bone microanatomy
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
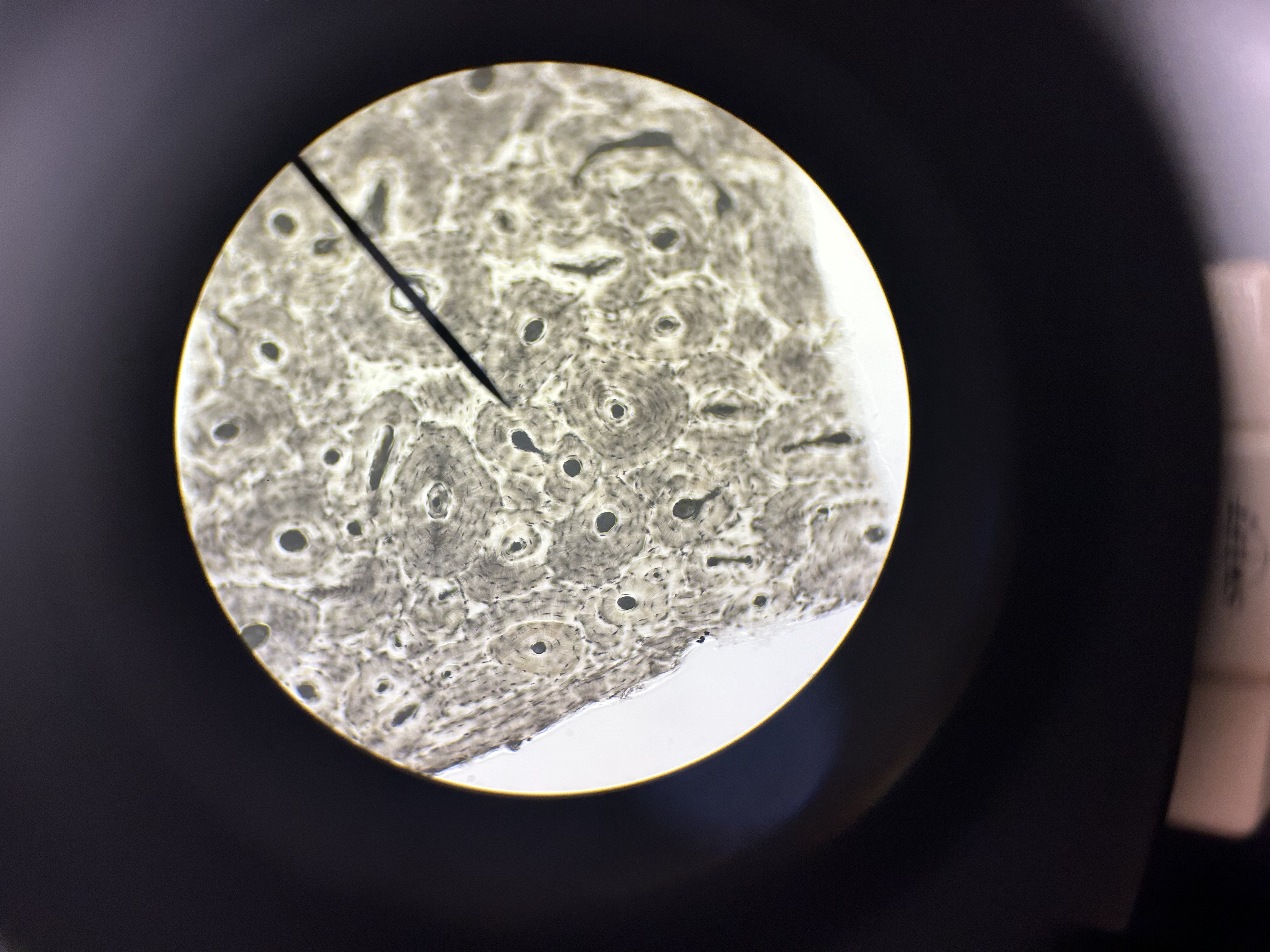
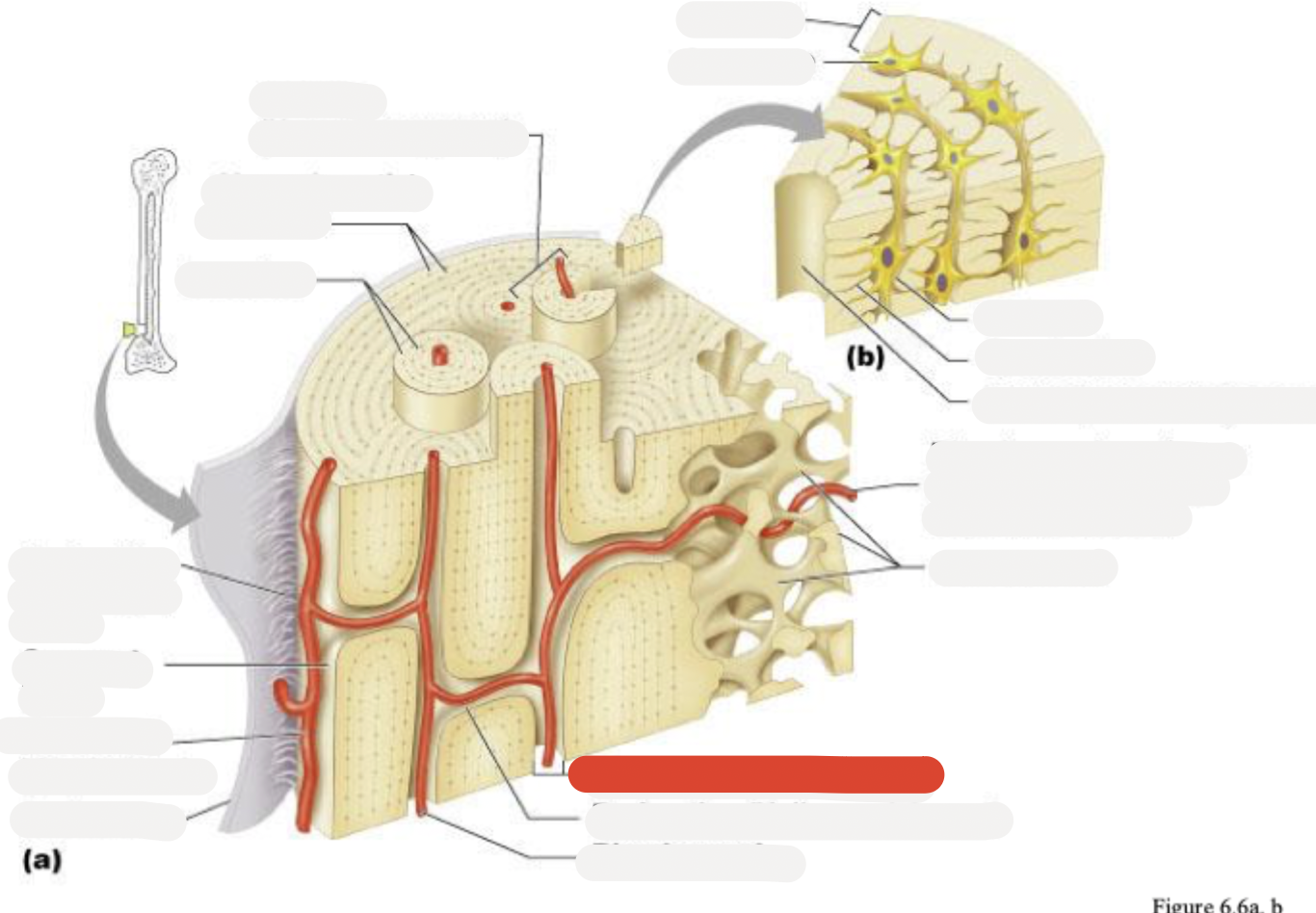
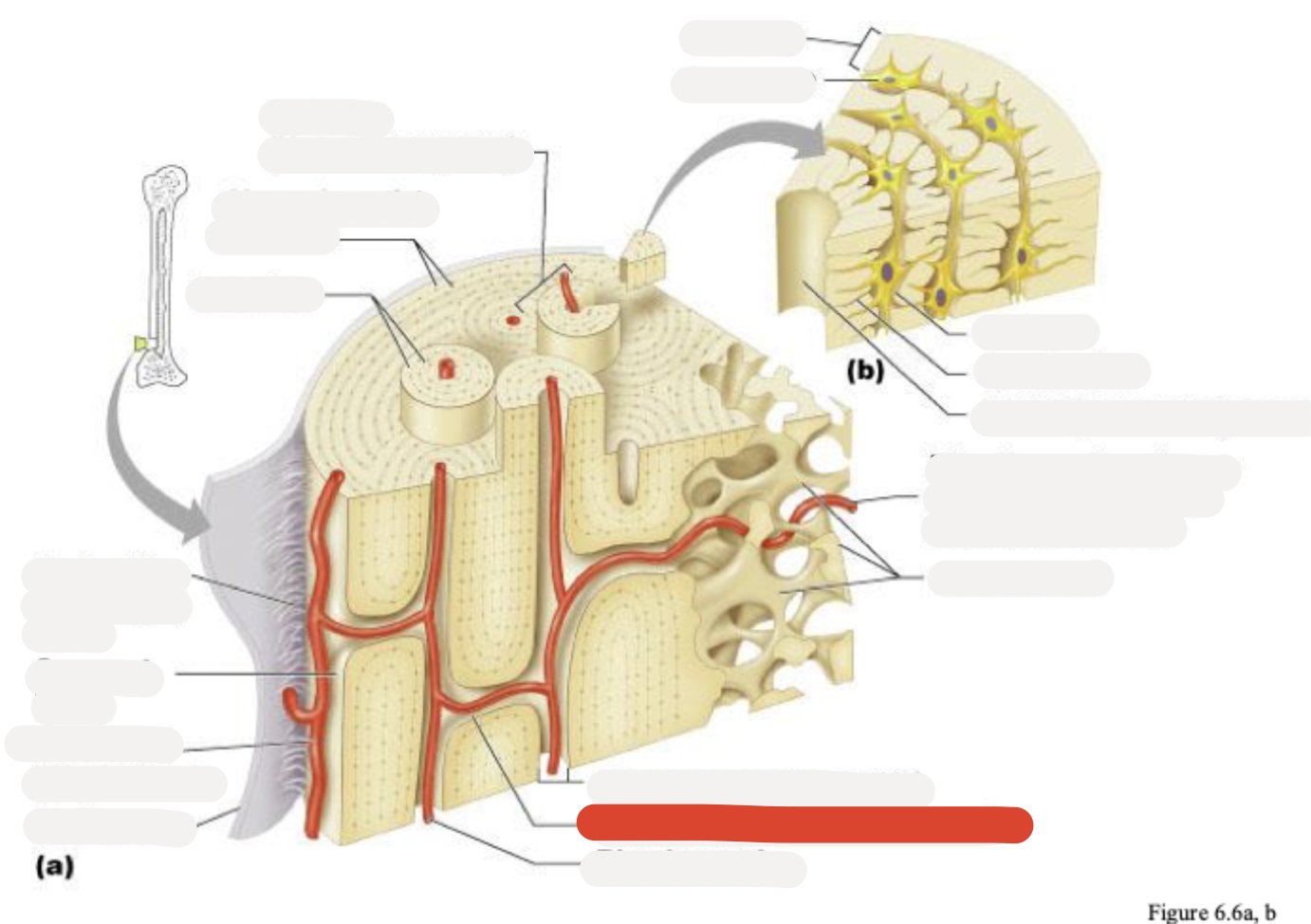
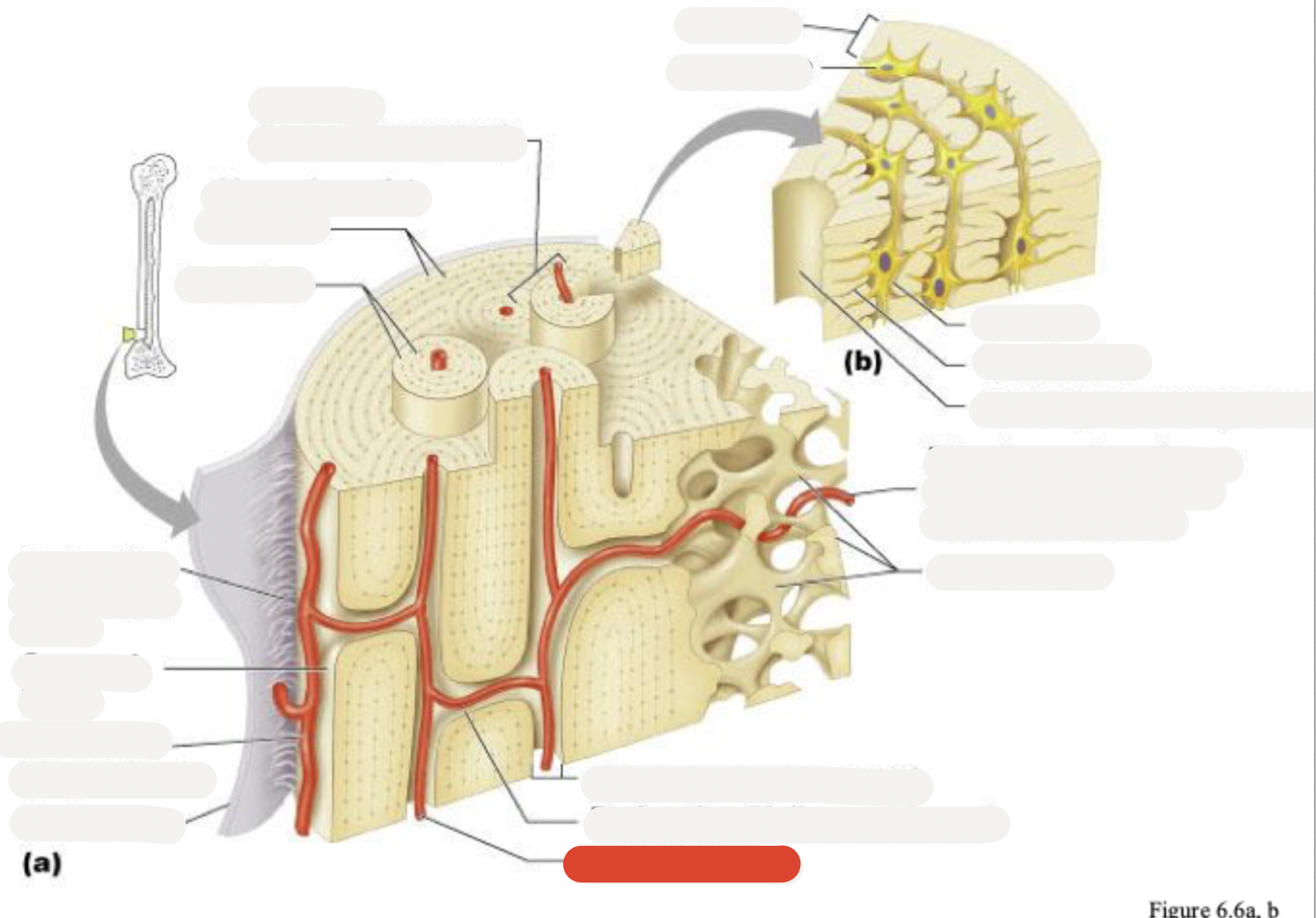
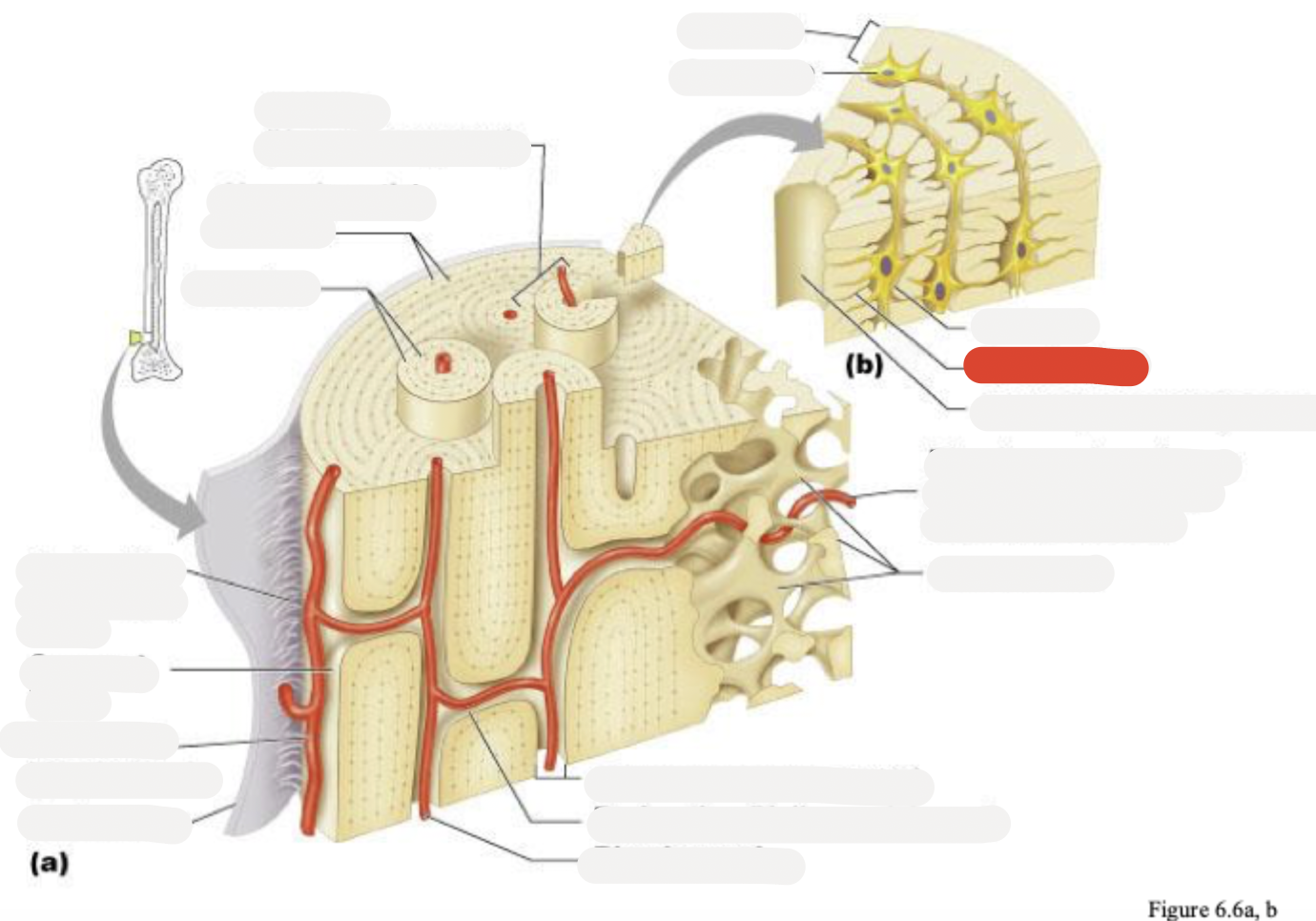
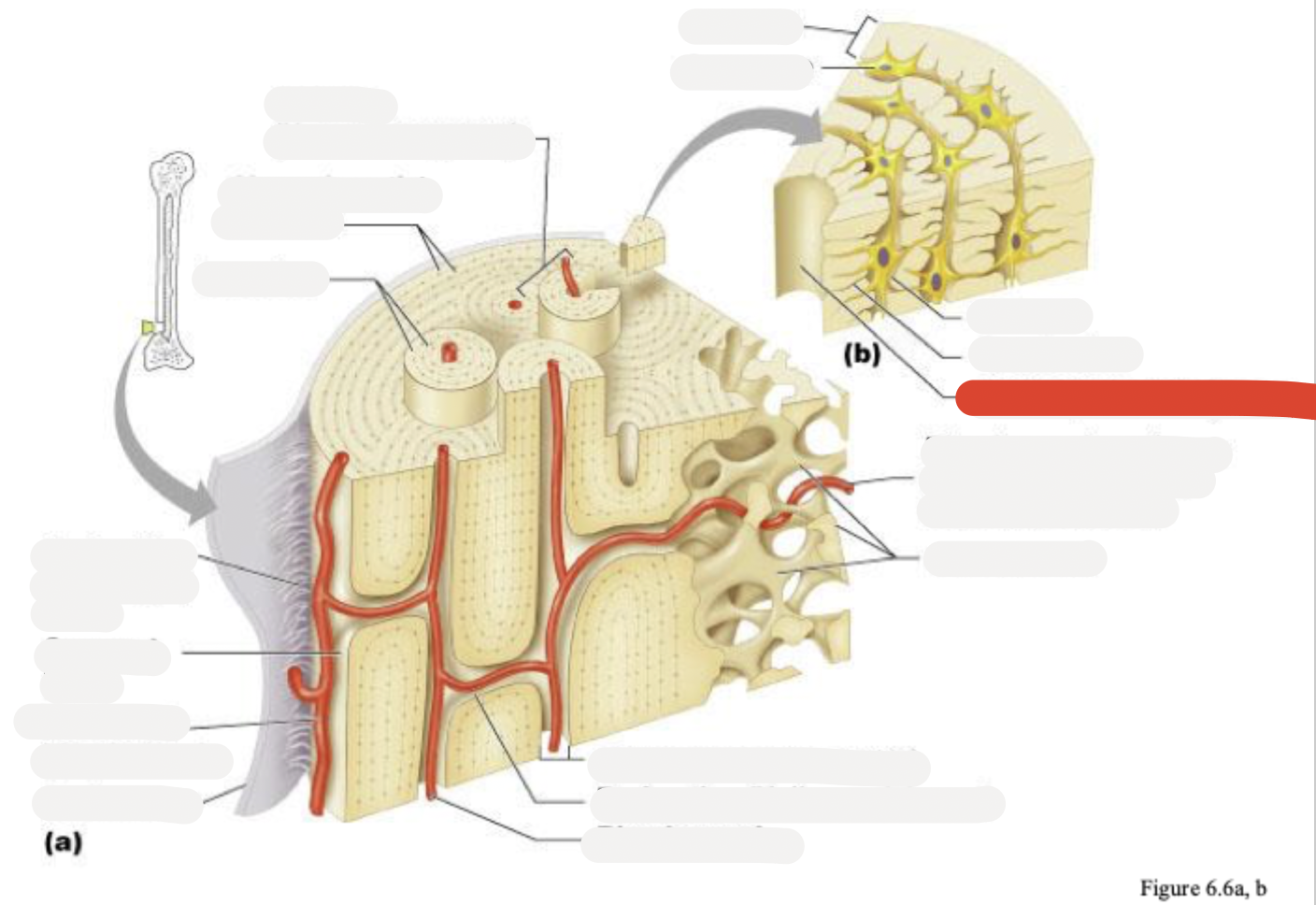
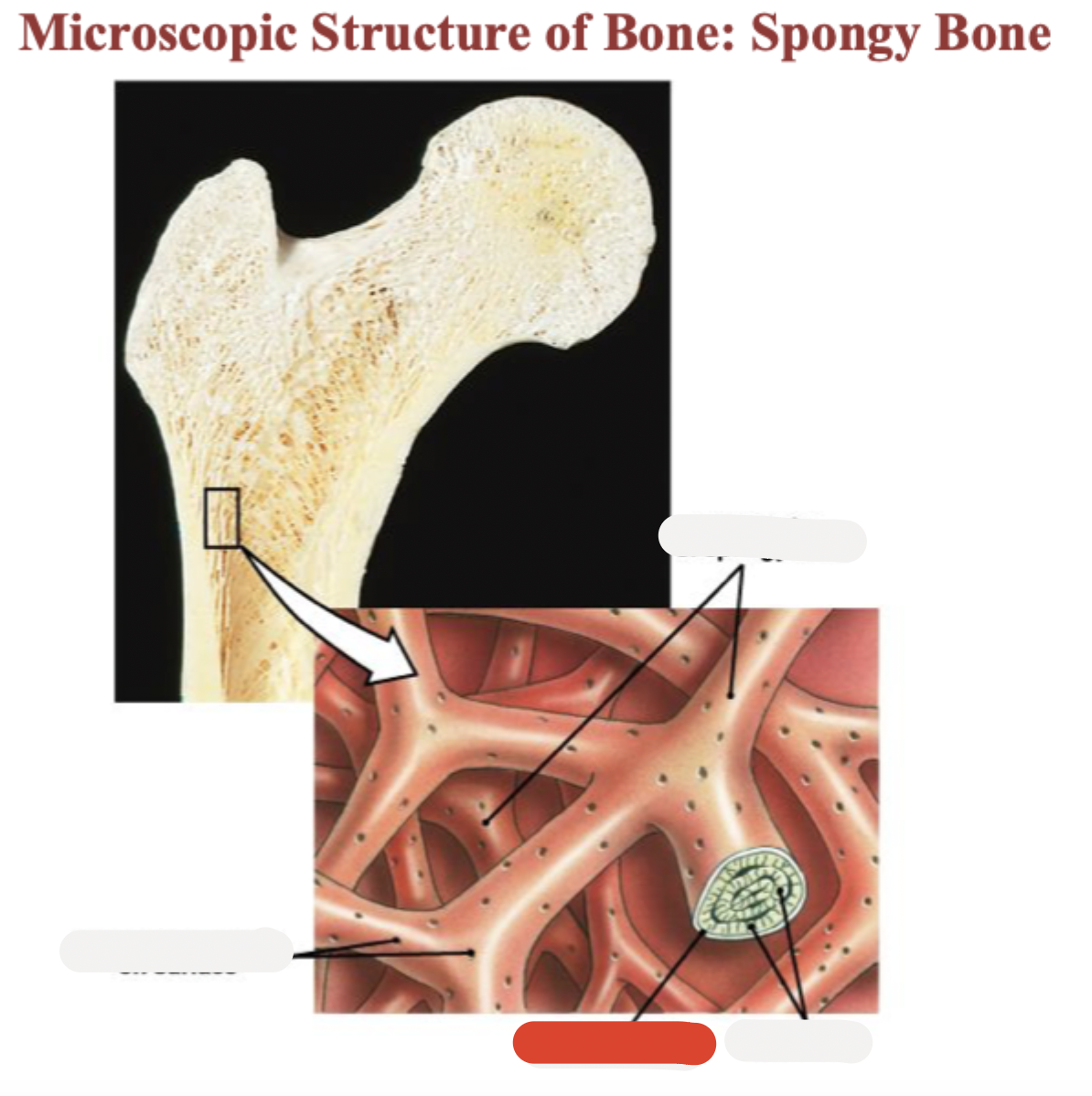
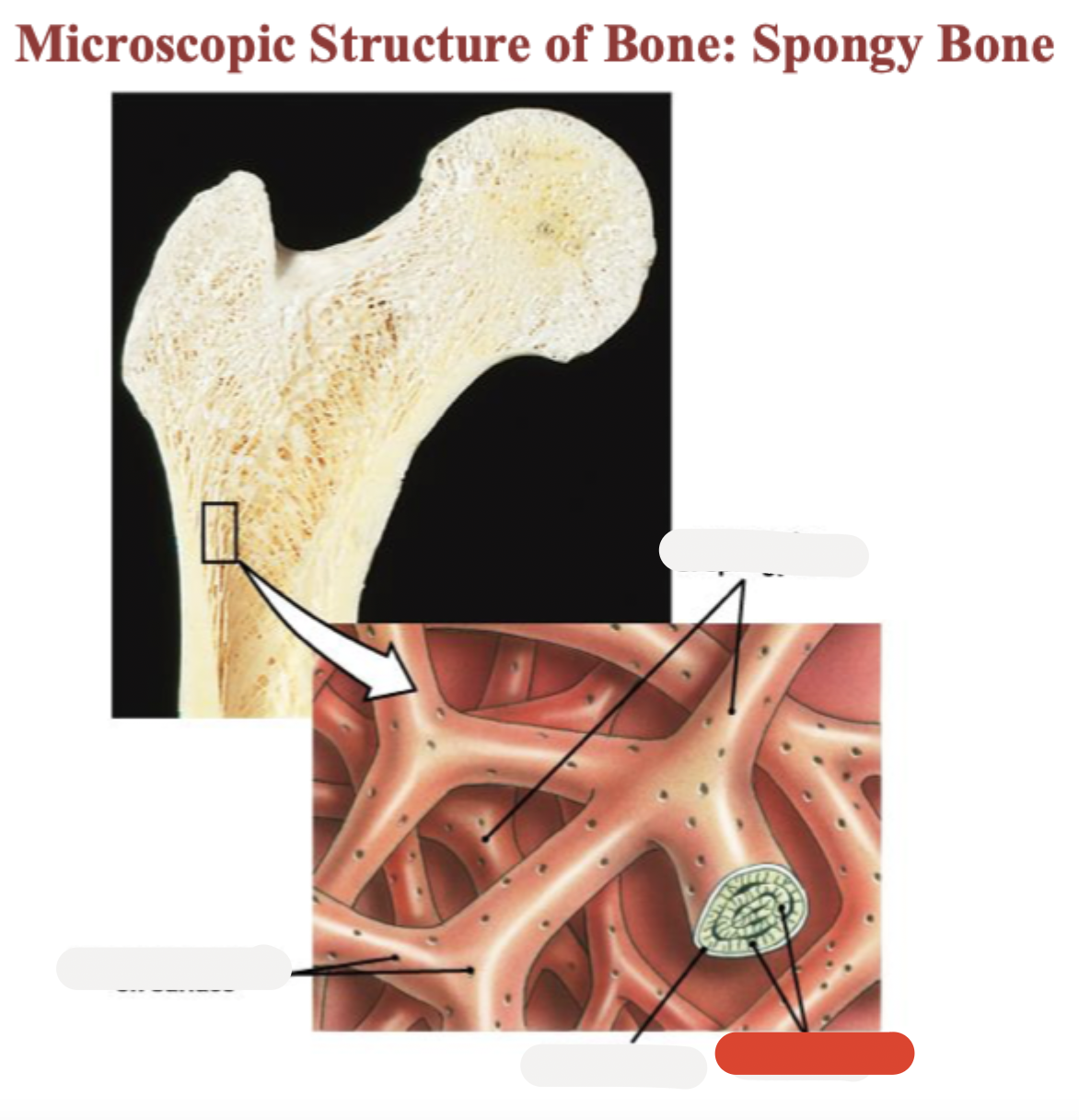
Osteon (Haversian system)
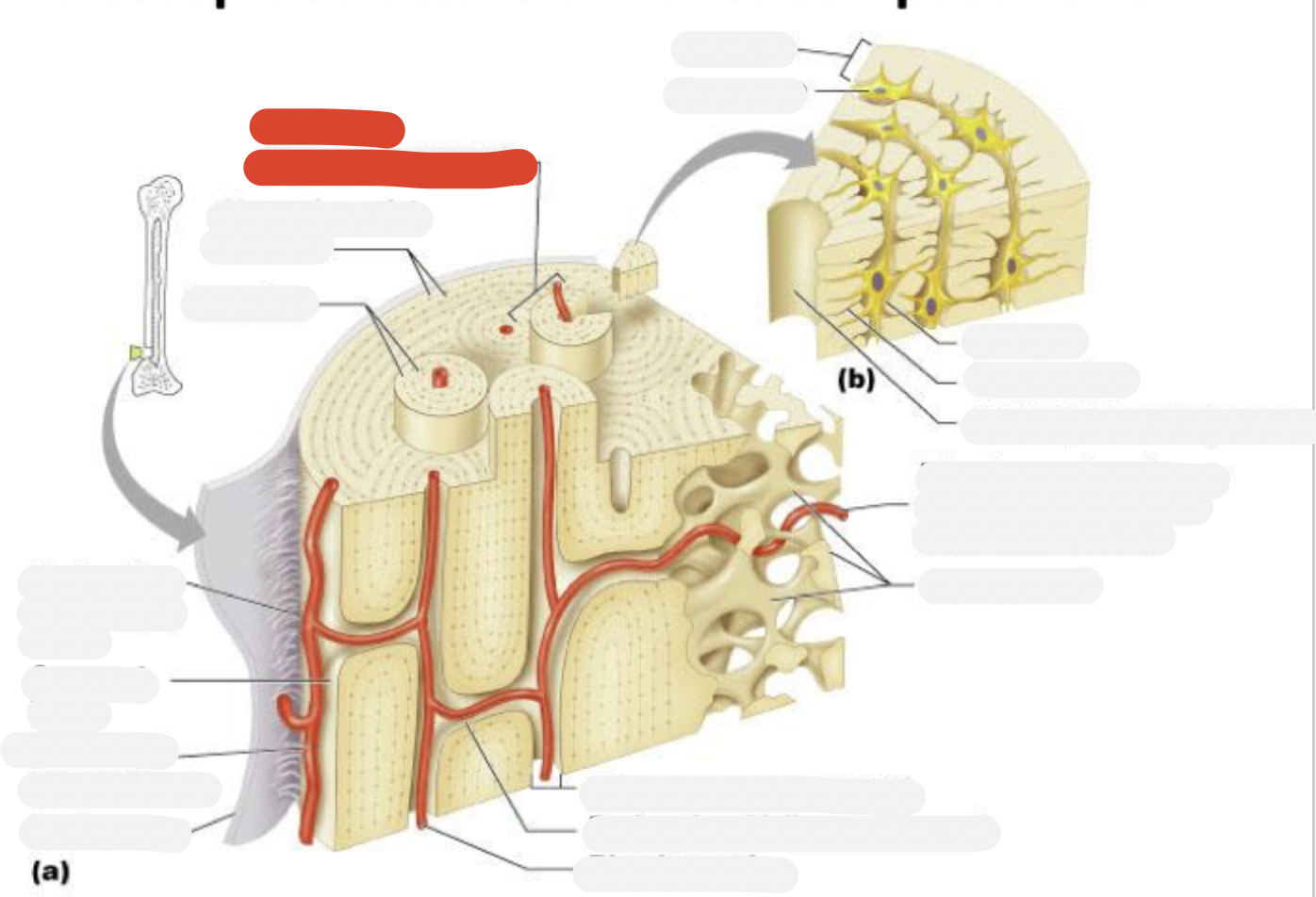
Circumferential lamellae
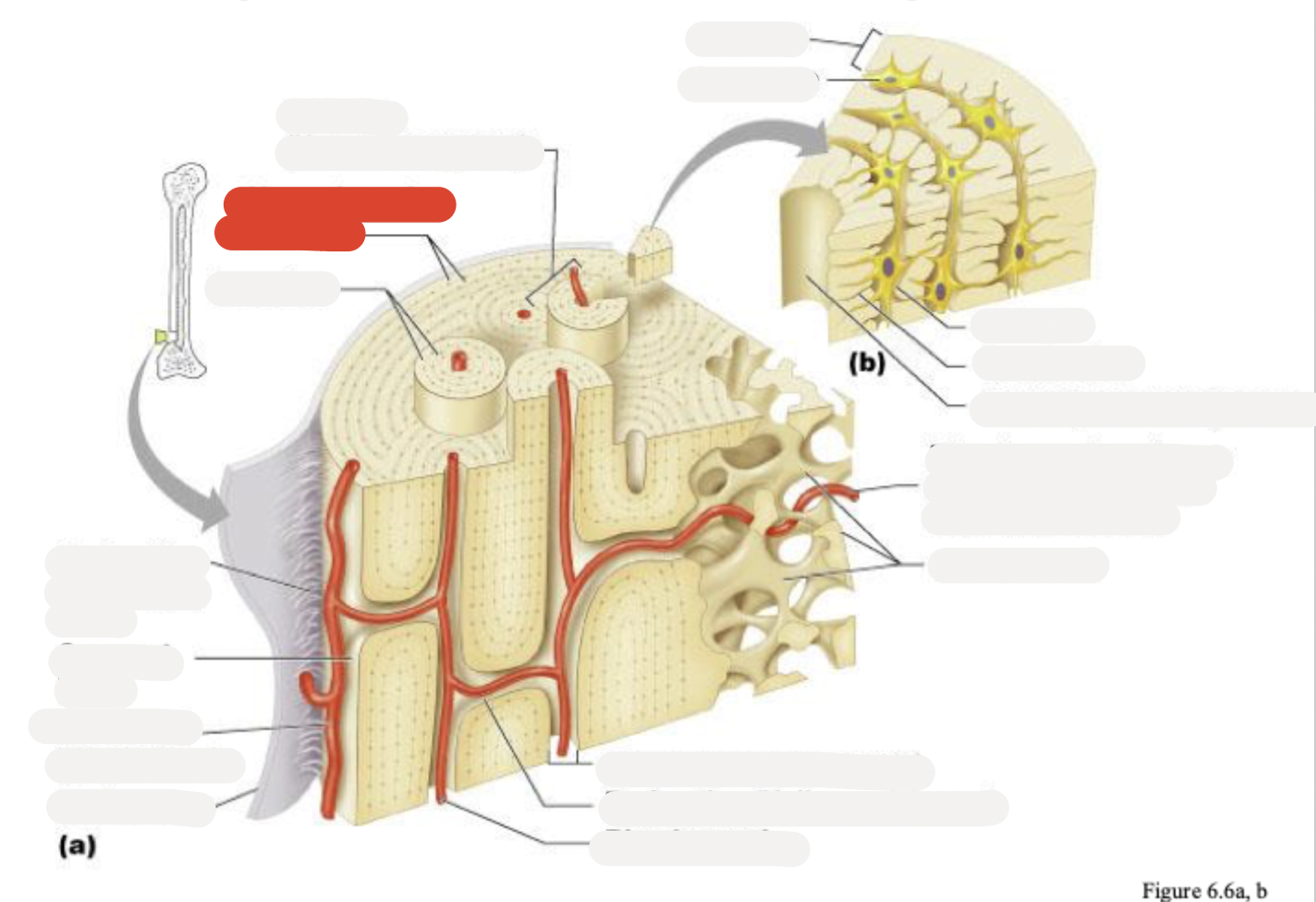
Lamellae
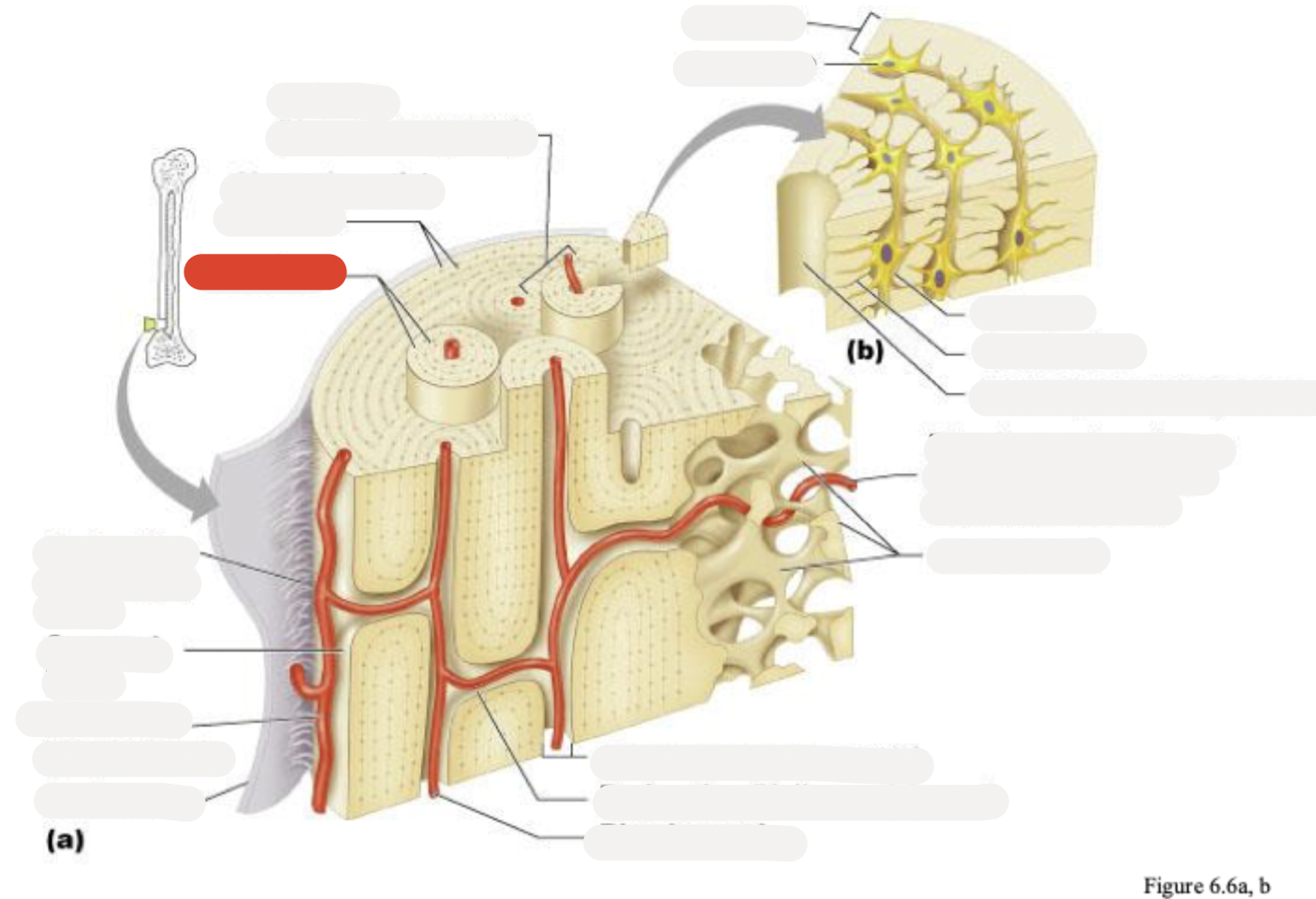
Perforating (Sharpey’s) fibers
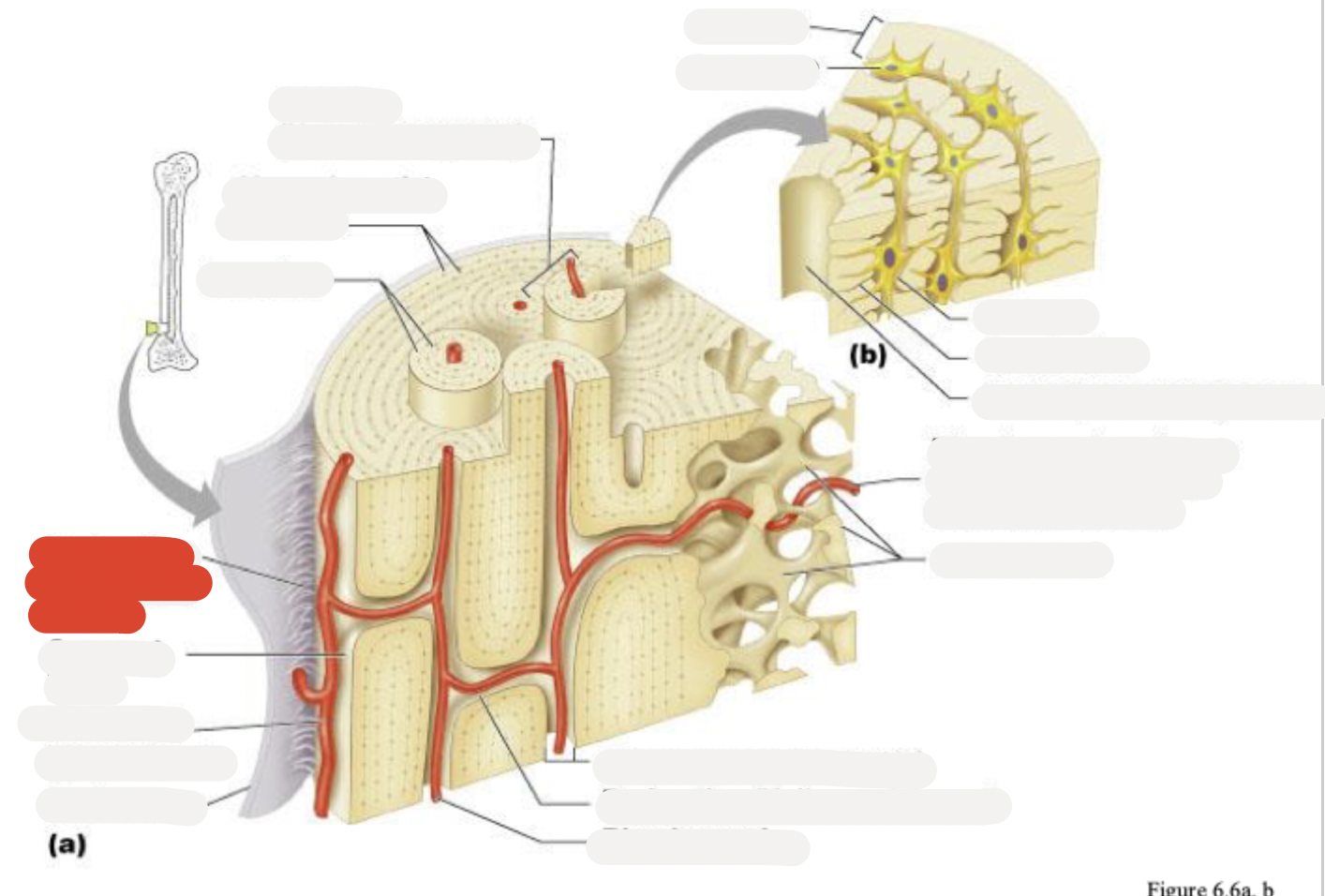
Compact bone
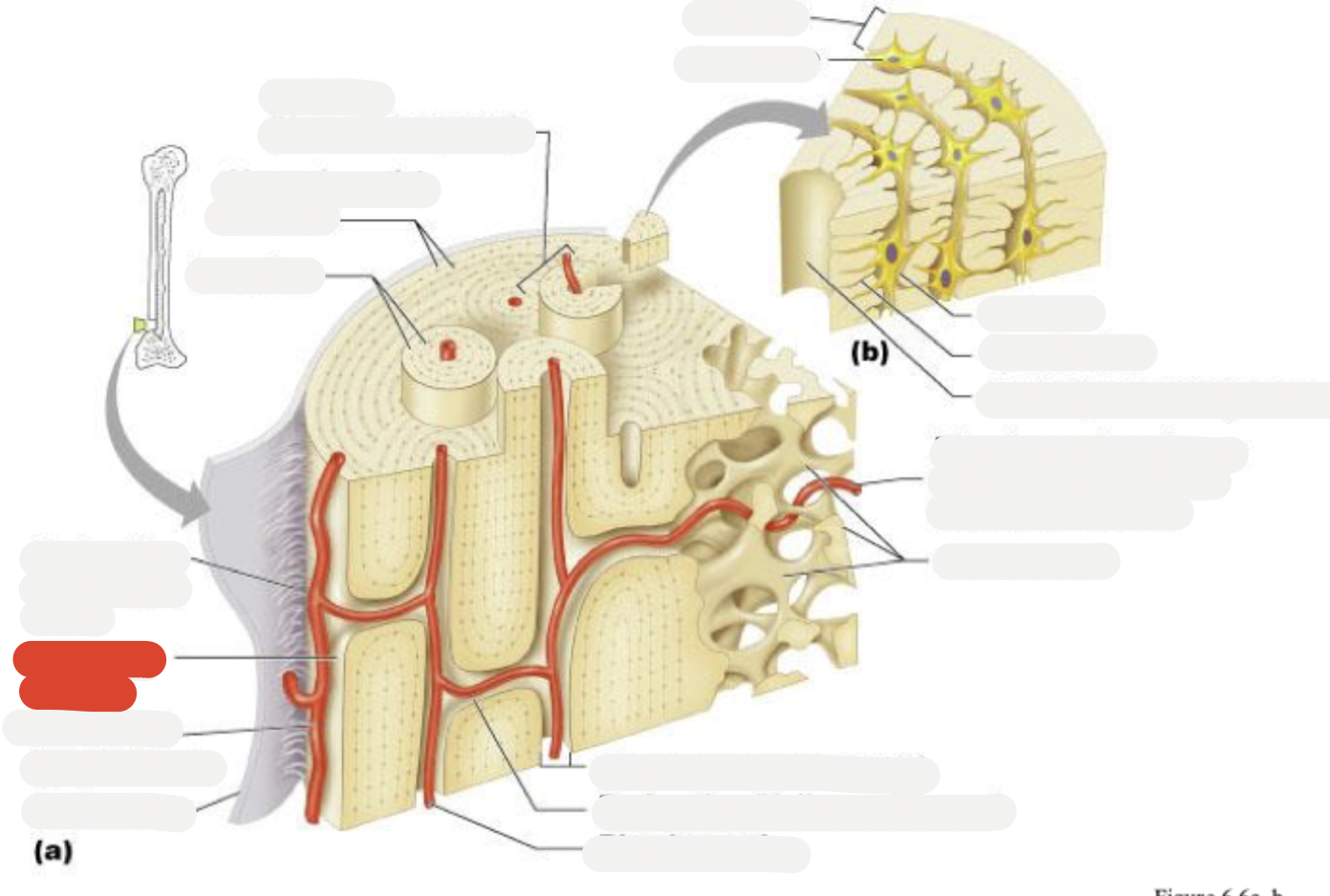
Periosteal blood vessel
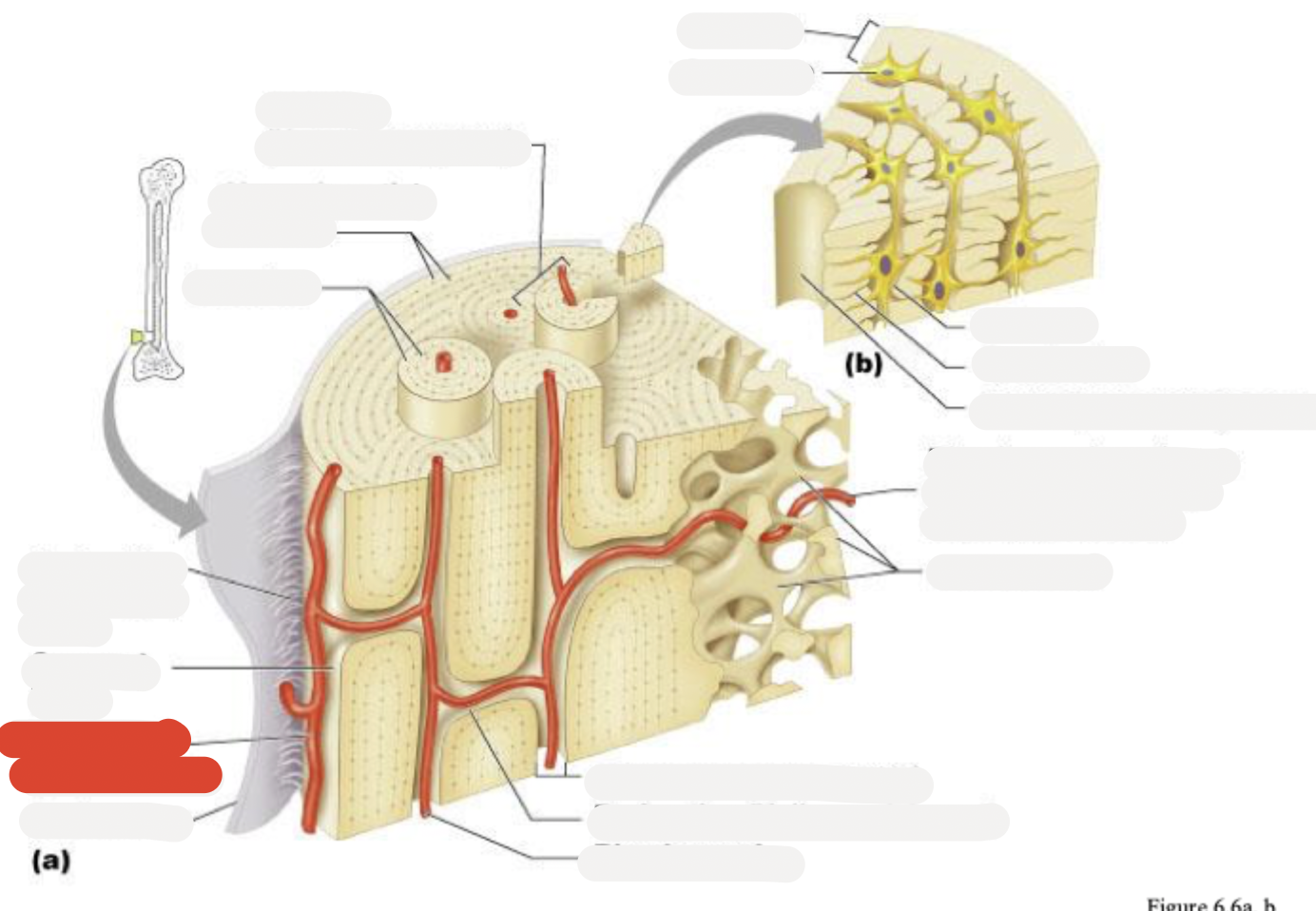
Periosteum
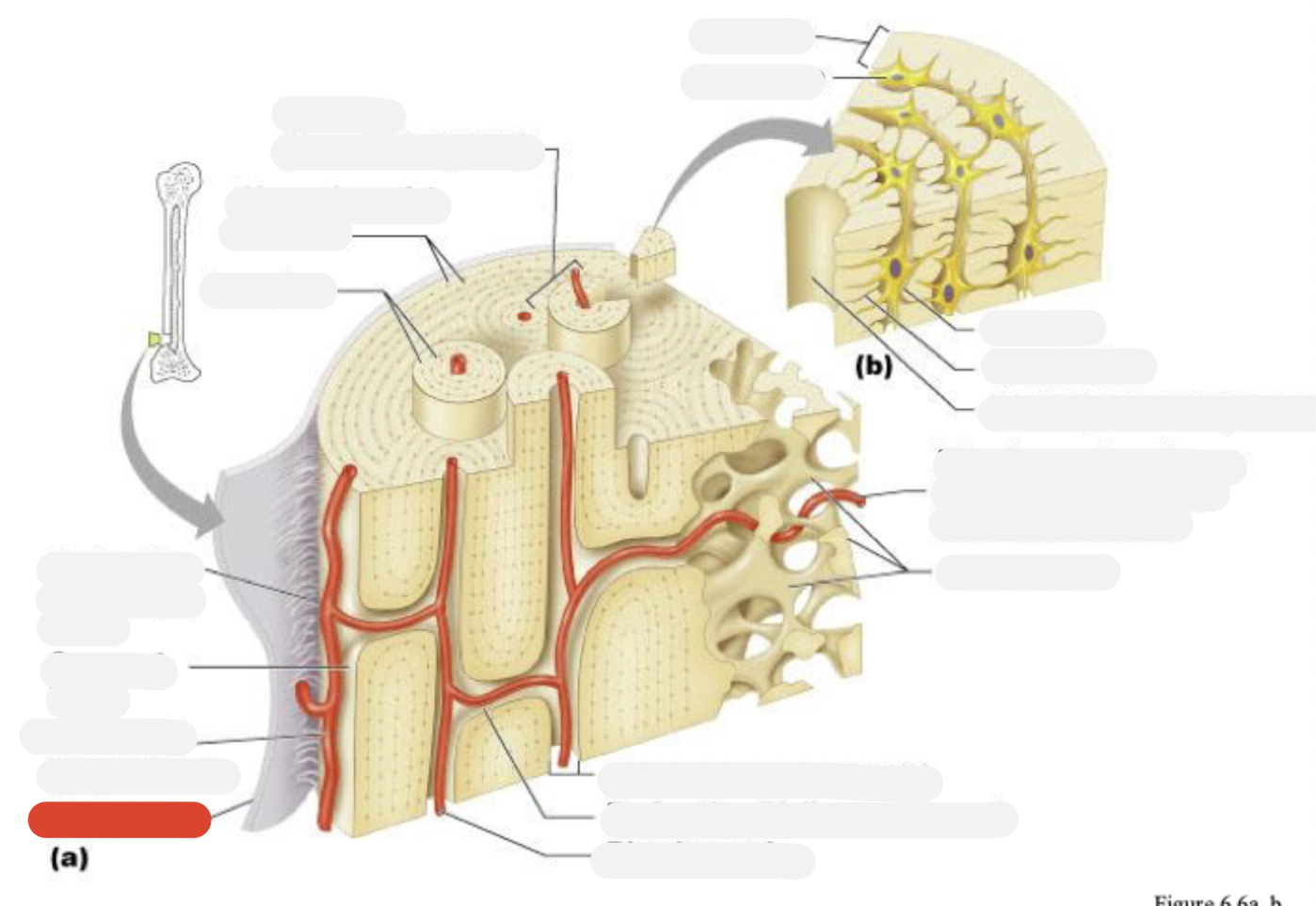
Central (Haversian) canal
Perforating (Volkmann’s) canal
Blood vessel
Blood vessel continues into medullary cavity containing marrow
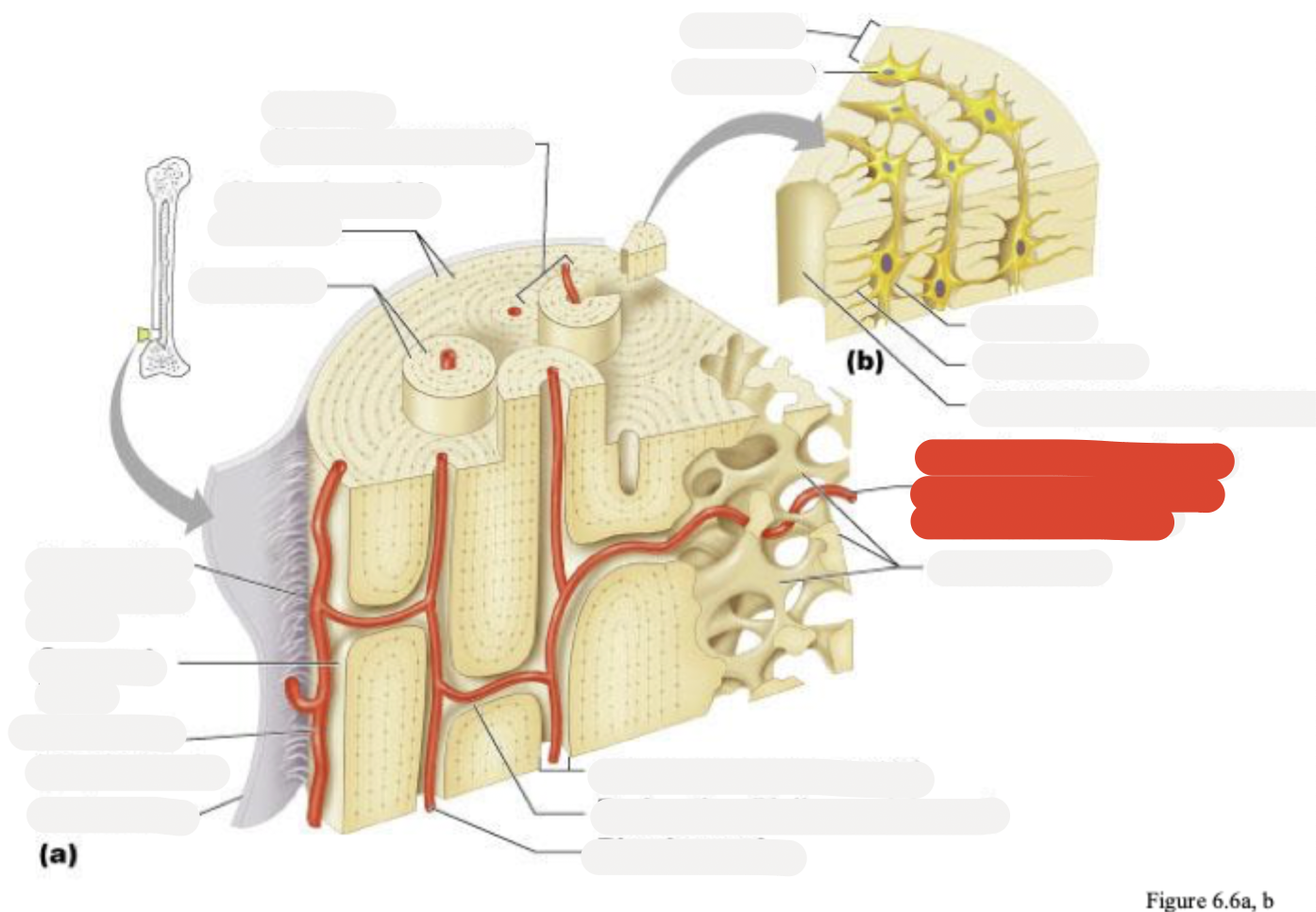
Spongy bone
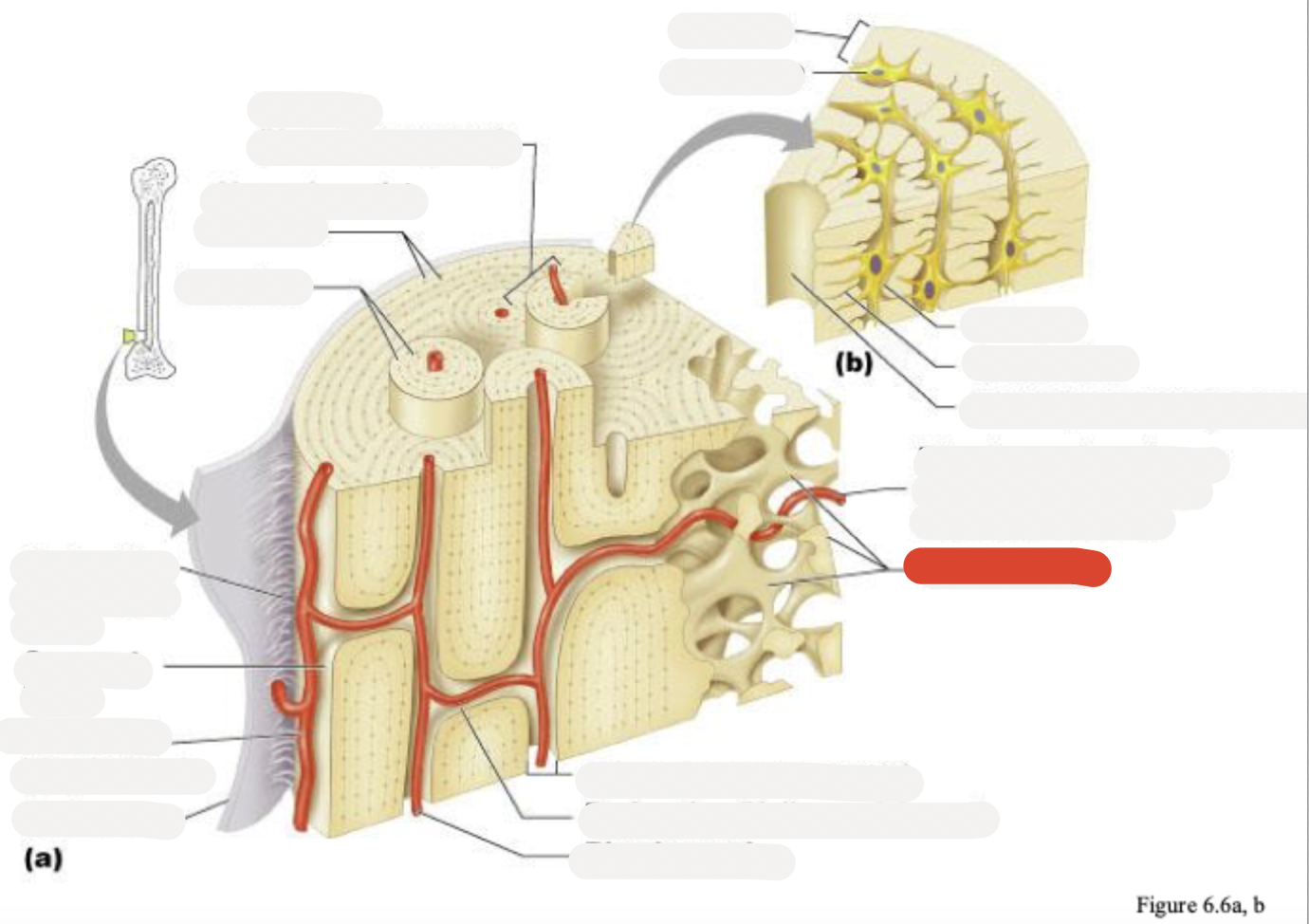
Lamella
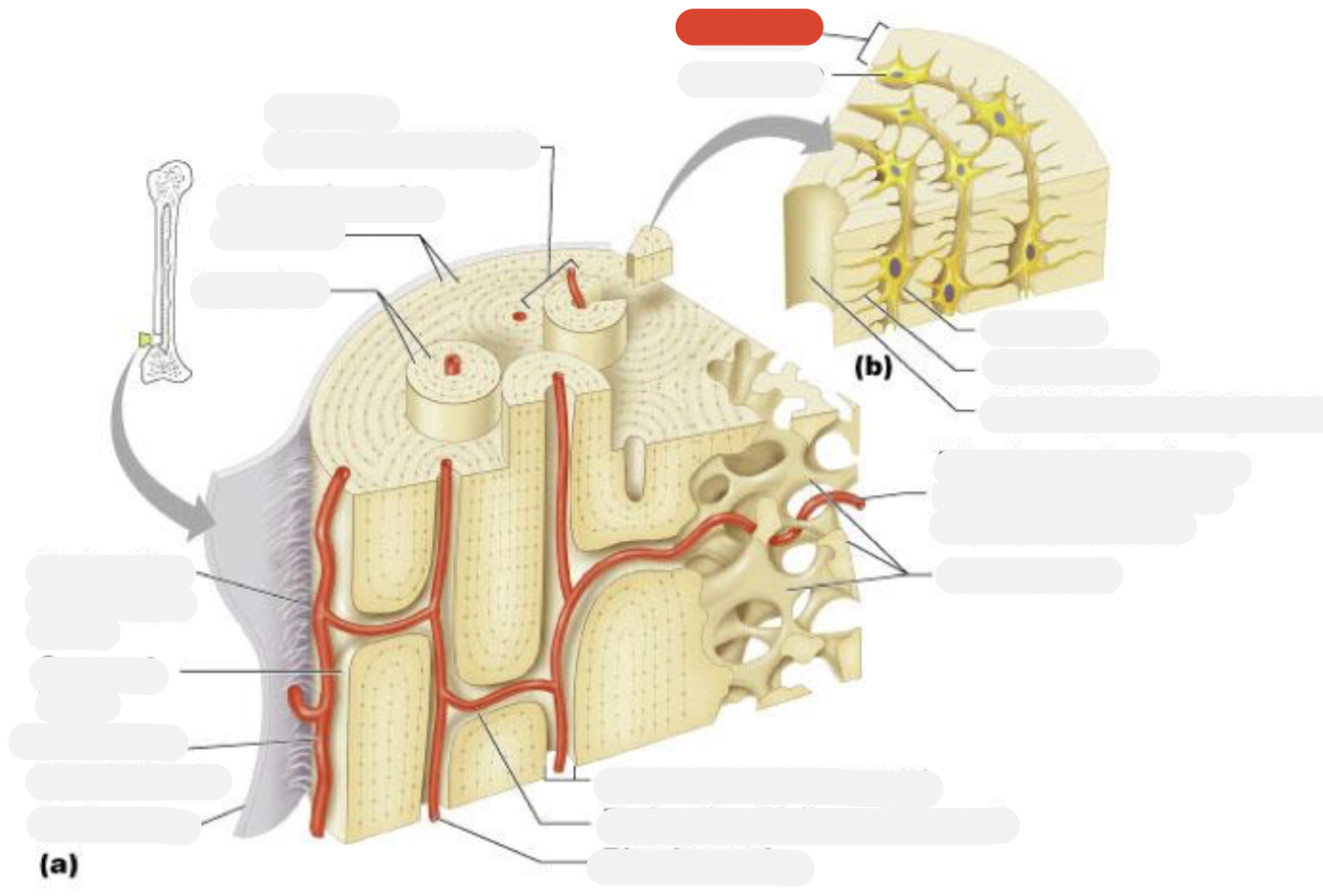
Osteocyte
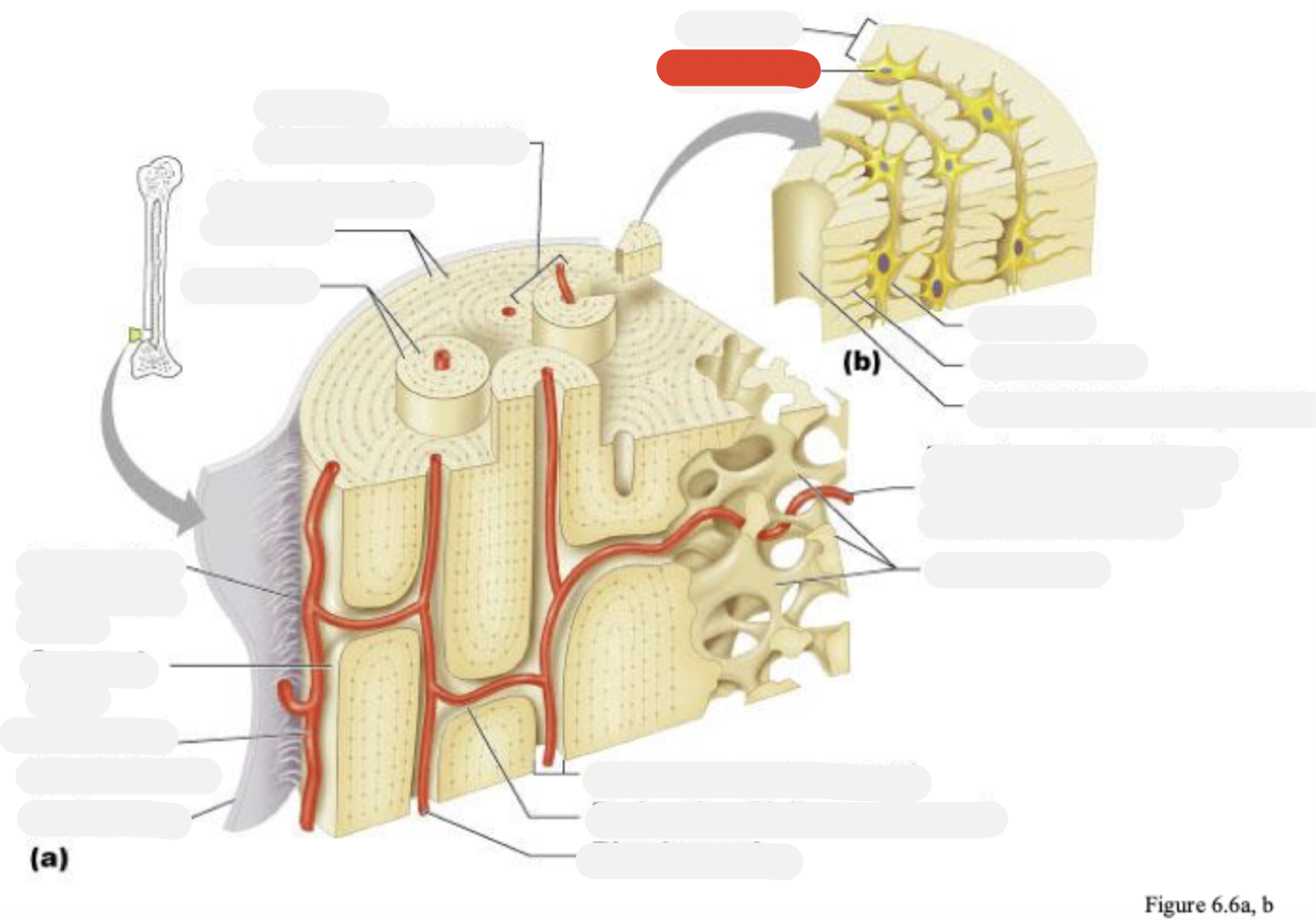
Lacuna
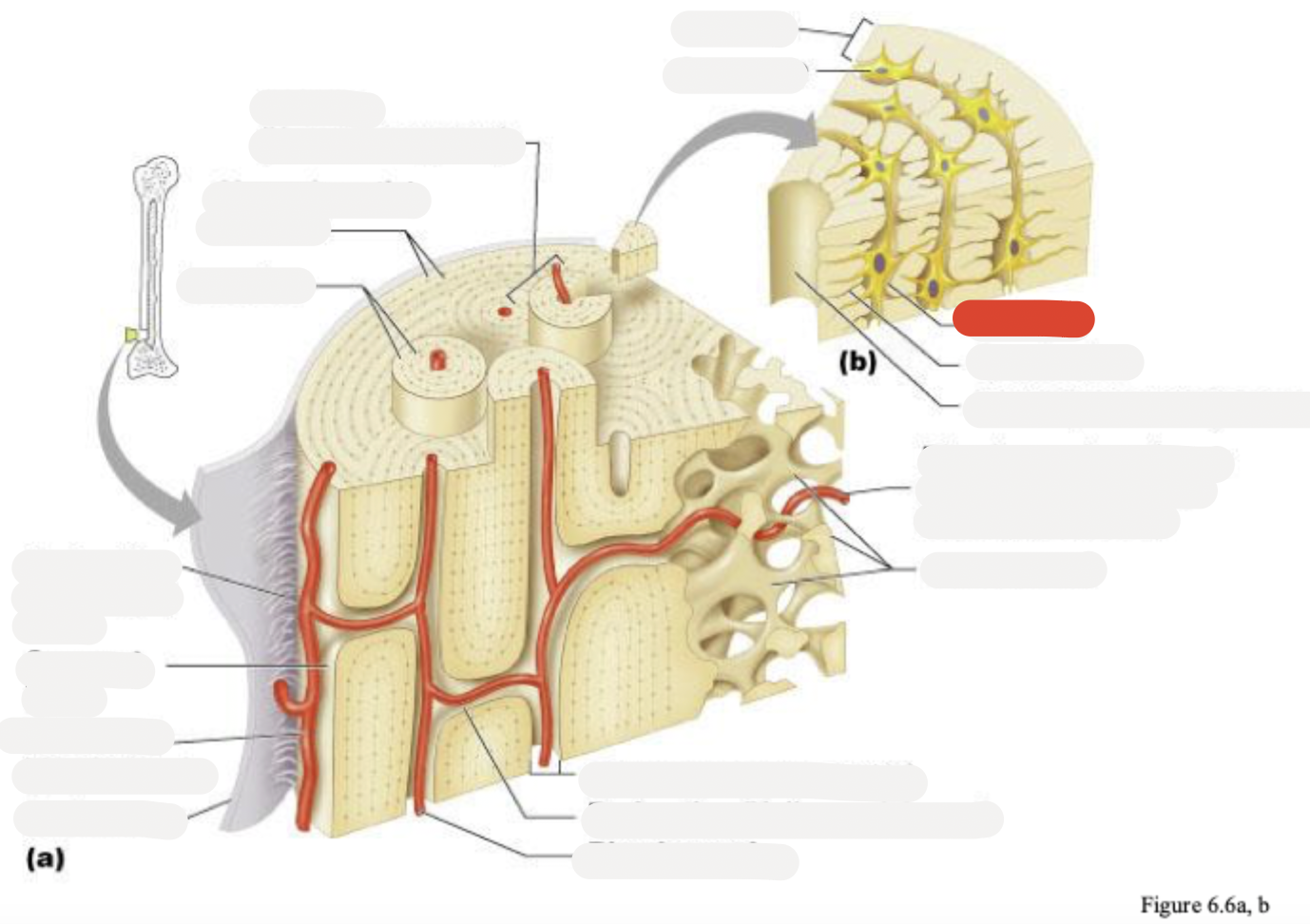
Canaliculus
Central (Haversian) canal
Canaliculi opening on surface
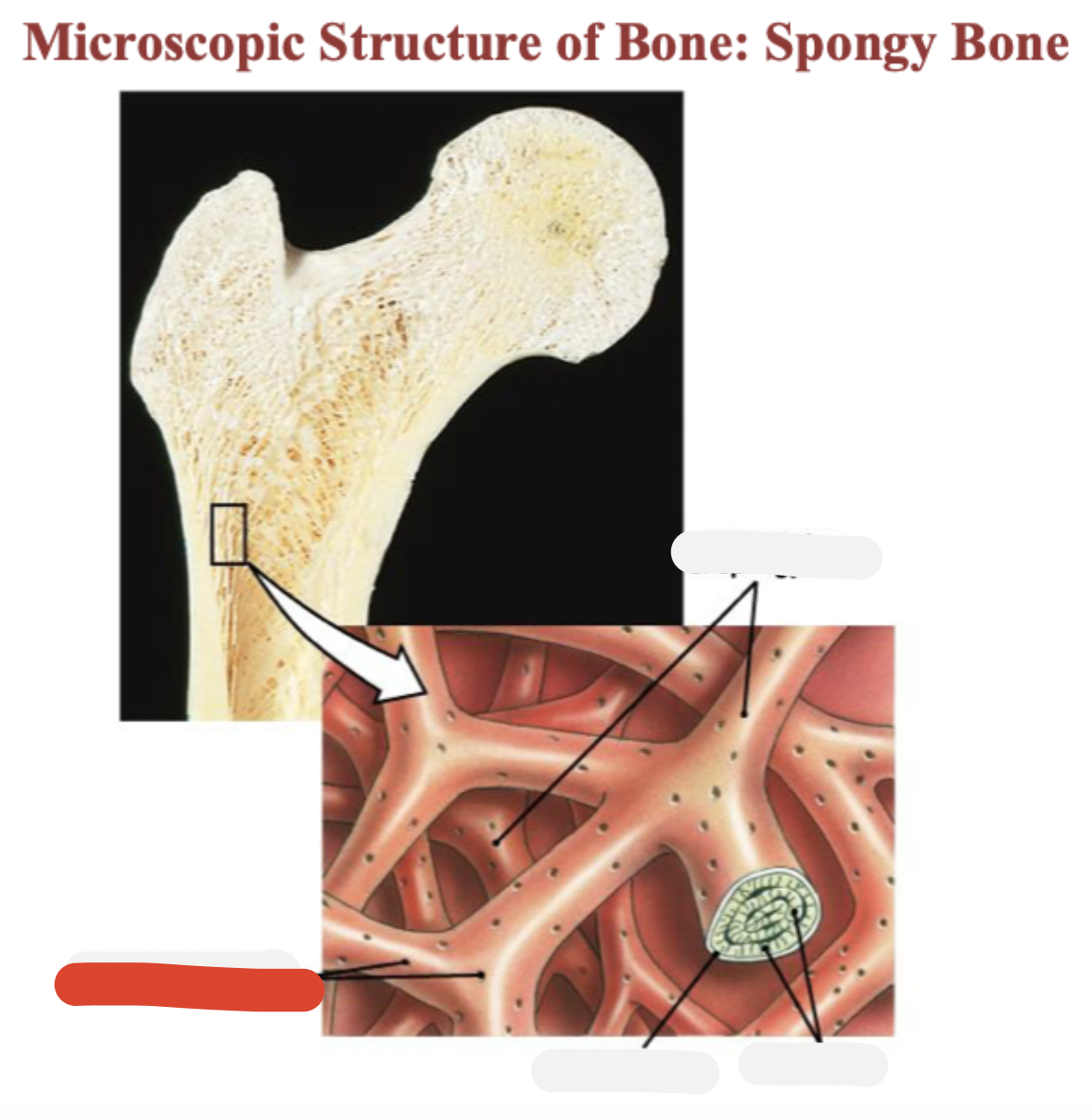
Trabeculae of spongy bone
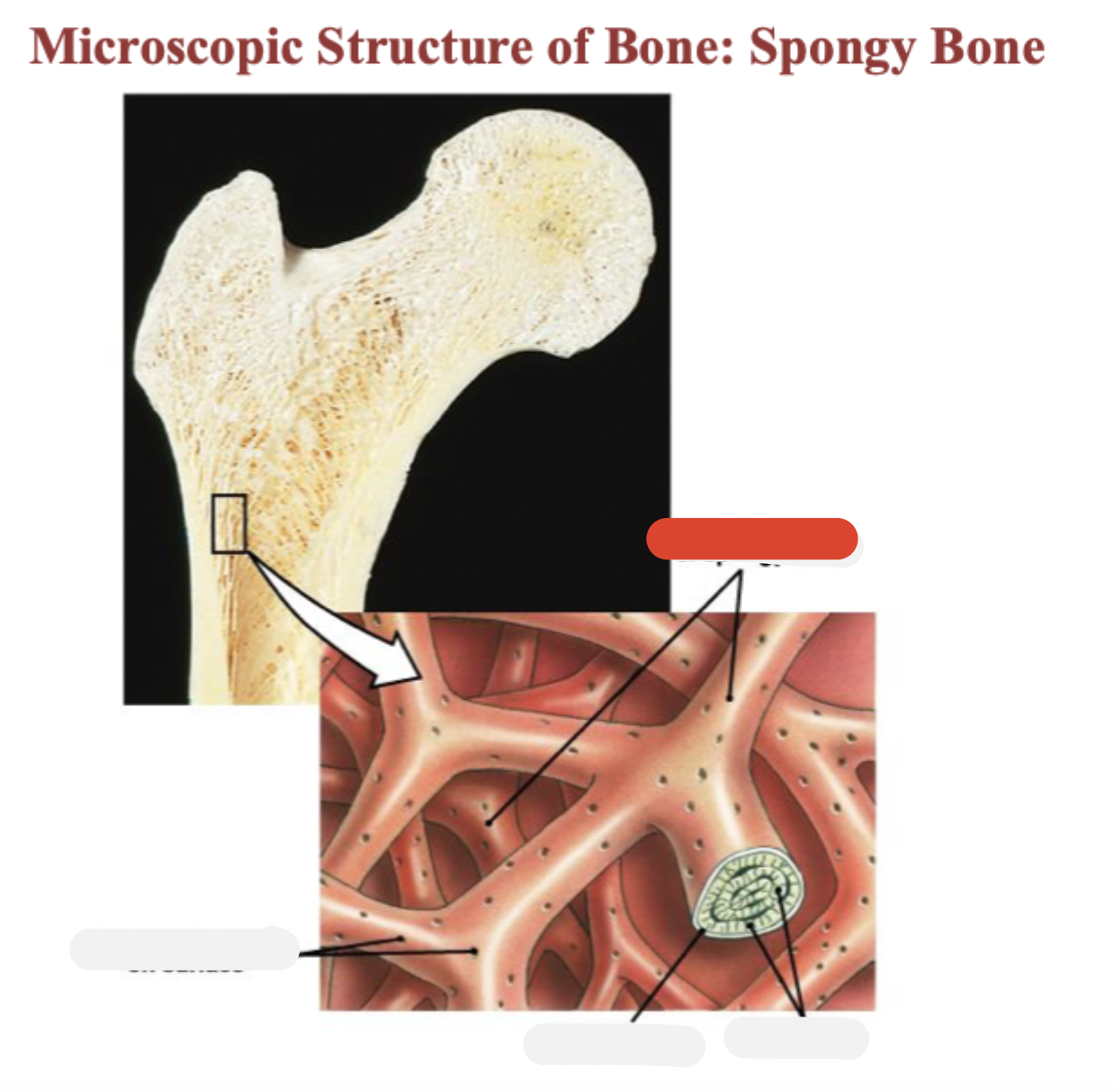
Endosteum
Lamellae
Osteocytes in lacunae
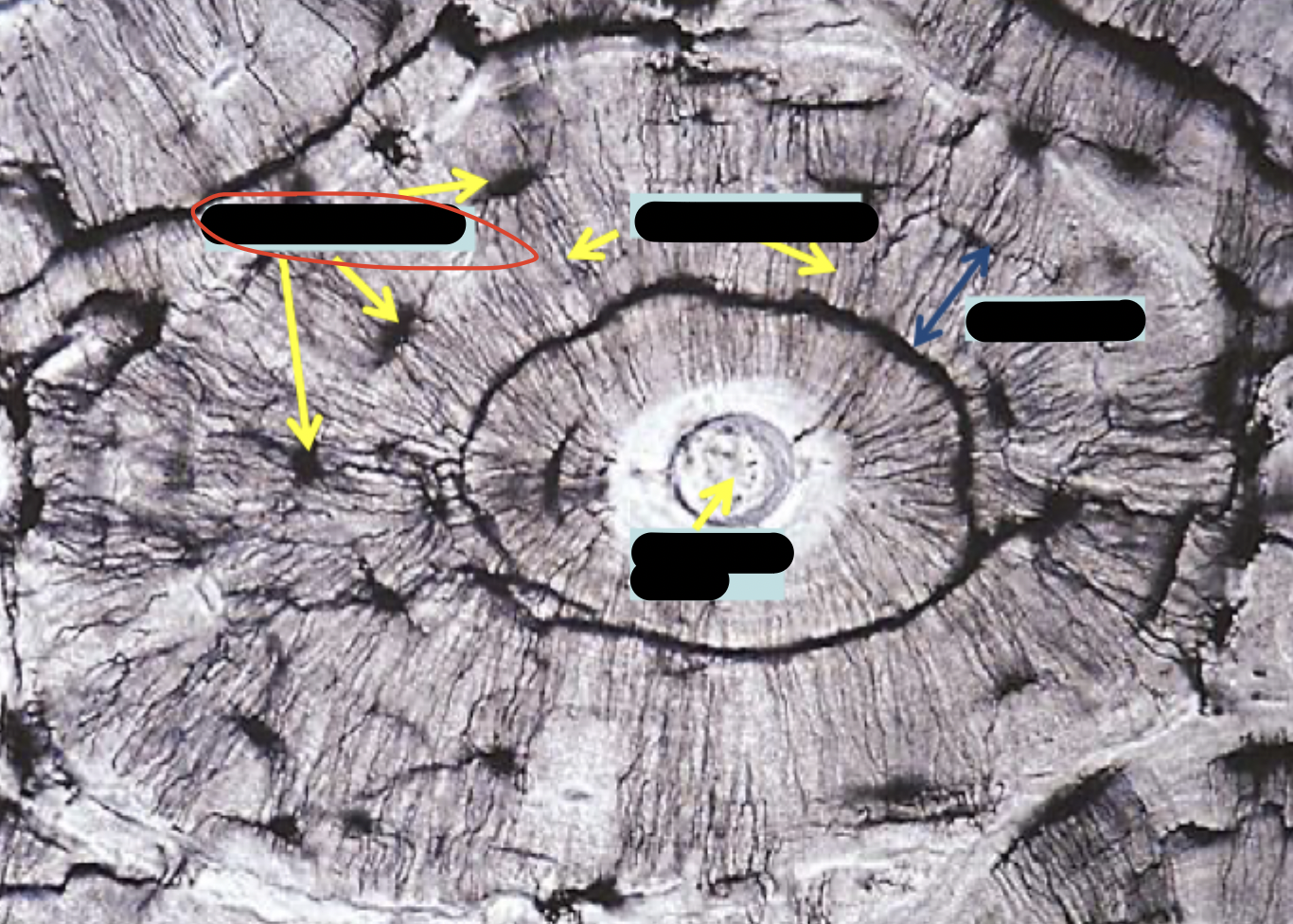
One lamella
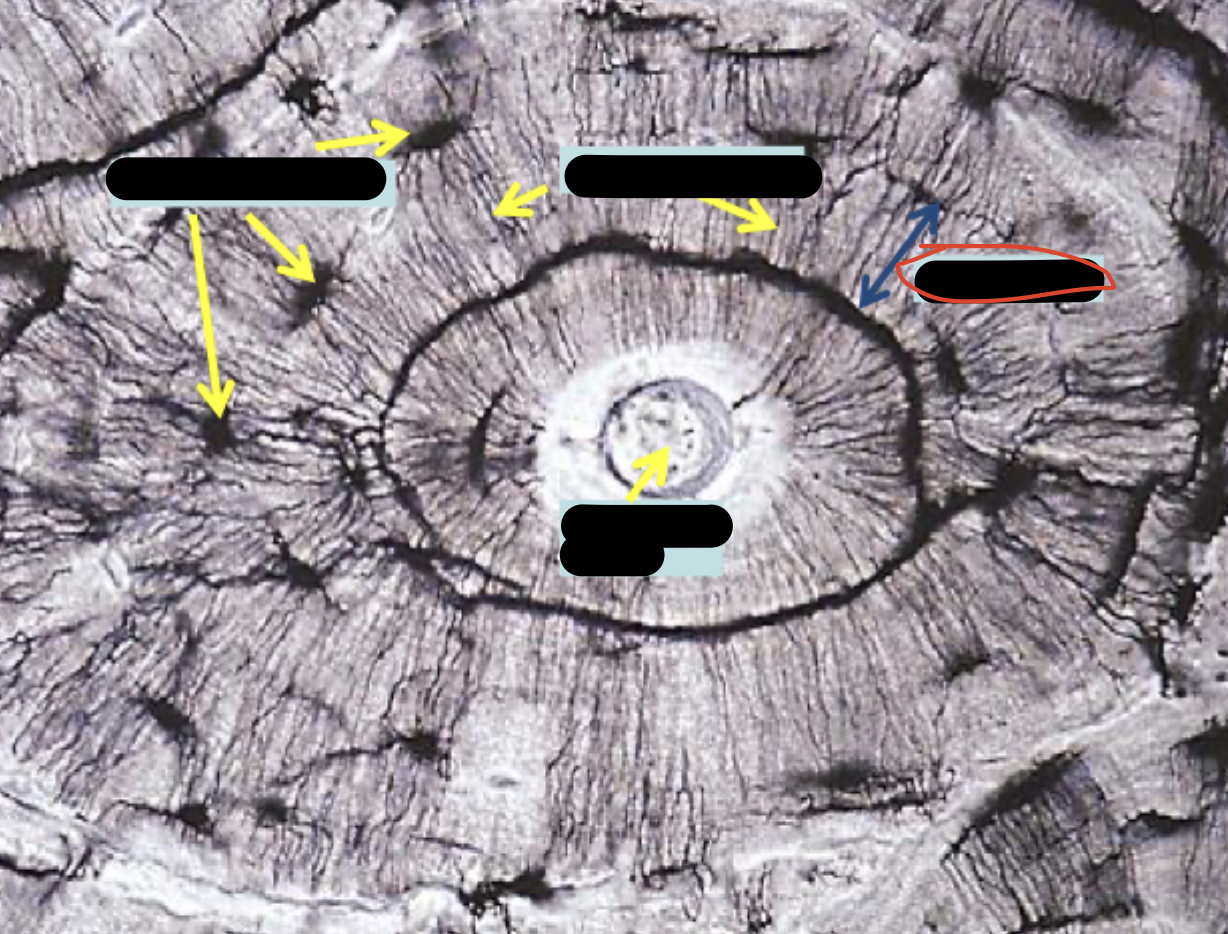
Canaliculi (lines)
Harversion canal
osteoblasts
osteoclasts
osteocytes in lacunae
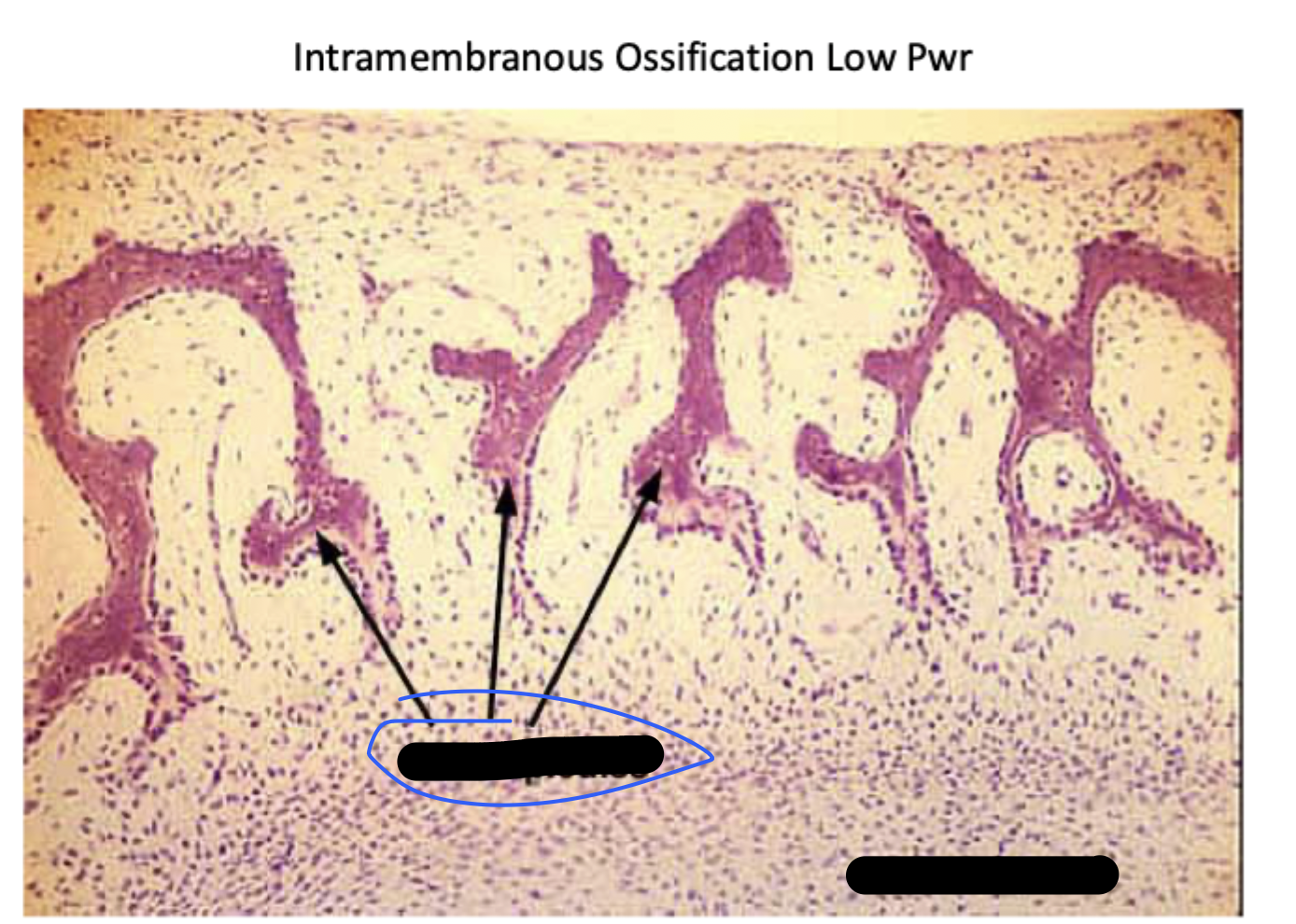
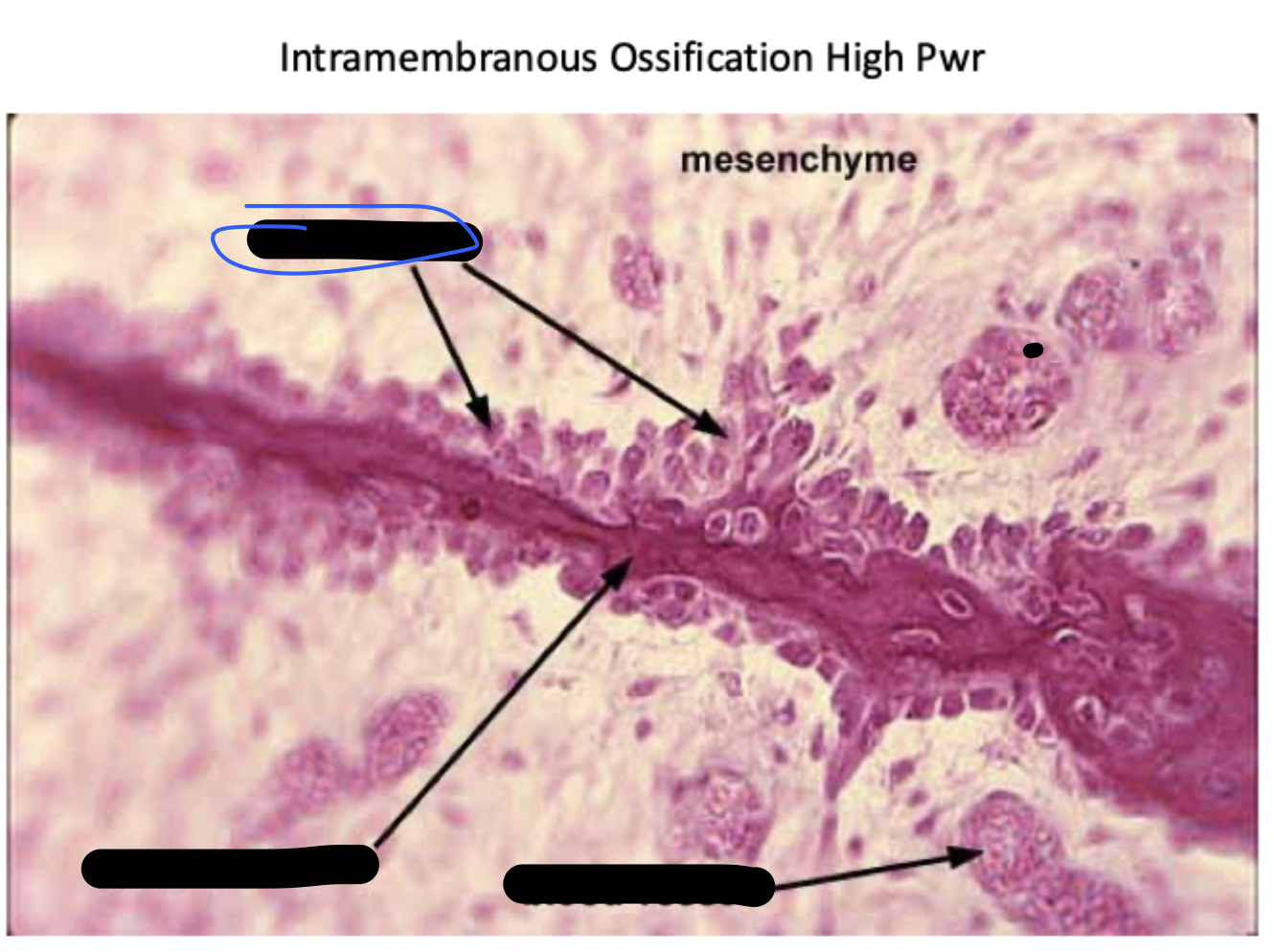
intramembranous ossification
bone develops from a mesenchymal or fibrous connective tissue. In the right microenvironment, mesenchyme cells turn into osteoblasts and begin forming bone. Many skull bones and the clavicle from this way.
Endochondral ossification
bone forms by replacing hyaline cartilage. Many long bones form this way in the fetus. Long bones grow in length using this method after birth.
intramembranous ossification
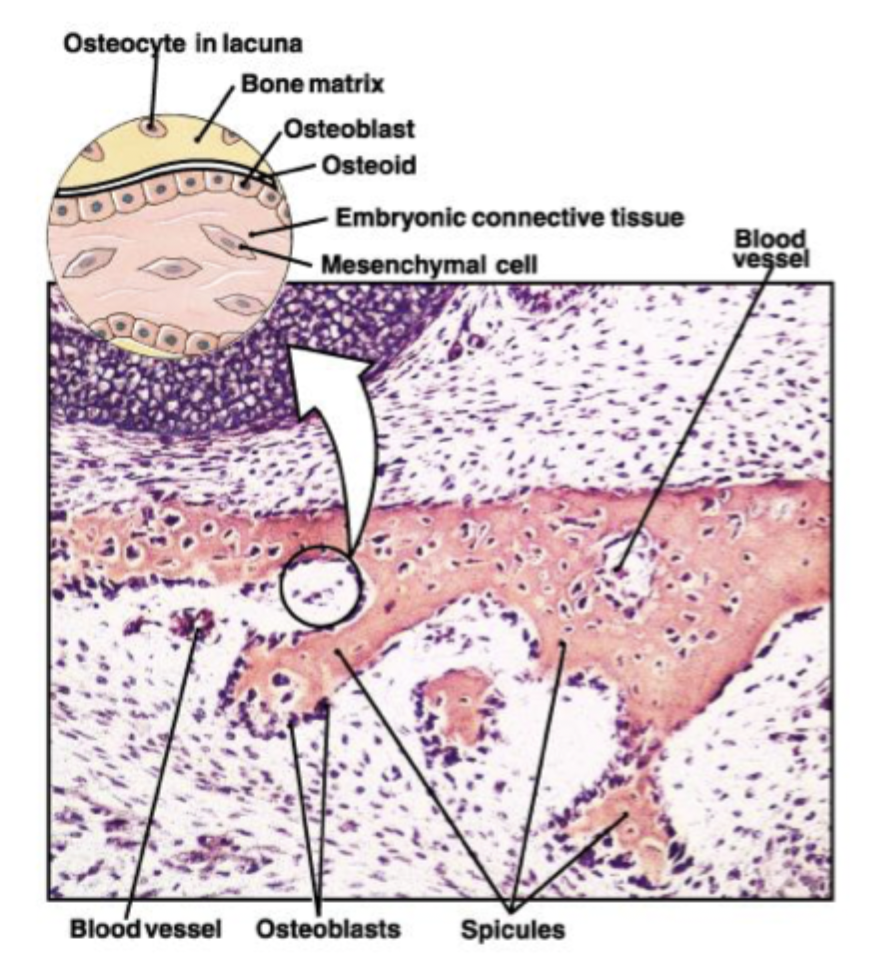
Mesenchymal cells aggregate, differentiate, and begin the ossification process. The bone expands as a series of spicules that spread into surrounding tissues.
(STEP 1/3)
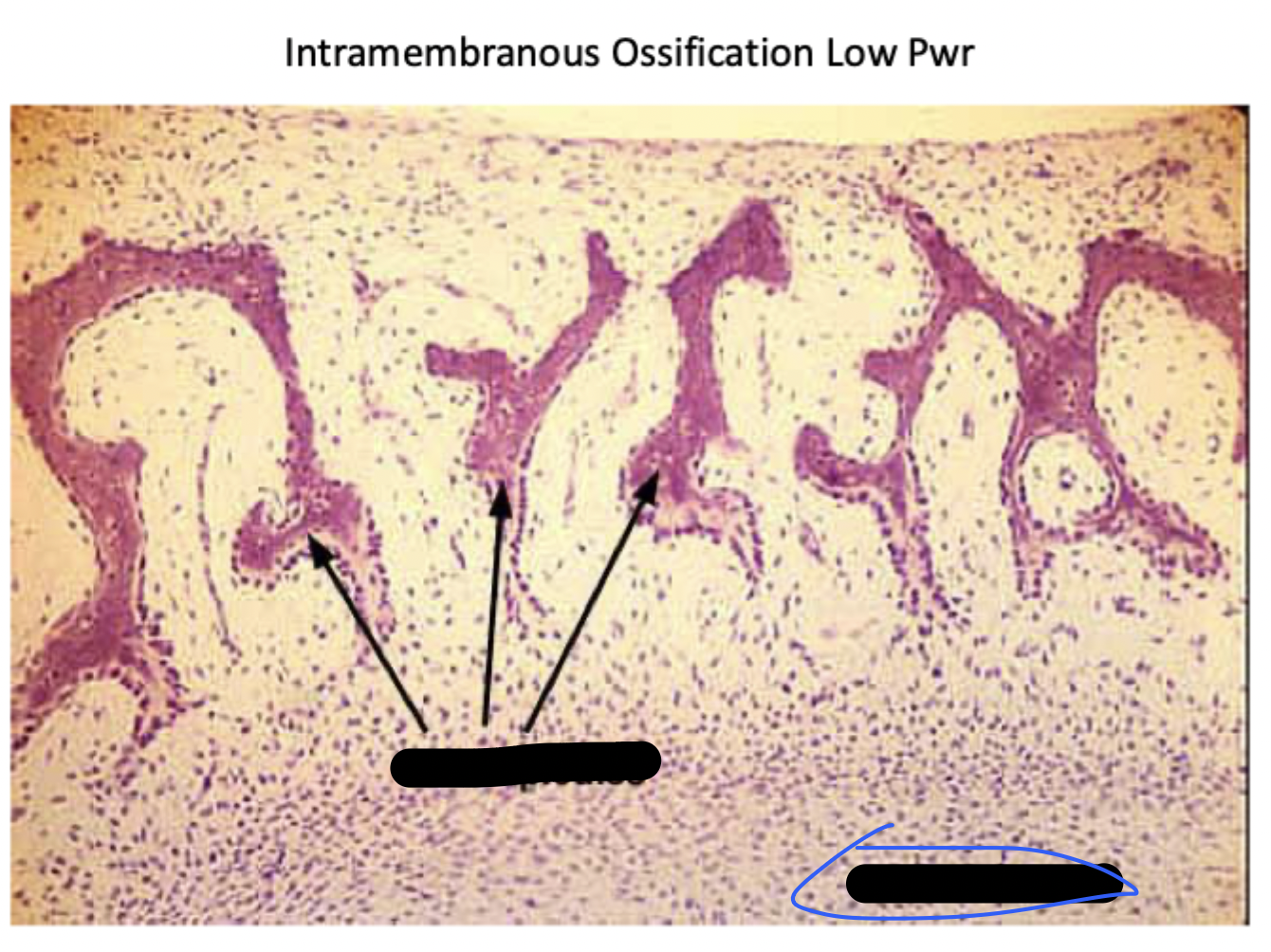
intramembranous ossification
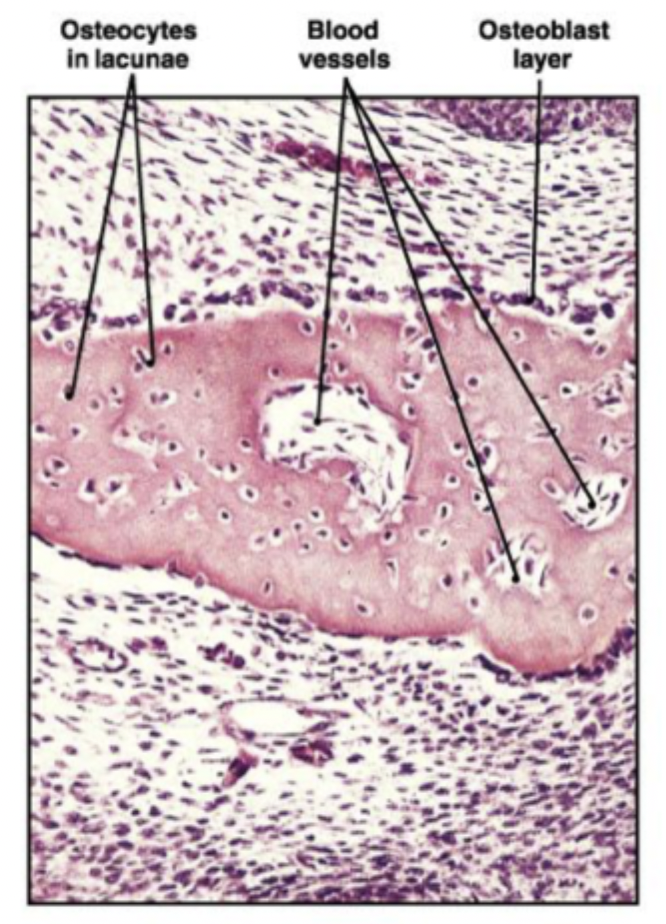
As the spicules interconnect, they trap blood vessels within the bone
(STEP 2/3)
intramembranous ossification
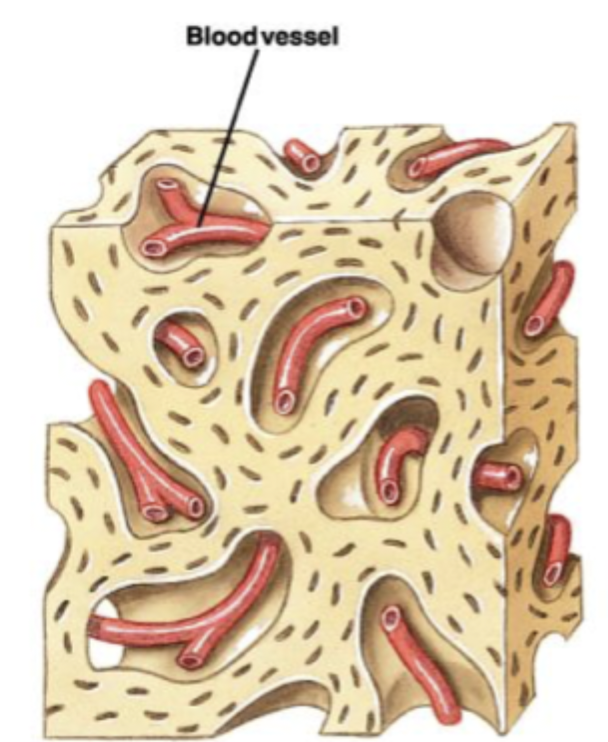
Overtime, the bone assumes the structure of spongy bone. Areas of spongy bone may later be removed, creating marrow cavities. Through remodeling, spongy bone formed in this way can be converted to compact bone.
(STEP 3/3)
Bone spicules
Mesenchyme
blood vessel
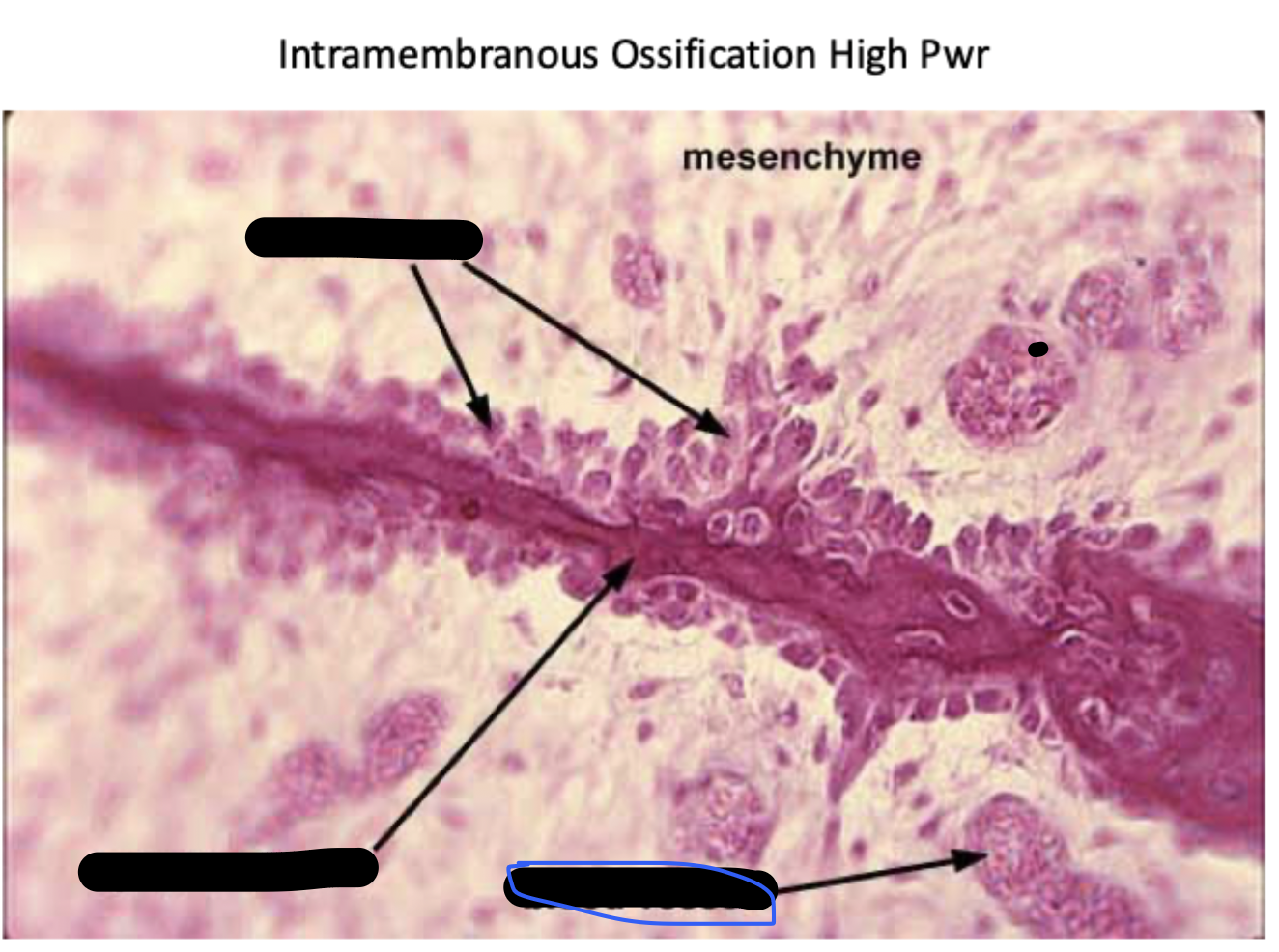
spicule of bone
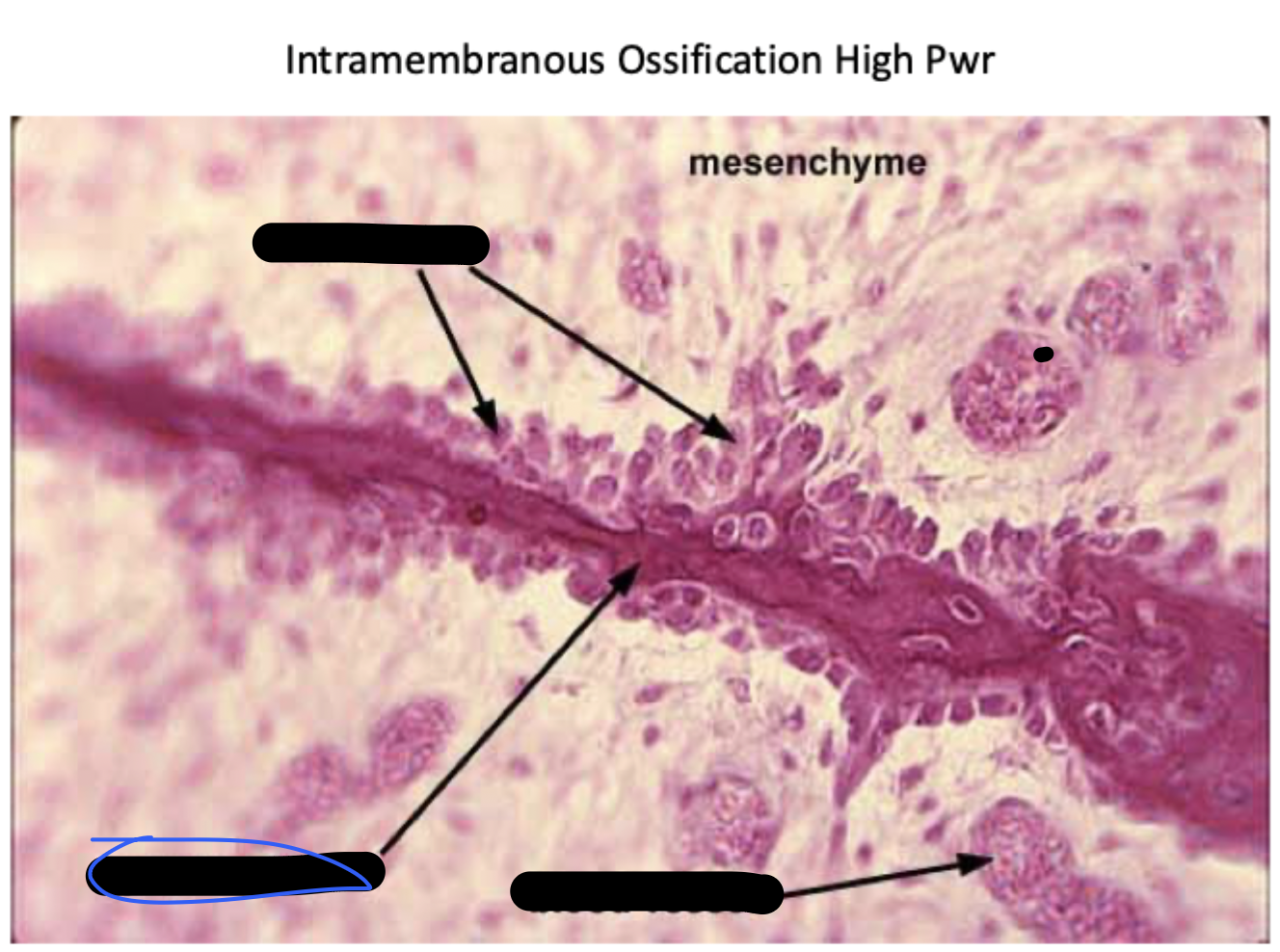
osteoblasts
endochondral ossification
begins in early embryonic development
uses hyaline cartilage “skeleton” as models for bone construction
requires breakdown of hyaline cartilage prior to ossification
histologically, cartilage breaks down in the order: hypertrophy, calcification, and ossification. This order is repeated later at the epiphyseal cartilages during bone growth in length
hypertrophy, calcification, ossification
histologically, cartilage breaks down in this order:
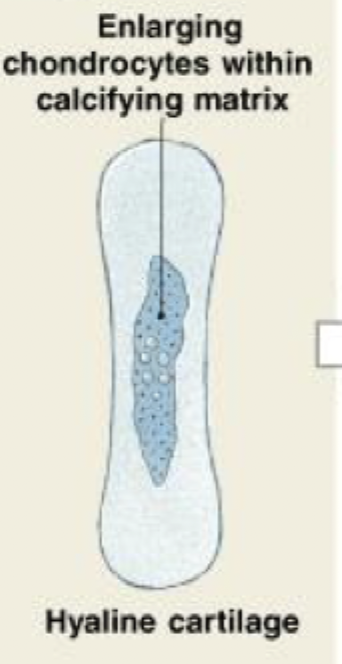
endochondral ossification
As the cartilage enlarges, chondrocytes near the center of the shaft increase greatly in size. The matrix is reduced to a series of small struts that soon begin to calcify. The enlarged chondrocytes then die and disintegrate, leaving cavities within the cartilage
(STEP 1/6)
endochondral ossification
Blood vessels grow around the edges of the cartilage, and the cells of the perichondrium convert to osteoblasts. The shaft of the cartilage then becomes ensheathed in a superficial layer of bone
(STEP 2/6)
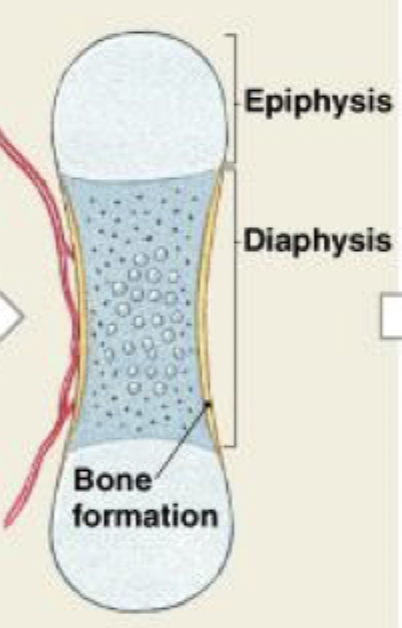
endochondral ossification
Blood vessels penetrate the cartilage and invade the central region; Fibroblasts migrating with the blood vessels differentiate into osteoblasts and begin producing spongy bone at a primary center of ossification. Bone formation then spreads along the shaft toward both ends.
(STEP 3/6)
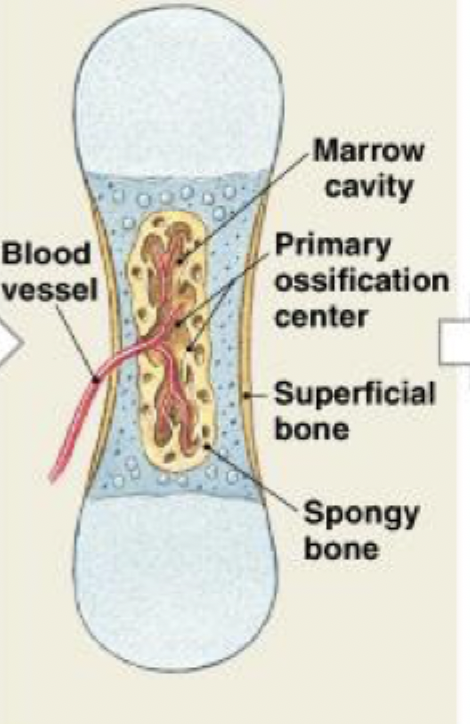
endochondral ossification
Remodeling occurs as growth continues, creating a marrow cavity. The bone of the shaft becomes thicker, and the cartilage near each epiphysis is replaced by shafts of bone. Further growth involves increases in length and diameter.
(STEP 4/6)
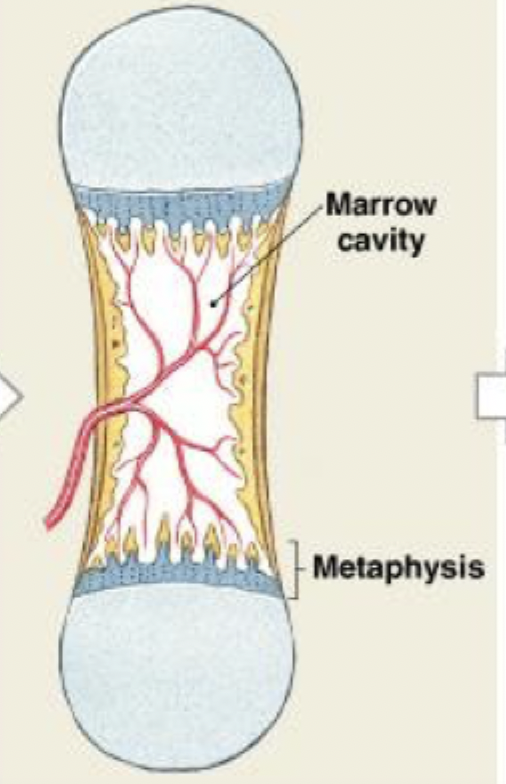
endochondral ossification
Capillaries and osteoblasts migrate into the epiphyses, creating secondary ossification centers
(STEP 5/6)
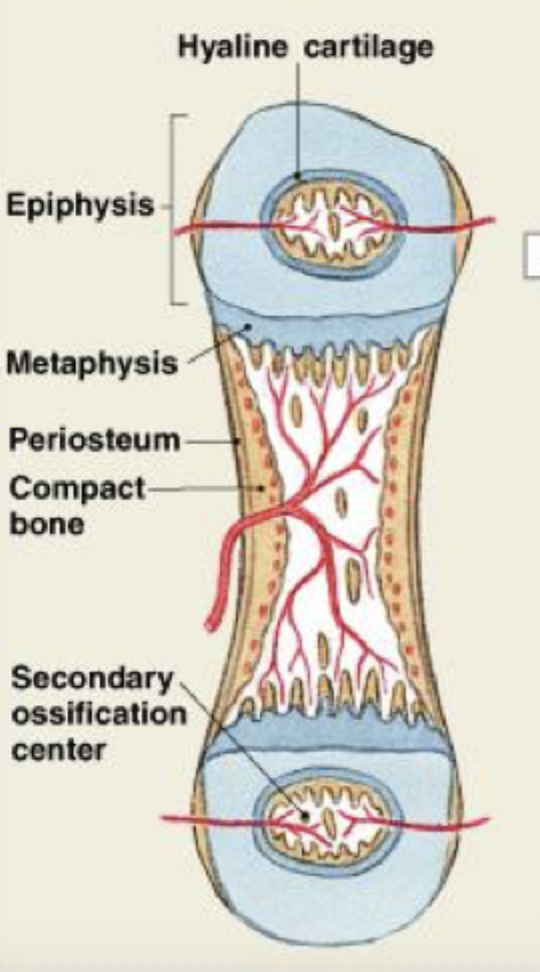
endochondral ossification
Soon the epiphyses are filled with spongy bone. An articular cartilage remains exposed to the joint cavity; over time it will be reduced to a thin superficial layer. At each metaphysis, an epiphyseal cartilage separates the epiphysis from the diaphysis.
(STEP 6/6)
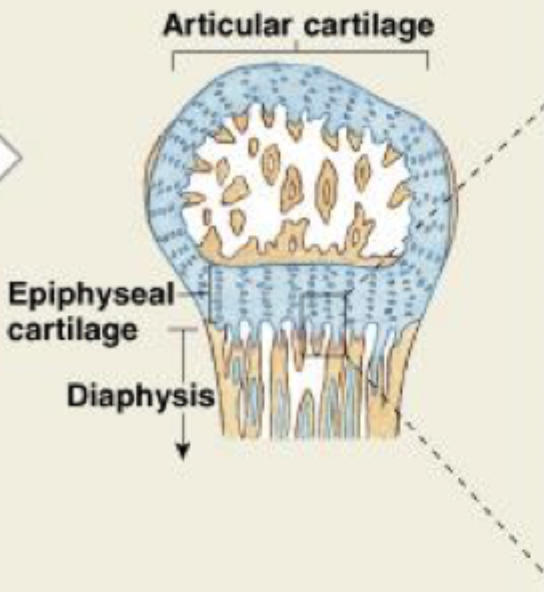
bone elongation at epiphyseal cartilages
growth in length cartilage growth and subsequent replacement with bone at the epiphyseal cartilages
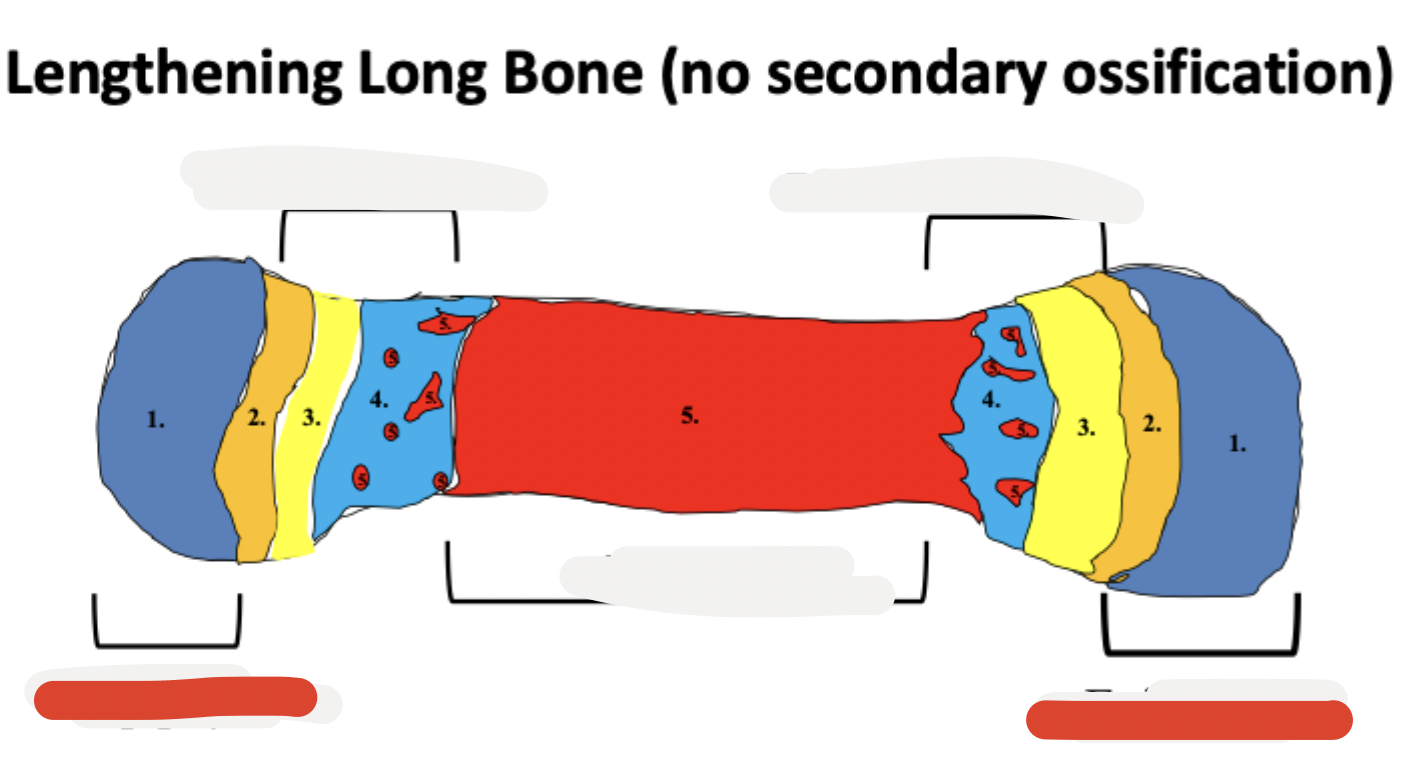
the sequence of zones at the epiphysis and epiphyseal cartilages is:
resting (hyaline) cartilage
proliferation of chondrocytes
hypertrophy (cell size increases) of chondrocytes
calcification of the ECM of cartilage (ECM color changes)
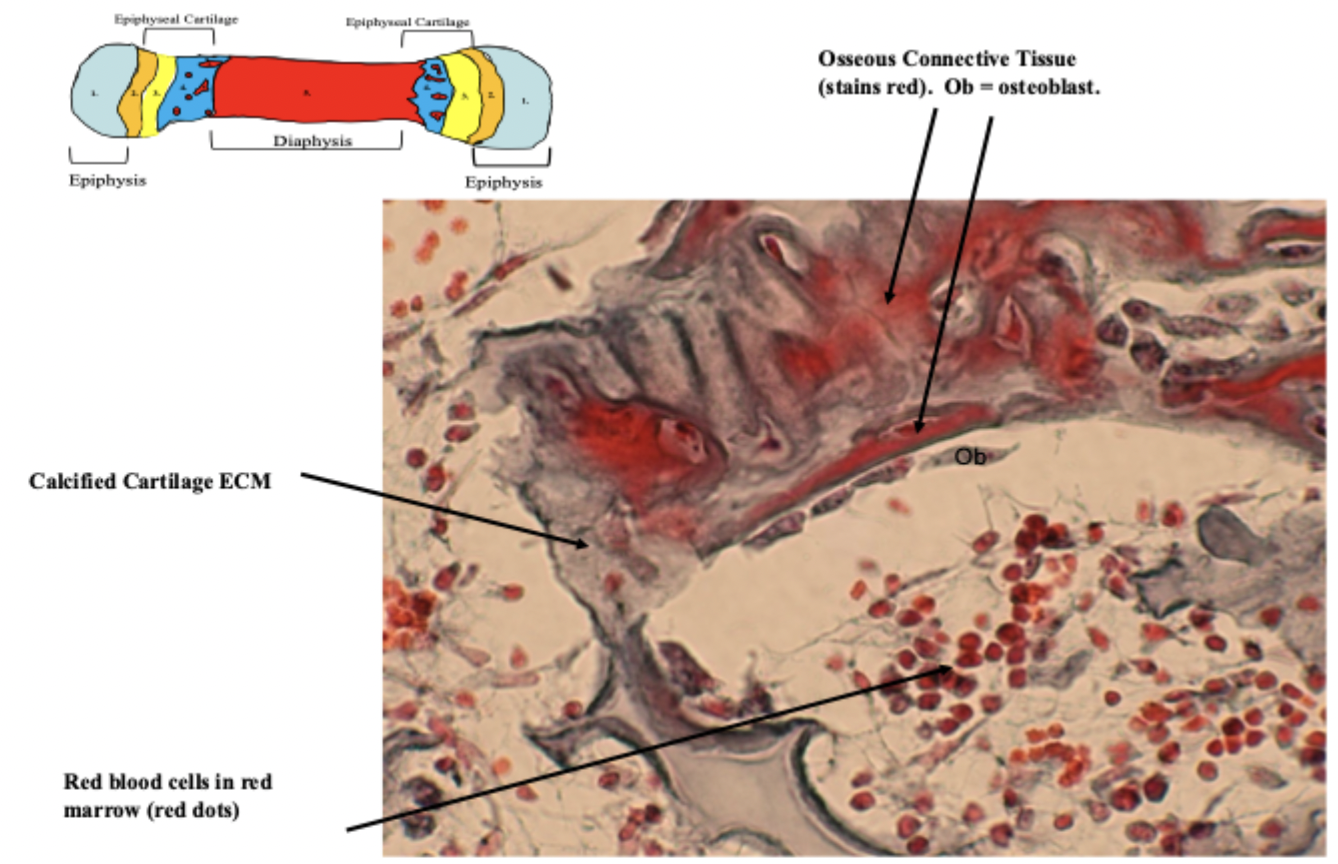
ossification occurring on top of decaying calcified cartilage
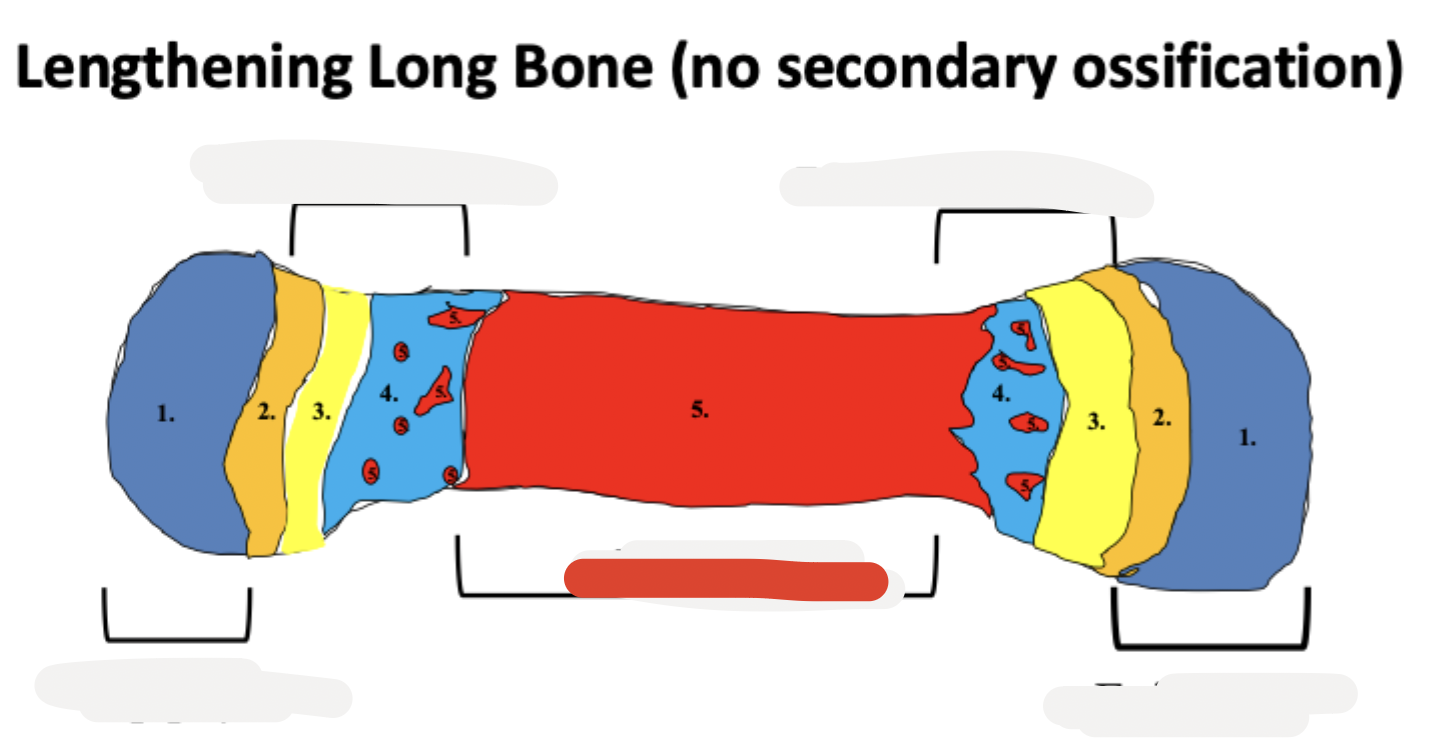
epiphysis
epiphyseal cartilage
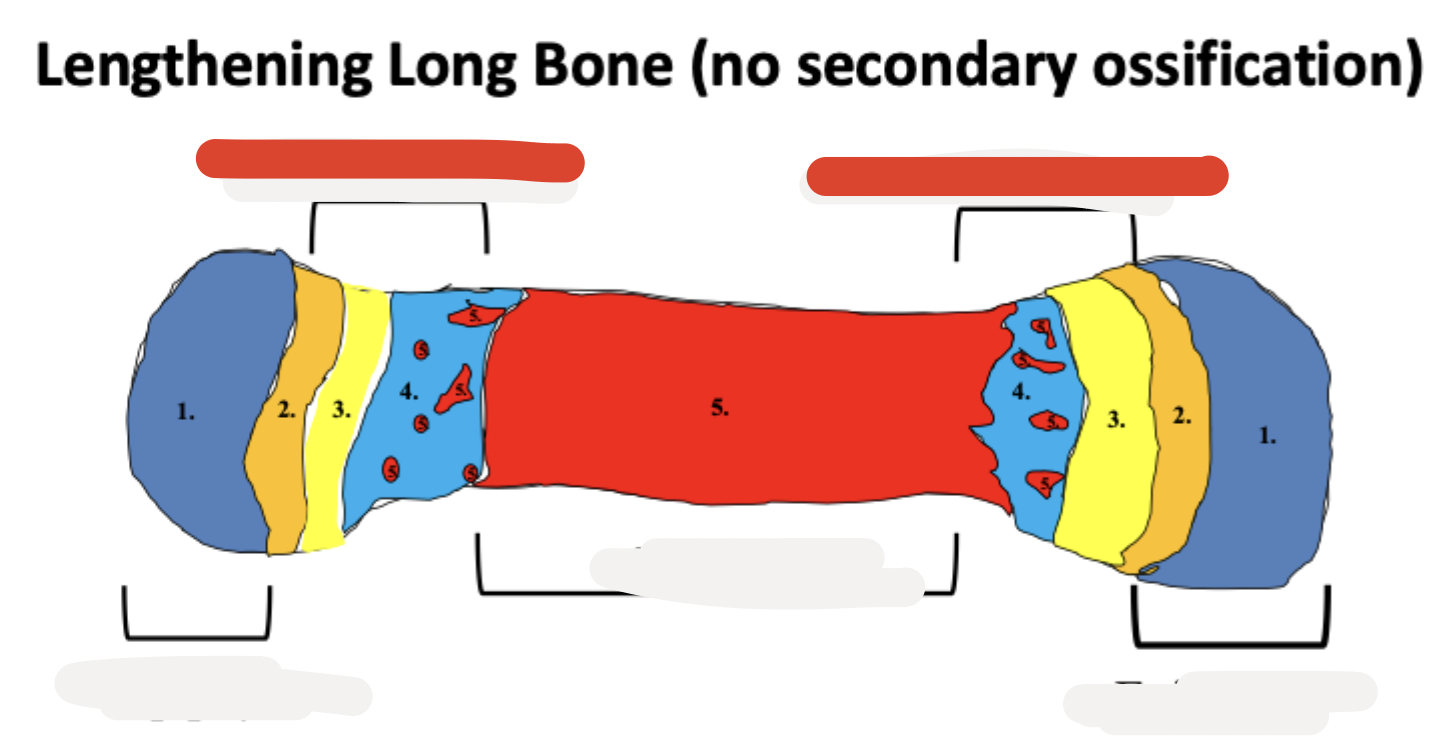
diaphysis
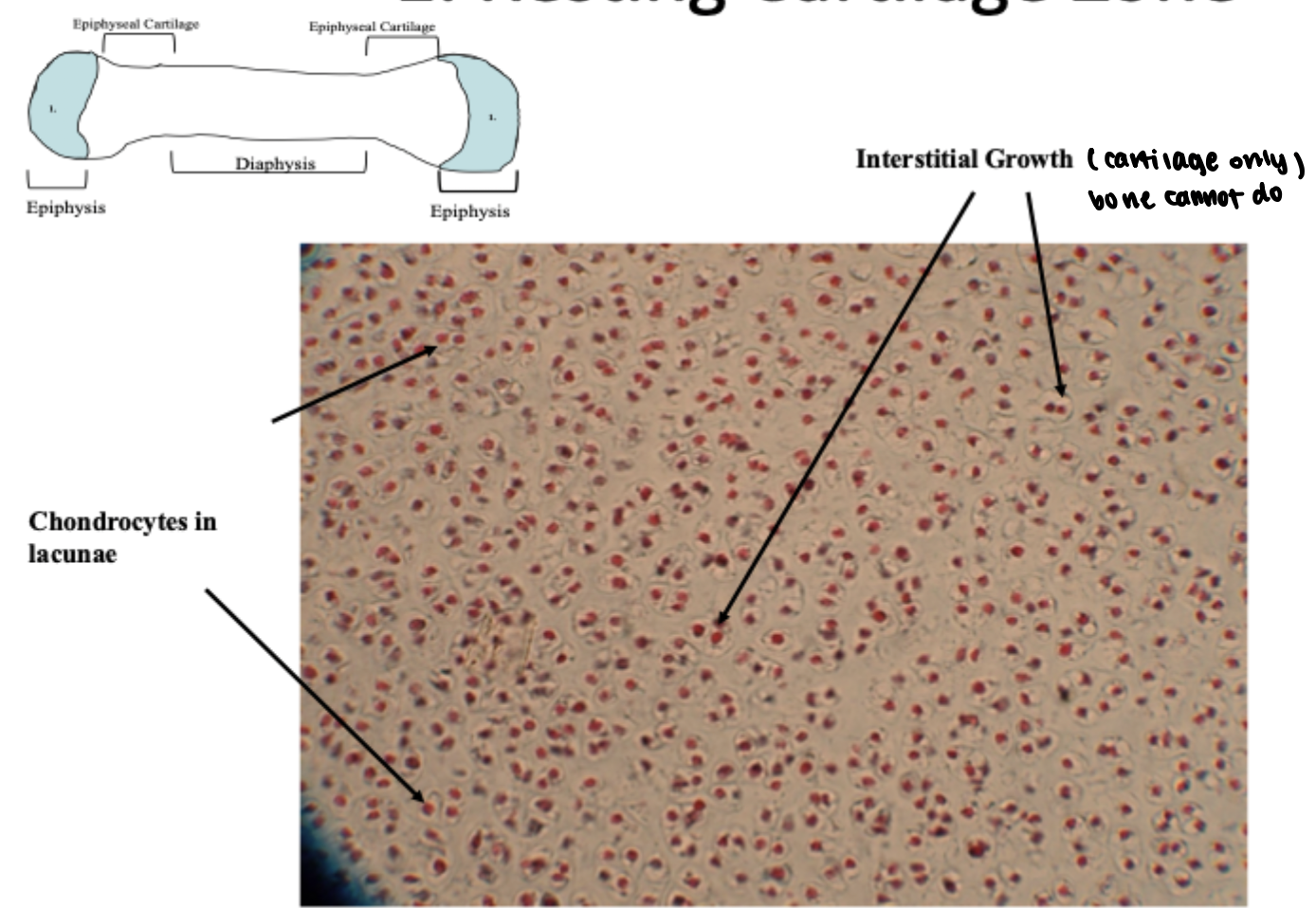
resting cartilage zone
hyaline cartilage connective tissue with scattered interstitial and appositional growth
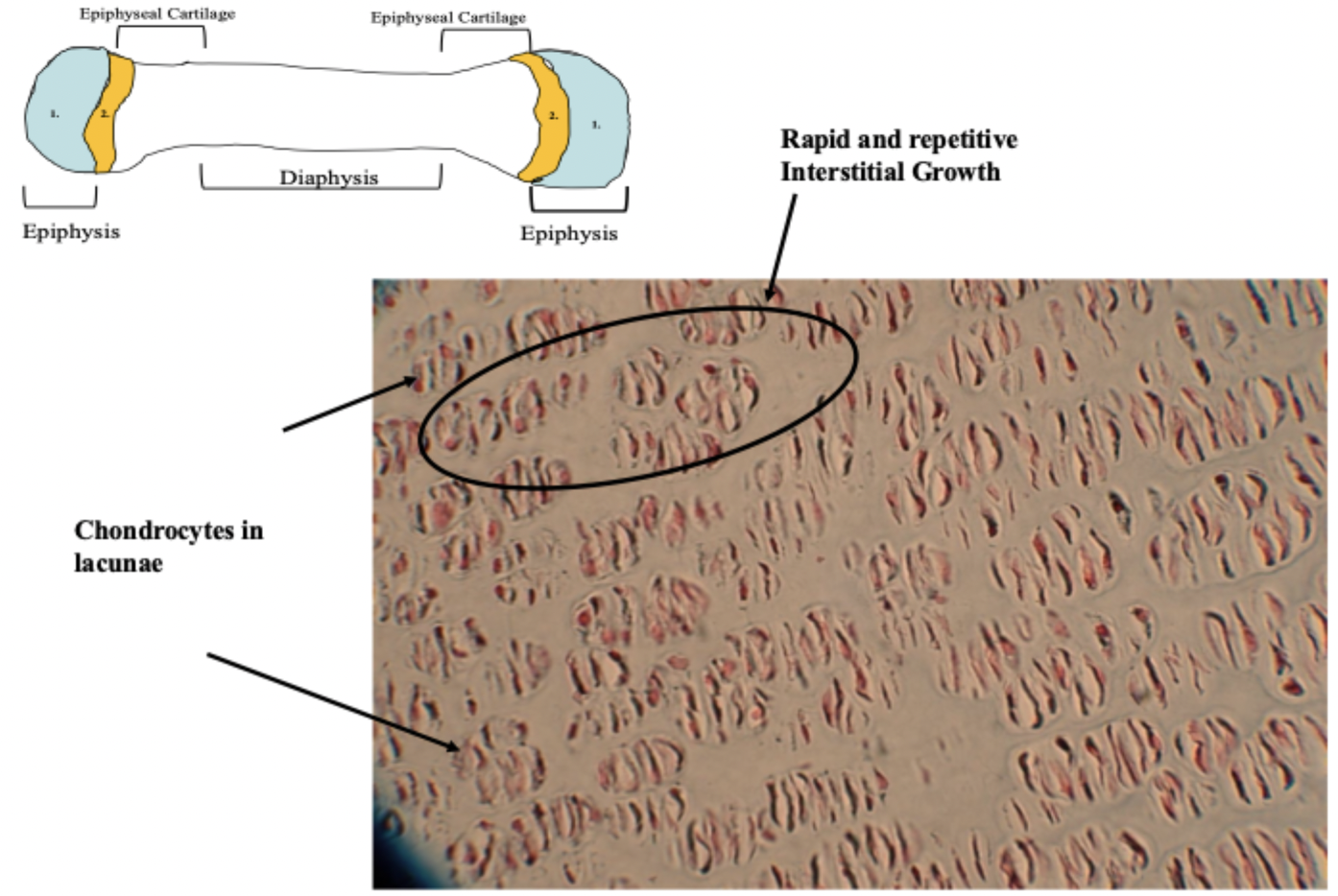
proliferation zone
hyaline cartilage under goes rapid, sequential, and continuous interstitial growth. chondrocytes line up in rows
hypertrophy zone
chondrocytes enlarge in size as proliferation continues
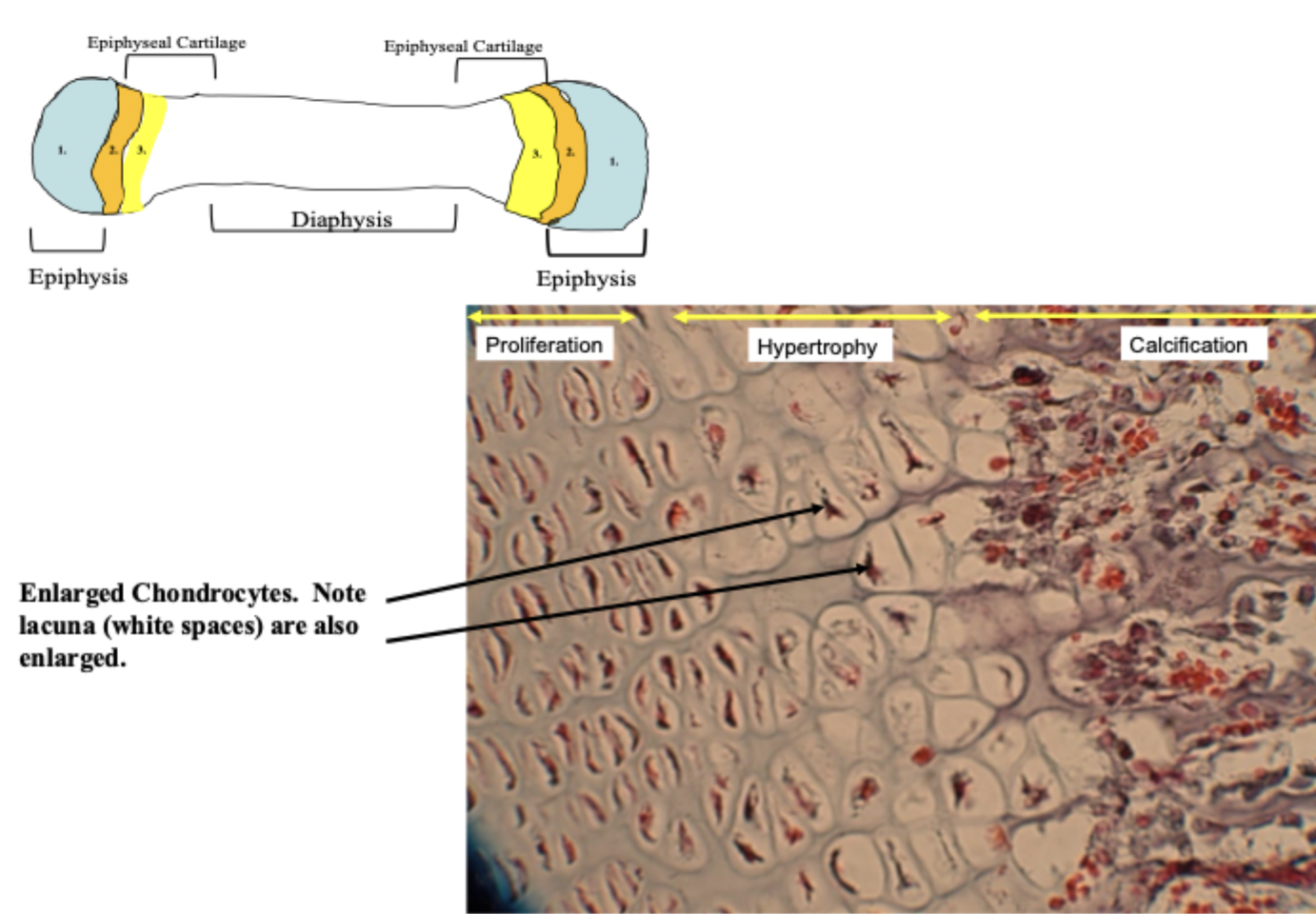
calcification zone
mineral deposits in the ECM of cartilage signals the eminent death of the chondrocytes. the color of the ECM on the slide changes
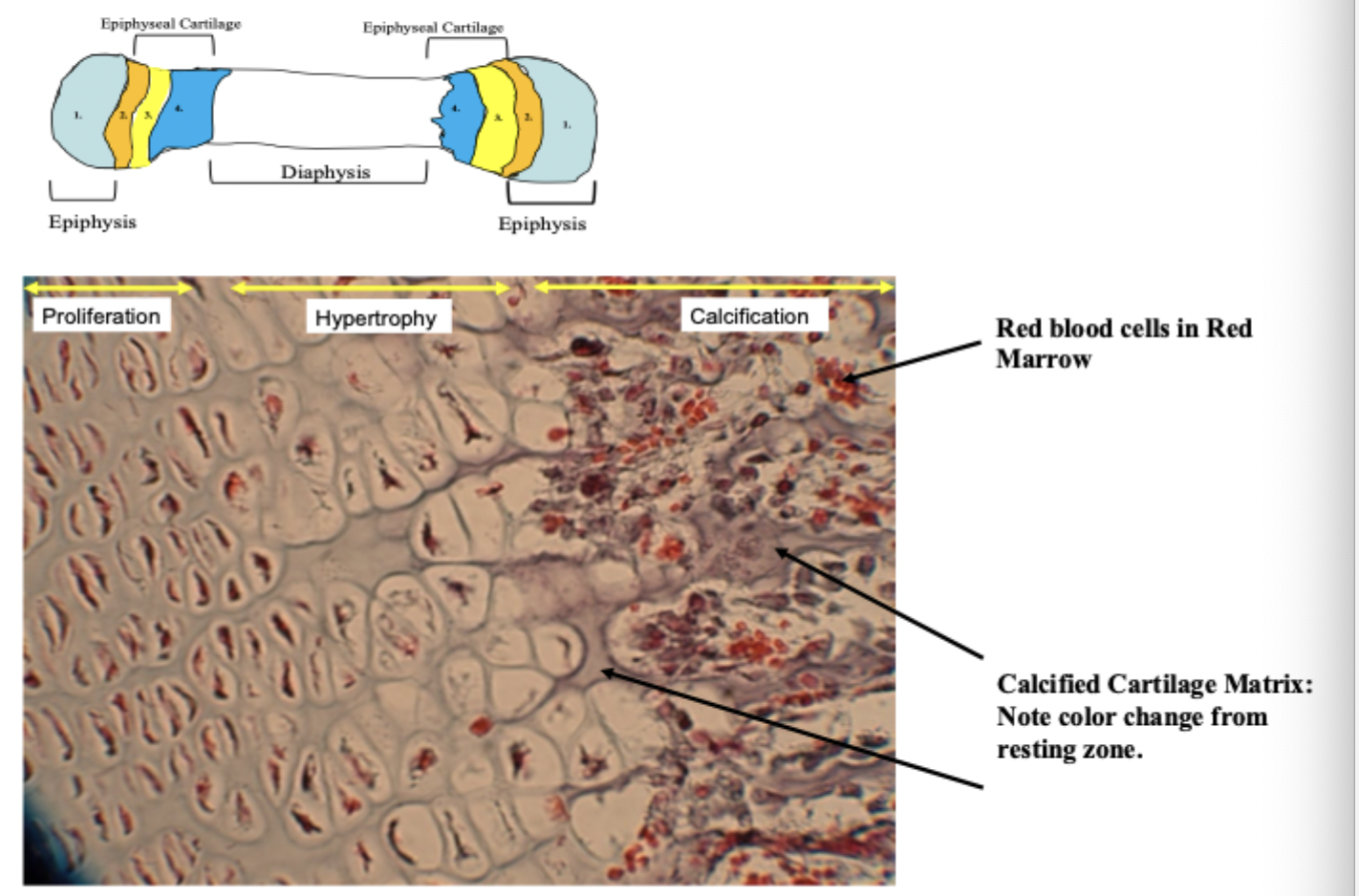
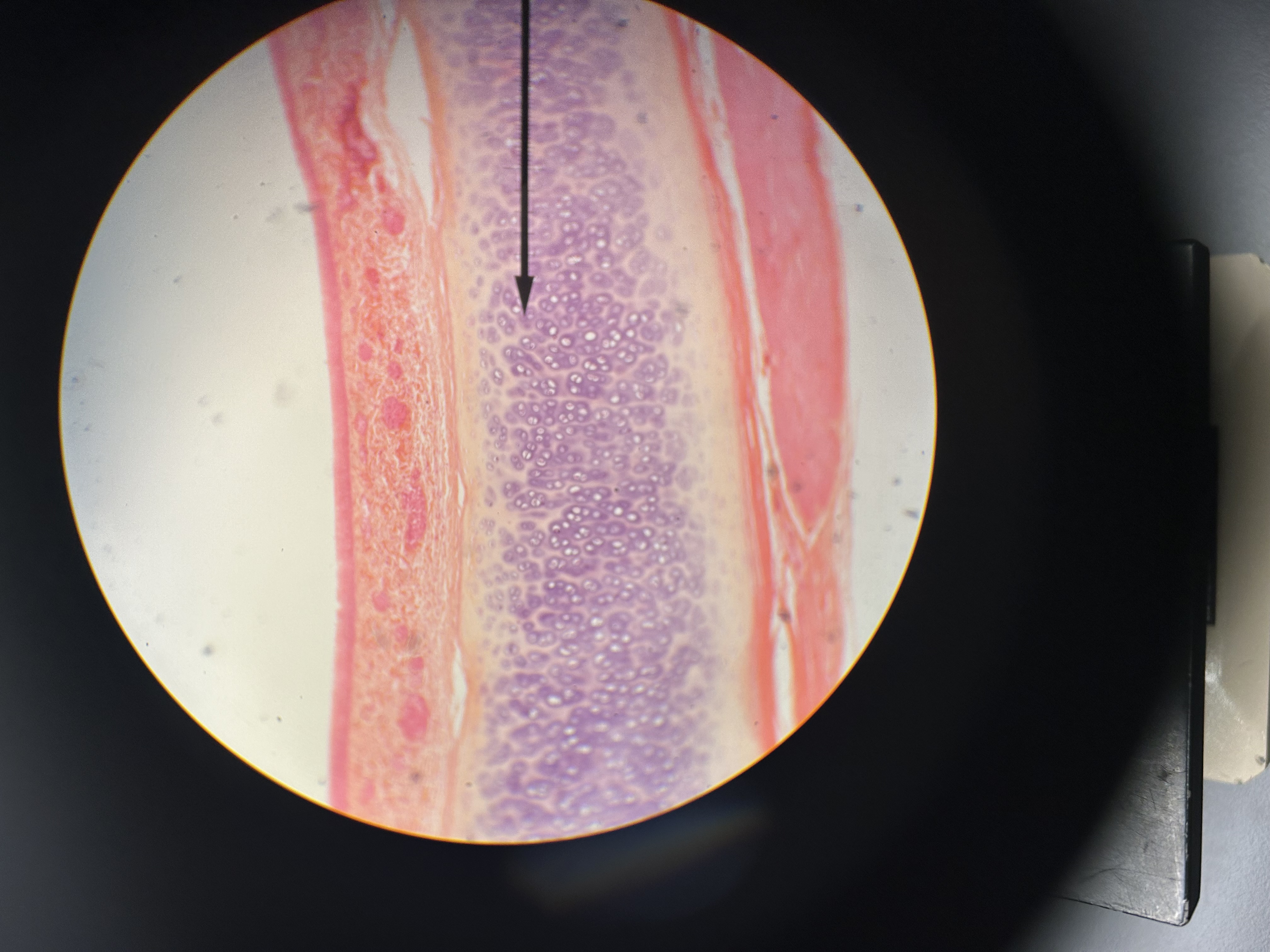
ossification zone
osteoblasts begin making osseous connective tissue on top of mineralized cartilage ECM. Osseous ECM stains a different color than calcified cartilage ECM and can be differentiated on the slide.
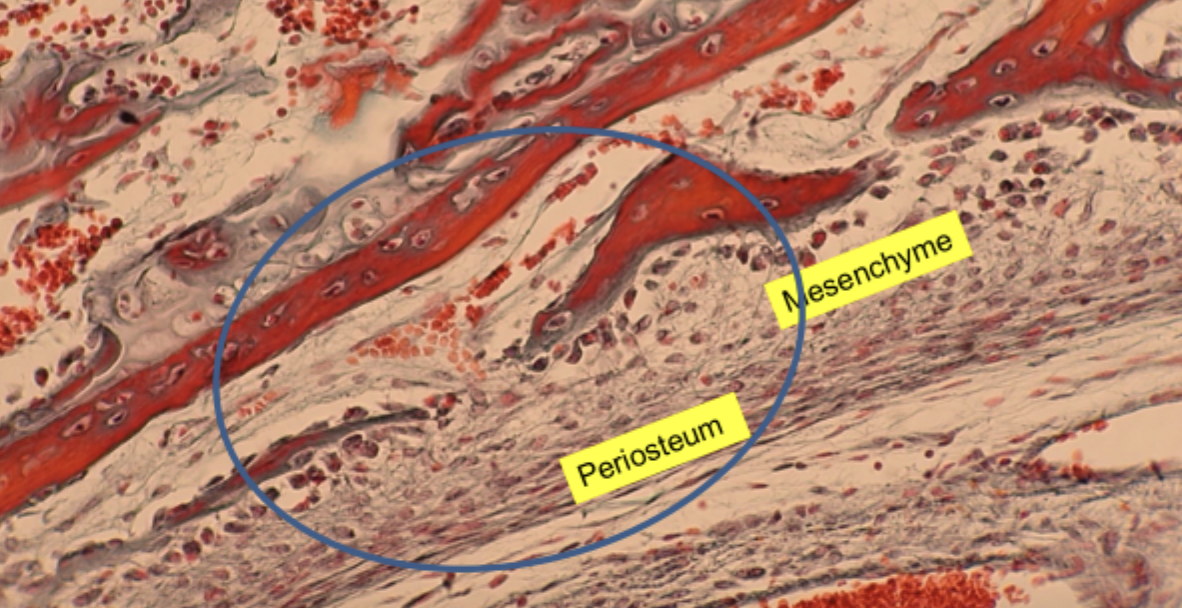
Periosteal bud and red marrow
ossification zone. What is the area circled blue? What about the red dots?
avascular
one reason cartilage is thin
Periosteum
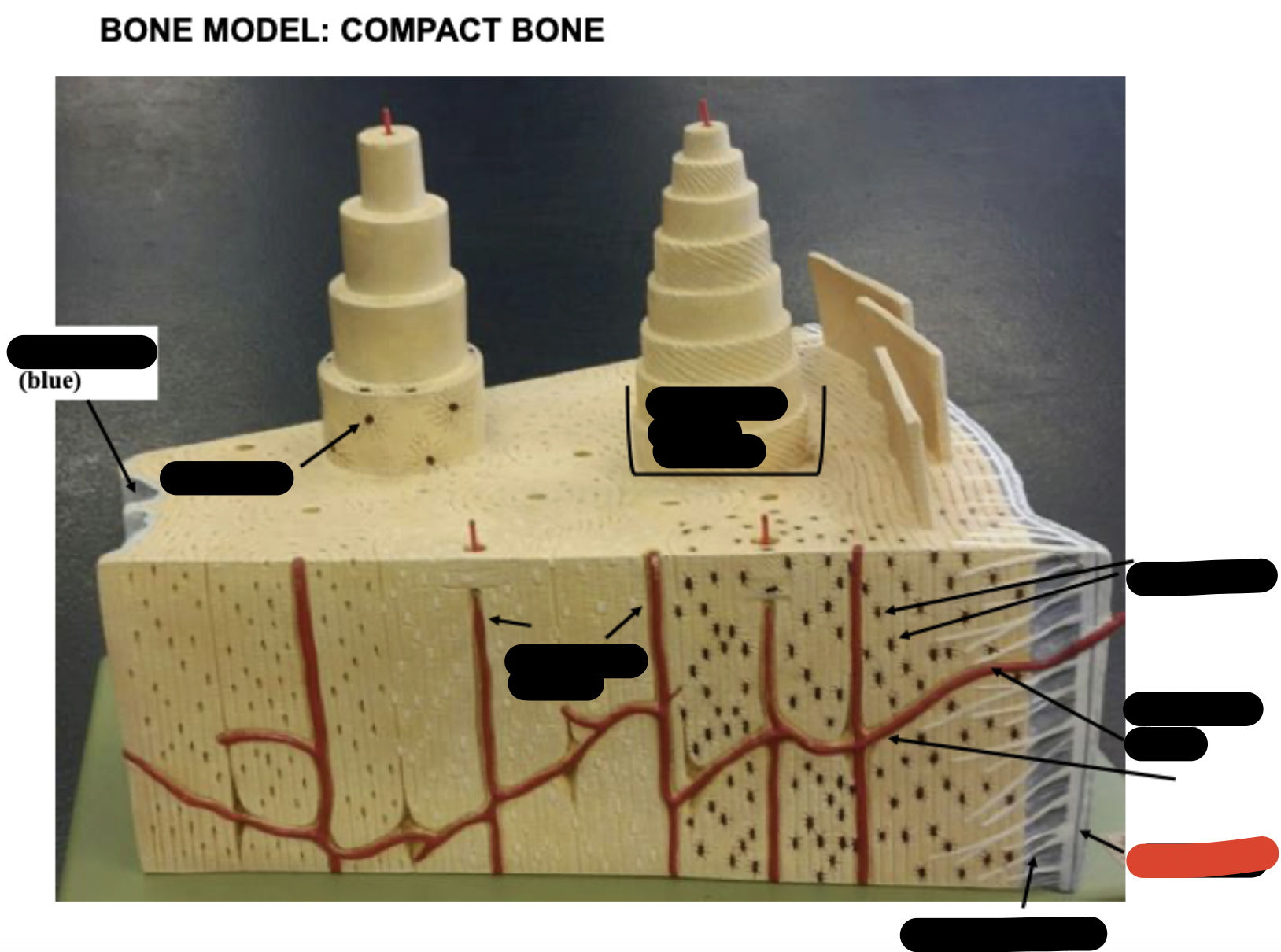
Sharpy’s fibers
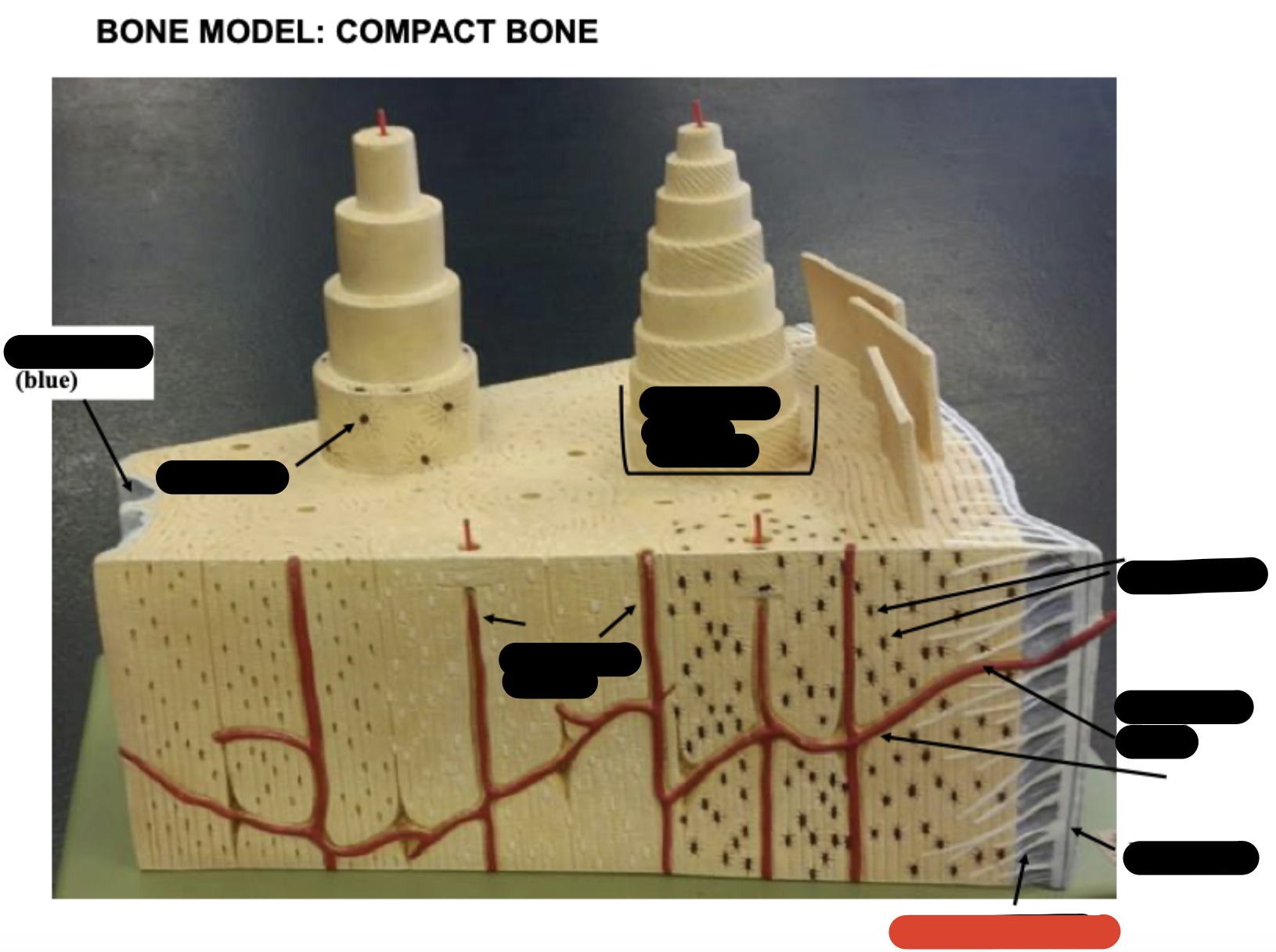
Haversion canals
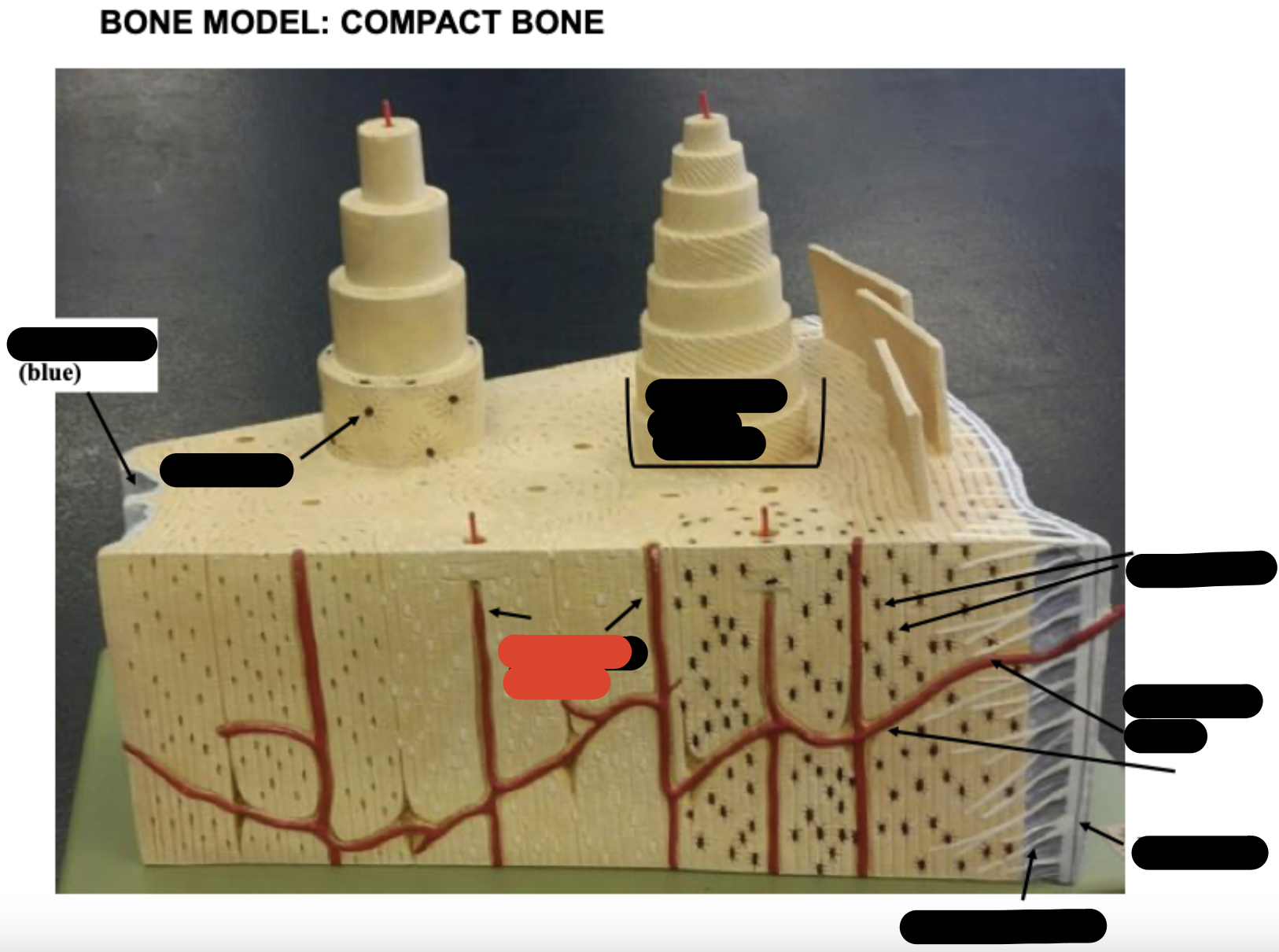
One osteon showing lamellae
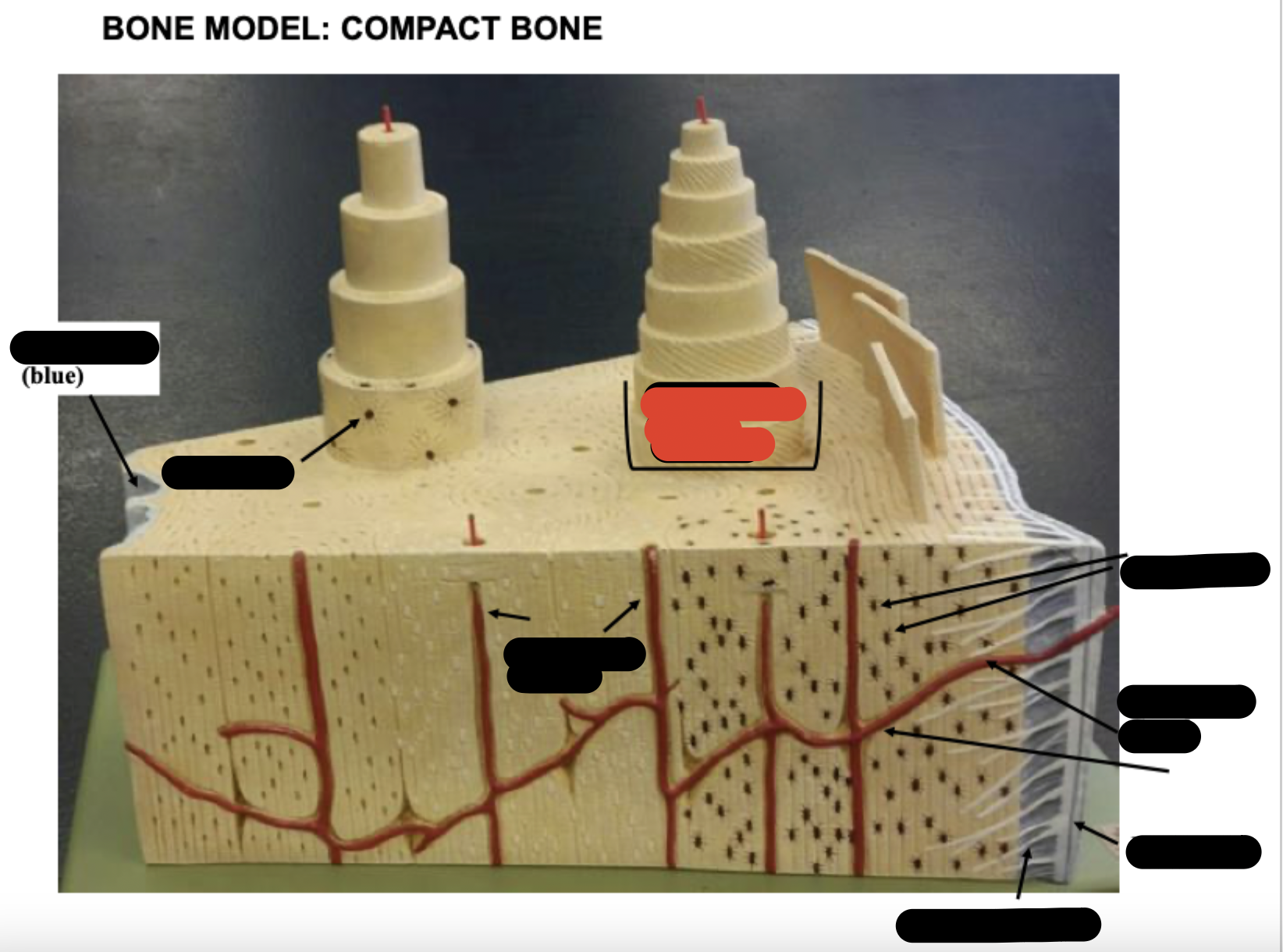
Osteocytes
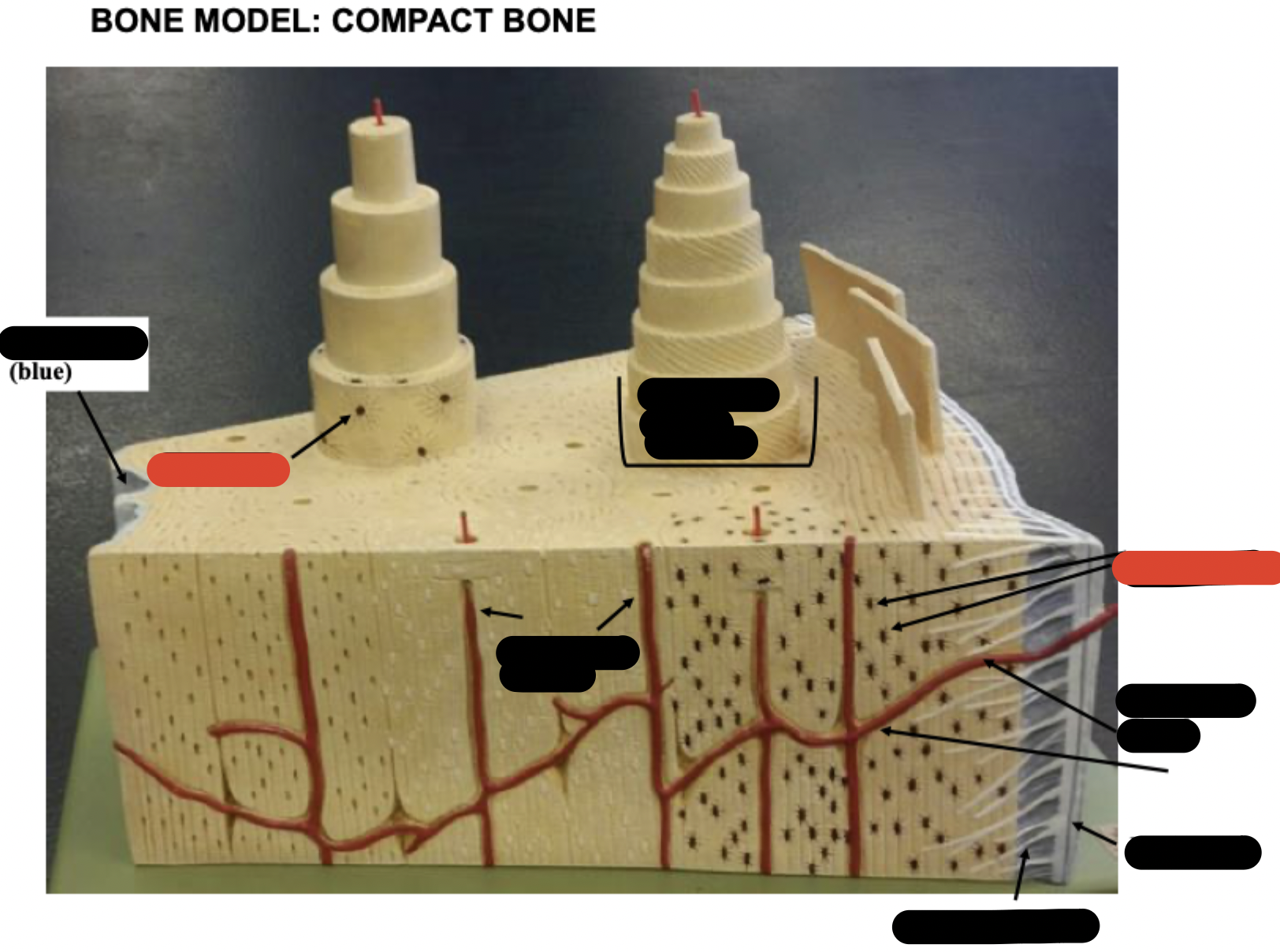
Endosteum
covering small amount of spongy bone just inside the innermost layer of compact bone
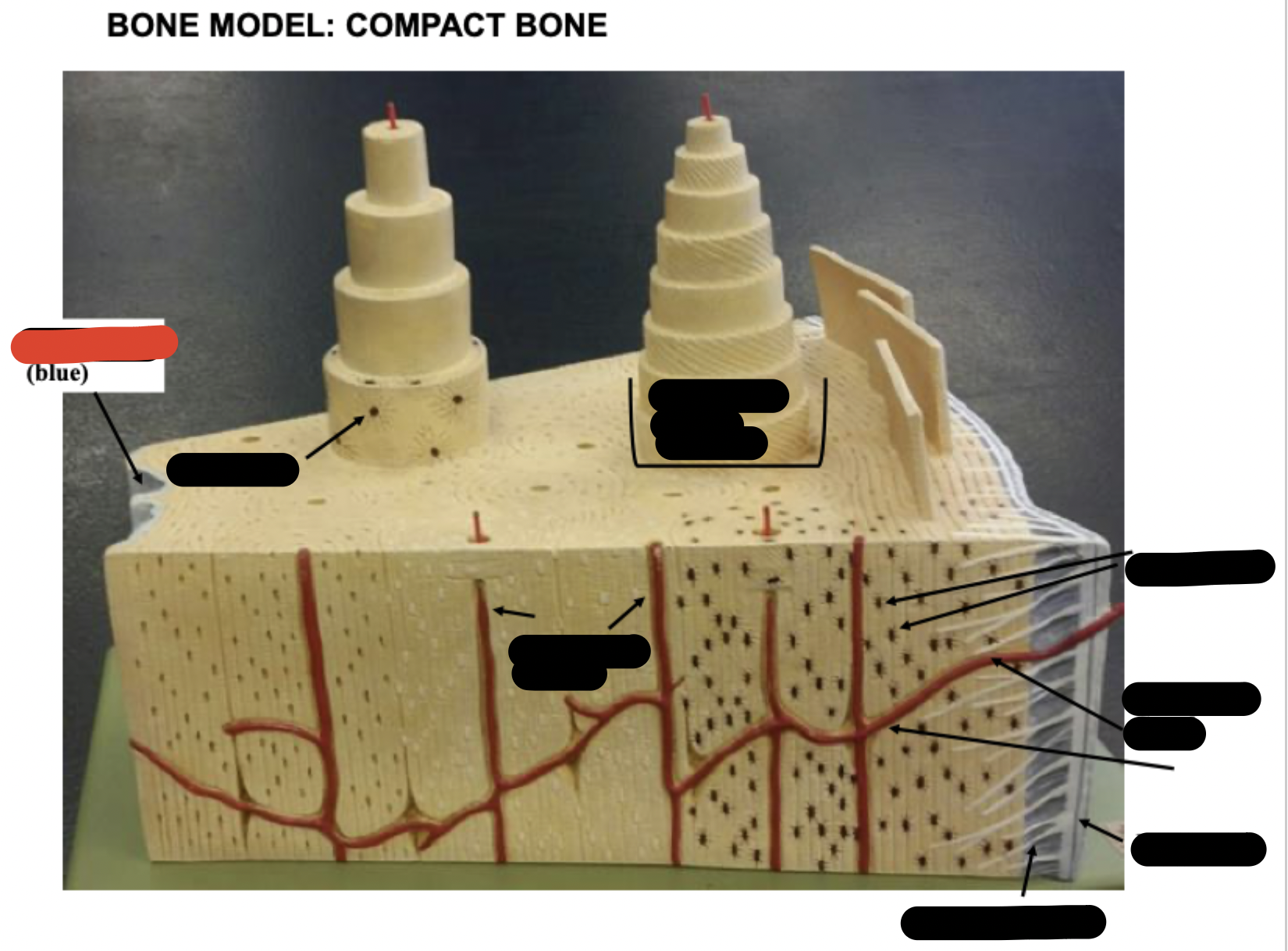
Volkman’s Canal
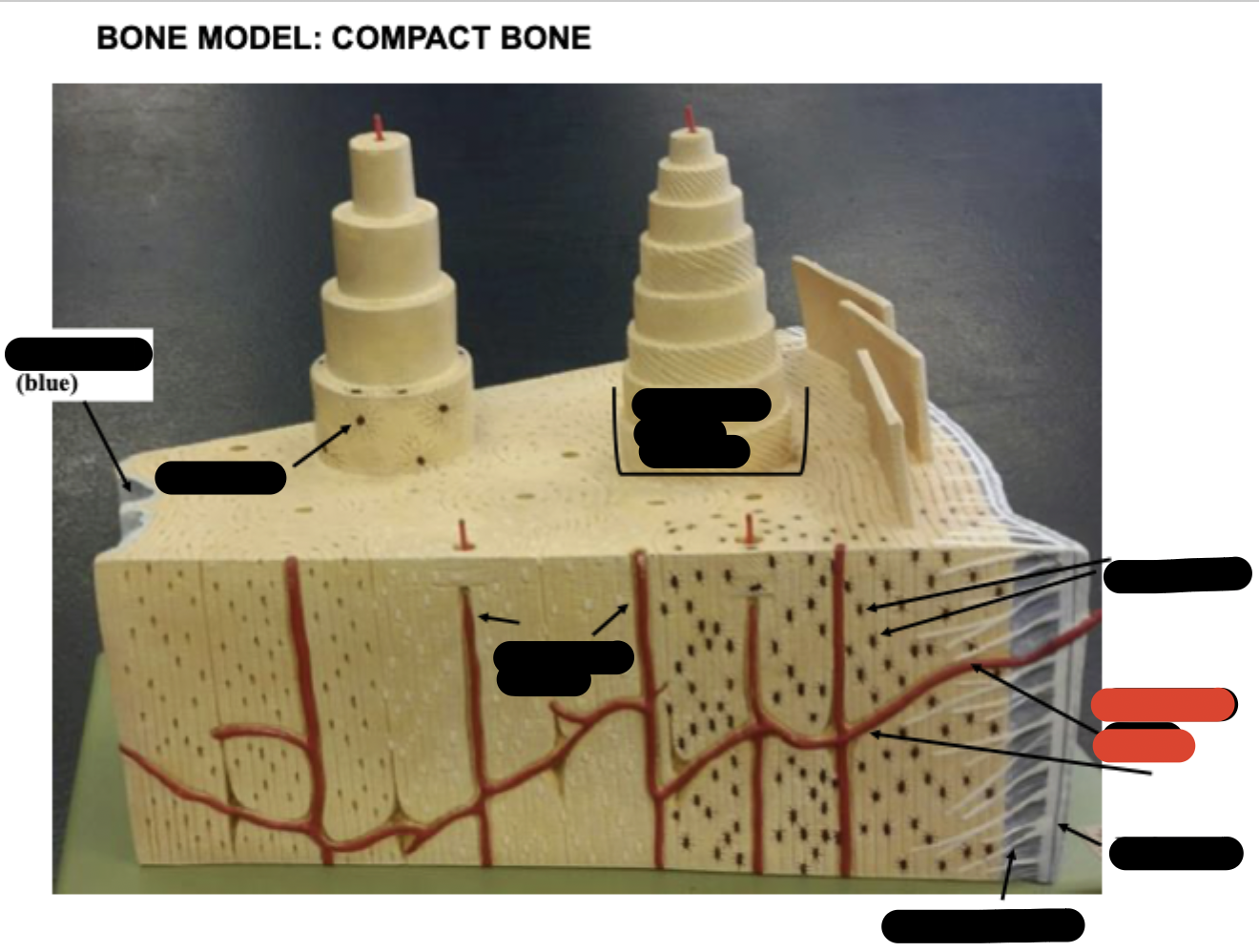
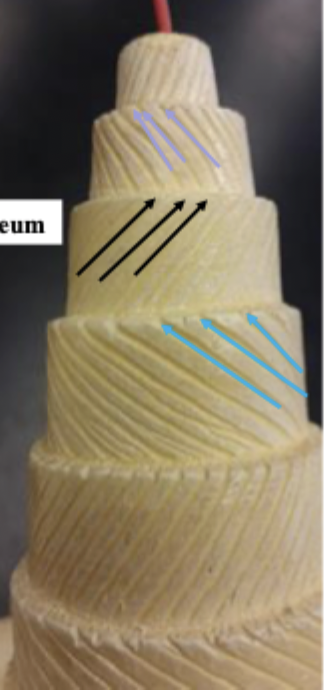
collagen fibers
______ _____ in each lamella of the osteon change direction in order to add strength to resist compression from top to bottom of long bones
intramembranous bone formation
pink = newly formed osteoid
purple = calcified bone
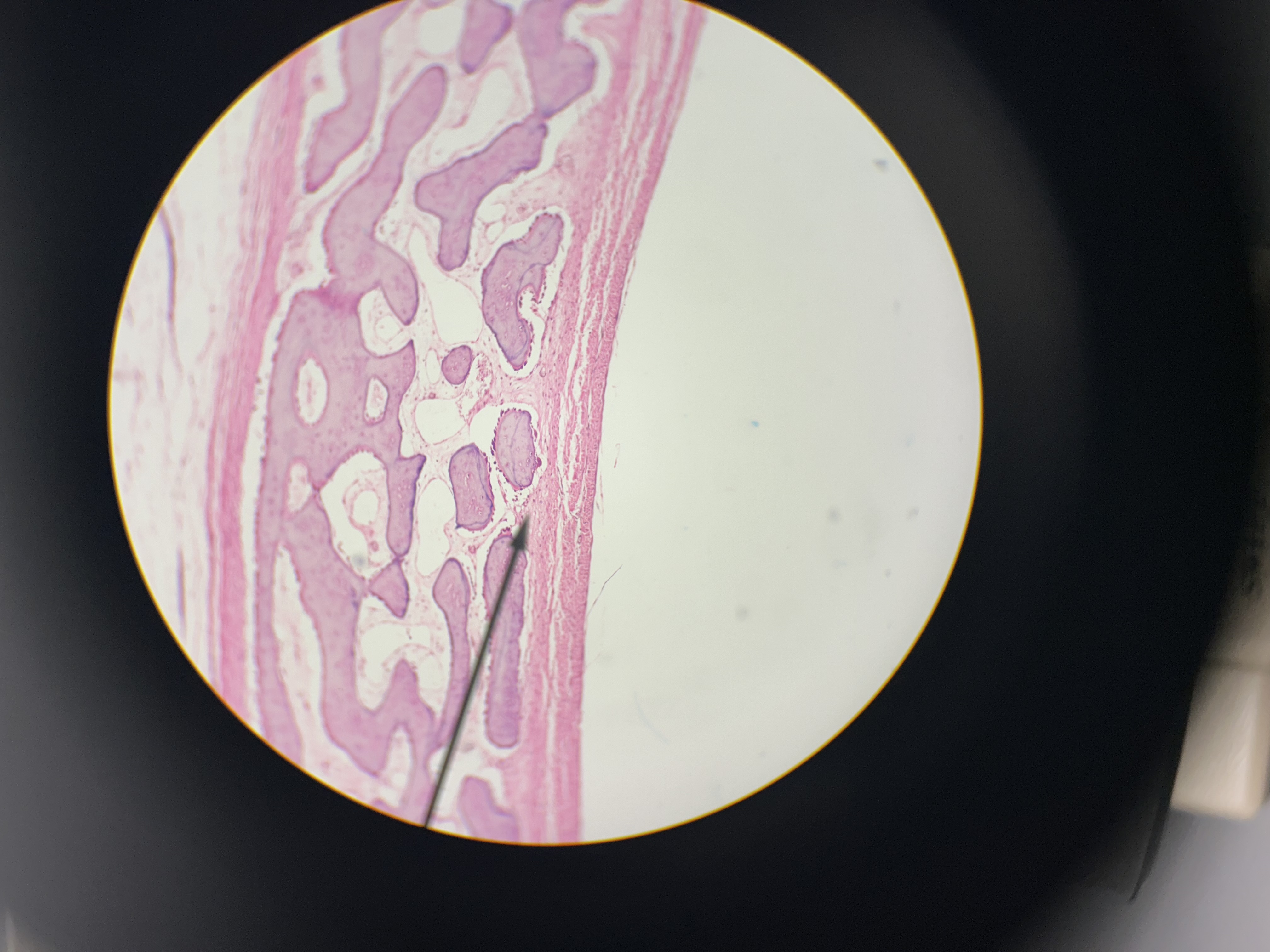
fibrocartilage
blue = numerous collagen fibers
chondrocytes in lacunae
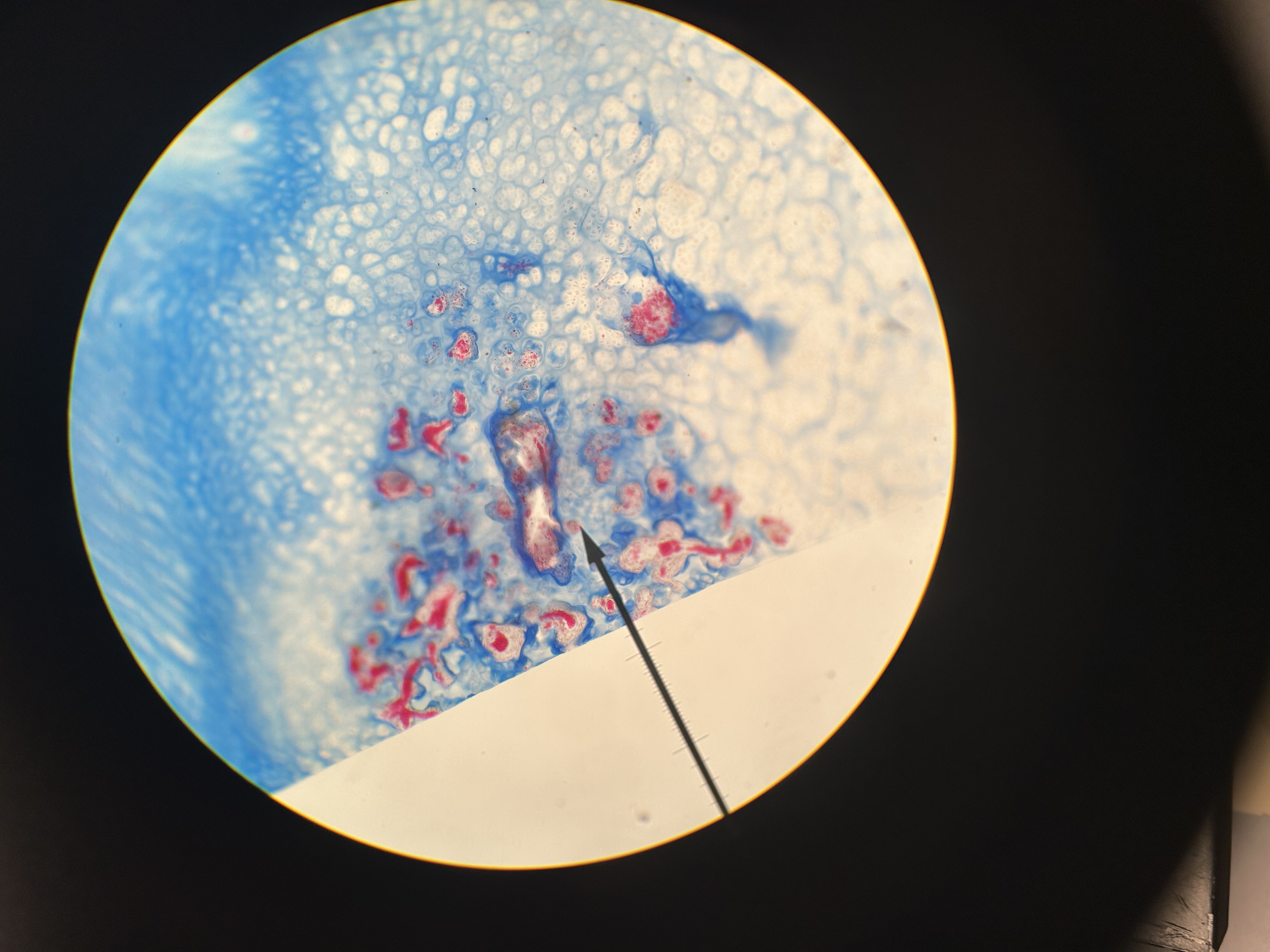
elastic cartilage
ear? (keratinized)
chondrocytes in lacunae
perichondrium (layer of fibrous connective tissue covering cartilage)
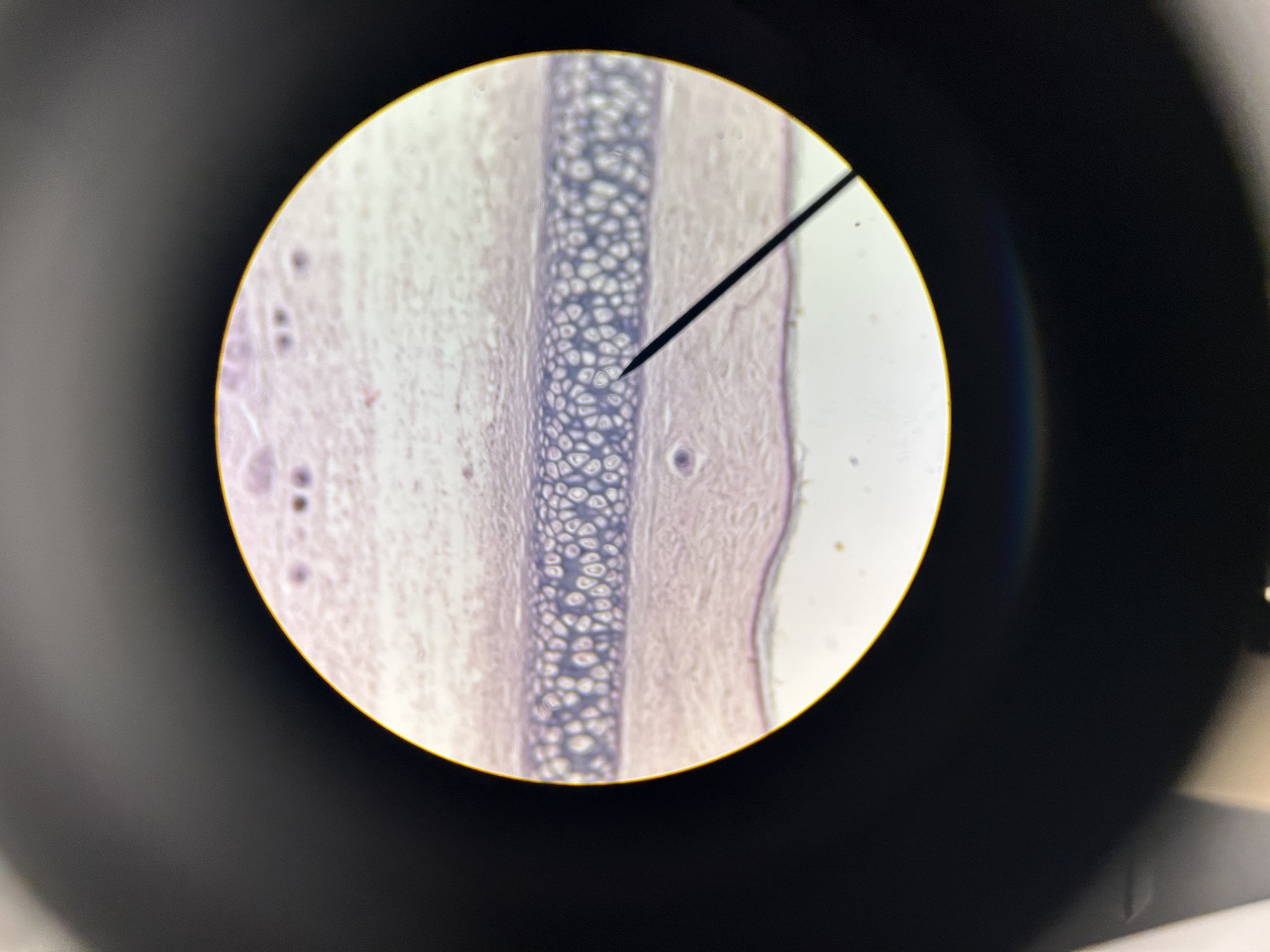
hyaline cartilage
chondrocytes in lacunae
perichondrium (layer of fibrous connective tissue covering cartilage)
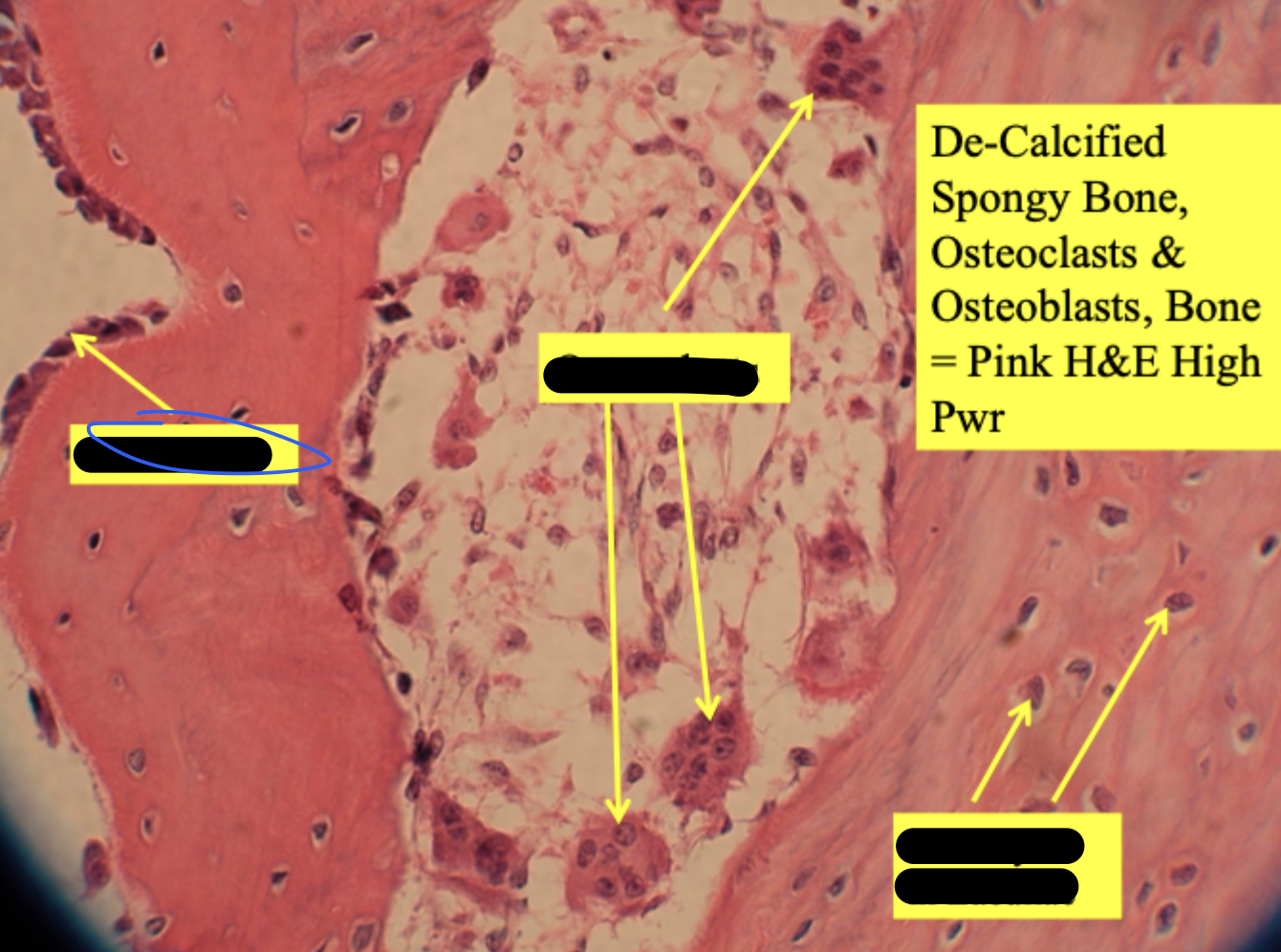
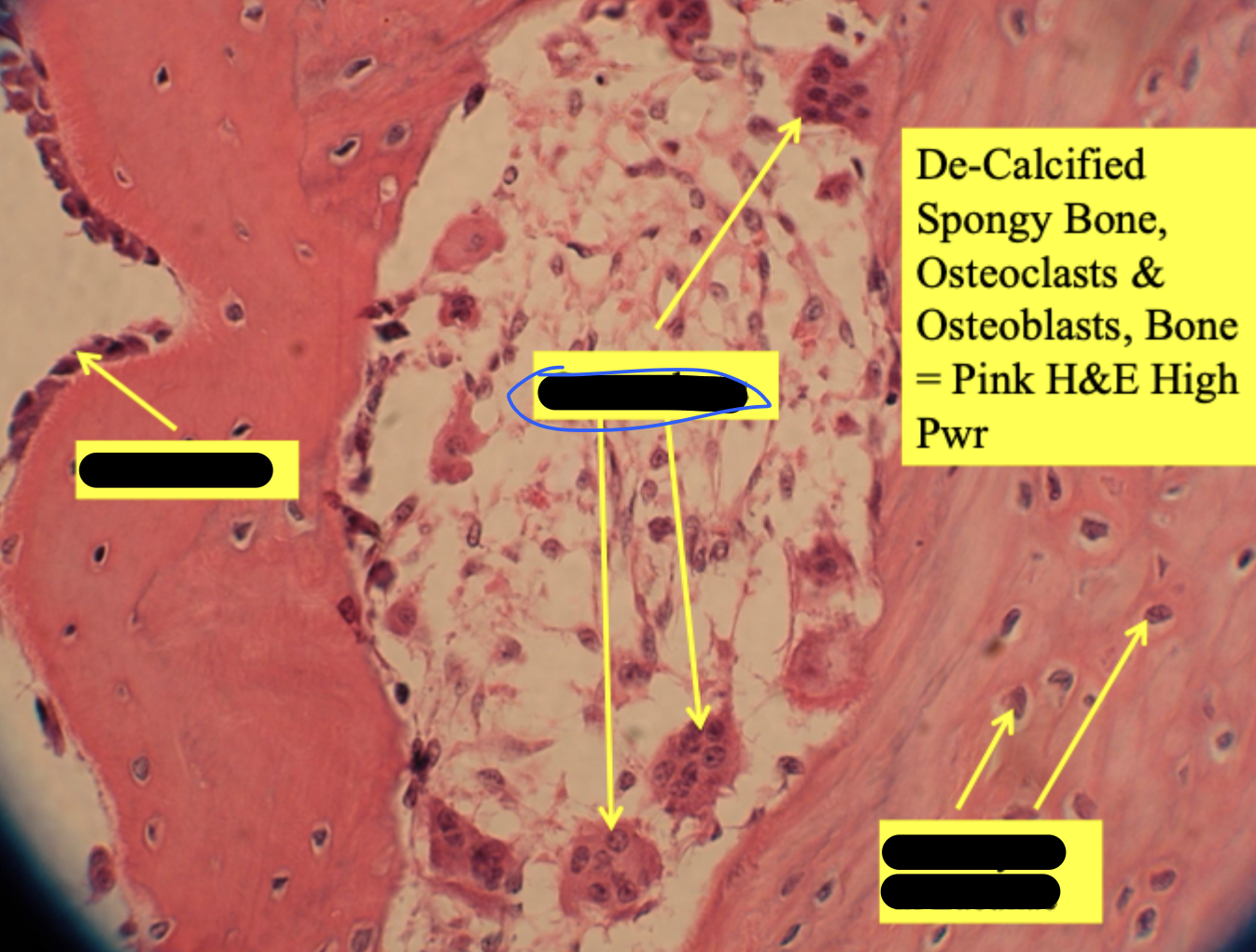
osteoclast
larger than osteoblasts & has multiple nucleii
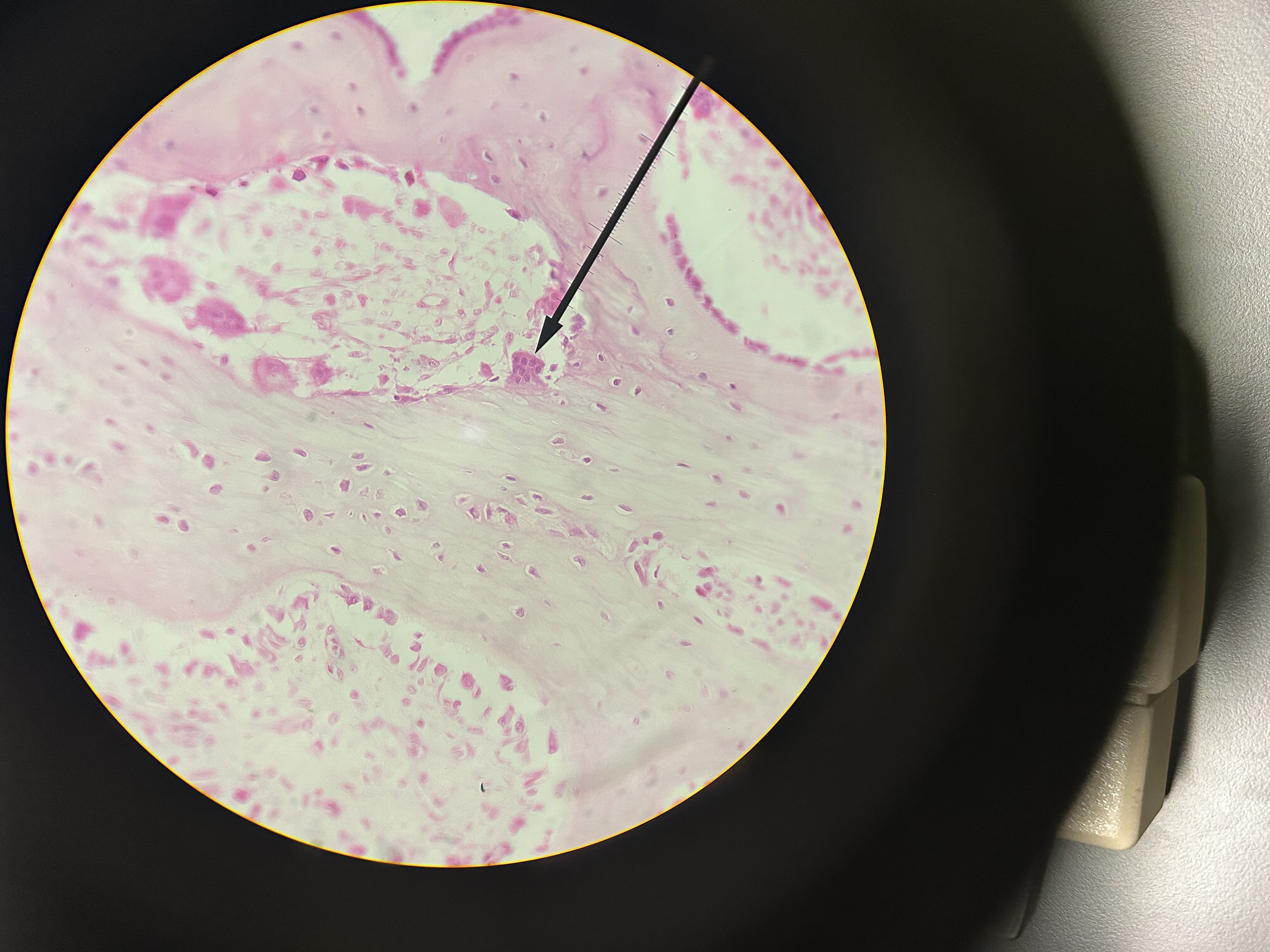
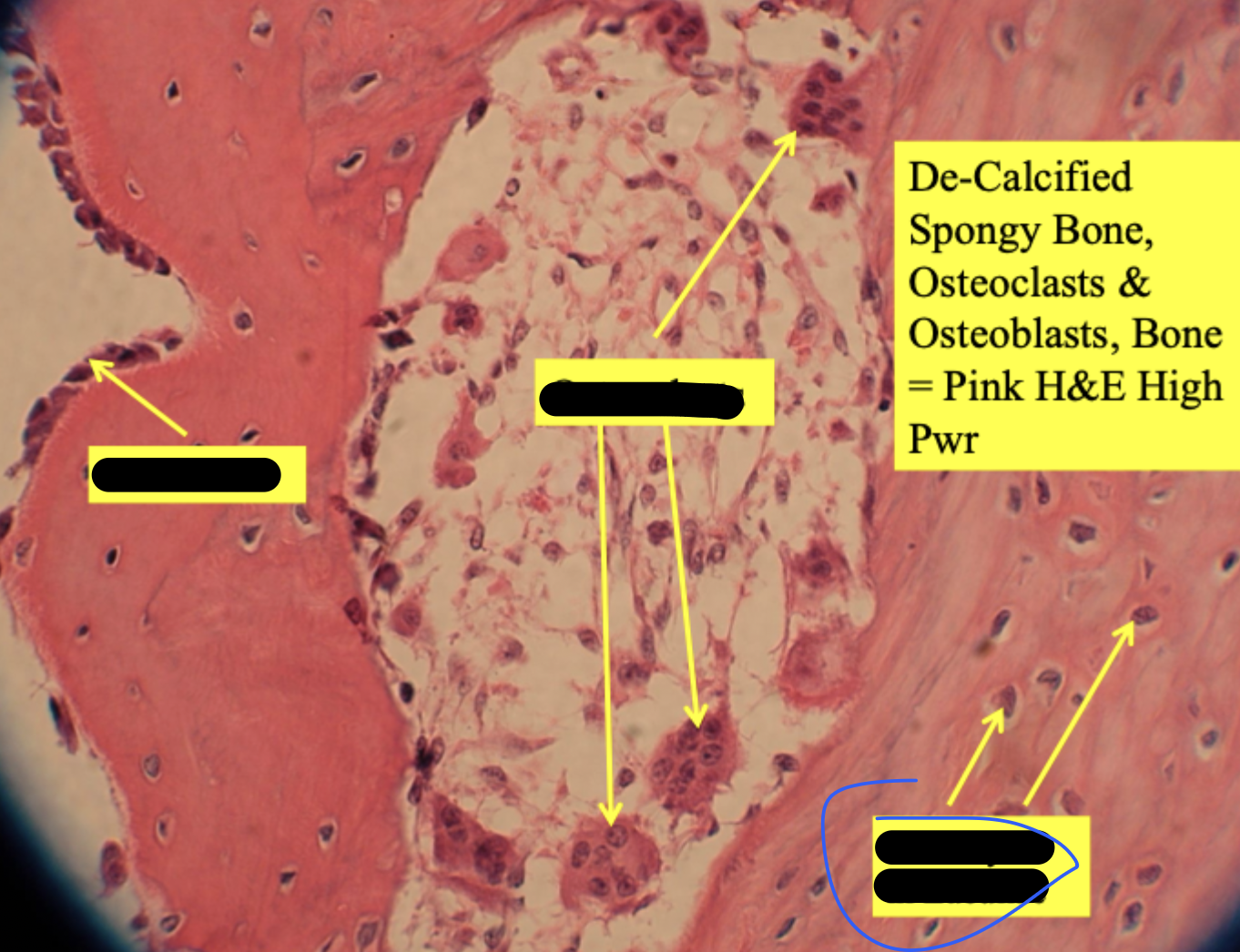
developing long bone
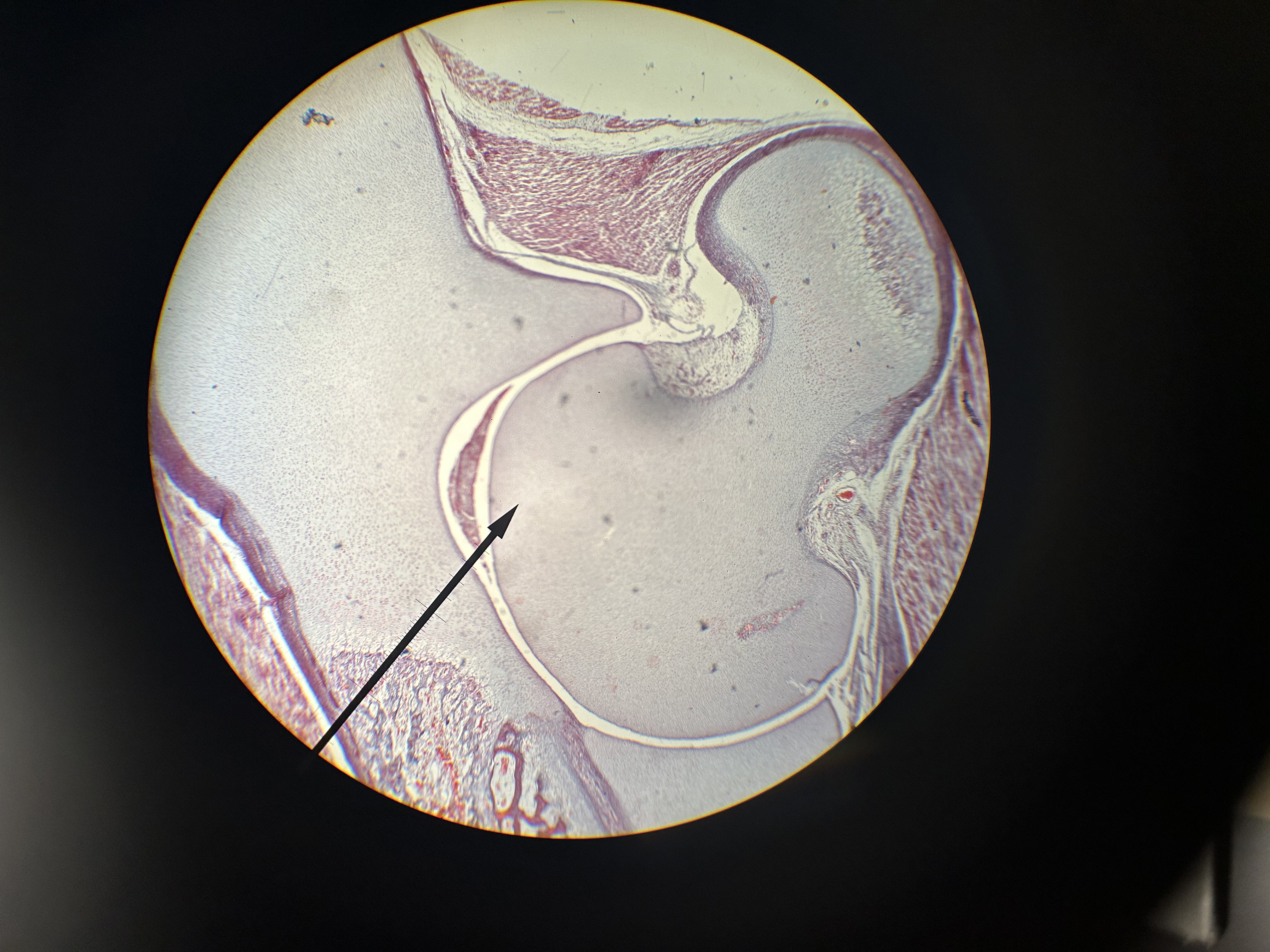
de-calcified spongy bone
osteocytes in lacunae
osteoblasts line surfaces of trabeculae
endosteum = layer around white circles
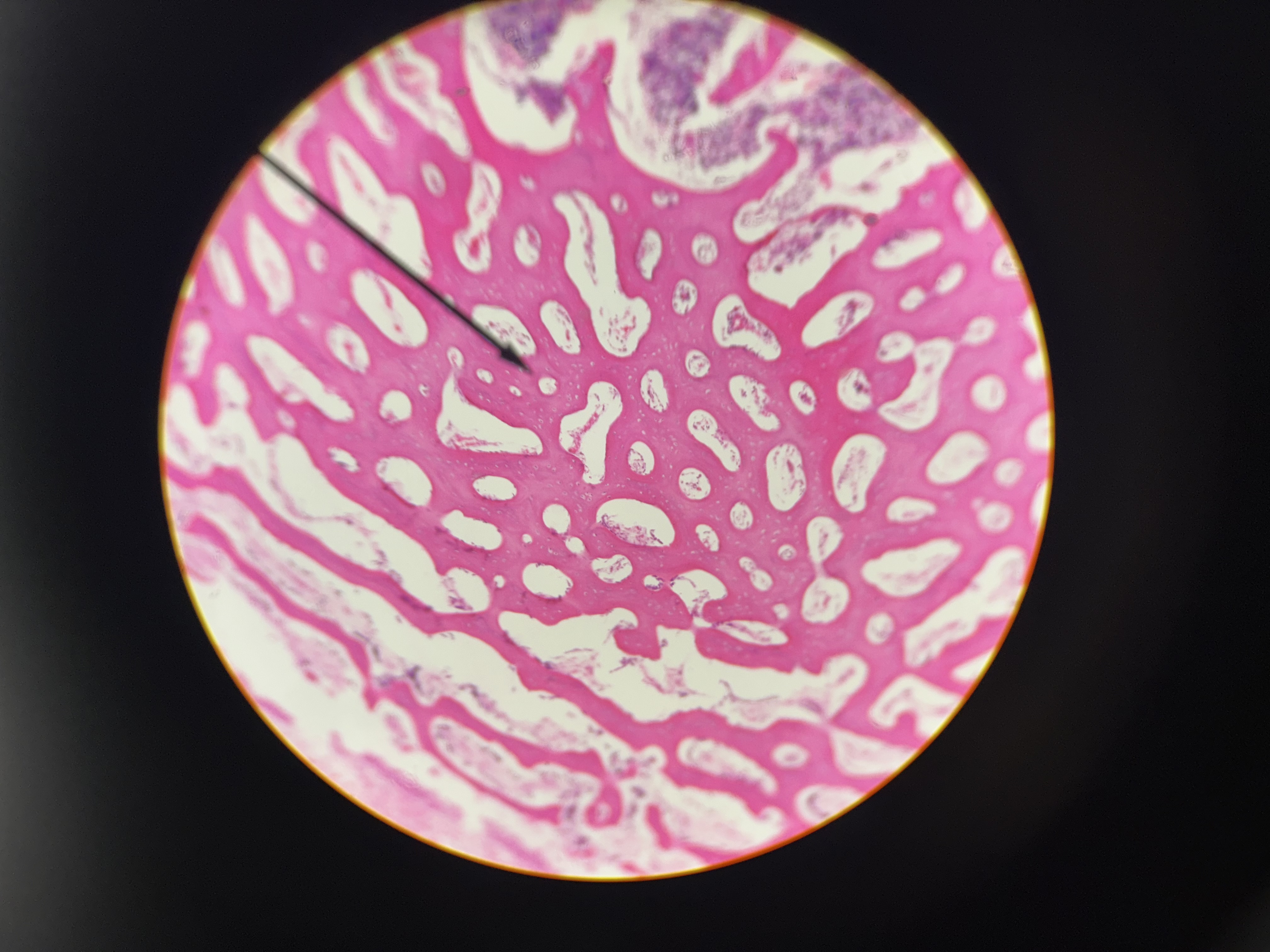
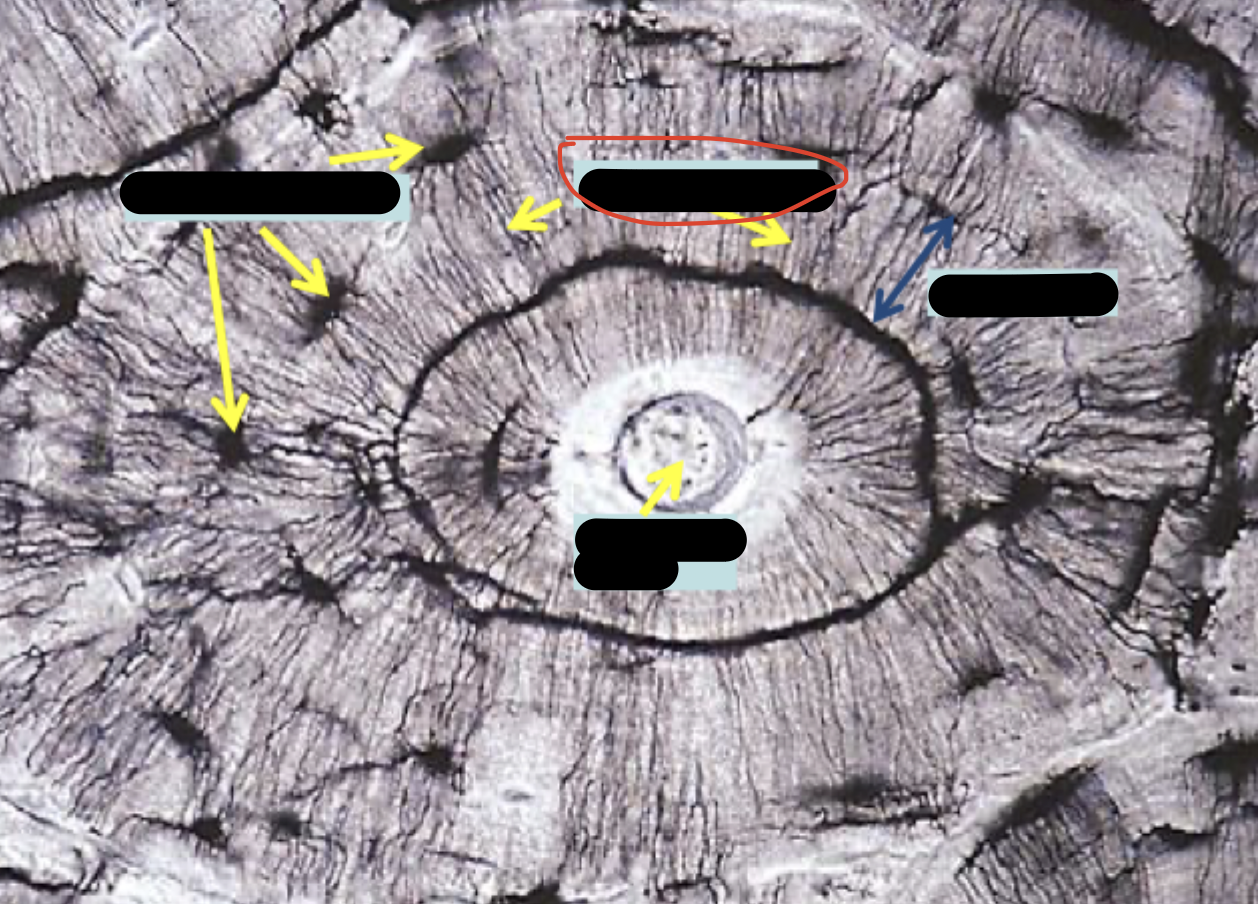
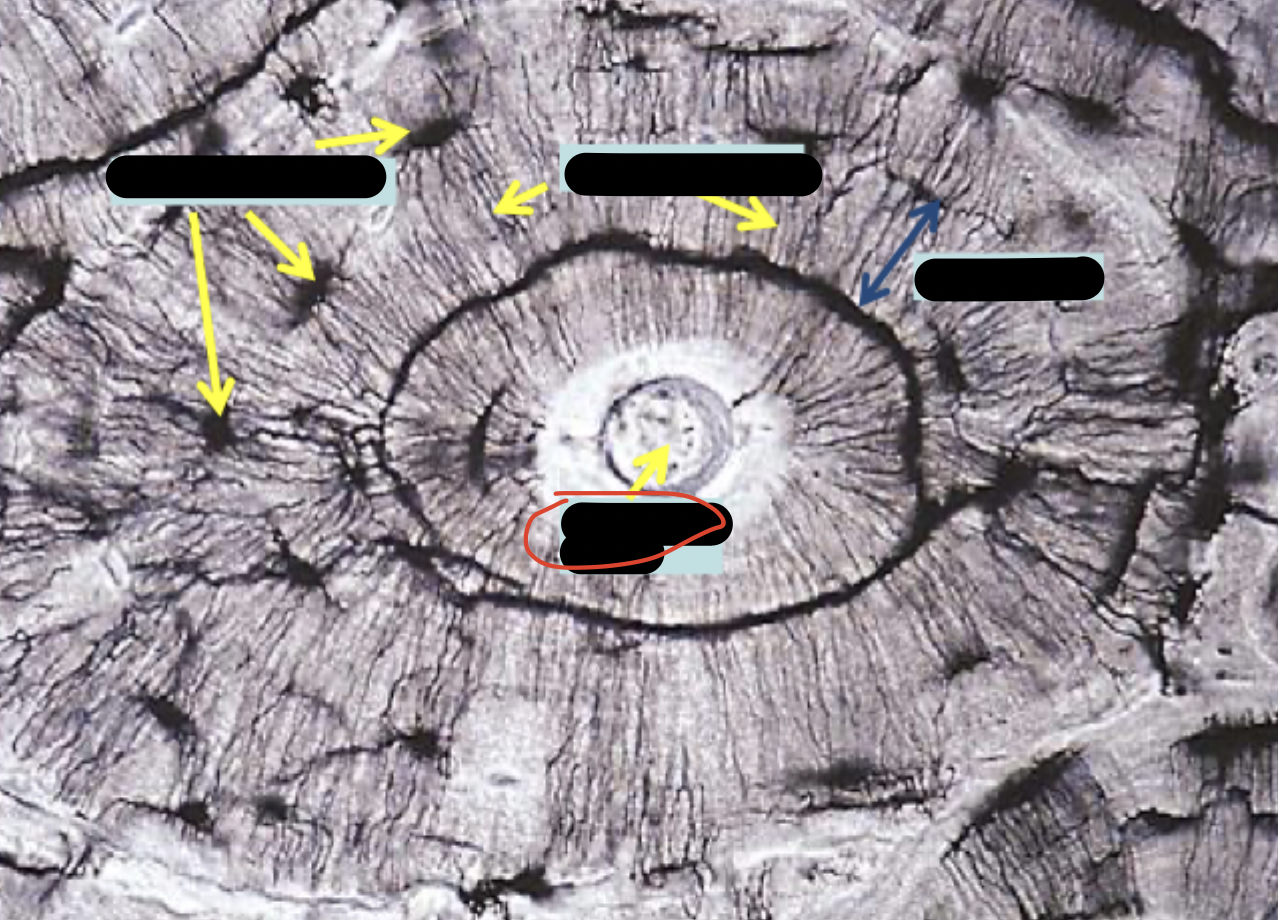
decalcified compact bone (cross section)
osteocytes in lacunae
central canal & longitudinal section
periosteum
big white dots = harversion canal
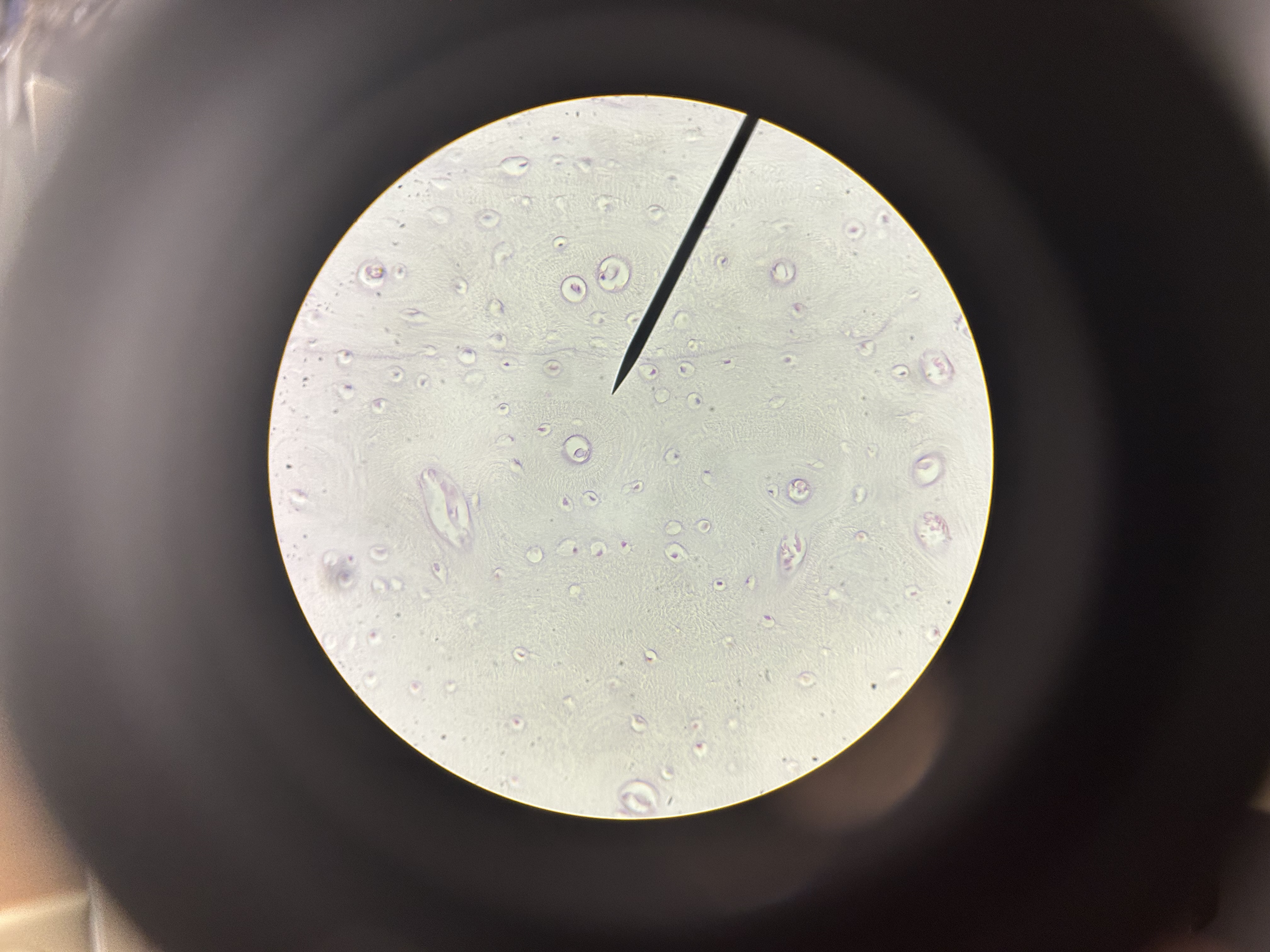
ground bone compact (cross section)
osteons
osteocytes in lacunae
canaliculi
haversion canals