Lecture 16 - Intro to Nematodes (Quiz 8)
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
pseudocoelomic
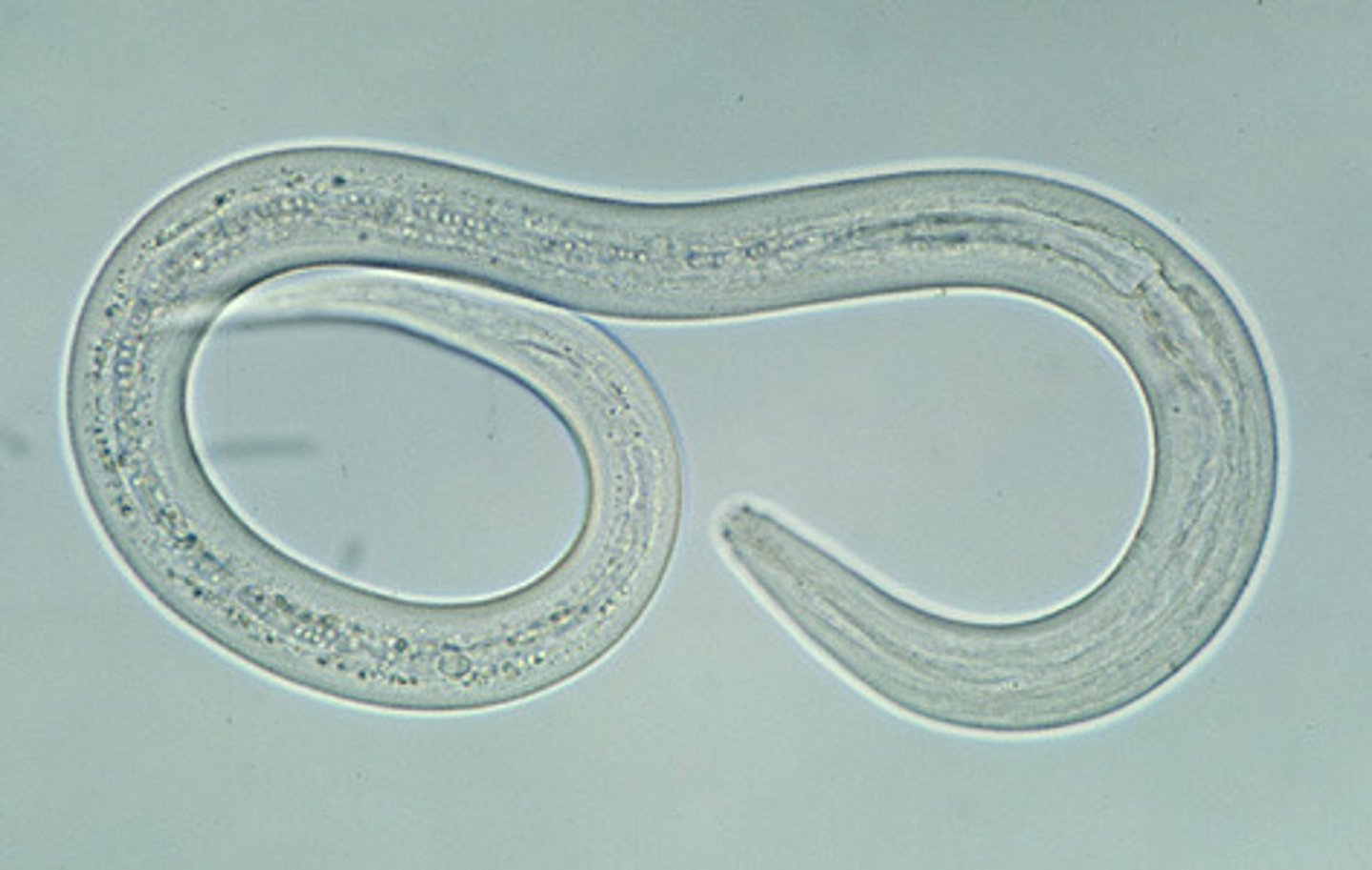
nematodes are ____, meaning that they have a body cavity but lack a peritoneal lining derives from the mesoderm
hemolymph
the pseudocoelom contains
digestive system
nematodes have a complete _____ _____ because they have a mouth and an anus
water
nematodes require a ___ film to survive
cuticle
a metabolically active, outermost covering that varies between species, sex, and life cycle stage
hydrostatic skeleton
the basal zone of the cuticle is imperative for the ____ ____, where it allows for stretching and compression that provides a means for locomotion
muscles
the cuticle provides resistance for ____ in the hydrostatic skeleton
alae
lateral/sublateral cuticular thickening

cervical
___ alae is at the anterior end
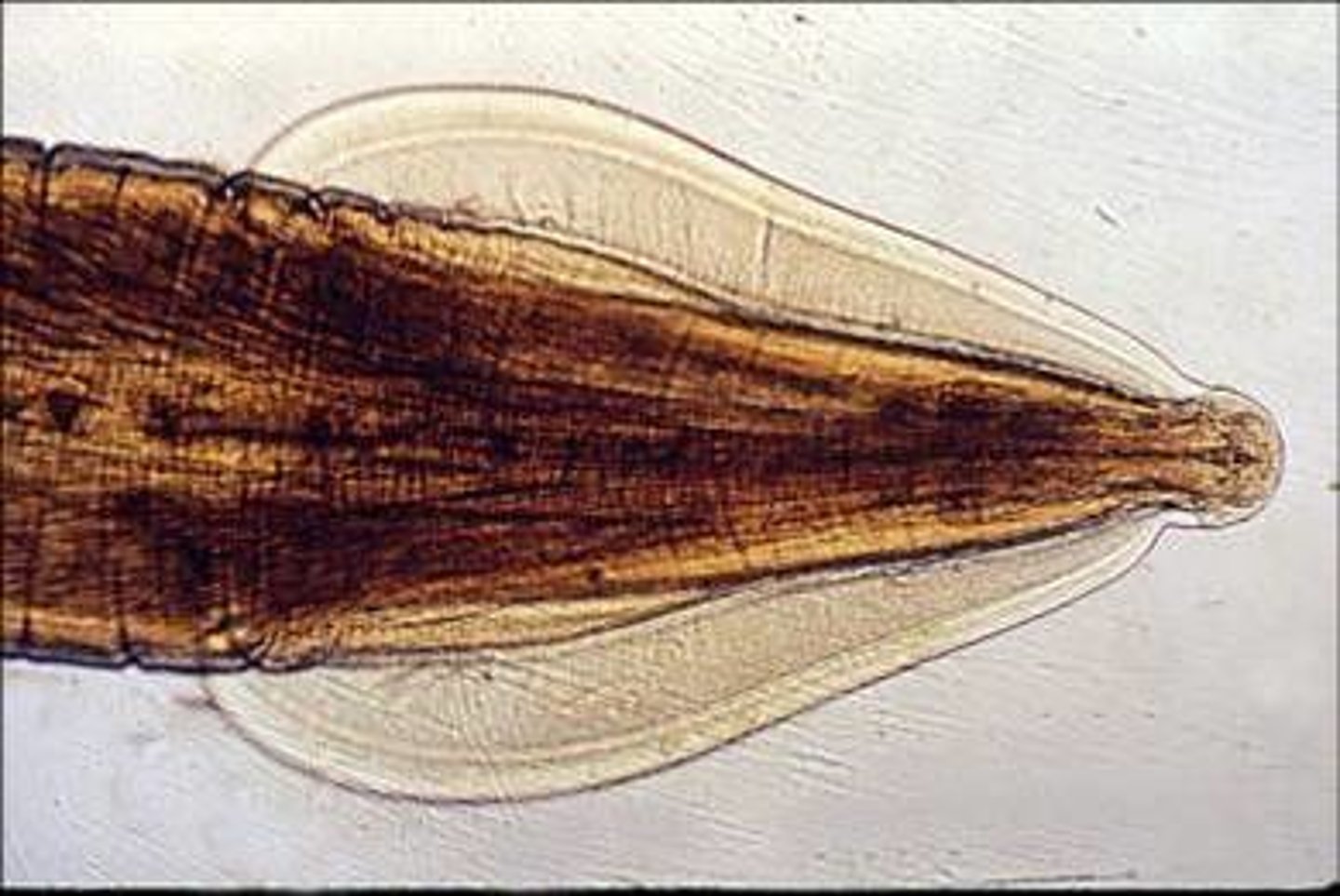

caudal
___ alae is at the tail end

hypodermis
the layer below the cuticle
functions of the hypodermis
- synthesizes cuticle
- metabolism
quadrants
cords divide body muscles into ____
longitudinal
nematodes only have ___ muscles as opposed to circular ones
hydrostatic skeleton
the pseudocoelom is a component of the ____ _____ that uses liquid to allow for locomotion
apply pressure
the hydrostatic skeleton requires ability to _____ ____ to the liquid (muscle contractions)
locomotion
(study this process separately) dorsal muscles contract and compress the cuticle on that side --> force transmitted through fluid to opposite side --> stretches cuticle on that side
sides
nematodes swim on their ___ (kinda funny)
anterior nerve ring
nerve cells encircling the esophagus (the "brain")
posterior nerve ring
the ____ ____ ____ is smaller than the anterior nerve ring and functions in defecation, copulation, and reverse movement
amphids
bilateral sense organs that replace the 5th and 6th cephallic papillae at a deep cuticular pit
host detection
amphids are about the only thing open in larvae infective stages as they allow for ___ ___ and development
cervical papillae (deirids)
paired somatic sensilla at the level of the nerve ring

phasmids
posterior sensilla that have similar structure to amphids but with fewer nerve endings and are less glandular --- may be involved in growth too
buccal cavity
the ___ ___ is between the mouth and esophagus and has taxonomic significance. it may form a rigid buccal capsule or have an armament
esophagus
the ___ is a cuticle-lined muscular pump that sucks food in and forces into the intestine against high pressure
FALSE
TRUE/FALSE: the intestine has muscular activity
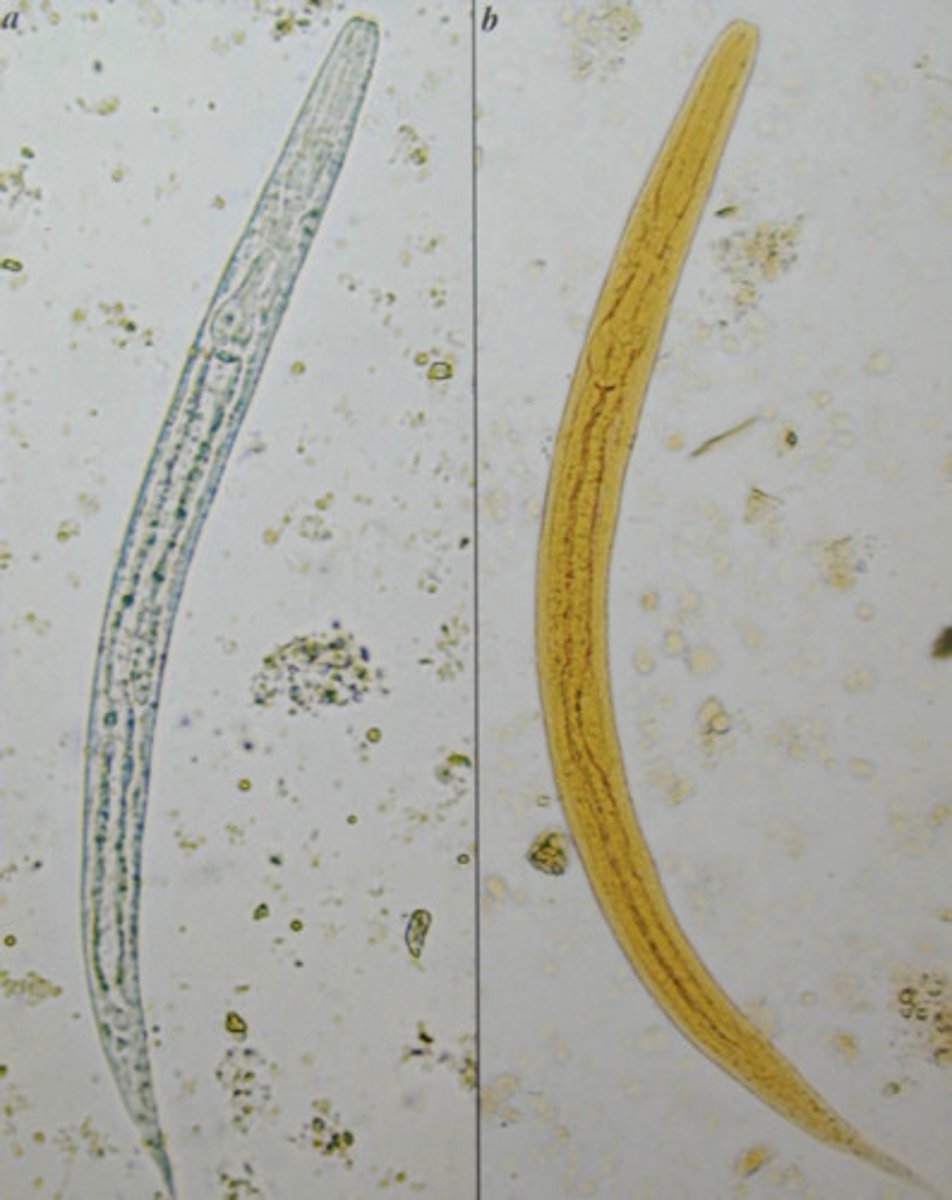
filariform
(aka strongyliform) type of esophagus that lacks an esophageal bulb
strongyliform
(aka filariform) type of esophagus that lacks an esophageal bulb
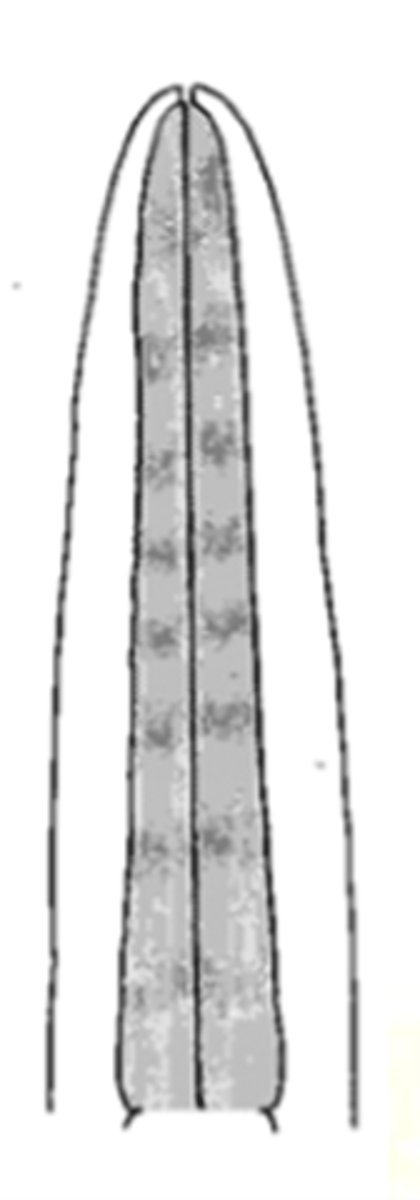
rhabditiform
type of esophagus with at least one esophageal bulb
rectum
this part of the digestive system causes hydrostatic pressure around the anus, leading to defecation
parthenogenic
Strongyloides spp. are ___ (no need for males! yay!) in the homogonic cycle
self-fertilizing
C. elegans think they're special because they're ___-____ hermaphrodites
live birth
most nematodes lay eggs but Trichinella and filarids give ___ ___ to L1 and vermiform embryos, respectively
amoeboid
nematode sperm is ___ instead of flagellated
villopodia
pseudopodia of nematode sperm used for locomotion
tails
male ___ are used for copulation
bursate
__- nematodes have "hand-like"/"fan-like" structures used to wrap around the female and run up and down until they find the vulva and mate

non-bursate
___-___ nematodes have a smaller tail --- which is really a modified caudal papillae

spicules
paired, hard structures on the dorsal wall of the cloaca that can be used taxonomically
spicules
___ are inserted into the vulva during copulation and hold the vulva open (yeesh)

ovary
where the germinal zone and its oogonia product lie
oviduct
where the maturation zone is and oocytes are produced and spermatheca fertilization occurs
uterus
muscular structure where shell formation occurs in addition to molding the shape of the developing embryo and adding additional components
vulva
the last part of the female's reproductive system where there is an opening in the body wall
ovijector
there is a muscular ___ at the distal end of the female (may not be important)
pheromones
nematodes use ___ as sex attractants
coiled
females seek the ___ tail of the male and may wander to find it
caudal papillae
___ ___ of the male detect the vulva
spicules
probing for mating occurs with ___ (sensory endings)
eggshell
the ___ of a nematode has 3 layers and some are operculated. the degree of development within the egg varies by species
stimuli
those with infective egg stages need to be ingested and exposed to host-specific ____ to hatch
lethargus
temporary cessation of growth associated with a molt (plateau in growth) where cuticle synthesis and protein expression occur
apolysis
after formation of a new cuticle, ___ occurs where the old cuticle separates
ecdysis
the shedding of the old cuticle following apolysis
ensheathment
the partial molt, typically in the infective stage, where a new cuticle forms and separates but doesn't shed (yet)
exsheathment
where the old cuticle performs ecdysis in response to a signal
infective
the first stage larva L1 are often ___ and are in the egg
microfilaria
Larval offspring of the group of filarids with a vermiform embryo that lacks a complete digestive tract
vector
microfilaria are infective for the ___
development
infective stages halt growth and typically require host-specific cues to resume ____ (such as eggs hatching or L3 molting)
L3
the infective stage in all Rhabditia; may be in egg or free-living (motile) and are ensheathed with specific behaviors and cuticular modifications to find a host
oral
route of transmission that eggs always use and larvae sometimes use
percutaneous
route of transmission that is only used by L3 (it is vector-borne)
vertical transmission
route of infection that involves parent to offspring
prenatal (transplacental) or lactogenic (transmammary)
vertical transmission may be ___ (____) or ____ (___)
(answer to parentheses are interchangeable with the term before)
migrate
infective stages may or may not ___ to find predilection sites
somatic migration
(study this process separately - see Dr. Hawdon's slides don't use this one it's too detailed)
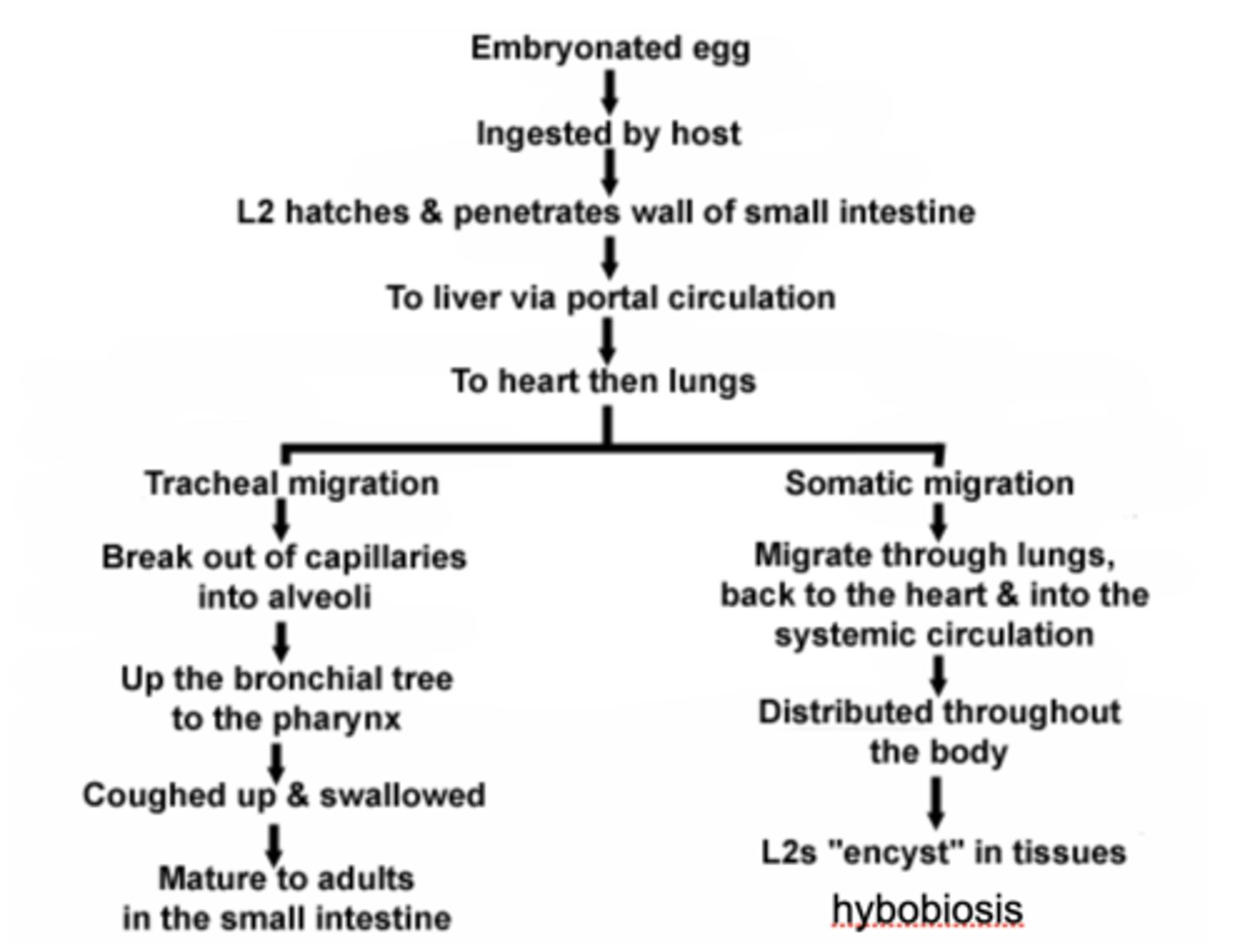
arrested development
an extended and variable period of time where development is halted
L3
as an infective stage, the ___ may prolong arrested development in the environment until it encounters a host, where it exsheathes and resumes development
hypobiosis
the ability of the invading population to prolong developmental arrest of L3 WITHIN hosts
BEFORE
in hypobiosis, the L3 larva enters the host and exsheaths (BEFORE/AFTER) it arrests development
TRUE
TRUE/FALSE: stage of arrest is species-dependent
infective stage
hypobiosis allows the survival of the ___ ___ such as in the case of seasonal variation and paratenesis
synchronize
hypobiosis may ___ life cycles by vertical transmission to offspring
naive
tissue-arrested larvae are transmitted to immunologically ___ offspring
Toxocara
___ larvae arrest in older dogs and transmit transplacentally to offspring
lactogenic
hookworm L3 arrests in muscle and activates around parturition, entering the mammary gland and spreading by ___ transfer