Biology 2- Animal Science 1.3
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
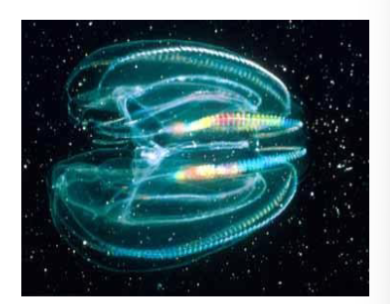
phylum ctenophora
comb jellies, propel through water via cilia, mostly hermaphroditic
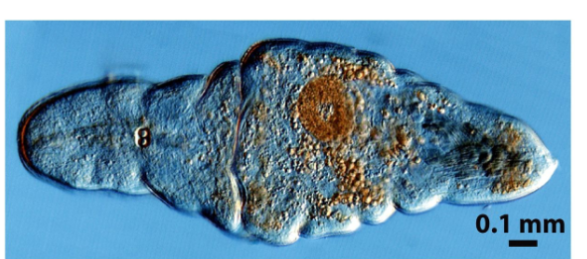
phylum acoelomorpha
acoelomorphic worms, triploblastic and bilaterally symmetric, lack coelom, small carnivores
aceolomates have ______, coelomates have _____
no enclosed body cavity, enclosed body cavity lined with mesoderm
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
skin, muscles and organs, gut
class tubellaria
phylum platyhelmithes, free living, flatworms with broad bodies, lack specialized structures so body must be moist,

class cestoda
phylum platyhelminths, parasitic tapeworms, live in gut, no mouth or digestive tract, hermaphroditic
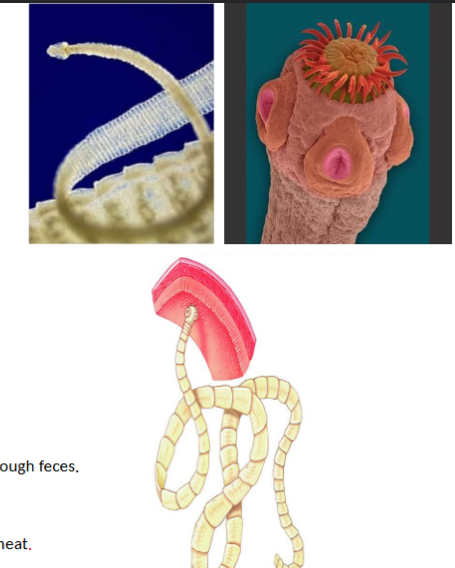
phylum rotifera
rotifers, moist soils and mosses, filter feed, coelomates
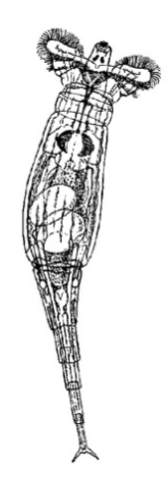
class polycheata
phylum annelida, sand worm, many setae, sand burrowers, mixed reproduction

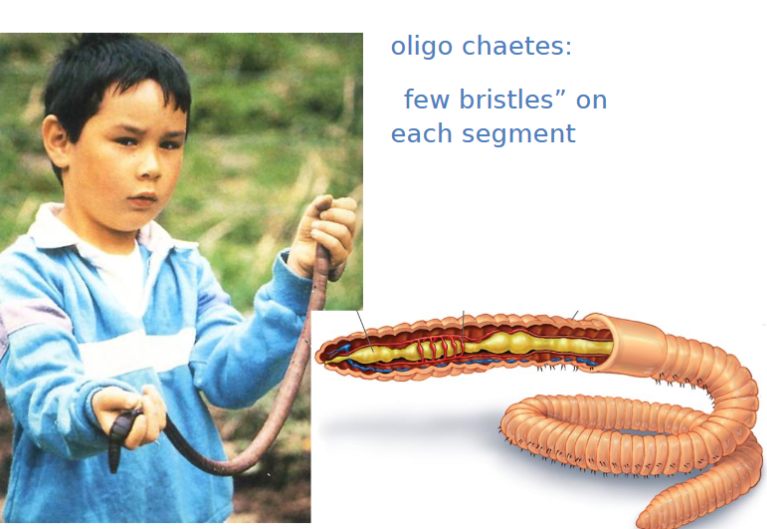
class oligochaeta
phylum annelida, earthworm, few setae, less marine, contracting movement

class hirudinea
phylum annelida, leeches, ectoparasites, low segmentation and setae, sexual reproduction

class polyplacophora
phylum molluska, chitons, marine plated

class gastropoda
phylum molluska, snails, have stomach foot, shell apart from slugs

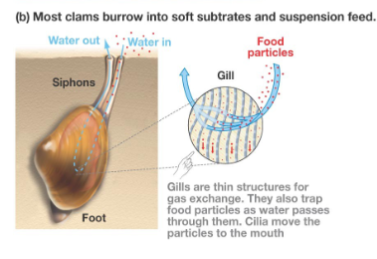
class bivalvia
phylum molluska, clams, oysters, two shells hinged, suspension and filter feeders, sexual external fertilization
class cephalopoda
phylum molluska, octopus, brain and well developed eyes, “Shell” is beak, internal fertilization and eggs

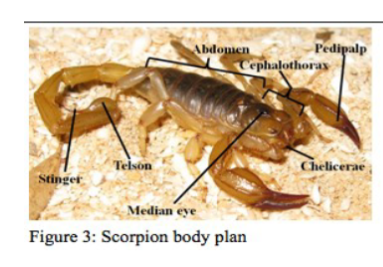
subphylum chelicerata
subphylum of arthropods, spiders scorpions and ticks, have chelicerae, feeding structures, pedipalps to catch prey, no metamorphosis
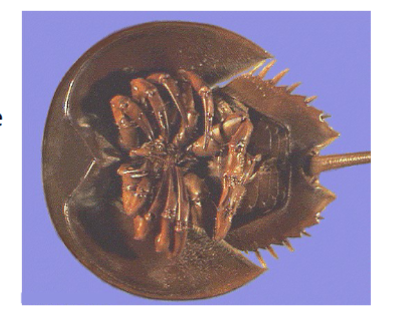
class merostomata
in subphylum chelicerata, horseshoe crab
class arachinida
in subphylum chelicerata, spiders, ticks, scorpions

subphyla crustacea
subphylum of arthropods, shrimp, lobster, crabs and more,
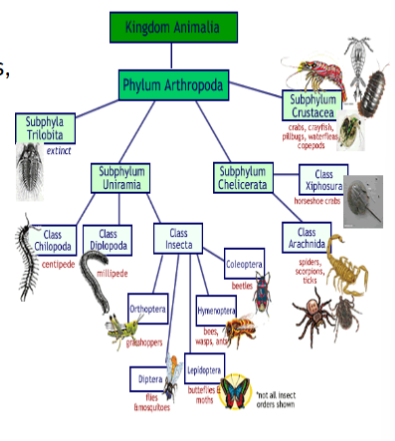
subphylum myriapoda
subphylum of arthropods, centipedes, millipedes
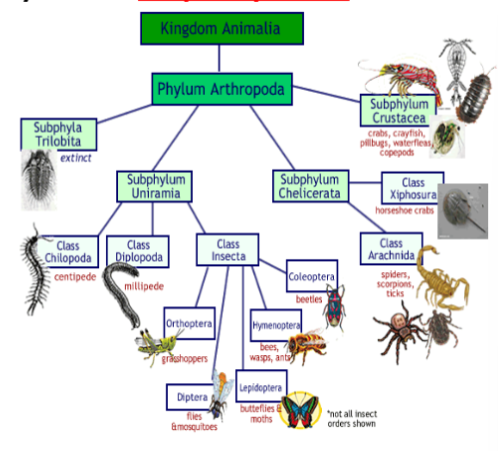
class diplopoda
in arthropod subphylum myriapoda, millipedes, 2 pairs of legs, slow moving herbivores

class chilopoda
in arthropod subphylum myriapoda, centipedes, carnivore hunters, 1 pair legs a body segment

subphylum hexapoda
arthropod subphylum, three part body plan

class insecta
arthropods in subphylum hexapoda, insects, successful, most undergo metamorphosis, 3 segments of head, thorax and abdomen, mostly lay eggs, internal fertilization

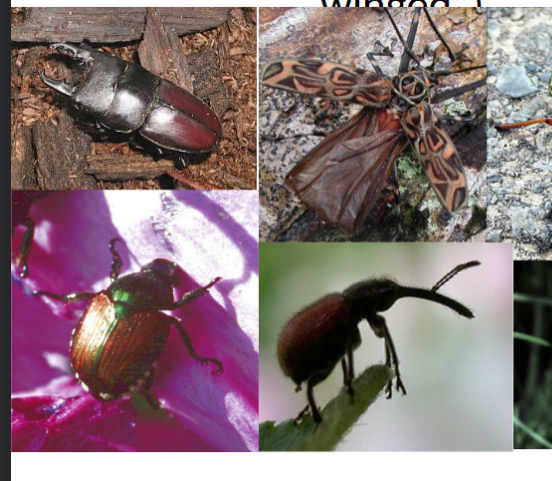
order coleoptera
in class insecta, beetles, sheath wings, 25% of all animals species, many hemimetabolous

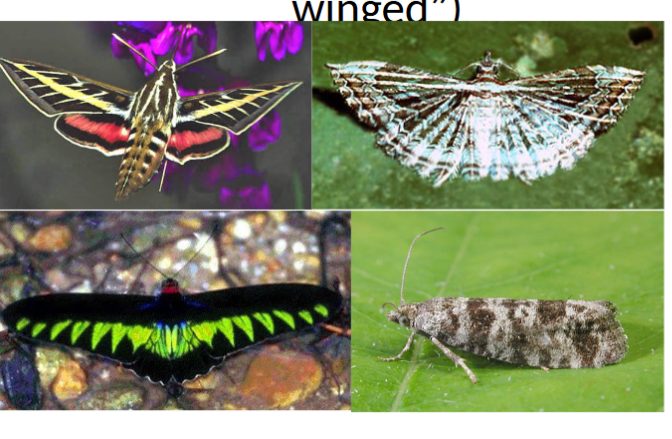
order lepidoptera
in class insecta, scale winged, butterflies and moths

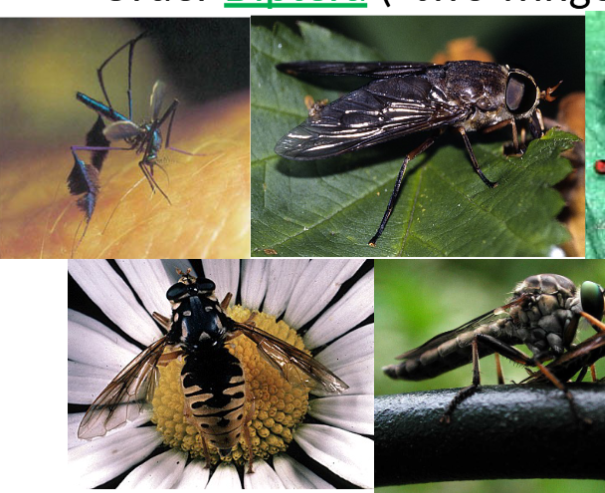
order diptera
in class insecta, two winged, flies

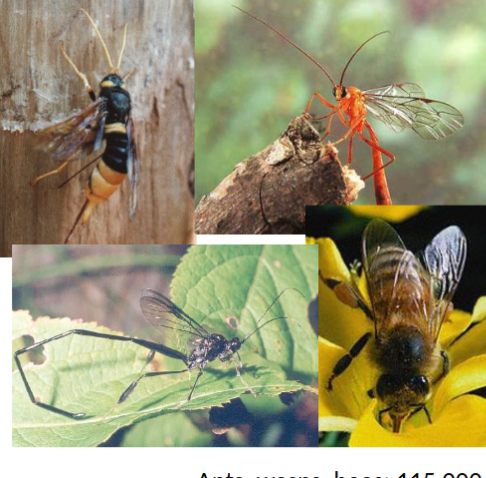
order hymenoptera
in class insecta, membrane winged, ants wasps and bees

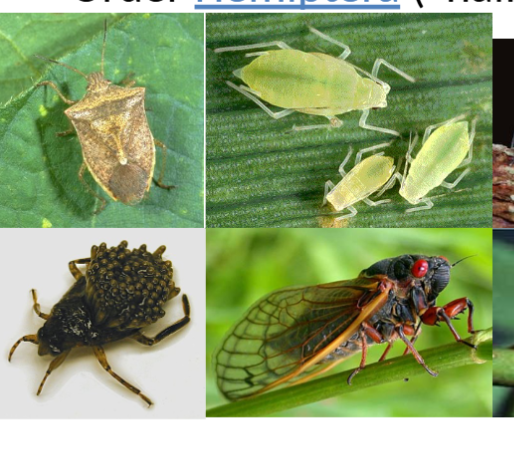
order hemiptera
in class insecta, half winged, “true bugs” aphids and cicadas

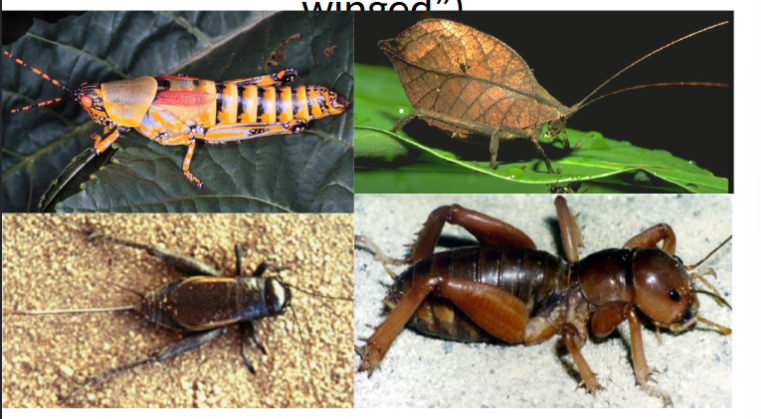
order orthoptera
in class insecta, straight winged, grasshoppers and crickets

class asteroidea
in phylum echinodermata, sea stars, arms from central disk, predators and scavengers, two sexes and external fertilization eggs

class echinoidea
in phylum echinodermata, sea urchins have beak mouths, and sand dollars, globe bodies that lack distinct arms, spiny herbivores, or for sand dollars suspension feeders

class ophiouroidea
in phylum echinodermata, brittle stars, large abundant class, 5 long rays, central disk, don’t move on tube feet, suspension feeders

class crinoidea
in phylum echinodermata, sea lilies and feather stars, suspension feeders with upward mouths,

class holothuridea
in phylum echinodermata, sea cucumbers, soft bodies, reduced ossicles, endoskeletons, eviscerate to defend self

subphylum vertebrata
spinal column replaces notochord

class agnatha
in phylum chordata, subphylum vertebrata, lamprey and hagfish, jawless fish, no appendages, lack full vertebral column,

class chondrichthyes
in phylum chordata, subphylum vertebrata, cartilaginous fish, sharks and rays, have jaws, first to develop teeth, lack operculum and swim bladder, internal fertilization

class osteichthyes
in phylum chordata, subphylum vertebrata, bony fish, diverse and successful, have operculum door structure and swim bladder, lateral line, external fertilization

class amphibia
in phylum chordata, subphylum vertebrata, “two lives”, frogs, salamanders, can live but not reproduce on land, lungs and gas exchange, can have internal or external fertilization

order anura
class amphibians without tails, frogs and toads, live near water and metamorphosize

order urodela
class amphibians, salamanders, elongated bodies

class reptilia
in phylum chordata, subphylum vertebrata, reptiles, aminiotic egg for terrestrial habitats, internal fertilization, pokilothermic and body temp depends on environment
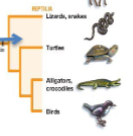
order chelonia
in phylum chordata, subphylum vertebrata, turtles and tortoises, hard shell, bony plates fuse to vertebrae, turtles more aquatic and carnivorous, oviparous

order sqaumata
in phylum chordata, subphylum vertebrata, lizards and snakes, kinetic skulls

suborder sauria
order sqaumata, lizards

suborder serpentes
order squamata, snakes

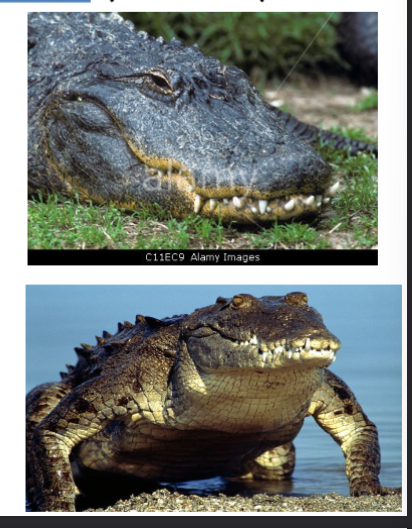
order crocodilia
in phylum chordata, subphylum vertebrata, crocodiles, alligators, closer related to birds than reptiles, complex heart, oviparous

class aves
in phylum chordata, subphylum vertebrata, birds, feathered, wings and hollow bones, oviparous, fast metabolism, complex heart and efficient lungs

order passeriformes
class aves, songbirds, perching and most of birds
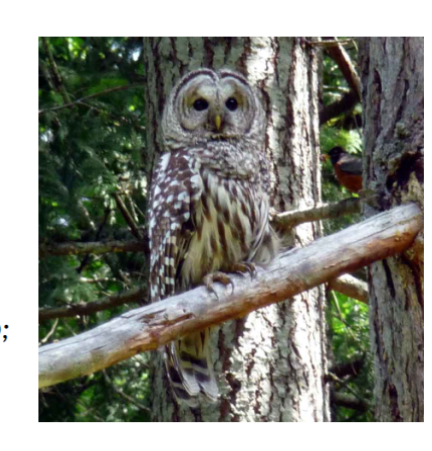
strigiformes
class aves, owls,

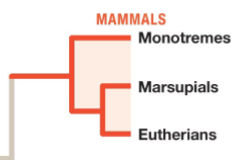
class mammalia
in phylum chordata, subphylum vertebrata, mammals, have mammary glands and milk, hair, specialized teeth, large skulls, have placenta (some) to allow nutrients to get from mother to child, endothermy (self regulate body temp), complex heart, can’t digest cellulose on own
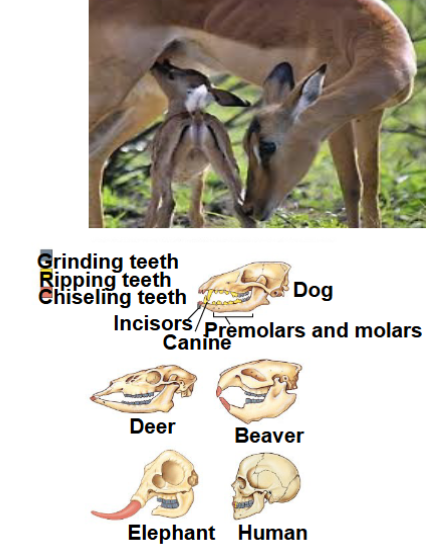
subclass protheria
mammals, platypus, lay eggs and no placenta

subclass metatheria
mammals, marsupials, kangaroo, birth underdeveloped young

subclass eutheria
mammals, placental
order rodentia
mammal subclass eutheria, rodents, mice

order primates
mammal subclass eutheria, monkeys and apes, humans, opposable thumbs and grasping, binocular vision

suborders of primates
prosimians, lemurs, smaller brained; anthropoids, monkeys, tails; hominoids, oragutans, gorrila, human, great apes, bipedal