Forensics Exam 2
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Elements
Basic chem subs that make up all matter and cannot be broken down into simpler substances.
Compound
A chem sub made of two or more elements
Solids vs Liquids vs Gases
S: definite shape and volume and particles that vibrate in place
L: definite volume, takes shape of container
G: no definite shape or volume, expands to fill container
Phase
Separation of a mixture into its compounds based on the distribution of the two subs
Organic vs Inorganic Compounds
Organic comps include all carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen Inorganic comps don’t
Qualitative vs Quantitative Analysis
Type of subs present vs How much of sub
How does liquid reach equilibrium with its gaseous phase (Henry’s Law)
At a constant temperature, the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above the liquid (more gas pressure, more gas dissolves in liquid)
Process of Chromatography
Separating a mixture into its components and passing through a stationary phase as a mobile phase
Parts of Gas Chromatograph (GC)
Gas flows through column, stationary phase is film of liquid in column spiral, separated into its components by the stationary phase
Retention Time
Time required for component to emerge from GC column
Thin-layer (TLC) vs Gas Chromatography (GC)
TLC uses a liquid mobile phase and solid stationary phase GC uses a gas mobile phase and a solid stationary phase
Rf Value (retention factor)
How far a sub travels relative to the solvent (component traveled / solvent traveled)
Electrophoresis
Technique that forces materials to move across a gel-covered plate under electrical potential (charge)
Wave vs Particle Theories of Light
Wave: continuous wave
Particle: stream of discrete energy particles
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Entire range of radiation energy
Relationship between color and the absorption of light by molecules
The specific color it absorbs identifies exactly what the compound is made up of
Beer’s Law
The amount of light a sub absorbs is directly proportional to its concentration
Parts of simple Absorption Spectrophotometer
Radiation source, sample holder, frequency selector, detector from electromagnetic radiation to electric signals, recorder to make record of signal
UV and IR absorption spectrum use for identifying organic comps
Each absorption acts as a “fingerprint” of a sub directly identifying it
Concept of Mass Spectrometry
The identification of each chem by a high-energy electron beam that makes positively charged ions (cation)
Significance of Mass Spectrum
Identifying unknown subs and finding its abundance
Usefulness of Trace Evidence for type of physical evidence
Helps establish the source of physical evidence by making it individual evidence
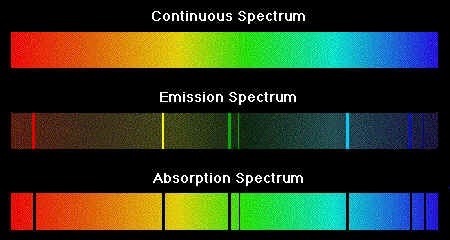
Continuous vs Line Emission Spectrum
Protons vs Electrons vs Neutrons
P: positively charged, large mass
E: negatively charged, small mass
N: no charge, large mass
Atomic Number and Atomic Mass Number
A#: # of protons
AM#: # of protons and neutrons combined
Orbital Energy Levels
Regions in atoms where there is a high probibility of finding an electron
What happens when an atom absorbs a certain amount of energy
They become “excited,” higher, and more unstable
Atom releasing energy in light form
Releasing a photon
Isotope
Atoms with same # of protons but different # of neutrons creating different atomic masses
Radioactivity
Emission of electromagnetic energy particles
How can elements become radioactive
By losing or gaining a neutron making a different isotope
Why are X-ray Diffraction patterns useful for chem identification
Used for solid and crystalline structures, there are different patterns for each element, making them “fingerprints”
Psychological vs Physical Dependance
Psy: an emotional and metal craving for a high
Phys: an adaption to the drug causing withdrawal without it
Controlled Substances Act Schedules
I: high risk for abuse and no accepted medical use; heroin, LSD
II: high risk and medical use with severe restrictions; cocaine, PCP, amphetamines
III: less risk and current medical use; codeine
IV: low risk and current medical use; darvon, tranquilizers
V: low risk and common medical use; opiates, nonnarcotics
Lab Tests for Identifying Drugs
Screen test by color and property (pill, powder, liquid) and then use NIK flow chart with small amount to identify common drugs
Proper Collection of Drugs
Prevent loss, label correctly, cause no cross-contamination, original container can suffice
Individuals who made significant contributions to fingerprinting
Francis Galton: wrote a fingerprinting book
Juan Vucetich: created a workable system and solved first murder case with fingerprints
Sir Edward Henry: created categories of fingerprints based of order and type of patterns
Ridge Characteristics
ridge ending, bifurcation, trifurcation, dot, island,
Fingerprint Classes
Loop: ulnar (pinky), radial (thumb)
Whorl: plain, accidental, double, and central pocket loop
Archs: plain and tented
IAFIS
Integrated Automated Fingerprint Identification System
Visible vs Plastic vs Latent Prints
Visible: fingerprint in liquids
Plastic: fingerprints in soft solids (soap bars, putty)
Latent: oils and water left from fingers of solid surface
Types of Fingerprint Development
Powder (volcanic ash and magnetic): nonporous solid surfaces (glass, tile)
Super Glue Fuming: nonporous surfaces that are movable (leather, plastics)
Iodine Fuming and Ninhydrin: porous surfaces (paper, cloth)
How to Preserve Prints
Take pictures before removing and lifting with tape and transporting it to a labeled paper card