the anterior pituitary to produce and secrete hormones
tropic hormone!
Hypothalamus produced hormones are…
Thyrotropin Releasing hormone: this hormone which is released from the Hypothalamus stimulates the anterior pituitary gland to secrete Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GRH or GHRH): it’s the hormone secreted by the hypothalamus which stimulates the release of Growth Hormone from the anterior pituitary
Prolactin Releasing Hormone (PRH): it’s secreted by the Hypothalamus which stimulates the secretion of Prolactin from the anterior pituitary gland
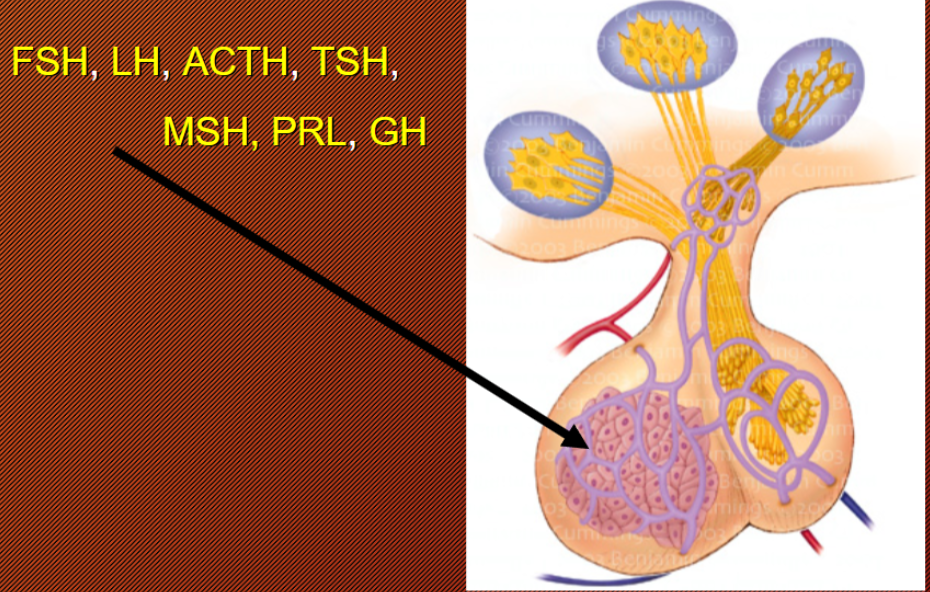
Hypothalamus 1st Influence
The hypothalamus hormones stimulate the Anterior Pituitary gland to produce and secrete more hormones + send them to diff parts of the body
FSH → Follicle-stimulating hormone
LH → Luteinizing hormone
ACTH → Adrenocorticotropic hormone
TSH → Thyroid stimulating hormone
MSH → Melanocyte stimulating hormone
PRL → Prolactin
GH → Growth hormone

Hypothalamus 2nd influence
Posterior pituitary hormones are made up by the hypothalamus
ADH (Antidiuretic hormone) and Oxytocin
these hormones travel down the axons in the infundibulum to be released by the Posterior pituitary gland into the bloodstream
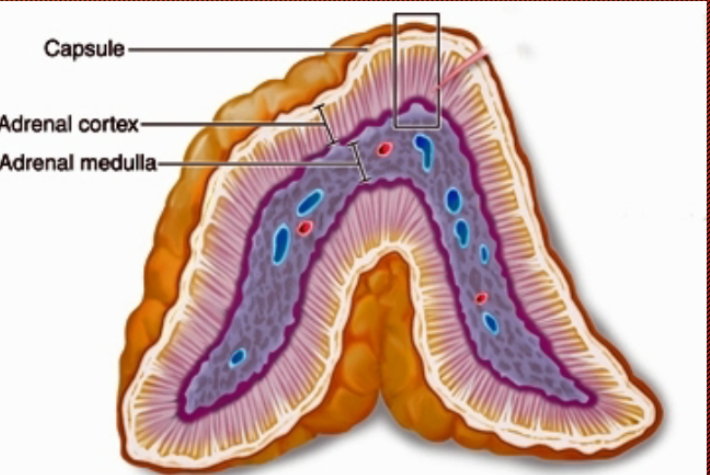
Hypothalamus 3rd influence
Hypothalamus stimulates the Adrena Medulla directly through Autonomic Nerv system (sympathetic)→ fight or flight response
producing Adrenaline/Epinephrine and Noradrenaline/Norepinephrine
EpiPen→ device used to deliver epinephrine, delivering adrenaline
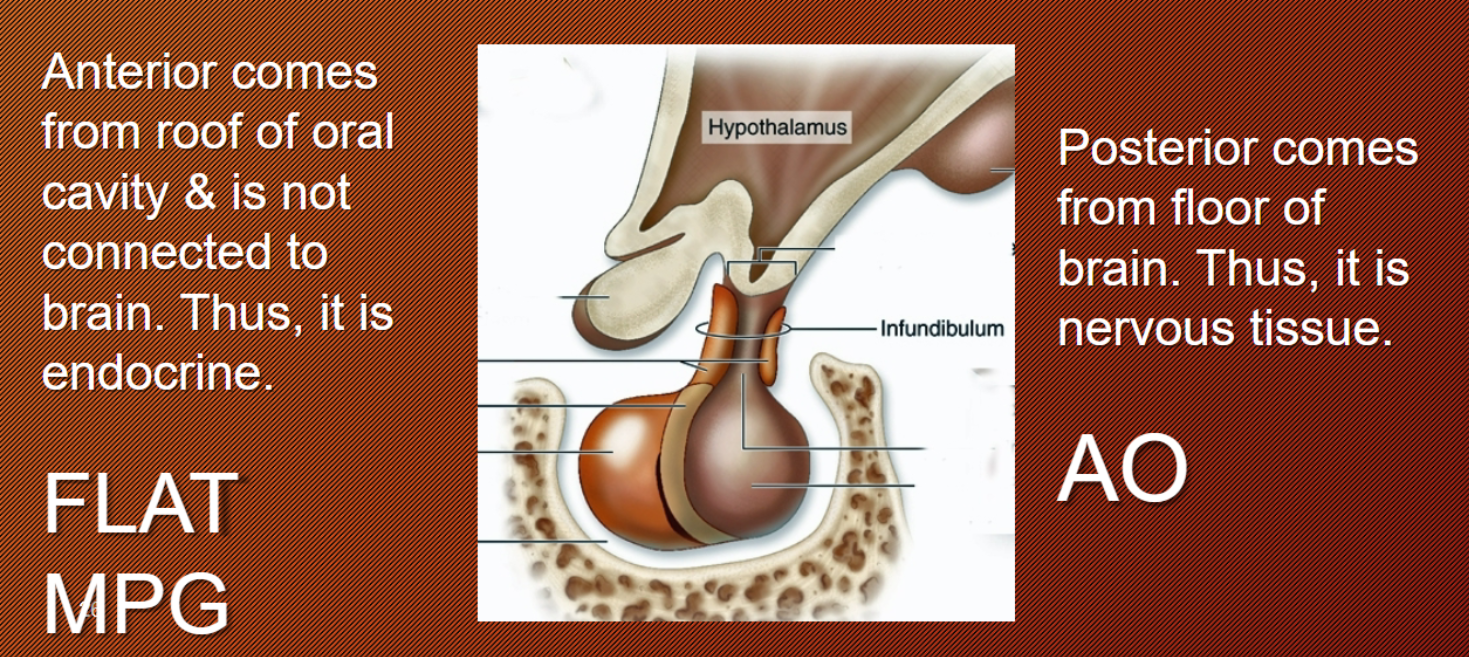
Pituitary Gland
controlled by the hypothalamus (Nerv and endocrine system combined)
Anterior pituitary gland
comes from roof of oral cavity and is not connected to brain → endocrine
Posterior pituitary gland
comes from floor of brain → nervous tissue
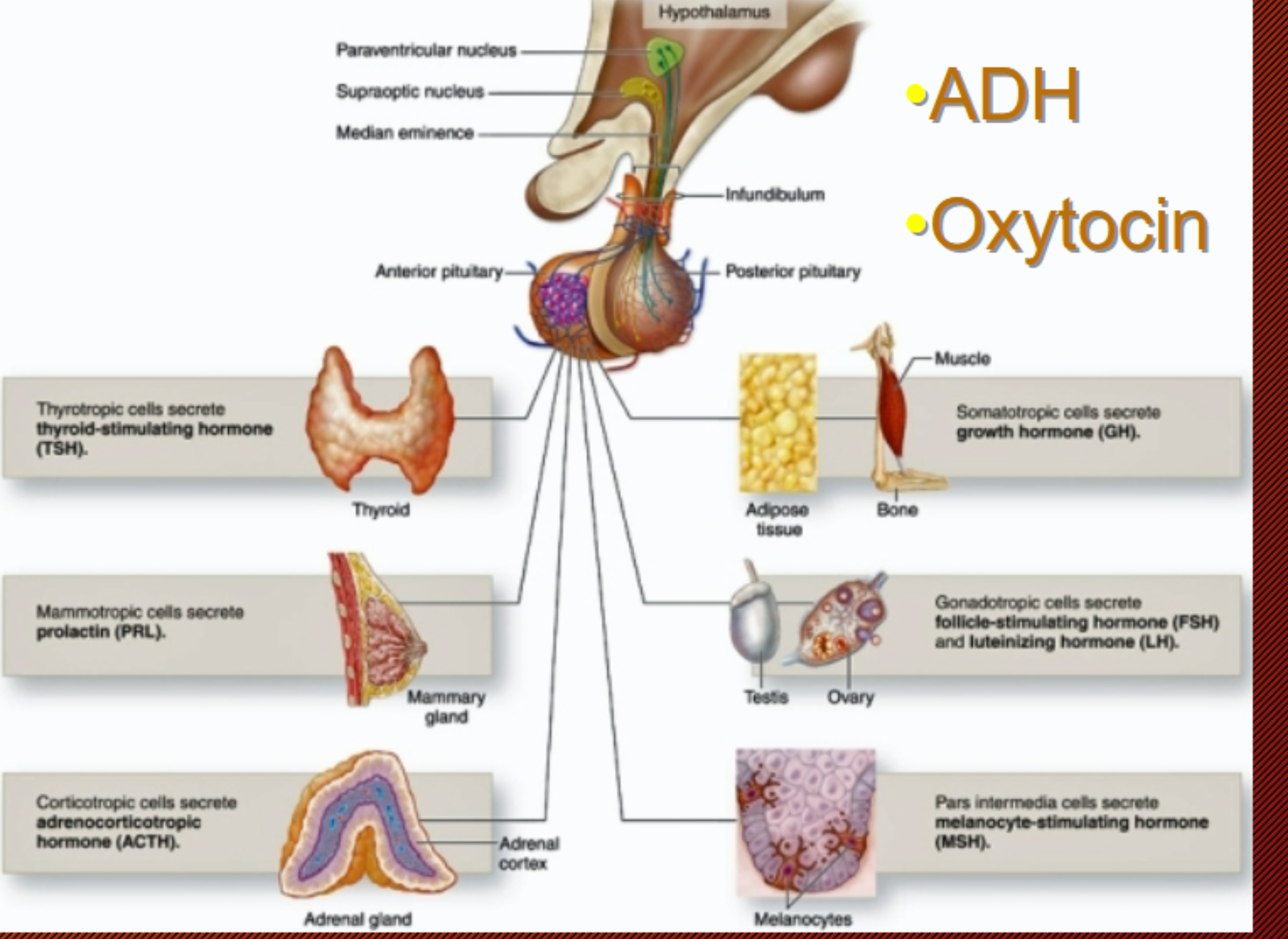
Pituitary hormones
sometimes called the “master gland”
Produces many hormones that affect other endocrine glands (tropic hormones)!
FSH
LH
ACTH
TSH
MSH
Prolactin
GH
+ ADH
+ Oxytocin
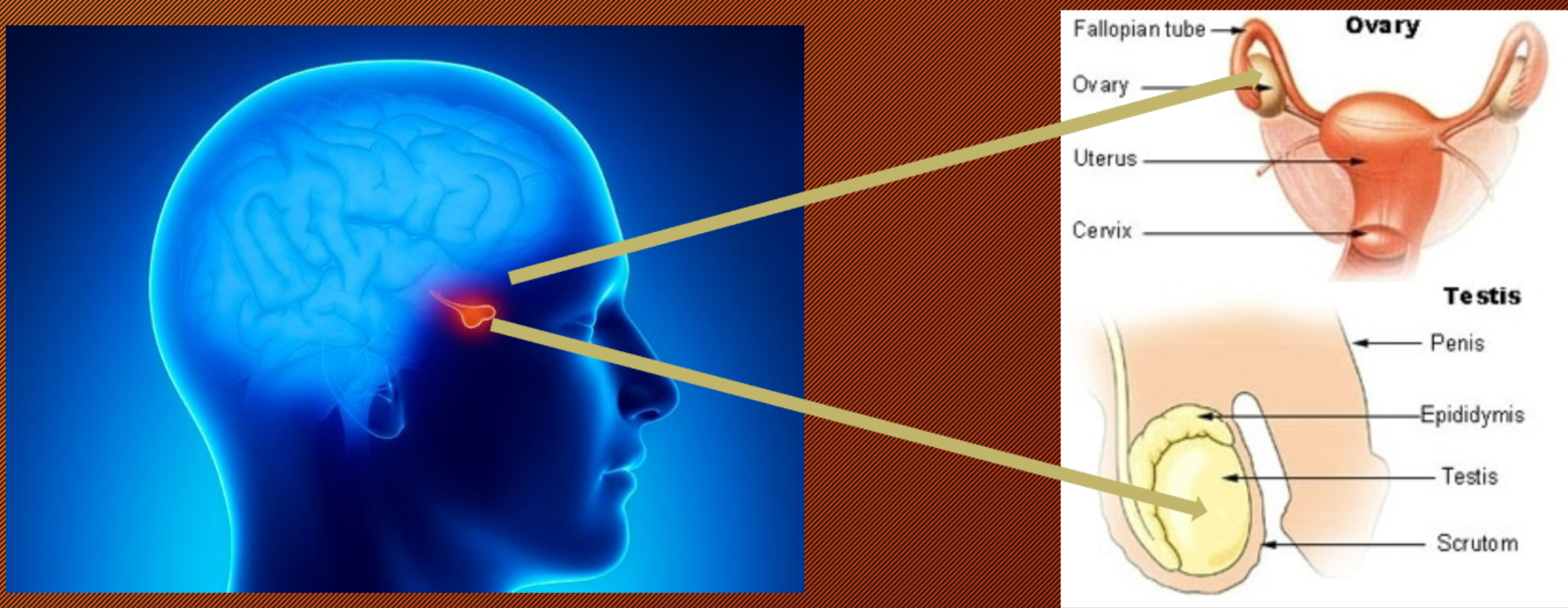
FSH: Follicle Stimulating Hormone and LH: Luteinizing Hormone (Anterior pituitary gland)
act on gonads and stimulate gamete formation
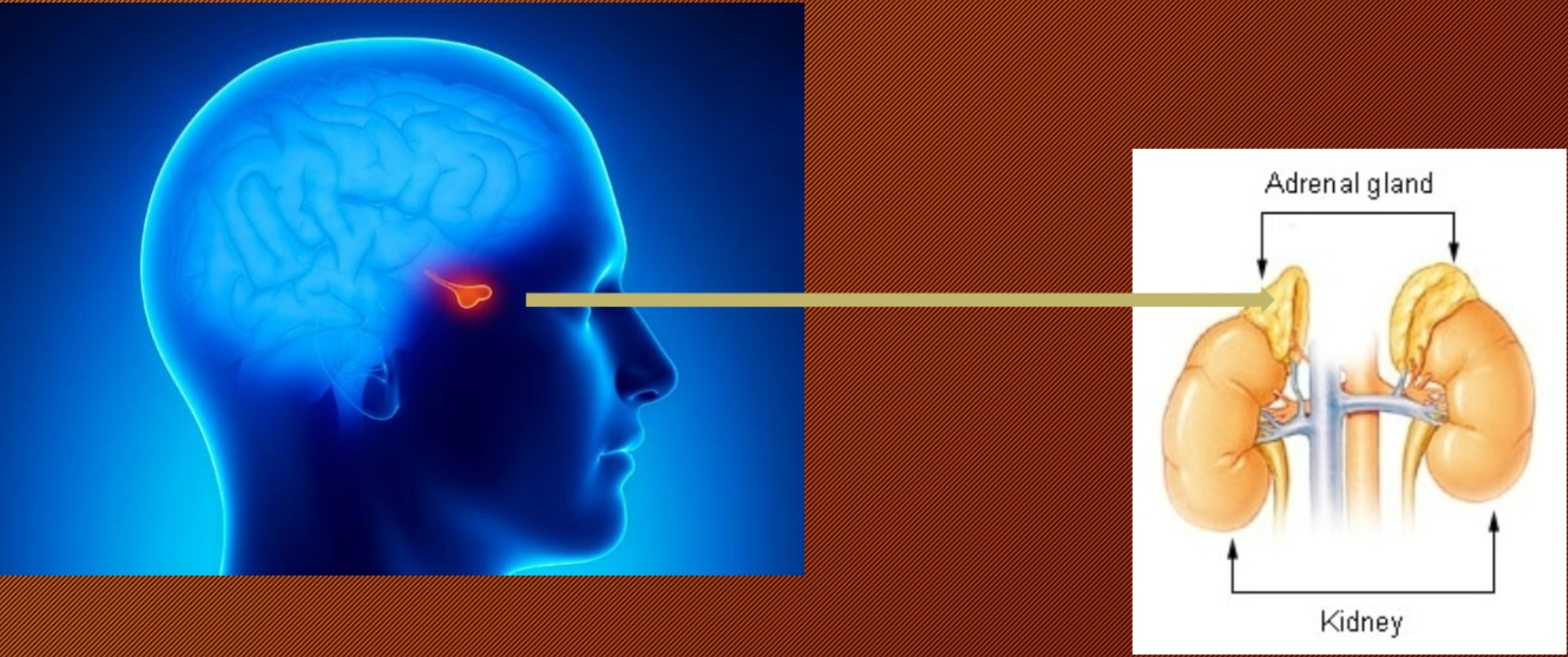
ACTH: Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (Anterior pituitary gland)
cause release of corticosteroids from adrenal cortex
→ influence on metabolism
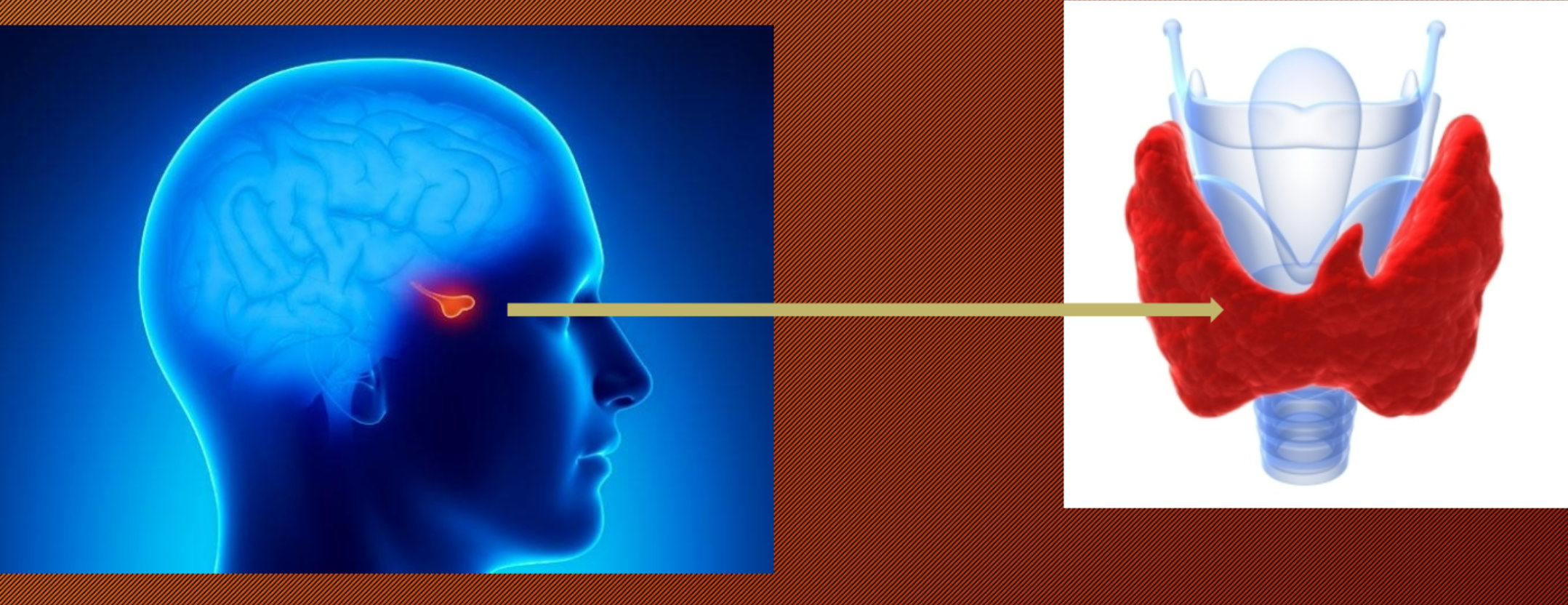

TSH: Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (Anterior Pituitary Gland)
release of thyroid hormones
MSH: Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (Anterior pituitary gland)
melanin release = darker skin and hair
Prolactin (Anterior pituitary gland)
milk production
GH: Growth Hormone (Anterior Pituitary Gland)
all body tissue growth!
ADH: Antidiuretic Hormone (Posterior Pituitary gland)
water retention from kidney
regulates water balance by telling the kidneys to transport water from your urine back into the bloodstream when you are dehydrated
Oxytocin (Posterior pituitary gland)
milk ejection
uterine contraction
causes uterine contractions during childbirth and allows milk to be released during nursing
→ also involved in social bonding, esp mother-infant

Pineal Gland
produces melatonin
Circadian rhythm — day and night cycle
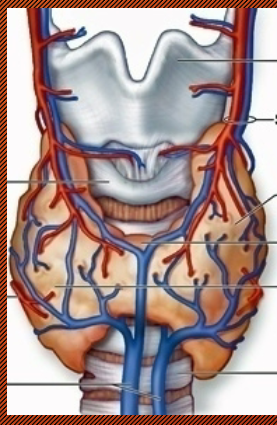
Thyroid Gland
located in the throat
produces thyroid hormones → Metabolism
Calcitonin → Decrease Ca++ in blood, can result in bone growth
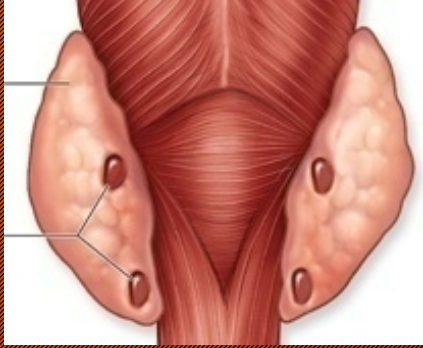
Parathyroid Gland
Parathormone
Increase Ca++ in the blood
→ bone density decrease
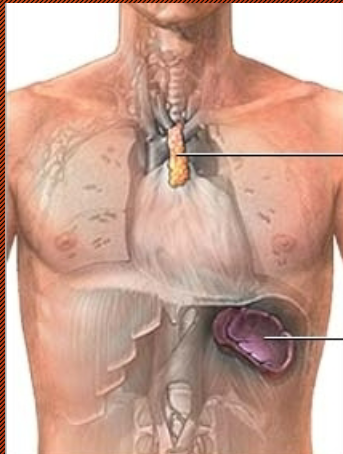
Thymus Gland
Located behind the sternum
Numerous thymic hormones → immune response (really big in babies)
as we get older, our thymus gland gets smaller and smaller
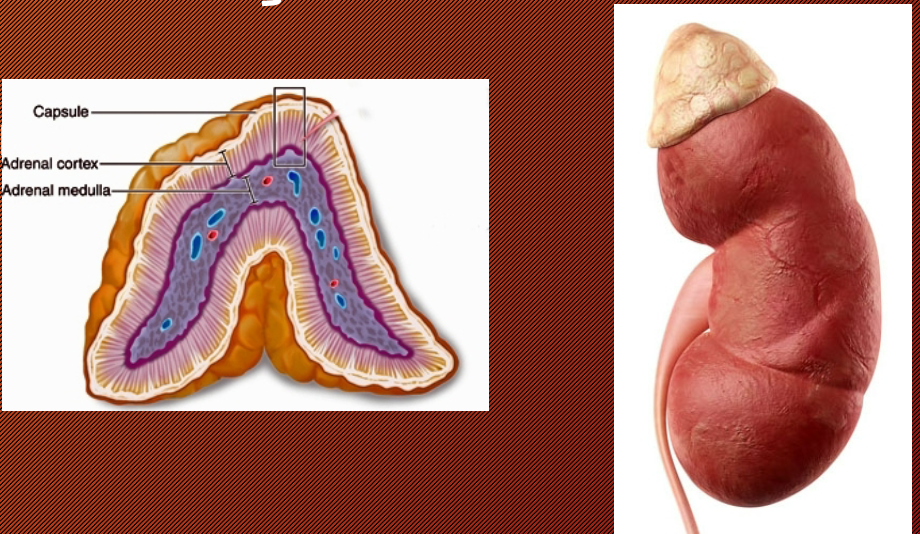
Adrenal Gland
Located in the cortex and medulla (fight or flight)!!!
Adrenaline (epinephrine)
Noradrenaline (norepinephrine)
Corticosteroids
→ Electrolyte hormones
→ Metabolism
→ Gonad stimulation
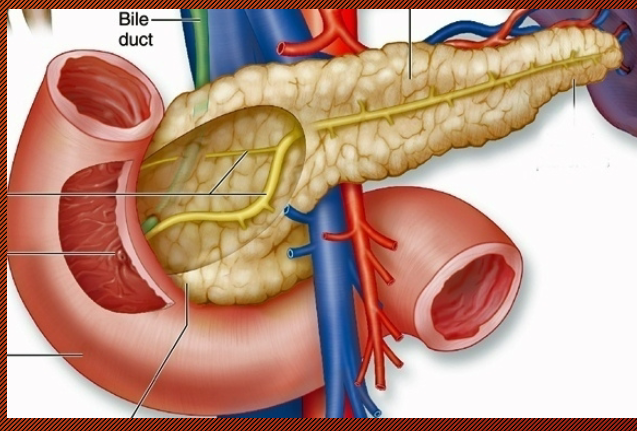
Pancreas Gland
Located behind the stomach and under the liver
Produce insulin(lowers blood sugar) + glucagon(increases blood sugar) → glucose balance
Composed of 2 tissue types: Endocrine and Exocrine cells produce and secrete digestive enzymes and mucus
Pancreas Endocrine Function
Endocrine cells (Islets of Langerhans) produce and secrete two hormones that regulate blood glucose levels in a NEGATIVE FEEDBACK LOOP!
Insulin: secreted by pancreatic beta cells when blood glucose is TOO HIGH; stimulates the uptake or storage of glucose by cells (mostly in muscle and liver cells)
Glucagon: secreted by pancreatic alpha cells when blood glucose is TOO LOW; stimulates the breakdown of glycogen (the storage of polymer of glucose) in the liver and release of glucose into the blood for energy production throughout the body
Gonads Glands
What are they?
The ovaries and testes
Produce sex hormones (steroids)
→ Estrogen, Progesterone, Testosterone…