01 Measurements, Physical Quantities, Units
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
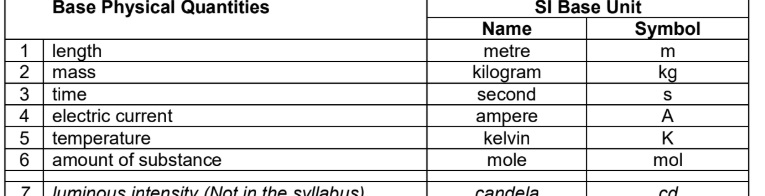
What are the SI base units?
A basic set from which all other SI units can be derived
Dervived units
defined in terms of the seven base quantities via a system of equations
SI derived units for these derived quantities can be obtained from these equations and the seven SI base units

Derived physical quantities
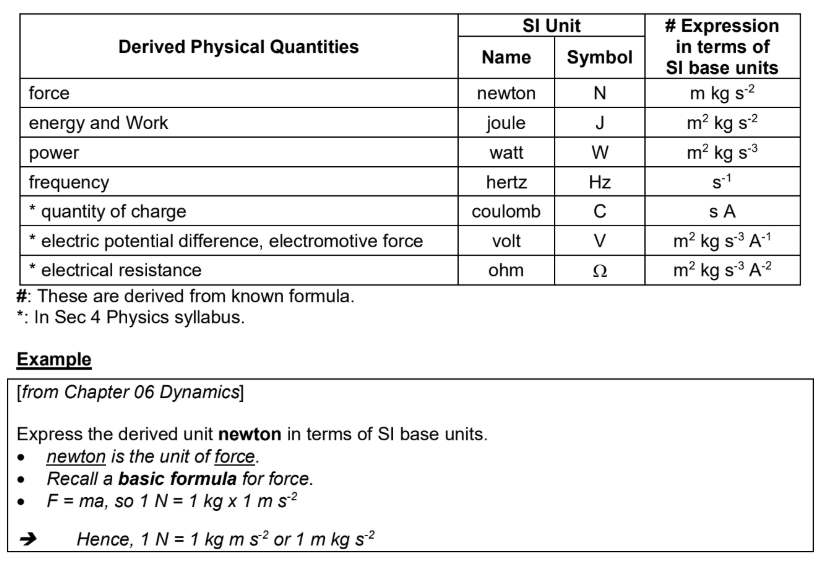
Prefixes
Reading
only one judgement is needed
precision is half the smallest division
Measurement
2 judgements are needed
precision is the smallest division of the scale
Precision
a measurement is precise if it is close to other values obtained by repeating the determination using the same procedure
also refers to the smallest measurement that can be read using an instrument
Resolution
smallest division that can be read off the scale of an instrument
instrument with a better resolution is more precise
Accuracy
a measurement is accurate if it is close to the true value
Error
anything that causes a measurement to differ
parallex error: incorrect positioning of the eyes while taking a reading on a measuring scale
random error: influences from environment, fluctuations in instrument etc. Does not cause the same error every time
zero error: occur when measuring instruments are not properly calibrated (i.e. not at 0)
Rules for significant digits
All non-zero digits are significant
Zeros between two significant digits are always significant
Trailing zeros (on the right) in a number containing a decimal point are significant
Leading zeroes (on the left) in a number containing a decimal point are not significant
The significance of trailing zeroes in a number not containing a decimal point can be ambiguous (see what question wants)
In scientific notation, all digits before the multiplicaiton sign are significant
Digital calipers (precisions + parts)
precision 0.1 mm or 0.01 cm (record one less than digital display, to account for significant source of error)
Outside jaws
Inside jaws
Tail
Digital calipers: use of parts
Outside jaws
To measure external diameter or width of an object
Inside jaws
to measure internal diamter of object
Tail
to measure depth of an object
Digital micrometer screw gauge (precision + parts)
precision: 0.01 mm or 0.001 cm (record 1 less dp than digital display, to account for other significant source of error, eg overtightening)
anvil
spindle
lock
scale
ratchet
thimble
How to use digital micrometer screw guage
1. Before measurement, wipe down the anvil and spindle surfaces with a clean cloth. This removes dirt and dust from the surfaces, which enables accurate measurements.
2. Switch on the micrometer.
3. Turn the ratchet until the anvil just meets the spindle (clicking sound).
4. Press the zero button to reset the displayed length to zero.
5. Ensure the unit chosen is mm.
6. Place the object between the anvil and the spindle and rotate the thimble till the two surfaces are close to (but not touching) the object.(prevents damage to instrument and inaccurate reading
7. Then turn the rachet until the object is just gripped between the anvil and spindle (you hear a clicking sound). This prevents over-tightening and ensures that there is identical pressure applied on the object.
8. Record the reading displayed.
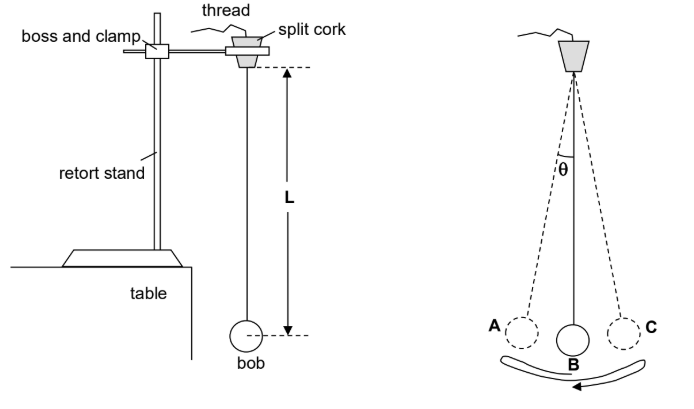
Simple pendulum
One complete oscillation is from B to A to C and back to B
T, Period: time taken for the pendulum to complete one oscillation
frequency refers to the number of complete oscillations the pendulum makes in one second
f = 1/T where T is in seconds
SI unit for frequency is Hertz (Hz)
period T is only dependent on length of the simple pendulum
errors increase when the pendulum is swinging
with large angular amplitude
not swining in a vertical plane
Density
defined as the mass per unit of volume of a body
ρ = m/v
measures how compact the particles are packed in a unit volume
for a mixture of substances, averge desnity = total mass/total volume
density of water = 1.0 g cm-3
= 100 kg m-3