Suture Materials and Patterns - LA
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
What factors should you be using to choose suture?
strength of closure and how long does it need to last? -- size and chemical make-up (natural vs synthetic)
inside or outside the body and inflammatory response? — absorbable vs nonabsorbable
wound contamination presence — monofilament vs multifilament
What size suture is generally used in LA for SQ closure?
2-0
What size suture is generally used in LA for linea alba closure?
2 or 3
True or false: The suture should be as astrong as the normal tissue through which it is placed.
true
Tensile strength reduction of suture over time should correspond to what?
the healing of the affected tissue
The _____ is more dependent on the tissue’s ability to hold the suture than the suture material itself.
strength of the wound
Suture with elasticity is ideal for skin closure because?
it adapts to wound edema
Suture with ___ stiffness is chosen for abdominal closure, herniorraphy, prothesis, etc.
high
Will oversized suture strengthen or weaken you closure?
weaken due to excessive tissue reaction
For wounds under tension, what should you do instead of increasing suture size?
increase the number of sutures placed or use a tension relieving suture pattern
Better apposition leads to decreased what?
healing time
How long does it take internal organs and SQ layer to heal?
few days, full strength in a couple weeks
How long does it take fascia to heal?
couple weeks, full strength in a couple months
The linea alba is healed back to baseline strength in what time?
at 8 weeks
Skin heals based on the quality of what?
apposition
How long does it take the skin to seal post-op?
within 1 day
Primary skin incision heals in how long?
10-14 days
Primary skin incision heals back to full strength in what time?
<30 days
If you can’t remove the sutures later on (placed in SQ, organs, ligatures), what type should you use?
absorbable
If you can remove the sutures later on (placed in skin), what type of suture should you use?
non-absorbable
Ideally, non-absorbable suture should be what to reduce inflammation?
inert
A suture needle that is ¼ circle is ideal for use in what procedures?
opthalmologic surgery
A suture needle that is 5/8 circle is ideal for use in what procedures?
confined or deep locations
What is the most common needle size to use in large animal?
3/8 or ½ circle
What needle type has a round needle shaft that does not enlarge hole as it passes through and can be used on delicate tissue?
taper point
What needle type has a cutting edge on the convex (outer) side and can be used on skin or fibrous tissue but has less risk of tissue cut out?
reverse cutting
What needle type is used to purse string prolapses?
Buhner needle
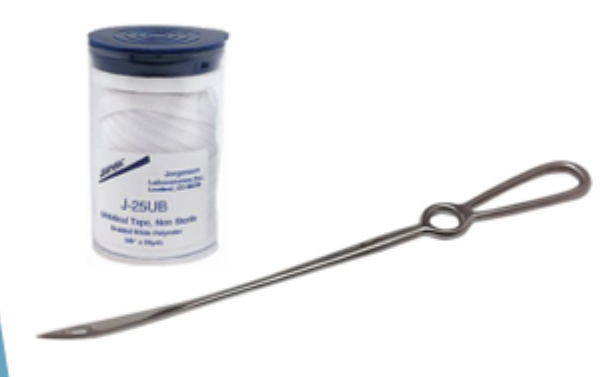
What needle type is this?
Buhner needle
What needle type is used to close cow skin, negates the need for needle drivers but requires the use of suture on a reeel, and is easier to punch through thick skin?
S needle

What needle type is this?
S needle
What is the weakest point in your suture pattern?
knot
Polypropylene (Prolene) and Nylon are examples of what type of suture?
nonabsorbable
What may cause the suture to pull through if skin sutures are placed within 5mm of a wound edge?
collagenase activity
What type of suture decreases bacterial transport into deeper tissues?
monofilament
How far from the edge should your bites be when suturing the linea alba of large animals?
15mm
What suture can you use to suture the linea alba of large animals?
Size 2-7 (most common 2 or 3) Polyglactin 910 (Vicryl) or Polydioxanone (PDS)
What suture is commonly used in cattle because it is cheap but is not used in other species due to inflammation?
CatGut
What suture should be used for delicate organs such as subcutaneous layer and GI organs?
Size 2-0
PDS (polydioxanone), Vicryl (polyglactin 910), Monocryl (poliglecaprone)
What suture pattern should be used when suturing the GI tract?
inverting suture patterns (Lembert, simple continuous oversewn with a Cushings)
What suture should be used for contamianted wounds?
monofilament, nonabsorbable, elastic
True ot False: All wounds in horses are contaminated.
True
What type of suture is Supramid?
braided nylon
What type of suture in Braunamid?
braided polyamide
How can we reduce cost of suture in farm animals?
Chromic cat gut
suture on a reel
When should you remove sutures in large animals?
10-14 days (Remember, skin is healed at approximately 14 days)
What can you do as far as suture removal for wounds under tension that you are worried may reopen if you remove all sutures at one time?
staged removal - take out every other suture or every 1/3 initially
Can you use skin staplers on wounds with tension?
NO
What are advantages to using skin staplers?
stainless steel staples are inert
fast to put in
requires patient recheck so you can see it again
What animals should you not use skin staples in?
mini horses, ponies, or foals (low to ground, more likely to kick your face off)
What are examples of inverting suture patterns?
Utrecht
Cushing
Lembert
What inverting suture pattern is commonly used on the uterus?
Utrecht
What inverting suture pattern is most commonly used on GI tract and urinary bladder and is often combined with a simple continuous first?
Cushing
What inverting suture pattern is used for GI tract or urinary bladder, can be interrupted ot continuous, but you have to be careful not to make a “cuff” of tissue deep to your suture line?
Lembert
What happens if you make a “cuff” of tissue deep to your suture line when using a Lembert pattern for intestine?
you will cause blockage of intestinal anastomoses
How does tension impede healing?
impairs blood supply and prevents perfect apposition due to shear stress on the wound
What are Langer’s lines?
relaxed skin tension lines
How should you consider Langer’s lines when making surgical incisions or suturing wounds?
make surgical incision parallel to Langer’s lines for least tension
Use langer’s lines to suture wounds closed with least amount of tension possible, but you don’t have control over where the wound is
What is preferable when suturing wounds inder tension?
use limb immobilization
add more sutures
use tension-relieving techniques
What are examples of tension relieving techniques?
release incisions
walking sutures
tension relieving suture patterns ± the use of stents or combo patterns and skin tension lines
How do we use relief incisions to close primary wounds?
make small incisions parallel and staggered to primary wound, suture primary wound and leave the relief incisions to heal by second intention
What tension relieving technique uses suture to “pull” the skin over the top of the defect, evens out tension, obliterate dead space, and can be no closer than 2-3cm apart as it can increase inflammatory response due to extra suture?
walking sutures
What tension relieving technique distributes tension more evenly along suture to prevent pull through?
stents
Can you use stents on their own?
No, always a combo of stents and other suture patterns
What tension relieving suture pattern has less impingement of blood supply compared to horizontal mattress, has good apposition but some eversion, is only an interrupted pattern, and bites are made perpendicular to the cut edge?
vertical mattress
What tension relieving suture pattern will not tear through tissue but tends to impede blood supply and is rarely used without stents, has the most eversion possible, and can be applied in a continuous pattern?
horizontal mattress
What tension relieving suture pattern allows excellent apposition and tension relief but is only an interrupted pattern and leaves the most suture in the wound?
near-far-far-near or far-near-near-far
What suture pattern can be used as a mild tension relieving continuous pattern, reduces suture disruption if one part breaks, allows good apposition, and is commonly used to close skin on cow flank incisions?
ford interlocking
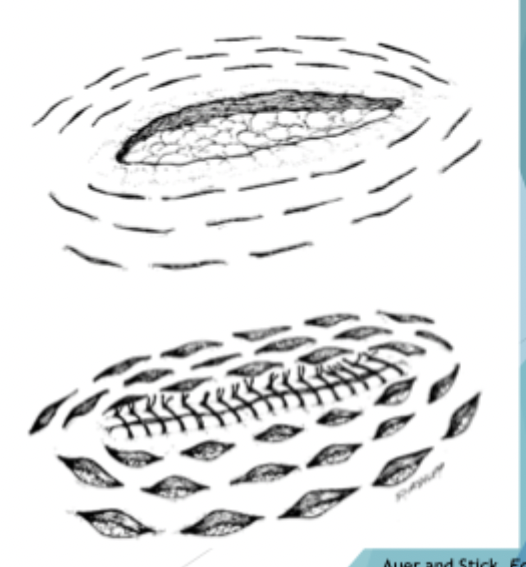
What is shown here?
relief incisions
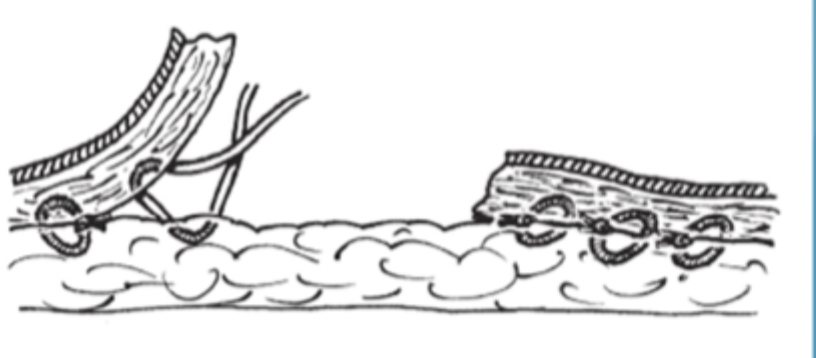
What is shown here?
walking sutures
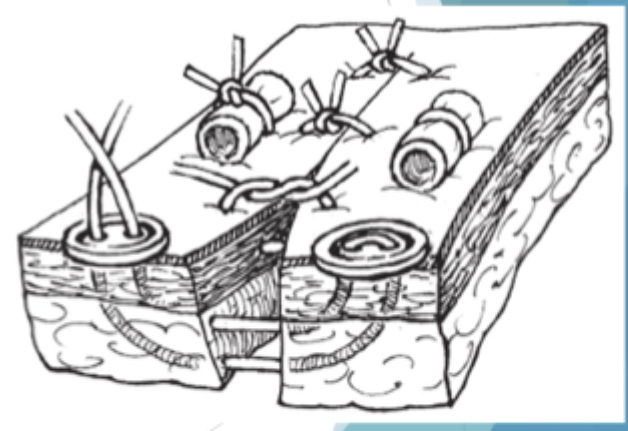
What is shown here?
stents
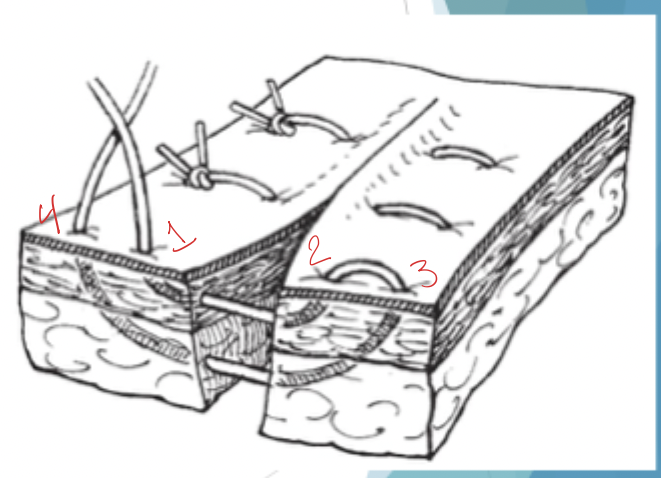
What is shown here?
vertical mattress pattern
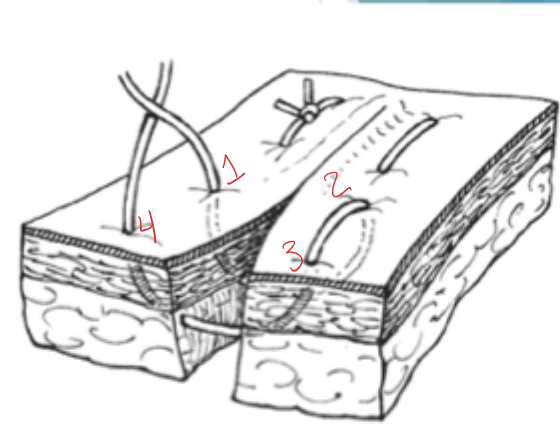
What is shown here?
Horizontal mattress pattern
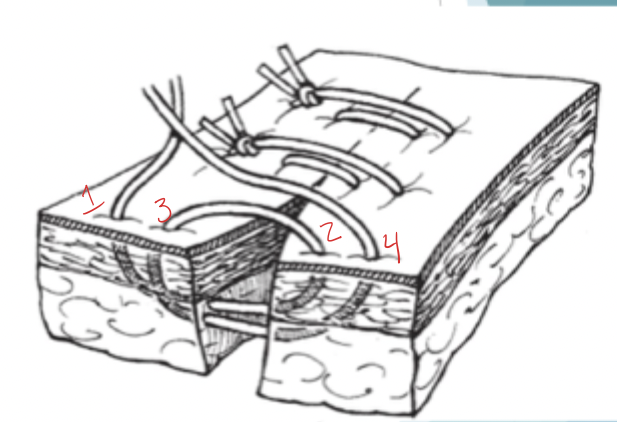
What is shown here?
far-near-near-far pattern
When using a continuous pattern like ford interlocking, what should you do at the bottom of your incision or wound?
a few simple interrupted sutures to allow for drainage and to anticipate risk of potential infection
What is the common name and filament type of Polydiaxanone?
PDS II, monofilament
What is the common name and filament type of Polyglactin 910?
Vicryl, multifilament
What is the common name and filament type of Poliglecarpone 25?
Monocryl, monofilament
What is the common name and filament type of Polyglyconate?
Maxon, monofilament
What is the common name and filament type of Polypropylene?
Prolene or Fluorofil, monofilament
What is the common name and filament type of Polybutester?
Novafil, monofilament
What is the common name and filament type of Nylon?
Ethilon, monofilament
What is the common name and filament type of coated polyester?
Ethibond, multifilament