NUTR250 - CH3
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Time Food is in Mouth
Less than a minute
Time Food is in Stomach
1 to 2 hours
Time Food is in Small Intestine
7 to 8 hours
Time Food is in Colon
12 to 14 hours
Digestion
breaks down food into nutrients for absorbtion
Gastrointestinal Tract’s Tasks Include:
– Mechanical and enzymatic (chemical) digestion
– Protection from pathogens
– Steady movement through GI tract
– Absorption of nutrients
– Excretion of waste
Where does digestion begin?
The mouth
Mechanical Breakdown
Chewing
Salivary Glands
facilitate in swallowing, helps prevent choking, moistens food for easy passage
Salivary Amylase
begins enzymatic breakdown of CHO (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen), initiates CHO breakdown as well
Bolus
chewed food that passes from the pharynx to the esophagus
What effects flavor?
Aroma, Texture, and Temperature
The 5 Flavors
Sweet, Sour, Bitter, Salty, Umami (Savory)
Chyme
semiliquid mass of food and digestive enzymes in stomach
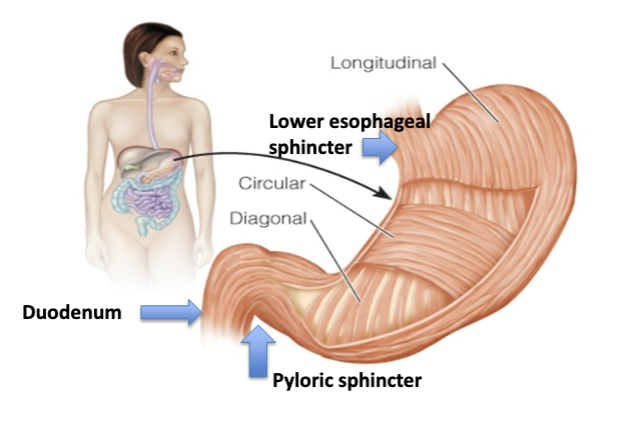
Parts of the Stomach
3 Segments of Small Intestine
Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum
Common Bile Duct
releases digestive fluids from pancreas and gallbladder
Ileocecal Valve
Connects small intestine to colon
Segmentation
When the inner circular muscles contract in the small intestine to mix chyme with more digestive juices
Enterocytes
Absorbing cells of the small intestine
Peristalsis
when outer longitudinal muscles push chyme forward
5 Digestive Organs
Salivary Glands, Stomach, Pancreas, Liver, Small Intestine
Digestive Fluids
Water, Mucus, Gastric/Pancreatic juices
Digestive Secrestions
Enzymes: names end in -ase like lipase, protease, carbohydrase
Hydrolysis
reaction that adds water to break food down into smaller particles
Gastric Juice
acts in protein digestion and a mixture of water, enzymes, and hydraulic acid
Bile
Produced in the liver, stored in the gallbladder, released into the duodenum, disperses fats into watery solutions for enzymes
What happens to fiber during digestion?
fiber is fermented/eaten by the microbiome in your colon. This fermentation produces water, gas, and short chain fatty acids that feed the walls of our colon
Gastric Glands
Fluid mixes with bolus; hydrochloric acid uncoils proteins;
enzymes break down proteins; mucus protects stomach cells.
Pancreas
Bicarbonate neutralizes acidic gastric juices; pancreatic enzymes break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
Hepatic Portal Vein
Water soluble nutrients travels through it to get to the liver
Villi
project from the enterocytes, and create a large surface area for absorption
Microvilli
hair-like structures that cover villi
Crypts
secrete intestinal juices
Goblet Cells
secrete mucus
The Bloodstream
– Delivers oxygen and nutrients
– Removes carbon dioxide and wastes
Systemic Circulatory System
Includes hepatic system that routes blood from intestines to the liver via the hepatic portal vein and out to systemic circulation
Cardiopulmonary Circulatory System
between heart and lungs
Lymphatic System
One-way route
– No pump: uses muscle contractions; lymph circulates
between cells of the body
– Circulates fat soluble vitamins and large fat molecules
– Collects fluids
• Entry into bloodstream via thoracic duct behind the heart
• Nutrients in lymphatic vessels bypass the liver during the
first pass through the body
Hepatic Vein
returns blood to the heart
Blood/nutrient route through intestines
Heart→ arteries → intestinal capillaries → hepatic portal vein → hepatic capillaries → hepatic vein → heart
Prebiotics
encourage microbial growth
Probiotics
live microbes
Homeostasis
regulation of digestion, body temp, blood pressure, blood pH, etc.
What systems coordinate digestive processes?
The endocrine and nervous systems
Postive Feedback
amplifies change, very rare
Negative feedback
the response reverses or causes the opposite effect of the stimulus, very common
Gastrin
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is secreted into the stomach to maintain an acidic pH
Low pH shuts off gastrin and HCl
Secretin
• Bicarbonate-rich juices secreted
into the small intestine to
maintain a slightly alkaline pH
• High pH shuts off secretin
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
• Bile is secreted into the
duodenum to emulsify fats
• Bicarbonate- and enzyme-rich
juices secreted into the small
intestine to maintain a slightly
alkaline pH, digest fats and
proteins, and slow GI tract
motility for thorough nutrient
digestion and absorption
• Fat breakdown shuts off CKK
What could effect a digestive system?
blood supply, lifestyle factors like: sleep, physical activity, mental health, foos eaten
How are carbs digested?
salivary amylase begins break down
stops digesting after stomach acid inactivates the salivary amylase
digestion picks back up again when pancreas sends pancreatic enzymes to the small intestine via the pancreatic duct
starch and sugars are absorbed through cell walls and sent through the bloodstream via the hepatic portal vein
How is fiber digested?
fiber is crushed by teeth
some fiber is partially digested by microbiome in your colon
most is excreted
Hot is fat digested?
some fat melts in your mouth
some fat separates from watery GI juices in the stomach
in the small intestine fat is emulsifies by bile so so pancreatic and intestinal lipases can break it down
cell walls then absorb it
How is protein digested?
protein is moistened by saliva
gastric acid and protease enzymes break down proteins as they uncoil in the stomach
small fragments of protein are absorbed through cell walls and into the hepatic portal vein