Module 2- Endochondral Ossification & Condylar Cartilage
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
posterior parts of first pharyngeal cartilage become
-malleus and incus of middle ear by endochondral ossification
endochondral ossification of secondary cartilage in
-condylar process of developing TMJ
-sits in same periosteal membrane the rest of the mandible was in
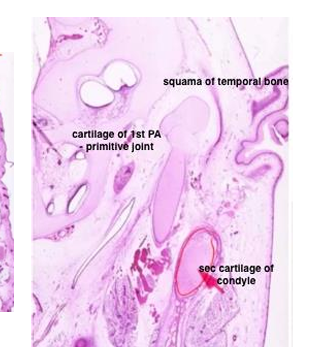
endochondral ossification of secondary cartilage
-secondary cartilage in condylar process area not only forms articular cartilage of mandibular condyle, but also the condylar process itself by endochondral ossification
-endochondrally formed bone of condylar process has coarser, more irregular trabeculae than the intramembranously formed bone of the adjacent coronoid and angular processes
-head of mandibular condylar process of a newborn (and individual throughout the growth period) composed of secondary cartilage
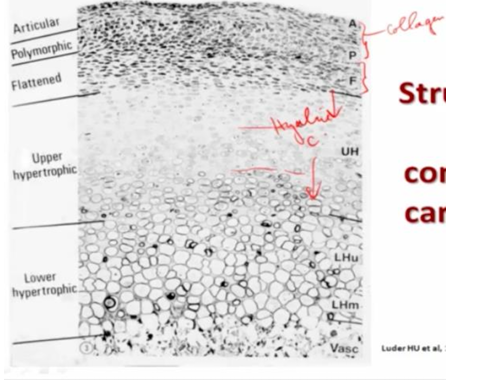
secondary cartilage in head of mandibular condylar process
-articular surface of cartilage covered by a layer of dense fibrous connective tissue, which may become fibrocartilage in some areas; found when a component of shear is added to the compressive functional loading that usually occurs in the articular cartilages
-below fibrous layer is the proliferative cellular layer with progressively differentiating chondrogenic cells
-IMPORTANT: in growth plates of long bones, mitotic activity occurs in the proliferative zone and the chondrocytes are arranged in cell columns; BUT in mandibular condylar cartilage, proliferation occurs in the pre-chondroblast layer ONLY; chondrocytes are post-mitotic (distributed randomly in cartilage and almost immediately undergo hypertrophy)
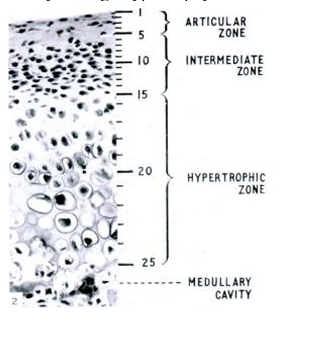
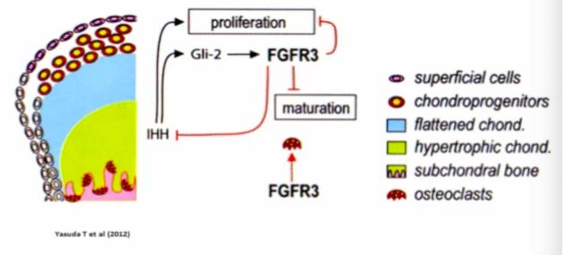
essential elements of endochondral ossification
-hypertrophy of chondrocytes up to 24 fold increase in volume (terminal differentiation)
-expression of Cba1/Runx2 gene
-modification of ECM (removal of CS, deposition of type X collagen, MMP-14-collagenase and MMMP-9 gelatinase) to permit calcification and to degrade interterritorial and pericellular ECM to be followed by resorption
-DO NOT SEE CELL COLUMNS
structure of condylar cartilage
-articular surface formed by collagen
-underneath are proliferative cells (located at surface of cartilage, not within the cartilage itself)
-no column formation in hyaline cartilage
-cells hypertrophy below hyaline cartilage
model for condylar growth
***condyles are like ____, NOT like _____
-articular cartilages; growth plates
-growth plate on left, condyle on right
-condyle has NO chondrocytic mitoses, only in pre-chondroblasts, NO cell columns, rapid chondrocyte hypertrophy with perilacunar mineralization
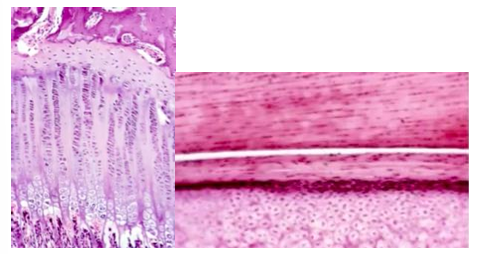
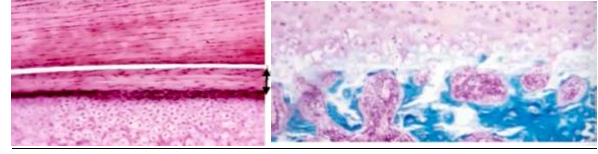
-mandibular cartilage v articular cartilage
-condylar cartilage has fibrous layer
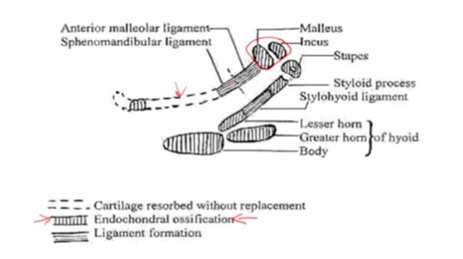
fate of Meckel’s cartilage
-disappears in most places without replacement
-undergoes endochondral ossification- contributes to bone of mandible and incus/malleus/stapes
-in anterior and middle segments, chondrocyte hypertrophy and atypical ECM calcification then resorption (no bone replacement!)- unique for Meckel’s cartilage
-between middle and posterior segments, apoptosis of non-hypertrophic chondrocytes and degradation of non-mineralized ECM by MT1-MMP
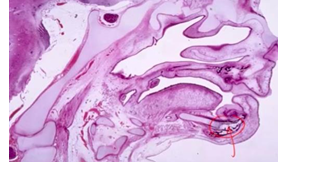
molecular mechanisms of cartilage remodeling
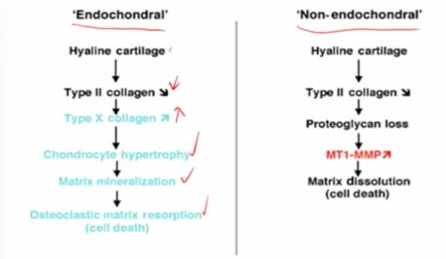
apoptotoci resorption of unmineralized cartilage
-occurs in some cartilage of viscerocranium and selected parts of chondrocranium
-no chondrocytic hypertrophy but apoptosis
-no ECM calcification but dissolution by MT1-MMP
-remodeling into tendons or ligaments
pharyngeal arch cartilage