2-Gametogenesis
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Teratogens
Agents that can cause fetal abnormalities
Teratogens Examples
Cytomegalovirus
X-rays
Thalidomide, Warfarin, ACE inhibitors
Maternal Diabetes and Obesity
Germinal Stage of Embryonic Development
0-2 weeks of embryonic development
Embryo loss can happen due to chromosomal abnormalities
Embryonic Stage of Embryonic Development
3-8 weeks of embryonic development
Teratogen sensitivity is highest
Organs form
Fetal Stage of Embryonic Development
9 weeks to birth
Teratogen sensitivity is lowest
Sex organs, CNS, and organ systems form
Malformation
Primary poor formation of tissue (e.g., congenital heart defect)
Disruption
Secondary disruption of previously normal organ, breakdown of normal tissue (e.g., amniotic bands)
Deformation
Extrinsic disturbance of development by biomechanical forces, unusual forces on normal tissue (e.g., uterine constraint)
Dysplasia
Abnormal organization of cells in tissue (e.g., hip dysplasia)
Syndrome
Constellation of developmental abnormalities that are pathologically related (e.g., Turner syndrome)
Mitosis
1 parent cell becomes 2 identical daughter cells
Includes prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Meiosis
Diploid cell becomes 4 haploid cells, division happens twice
Primordial Germ Cell = Diploid Cell
Primordial Germ Cell
Diploid cell that becomes spermatocytes and primary oocytes (gametes)
Induce gonadal formation!
What happens if PGCs (primordial germ cells) fail to migrate?
Causes lack of testes/ovaries differentiation
Spermatogenesis Phases
Starts at puberty, regulated by LH
Includes:
Spermatogonia
Primary Spermatocyte
Secondary Spermatocyte
Spermatids
Spermatozoa
Spermatogonia
Stem cells for sperm, derived from PGCs
Primary Spermatocyte
46 chromosomes, 4N DNA, first meiotic division occurs here
Secondary Spermatocyte
23 chromosomes, 2x DNA, second meiotic division happens here
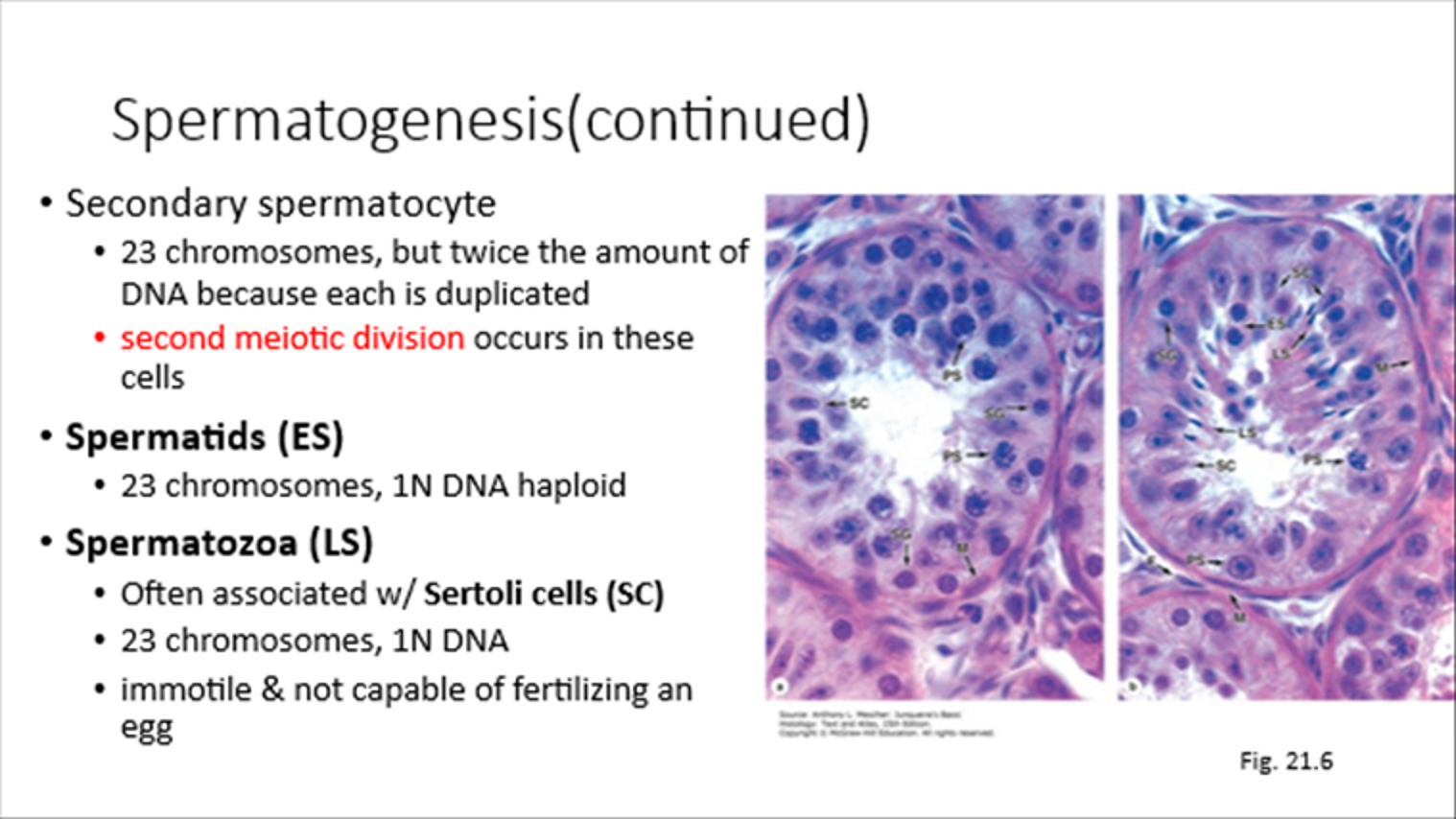
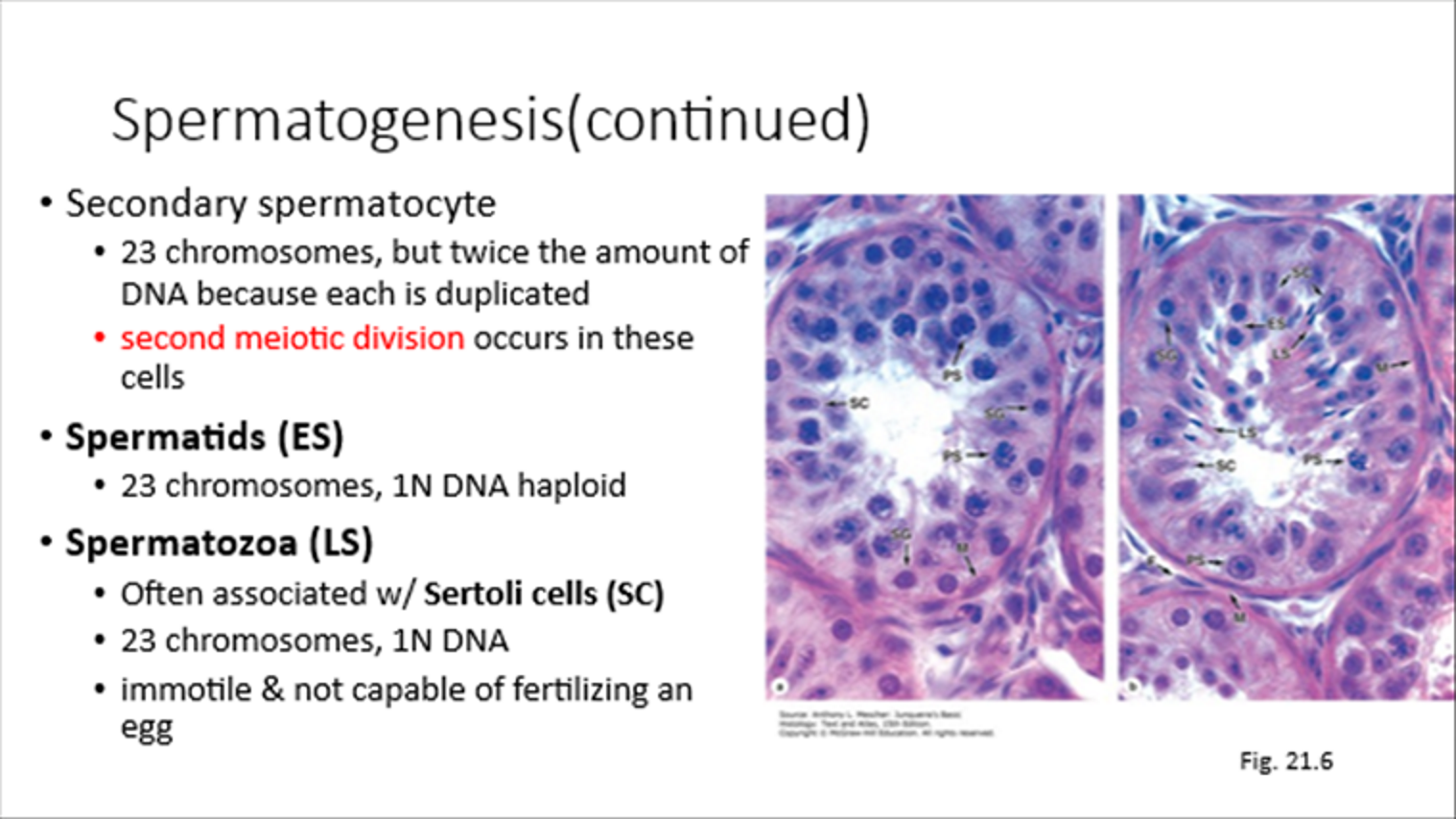
Spermatids
23 chromosomes, 1N DNA
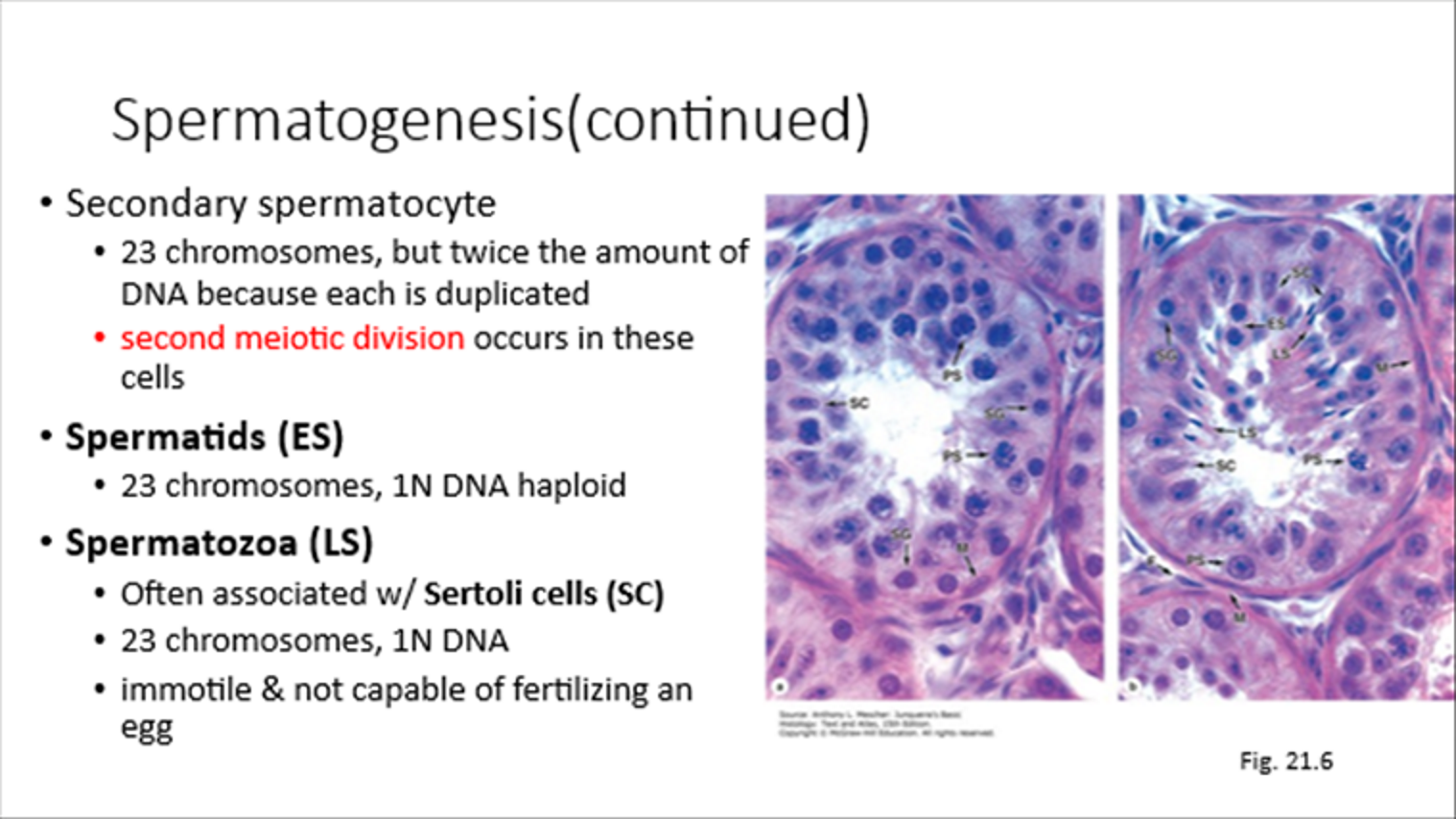
Spermatozoa
Associated with Sertoli Cells, 23 chromosomes, 1N DNA
Not fertilization-capable until cap removal and flagella activation
Spermiogenesis
Spermatid to Spermatozoa
4 phases to make sperm motile and fertilization-ready
Oogenesis and Phases
Process of oogonia becoming mature oocytes
Oogonia
Primary Oocytes
Follicular cells surround oocytes
Oogonia
Cells from mitotic division of PGCs
Primary Oocytes
Arrested in Prophase I of Meiosis I (P1 of M1)
Follicle Development Phases
Primordial Follicle
Primary Follicle
Secondary Follicle
Mature Graafian Follicle
Primordial Follicle
Made when you’re a baby, arrested until puberty
Primary oocyte covered in flat follicular cells
Primary Follicle
Responds to FSH and grows
Secondary/Antral Follicle
Primary oocyte with no further growth
Mature/Graafian Follicle
One follicle becomes secondary oocyte, completes 1st meiotic division, polar body released into zona pellucida
Ovulation (trigger and steps)
Triggered by LH surge
Causes primary oocyte to complete meiosis I
Secondary oocyte arrested in M2 of MII
Completes MII if fertilized, otherwise degenerates
Stimulates prostaglandins and hyaluronan to increase V, P, and viscosity
Theca cells contract to rupture follicle and ovary surface
Oocyte expelled with corona radiata
Corpus Luteum
Can become corpus albicans as a remnant
If pregnant, hCG maintains corpus luteum for progesterone production, regresses around 4th month of pregnancy
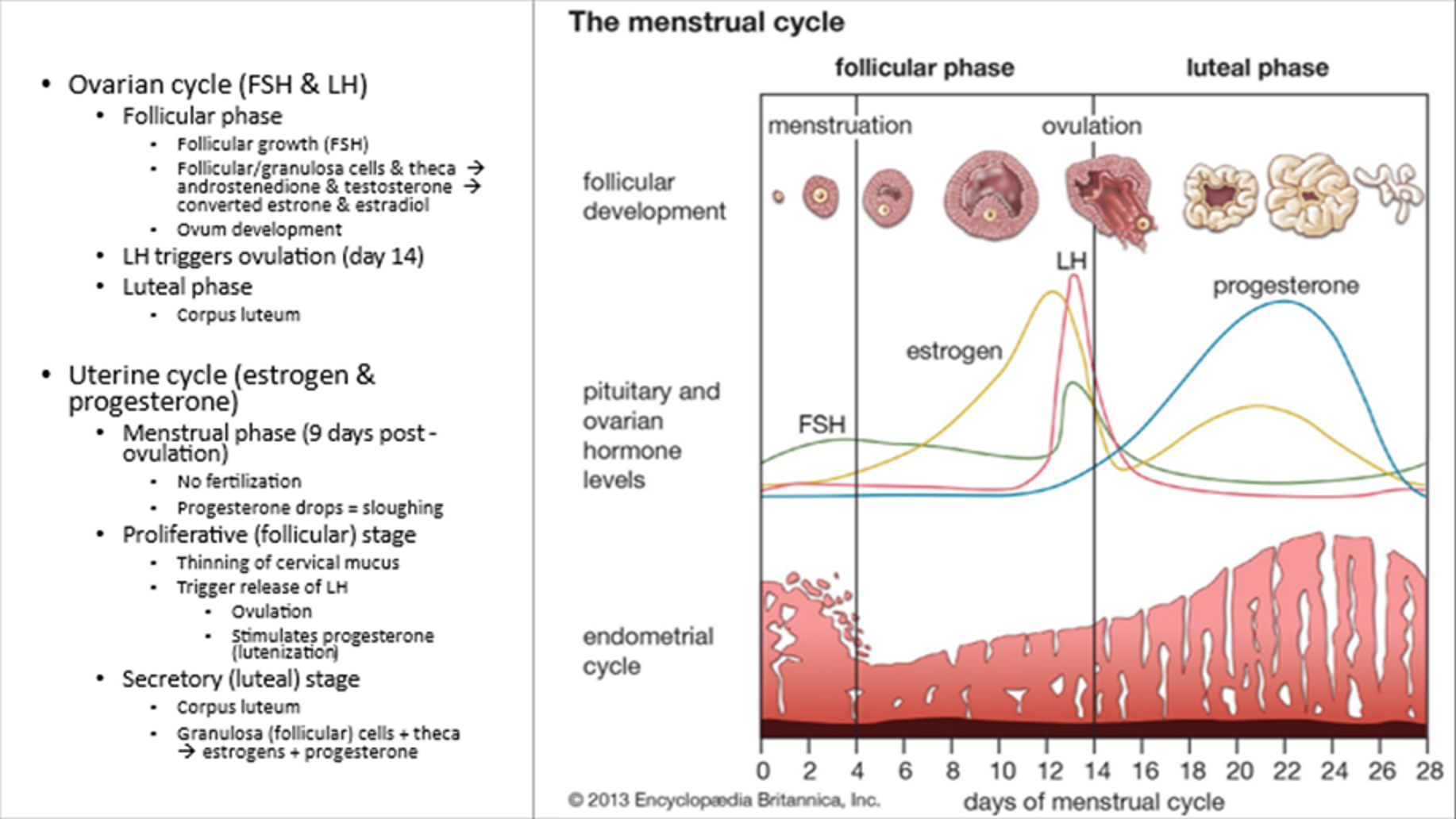
Menstrual Cycle Ovarian Cycle
Phases:
Follicular Phase
LH Triggered Ovulation (day 14)
Luteal Phase (corpus luteum)
If pregnancy, this continues.
hCG (synctiotrophoblast) keeps CL functioning (progesterone production)
Menstruation stops
Cleavage of zygote and blastogenesis
Corpus luteum of pregnancy begins regression around 4th month
Menstrual Cycle Uterine Cycle
Phases:
Menstrual Phase (sloughing off)
Proliferative Phase (follicular, thinning of cervical mucosa)
LH triggers ovulation and progesterone (luteinization)
Secretory Phase (luteal)
Corpus Luteum
Fertilization Phase I
Corona Radiata Penetration:
Sperm penetrates follicular cells, acrosomal reaction via hyaluronidase
Fertilization Phase II
Zona Pellucida Penetration:
Cortical vesicles secrete protease, making ZP impermeable to other sperm
Fertilization Phase III
Fusion of sperm and oocyte plasma membranes, oocyte completes second meiotic division, forms diploid zygote
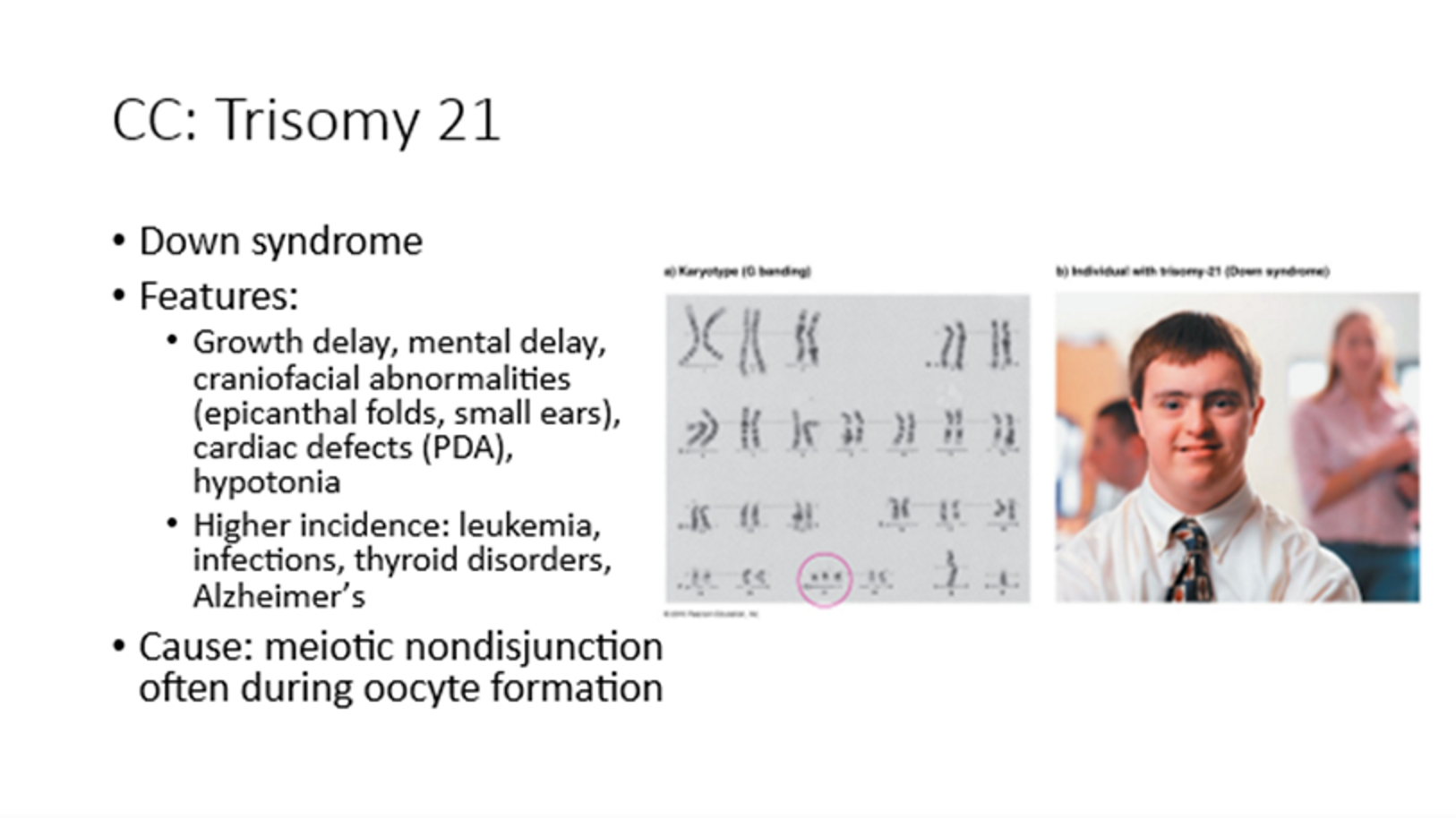
Trisomy 21
Down syndrome
Caused by meiotic nondisjunction
Growth and mental delay, craniofacial abnormalities, cardiac defects
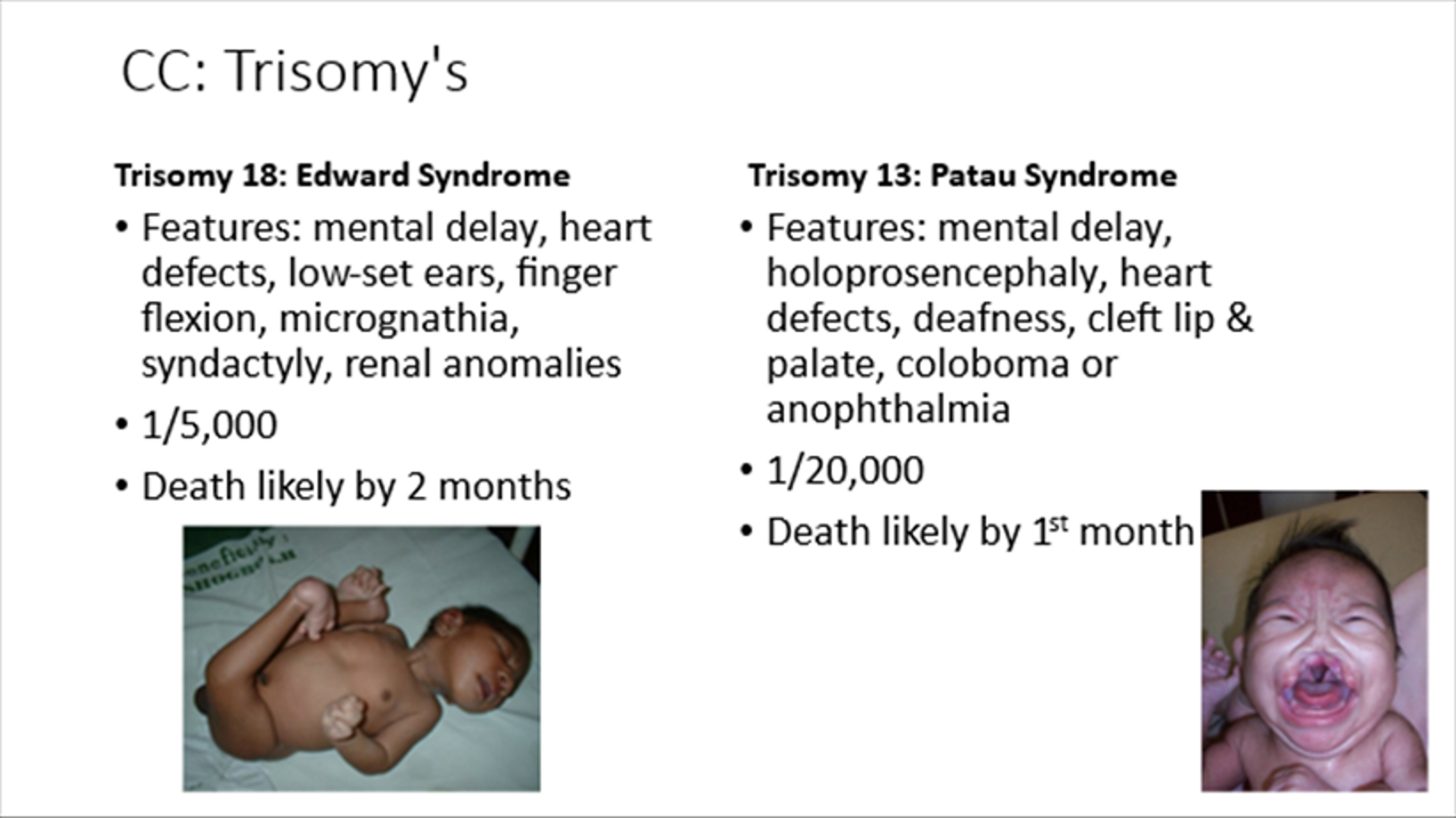
Trisomy 18
Edward syndrome
Mental delay, syndactyly, renal abnormalities
Death likely by 2 months
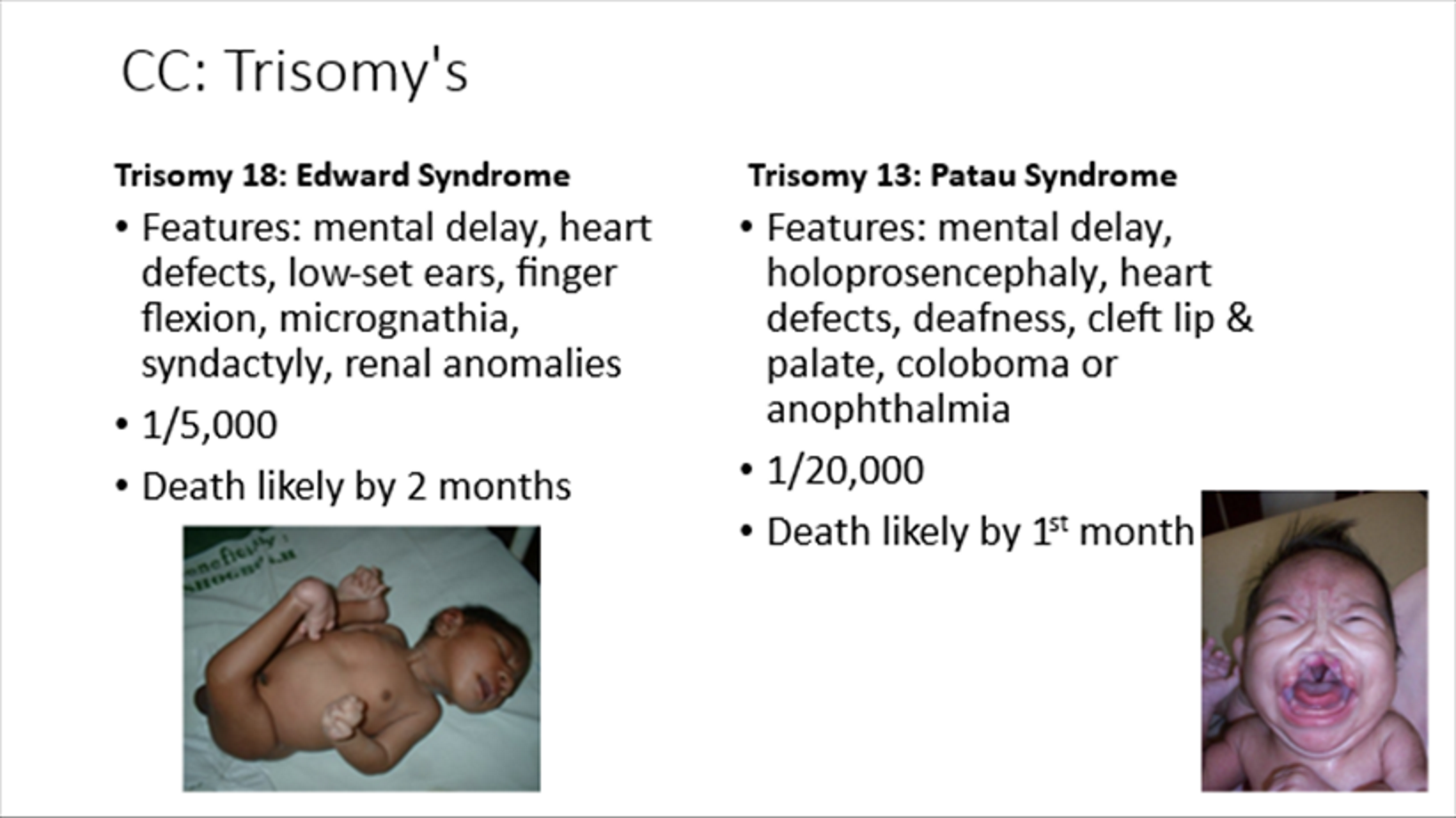
Trisomy 13
Patau syndrome
Mental delay, holoprosencephaly, cleft lip/palate
Death likely by 1 month
Klinefelter Syndrome
47, XXY
Male infertility caused by nondisjunction of XX chromosomes
Turner Syndrome
45, X,
Female with webbed neck & short stature
Caused by paternal nondisjunction
The only monosomy you can live with
Cri-du-chat
Partial deletion of short arm of chromosome 5
Cat-like cry
Deletion 4q Syndrome
Partial deletion of long arm of chromosome 4
Cleft palate and limb abnormalities
Angelman Syndrome
Maternal chromosome 15 microdeletion
Lack of speech, puppet-walk, laughter
Moms are angels, girls are more fun
Prader-Willi Syndrome
Paternal chromosome 15 microdeletion
Obesity, undescended testes
Dads have willies, guys are fat
Oogenesis and Follicular Development Concurrency
Oogenesis and follicular development occur concurrently during a woman's reproductive years. Oogenesis, the process of producing mature oocytes (egg cells), is intrinsically linked to the folliculogenesis process, which involves the growth and development of ovarian follicles. These follicles surround and nourish the developing oocyte.