AP HUG
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:09 AM on 8/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
1
New cards
**Social Norms**
ex: social indicators (literacy, education, etc.), demographic indicators (births, deaths, pop, etc.), gender, race, languages
ex: social indicators (literacy, education, etc.), demographic indicators (births, deaths, pop, etc.), gender, race, languages
Geo Category:
Social
Social
2
New cards
relates to government, public affairs, laws, borders/territory, etc.
Geo Category:
Political
Political
3
New cards
relates to monetary values
ex: standard of living, income, tariffs, GDP, unemployment, Imports/exports, etc.
ex: standard of living, income, tariffs, GDP, unemployment, Imports/exports, etc.
Geo Category:
Economical
Economical
4
New cards
describes the natural world and/or the human impact
Geo Category:
Environmental
Environmental
5
New cards
longitude/latitude, grid system, address
Absolute Location
6
New cards
compass direction
Absolute DIrection
7
New cards
measurement of space between two places
Absolute Distance
8
New cards
where a place is in relation to another place.
Relative Location
9
New cards
directions based on people’s surroundings and perception (left, right, down south)
Relative Direction
10
New cards
approximate measurement of space between two places **expressed in time, effort, or cost**
Relative Distance -
11
New cards
close together in high frequency
Clustered/concentrated/dense
12
New cards
far apart in low frequency
Dispersed/scattered/sparse
13
New cards
how high or low something occurs in relation to sea levels
Elevation Patterns
14
New cards
everything is related to everything else, BUT near things are more related than distant things
**Closer=more related**
**Closer=more related**
Tobler’s 1st Law of Geography
15
New cards
as the distance grows, similarities/connections shrink.
\-caused by friction decay
\-caused by friction decay
Distance Decay
16
New cards
the further away, the more friction, and the less connection
Friction Decay
17
New cards
how people interact with the physical world
Define Human Environment Interaction (HUI)
18
New cards
Physical things people need to survive
\- water, fertile soil, food
\- water, fertile soil, food
Depend
19
New cards
Theory that the **physical environment** and available resources **determine survival** and cultural development
Environmental Determinism
20
New cards
theory that people can adapt to any environment
Possibilism
21
New cards
Map shows entire globe
Global Scale of Analysis
22
New cards
one country divided into areas such as states
National Scale of Analysis
23
New cards
Regions of Earth
ex: Middle East
ex: Middle East
World Regional Scale of Analysis
24
New cards
state or city divided into groups
ex: counties, neighborhoods, census tracts, etc.
ex: counties, neighborhoods, census tracts, etc.
Local Scale of Analysis
25
New cards
Regions of a country
ex: The South, The MidWest
ex: The South, The MidWest
Country Regional Scale of Analysis
26
New cards
different scales = different interpretations.
\
ex: US election maps shows Texas as red, but Texas election maps show part of Texas as red and part as blue
\
ex: US election maps shows Texas as red, but Texas election maps show part of Texas as red and part as blue
Scale Impacts Perspective
27
New cards
Events at one scale can affect another scale
\
ex: war in the Middle East (global scale) affects US gas prices (national scale)
\
ex: war in the Middle East (global scale) affects US gas prices (national scale)
Local Global Continuum (Interdependencies)
28
New cards
An area with similar characteristics that set it apart from other areas
Region
29
New cards
\
\- high level of consistency and commonalities such as economic, social, political, or environmental characteristics that unify a space
\- borders do not change easily
\- high level of consistency and commonalities such as economic, social, political, or environmental characteristics that unify a space
\- borders do not change easily
Formal/Uniform Regions
30
New cards
\- connected by a hub, node, or center point
\- usually based on the movement of economic goods, transportation, and communications
\- usually based on the movement of economic goods, transportation, and communications
Functional/Nodal Regions
31
New cards
\-based on peoples opinions NOT facts
\- borders vary per person
\- borders vary per person
Vernacular/Perceptual Regions
32
New cards
Formal/Uniform
What type of region is this?
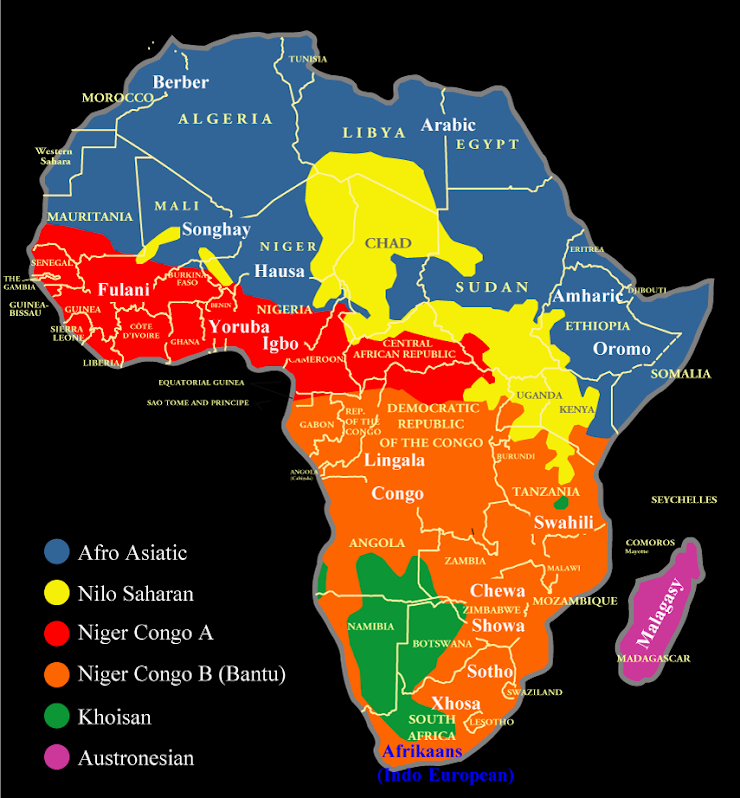
33
New cards
Uniform/Formal
What type of region is this?
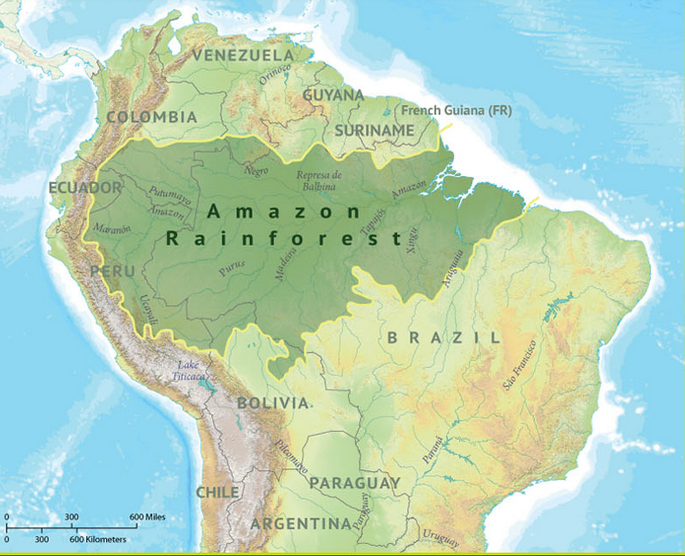
34
New cards
Functional/Nodal
What type of region is this?
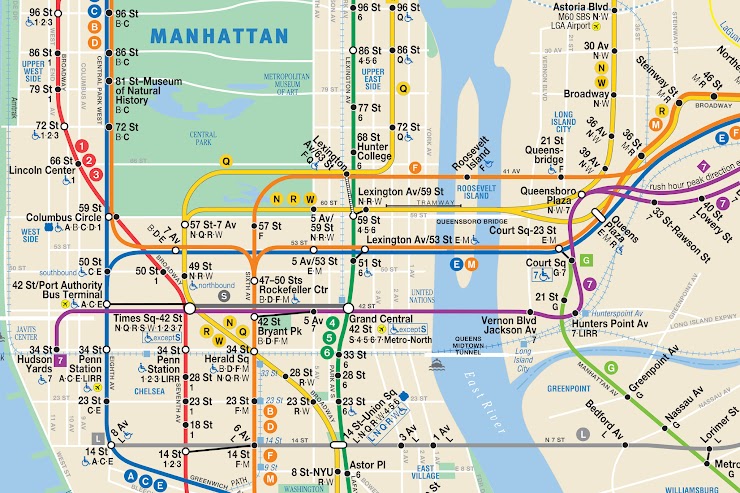
35
New cards
Vernacular/Perceptual
What type of region is this?
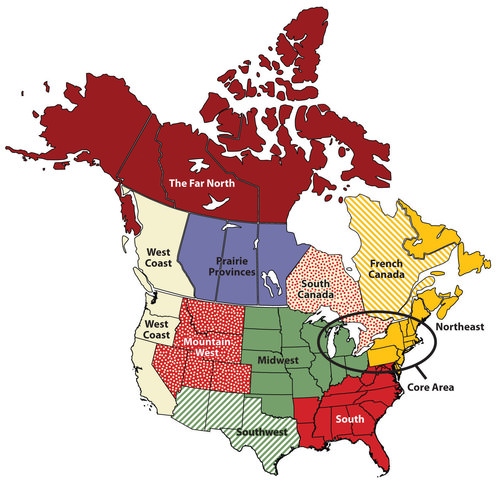
36
New cards
increased interaction around the world
Globalization
37
New cards
Divides Countries into 3 categories based on **economic values**, political influence, etc.
\- Core, Semi-Periphery, Periphery
\- Core, Semi-Periphery, Periphery
Wallerstein’s World Systems Theory
38
New cards
Newly Industrialized Country (NIC)
\- indicators ranked in between Core and Periphery
\- exploits Semi-Periphery
\- B.R.IC.S M.I.N.T.
\- indicators ranked in between Core and Periphery
\- exploits Semi-Periphery
\- B.R.IC.S M.I.N.T.
Semi-Periphery Countries
39
New cards
Developed Countries (MDC)
\- high development indicators
\- exploits Periphery and Semi-Periphery
\- high development indicators
\- exploits Periphery and Semi-Periphery
Core Countries
40
New cards
Developing Countries (LDC)
\- low development indicators
\- relies on Core and Periphery
\- low development indicators
\- relies on Core and Periphery
Periphery Countries
41
New cards
**B**razil, **R**ussia, **I**ndia, **C**hina, **S**outh Africa
**M**exico, **I**ndonesia, **N**igeria, **T**urkey
**M**exico, **I**ndonesia, **N**igeria, **T**urkey
B.R.I.C.S. M.I.N.T.
42
New cards
Tropic of Cancer
What does this line represent?
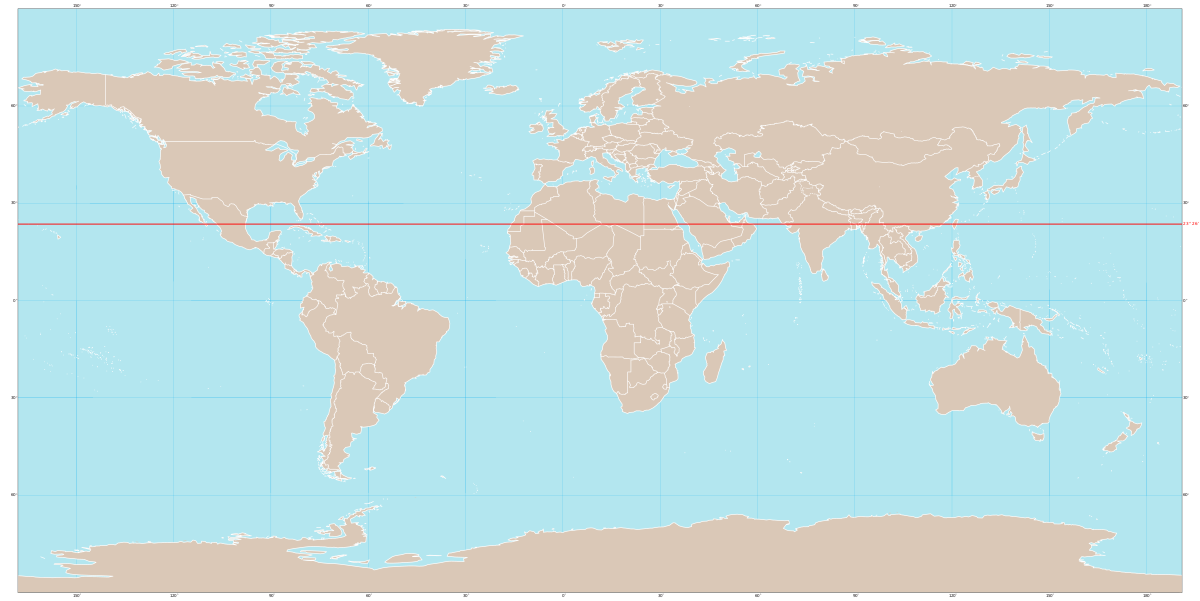
43
New cards
Tropic of Cancer
What line is at 22.3 N?
44
New cards
Tropic of Capricorn
What line is at 22.3 S?
45
New cards
Arctic Circle
What line is at 66.5 N?
46
New cards
Antarctic Circle
What line is at 66.5 S?
47
New cards
Prime Meridian
What line is at 0 E or W?
48
New cards
Arctic and Antarctic circles
Where are high altitudes?
49
New cards
equator
Where are low altitudes?
50
New cards
Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn
Where are middle altitudes?
51
New cards
\- boundary from which each calendar day starts
\- west is ahead, east is behind
\- west is ahead, east is behind
International Dateline
52
New cards
Large Scale maps
Which has more detail,
Large Scale of Small Scale Maps?
Large Scale of Small Scale Maps?
53
New cards
\- smaller areas
\- more detail
\- more detail
Large Scale maps
54
New cards
\- larger areas
\- less detail
\- less detail
Small Scale maps
55
New cards
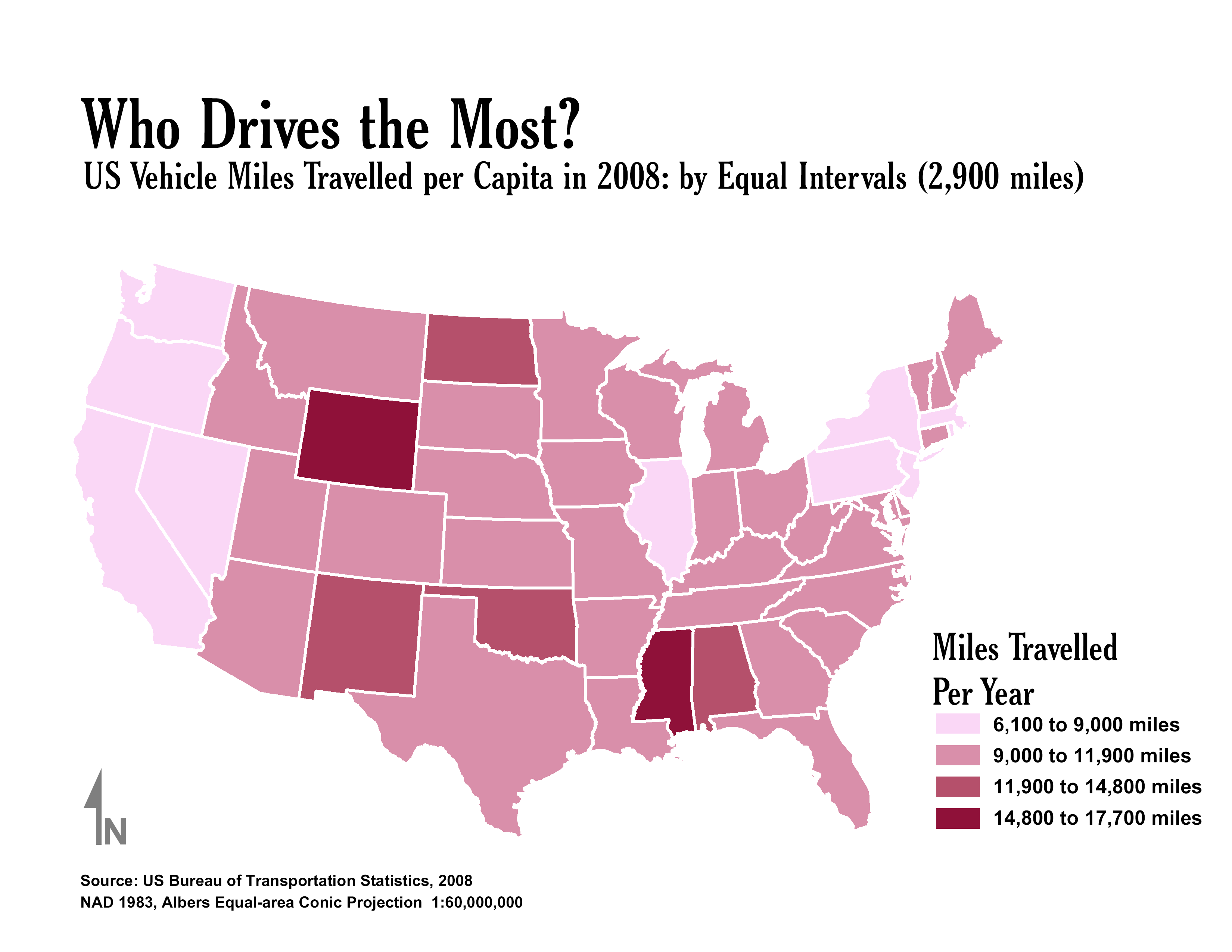
Show a specific them or type of data
Thematic Maps
56
New cards
Man-Made Features
\- boundaries, roads, cities
\- boundaries, roads, cities
Political Reference Map
57
New cards
Show where something is in space
Reference Map
58
New cards
Naturally Occurring Features
\- mountains, plains, rivers
\- mountains, plains, rivers
Physical Reference Map
59
New cards
Bothe Man-Made and Naturally Occurring Features
Combined Reference Map
60
New cards
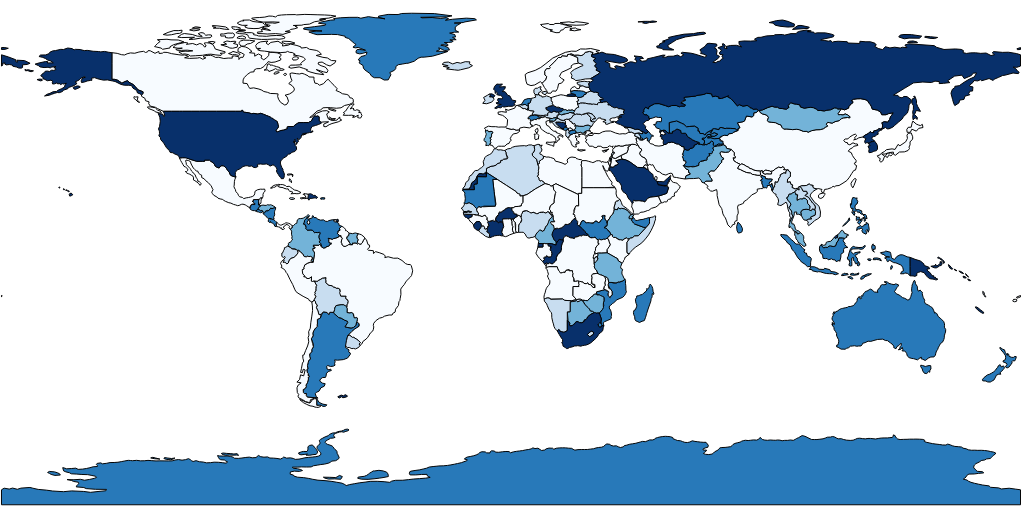
use **shading** to show different data levels
Choropleth Map
61
New cards
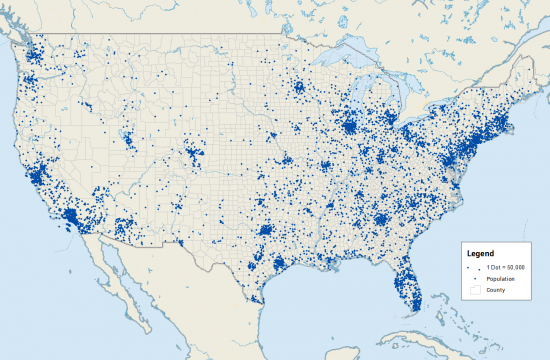
uses **dots** to dhow presence of quantity
Pindot/Dot Density Map
62
New cards
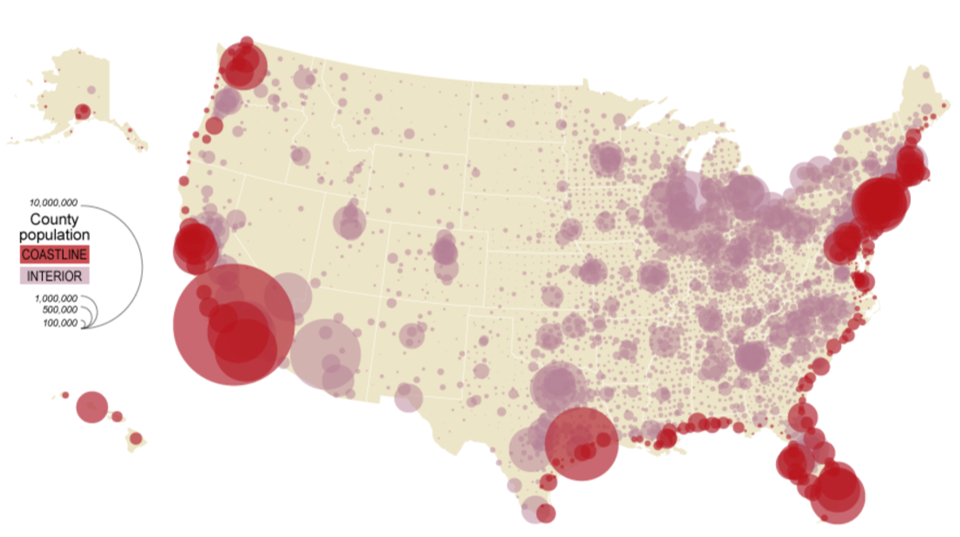
use proportionately scale symbols to represent value
**bigger symbol = bigger value**
**bigger symbol = bigger value**
Graduated Symbol Map
63
New cards
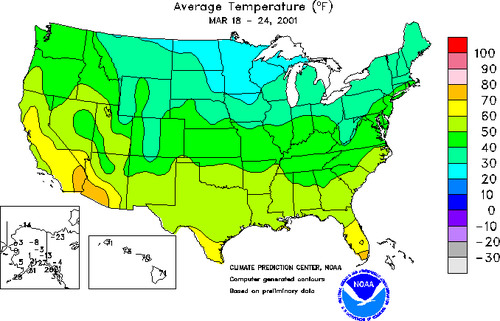
lines that connect equal points of value
ex: topography
ex: topography
Isoline Map
64
New cards
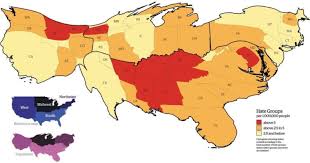
area sizes are scaled to data
bigger=more
bigger=more
Cartogram Map
65
New cards
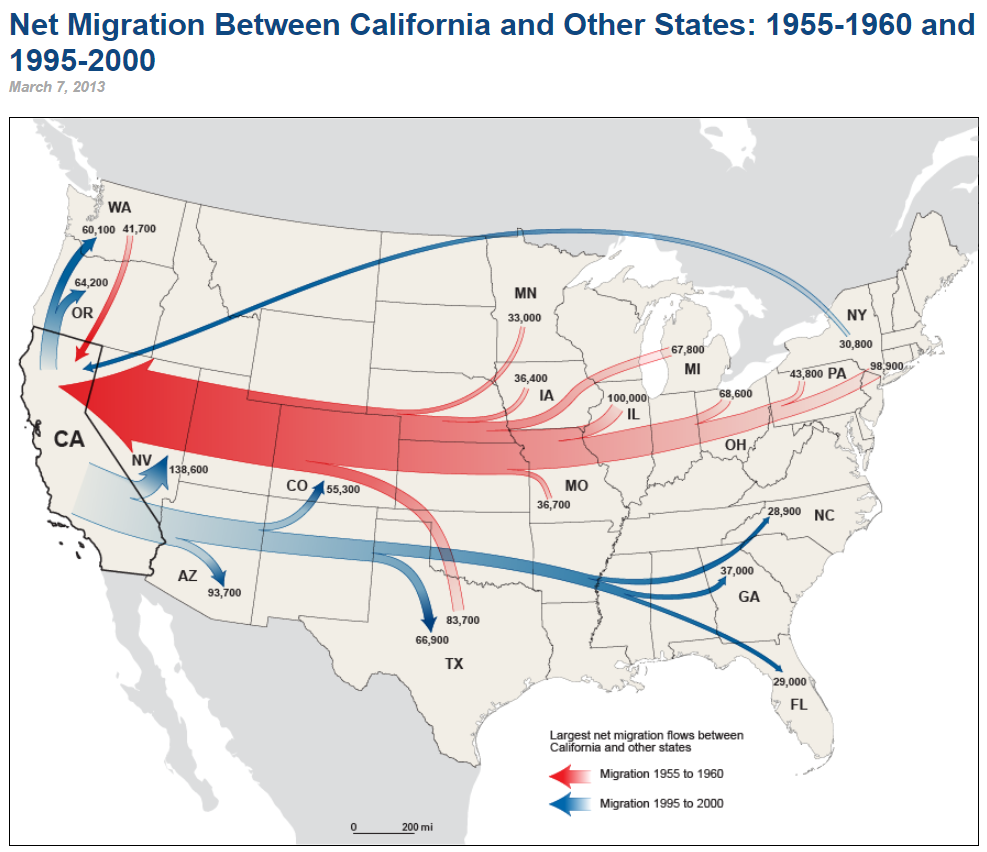
shows movement and volume with different sized arrow
Flowline Map
66
New cards
Pindot
What type of map is this?
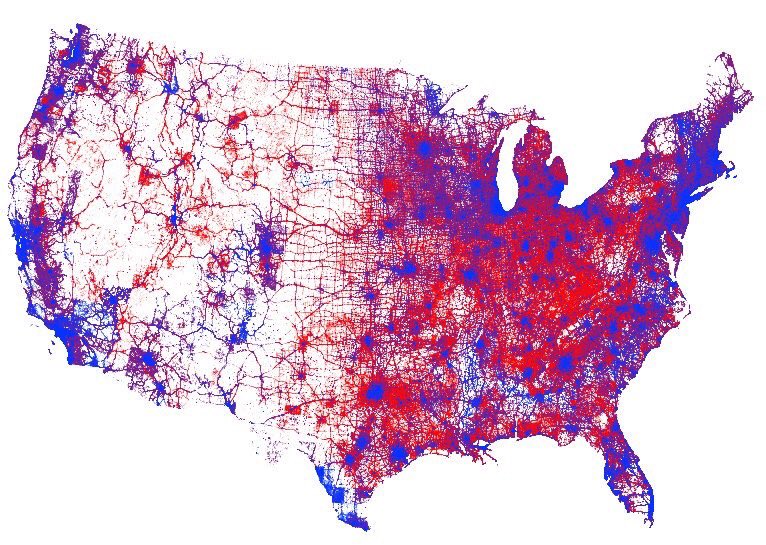
67
New cards
Cartogram
What type of map is this?
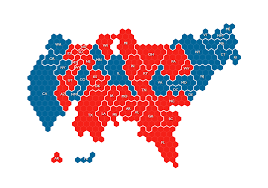
68
New cards
Flowline
What type of map is this?
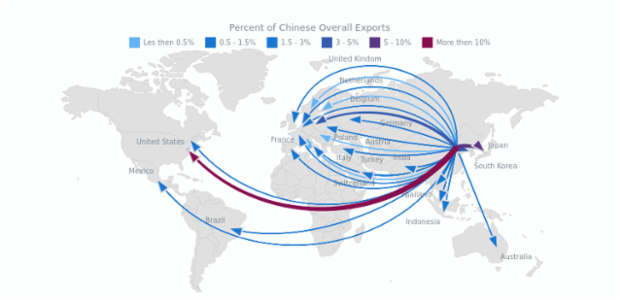
69
New cards
Choropleth
What type of map is this?
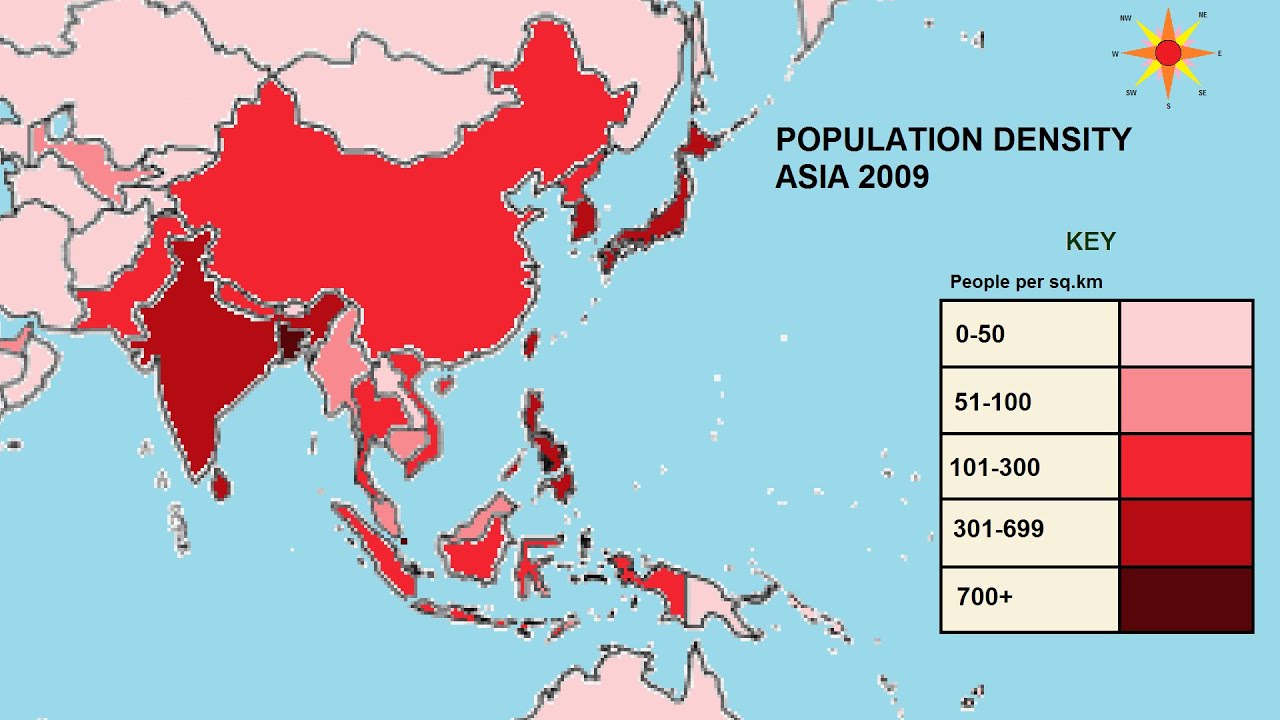
70
New cards
Graduated Symbol
What type of map is this?
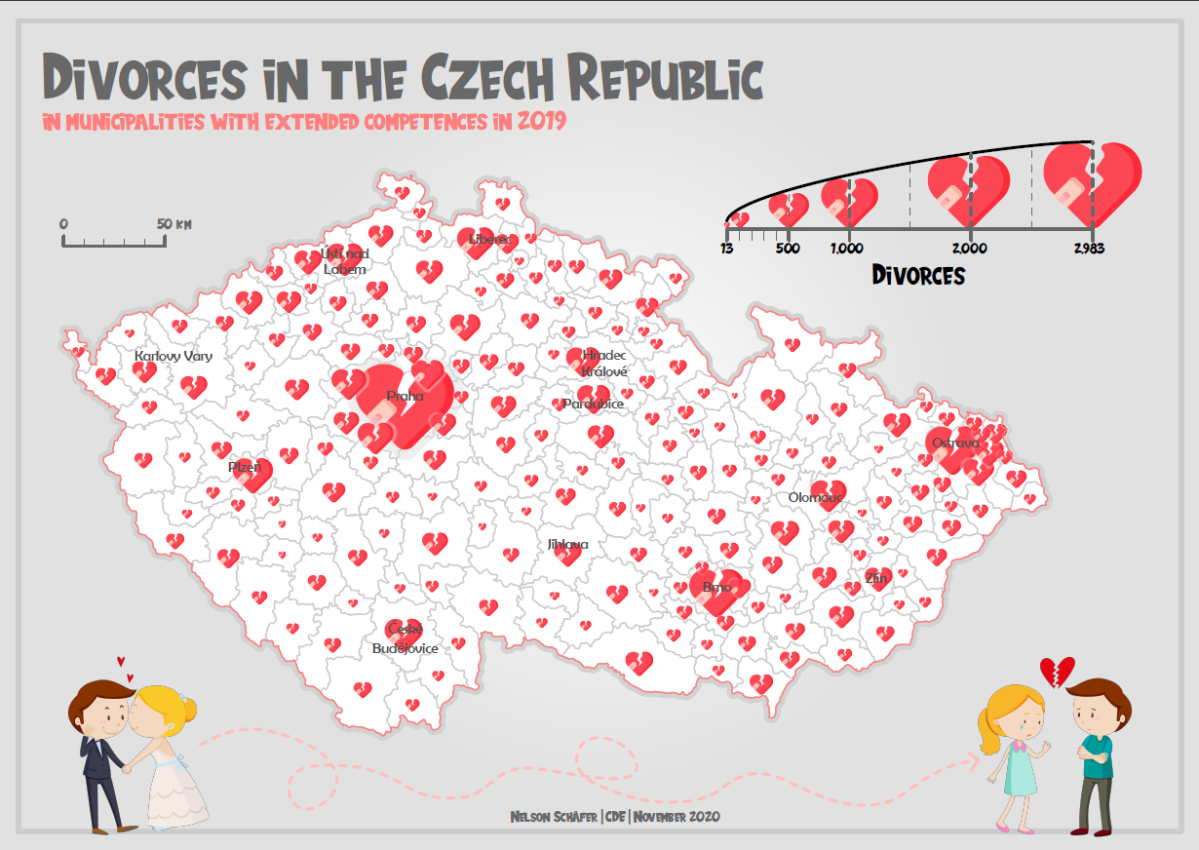
71
New cards
Isoline
What type of map is this?
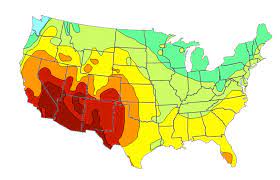
72
New cards
\- satellites gather information on Earth
ex: Google Maps
ex: Google Maps
Satellite Imagine
73
New cards
\- A computer system
\- determines the absolute location
\- creates multiOnline Mapping and Visualizationlayer maps for spatial observation
\
ex: Google Earth, Arc GIS
\- determines the absolute location
\- creates multiOnline Mapping and Visualizationlayer maps for spatial observation
\
ex: Google Earth, Arc GIS
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
74
New cards
\- satellite-based system
\- determines absolute location
\- determines absolute location
GPS/Satellite Navigation Systems
75
New cards
\- collects data reflected from Earth
\- creates multi-layer 3D visual renderings
\- creates multi-layer 3D visual renderings
Remote Sensing
76
New cards
\- understanding that modern tech makes map-making easier
Online Mapping and Visualization
77
New cards
Spacial Anaylysis
Where something is and why
78
New cards
Four Most COmon Distortions
Shape, Area, Distance, Directions.
79
New cards
Cylindrical/Mercator Projection
\- Used in Maritime Navigation
\- preserves angles and directions
\- size is distorted
\- preserves angles and directions
\- size is distorted
80
New cards
Conic Projections
Regional maps of mid-latitudes areas with East-West orientations
81
New cards
Map Projection
map formatting that makes an accurate 2D map of Earth
82
New cards
Plane/Polar/Azimuthal Projection
\-Used for Great Circle Routes
\-Distorted edge, especially around edges
\-Distorted edge, especially around edges
83
New cards
Robinson Projection
\- smaller around mid-level and polar areas than the Mercator
\- more accurate shapes and sizes
\- more accurate shapes and sizes
84
New cards
Gall-Peters Projection
\- more balanced ratio between North and South Hemisphere’s to remove North centric bias.