Medical Laboratory Science Review: Mycology | Quizlet
1/210
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
211 Terms
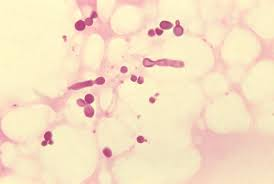
Mallessezia
Malassezia Furfur is a lipophilic yeast. Causes Tinea versicolor or pityriasis versicolor which is a very common dermatophytosis.
Hypopigmented macules on the trunk, scaley patches.
10% KOH preparations to diagnose. Reveals budding yeast.
Thought to cause dandruff
Seen in patients on lipid replacement therapy and causes disseminated infections
Yellow fluorescence under a woods lamp
Spaghetti and meatballs
budding yeasts (4-8 um) with septate, sometimes branched hyphal elements
Negative in routine fungal cultures
Colonies may be observed after using Olive oil.
colonies are cream colored, moist, and smooth
Piedraia
Piedraia hortae causes black peidra (hair infection)
Causes hard dark gritty nodules to grow on the hair shaft
Nodules contain asci (sac like structures) containing 8 ascospores.
Endemic in tropical areas of Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
When using 10% KOH, nodules can be broken to reveal asci. Thick walled rhomboid cells containtg ascospores are seen.
Grows slowly on Sabouraud dextrose agar at RT
Brown, restricted colonies that remain sterile.
Trichosporon
Trichosporon asahaii is the most frequent and severe of the genus in immunocompromised patients.
Trichosporon spp. are found as normal skin biota and can cause white piedra.
Other members of the genus are known to cause systemic infections in immunocompromised patients. They are rare, but usually fatal. Seen in people with hematologic malignancies and have been on chemotherapy.
Endemic in tropical regions
Produces both arthroconidia and blastoconidia
Grows rapidly on primary fungal media.
colonies are cream colored and yeastlike. smooth
confirmed ID by biochemical tests including absences of carbohydrate fermentation or utilization of potassium nitrate.
Urease pos
Trichophyton
T. mentagrophytes:
both macro and microconidia may appear globose and appear tear-shaped and measure 2.5-4 um
Microconidida are found in grape like clusters.
Macroconidia are thin walled, smooth, and cigar shaped, with four to five cells separated by parallel cross-walls. Measure 7-50 um and are produced singly on undifferentiated hyphae.
Relatively rapid growing, granular colonies
worldwide
T. Rubrum:
Epidermophyton
Epidermophyton floccosum only produce one size of conidia, which are macroconidia (12 to 25 um) have 3 to 15 cells.
Tapering, sometimes elongated, spiny distal ends of the macroconidia are key distinguishing factors
Colonies are white and fluffy, reverse is yellow
grows on potato dextrose agar
worldwide distribution
Micrococcus
Contamination of blood cultures, bacteria, water dust and soil.

Sporothrix
Most commonly seen in lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis.
Found in soil and decaying vegetation
distributed worldwide
asscociated with gardening
S. schenckii is small, cigar-shped yeast.
thing delicate hyphae bearing conidia developing in a rosette pattern.
Dark walled conidia
dimorphic (22 and 37 degrees)
grows well on most culture media
white colonies
to induce mycelia, must be inoculated on brain heart infusion agar supplemented with sheep red blood cells and incubated at 37 in a CO2 incubator.
Pseudoallescheria
P. boydii septate filamentous fungus
hyaline or dematiaceous
oval conidia singly at the tips of conidiogenous cells known as annellides.
ascospores
Homothallic
Rapidly porducing white to dark gray colonies on potato dextrose agar at 22 and 35 degrees
Fonsecea
.
Phialophora
.
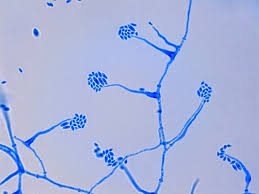
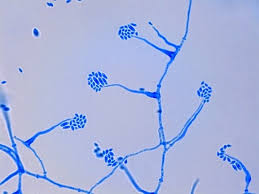
Acremonium
A. falciforme
mucoid clusters of single or two-celled, slightly curved conidia borne frome phialides at the tips of lon, unbranched, multiseptate conidiophores.
Conidia are held together in mucoid clusters at eh spices of the phialides.
this isolate is a hyaline, septate, filamentious mould.
Colonies grow slow and are grayish brown
Gliocladium
.
Blastomyces
Causes blastomycosis prevelent in middle aged men.
Flulike symptoms. Pulmonary disease may insue.
AKA Gilchrist disease or Chicago Disease.
North America and parts of Africa
Soil and natural environments
occurs in dogs and horses
Telemorph or sexual form of B. dermatitidis. Cannot be grown in laboratory.
Tissue or purulent material in cutaneouss skin lesions
may revel large, spherical, refractile yeast cells, 8 to 15 um in diameter, with double-contoured wall and buds connected by a broad base or calcoflour white may be used to aid examination for the presence of the yeast cells.
In the mould phase, conidia are borne on short lateral brances that are ovoid to dumbbell shaped and vary in in diameter from 2 to 10 um. Microconidia are not diagnostic.
colonies may be white, tan or brown and may be fluffy
can be confirmed using a double diffusion immunoassay to detect the exoantigens
Histoplasma
Acquired by inhalation
Usually asymptomatic, with only sequelae being calcifications in the lungs, liver, and spleen.
Pulmonary disease with heavy exposure
can stay in host for years
Histoplasmosis aka reticuloendothelial cytomycosis, cave disease.
worldwide, endemic in Central Africa.
Micro exam reveals small yeast cells 2-5 um. When stained, they are often seen in macrophages. Resemble blastoconidia or Candida glabrata but can be differentiated by fluorescent antibody or culture
Microconidia small, one celled, round, smooth
Macroconidida large, round
Slow growth
white to dark tan with age
Woolly, cottony, or granular
Coccidiodes
Most virulent of all human mycotic agents
Two species: C. immitis and C. posadasii.
Asymptomatic pulmonary disease and allergic manifestations.
Symtomatic patients have fever, respiratory distress, cough, anorexia, headache, malaise, and myalgias.
Filipinos and blacks run the highest risk, more males than females
Molecular ID is needed to distinguish between species
Barrel shaped arthroconidia (2.5- 6 um) round up as they convert to spherules.
Form endospores by process known as progressive sleavage.
diagnosis is made by histopathologic means only.
Microscopic exam shoes fertile hyphae at right angles producing alternating hyaline arthroconidia.
Growth 3-4 days
White, moist, and glabrous.
Abundant aerial mycelium "bloom"
Tan to lavender mature colonies
Paracoccidiodes
Slow growth
white to beige
leathery, flate to wrinkled, folede or velvety
Colonies frequently only produce sterile hyphae
fresh isolates may produce conidia similar to those of Blastomyces
Central and south America in soil
Primary lung, granulomatous, Ucerative nasal and buccal lesions, lymph node involvement, adrenals
thick walled yeasts (15-30 um), multiple buds, Mariners wheel
yeast form: multiple blastoconidia budding from single, large yeast (15-30 um)
Cryptococcus
meningitis, pulmonary disease, and septicemia.
capsule, india ink (latex agglutination test now)
Blastoconidia only, without producing true hyphae on corn meal agar. C. neoformans is urease pos
Candida
Normal biota of the mucosa, skin, and digestive tract
yeast infections, thrush
C. glabrata second most common, difficult to treat
Absidia
vasulare invasion causing thromosis and necrosis fo the tissues.
diabetic patients
worldwide
broad ribbon like hyphae with few septations
Erect sporangiophores either solitary or in groups terminate in ana apopphysis surrounded by a sporangium.
Sporangiospores are smooth and ovoid.
Rhizoids are present.
Colonies are woolly and grow rapidly
white, becoming grey-brown with age
Rhizopus
Most common sygomycete
diabetic patients with ketoacidosis
Extremely refractory to treatment
worldwide
decaying vegetation
erect sporangiophores terminated by dark sporangia and sporangiospores
umbrella shaped structure
rapidly grwoing
woolly colonies
white become grey with age
Mucor
Rhinocerebral sygomycosis
worldwide
Sporangiospores are formed in sporangia on erect sporangiophores. Rhizoids are not found
Sporangia remain intact
rapidly growing
cottony, dirty white colonies that become mousy brown to grey with age
Syncephalastrum
rare, cutaneous infections
soil and decaying vegetation
erect sporangiophores are noted
can be confused with aspergillus
white and becomes grey with age
Aspergillus
Second most isolated fungus
A. fumigatus, A terrus, and A niger are most common
high mortality rate
Neutropenia
MOst frequent among bone marrow transplant recipients
fever and fails to respond to antifungal therapy
Fungus balls in lungs
black to white and may include yellow, brown, green, gray, pnik, beige, and tan.
Beauveria
Rare human isolate kaeratitis
insect pathogen
worldwide
Abundant single-celled, tear shaped sympoduloconidia are formed on sympodulae, which taper extremely from a rather swollen base.
Conidiophores may cluster in some isolates to form radial tufts
Colonies are hyaline
rapid growing
fluffy, powdery, reminiscent of T. mentagrophytes
Chrysosporium
rare
recovered frome nails and skin lesions
worldwide
single-celled conidia are produced on nonspecialized cells. the conidiogenous cell disintefrates to release the conidia.
arthroconidia may be seen
colonies are hyaline with a moderate growth rate
with age, develops pink color, tan, or gray
Fusarium
Seen in mycotic keratitis.
Soft contact lenses
mortality in bone marrow recipients is 100%
High fever, disseminated skin leseions and fungemia.
Recovered in blood cultures
Appears yeast-like on initial recovery
abundant macroconidia with fewer microconidia are produced on hyphae.
Macroconidia are banana or canoe shaped and are formed singly or in small slusters together in mats termed sporodochia.
Macroconidia are typically multicelled
Rapid growing hyaline fungus
rose to mauve to purple to yellow
Paecilomyces
P. lilacinus
HIgh mortality, hospital outbreaks
Can be confused with Penicillium.
Phialides are generally longer and more obviously tapered
Cylindrical conidia
Grow rapidly
Flat, granular to velvety colonies in shaeds of tan, brownish gold or mauve.
Serious infections and difficult to treat
Penicillium
rarely cause infections, chronic fungal sinusitis
Worldwide
Conidiophores are erect, sometimes branched with metulae bearing one or several phialides on which oval conidia are produced in long, loose chains.
Rapid grower
Green or blue colonies
Scopulariopsis
nail specimens
pulmonary disease in immunocompromised
worldwide
conidiophores are formed singularly or can be in clusters.
conidia are formed from annellides, increased length in conidia.
Truncate-based conidia tend to remain in chains
Grows moderately and forms colonies covered by tan to buff conidia.
Some species are dematiaceous.
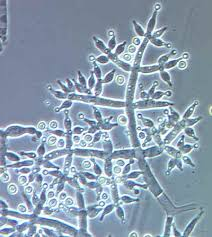
Trichoderma
emerging pathogen in immunocompromised
pulmonary and skin infections
worldwide
Rapidly growing
Hyaline hyphae
yellow-green conidia formed on clusters of tapering phialides
Conidia may be clustered in baslls at the phialides tips.
colonies are intensely green and granular with an abundance of conidia
Alternaria
recovered from any source
Chronic fungal sinusitis, misdiagnosed
worldwide
Short conidiophores bearing conidia in chains that lengthen in an acropetal fashion.
Multicelled conidia have angular cross-walls and taper towrd the distal end.
Dematiaceous
rapid growing
colonies grey to brown, to black
Aureobasidium
Rare but can be traced to contaminated dialysis lines
recovered from blood, tissues, abscesses.
worldwide, wet conditions
Hyaline hyphae giving rise to hyaline conidia
grow moderate to rapid
yeast consistency
off white to pink, old becomes black
Sepedonium
.
Cladosporium
infrequent, laboratory contamination
Sinuses or traumatic inoculation
worldwide
brown to olive to black hyphae and conidia.
Conidiophores are erect and may branch into several conidiogenous cells.
moderately growing olive, brown, or black
fluffy
Curvularia
chronic sinustitis
worldwide
from leaves and grass
multicelld conidia on conidiophores
crescent-shaped conidia with three to five cells of unequal size and an enlarged central cell. easy to ID
Rapid growth
dematiaceous colony that is cottony and dirty grey to black
Ulocladium
subcutaneious infections
Conidiophores bear dark, multicelled conidia on sympdial conidiophores. Conidia have angular cross-walls
rapidly growing dematiaceous fungi
brown to black colonies
Bipolaris
.
Exophiala
.
Wangiella
.
Phaeoannellomyces
.
Excerhilum
.
Epicoccus
.
Stemphilium
.
Microsporum audouinii
Slow growing anthropomorphic dermatophytes
grey-patch tinea captitis of children
conidia are rarely produced
cottony white and generally form little or no pigment on reverse
Microsporum canis
Microconidia are spindle shaped with echinulate, thick walls. abundant
colonies are fluffy and white with the reverse being yellowon potato dextrose agar
worldwide distribution
Microsporum gypseum
Has fusiform, moderately thick-walled conidia have as many as six cells.
The distal end of the macroconidium might bear a think, filimentlous tail.
Abundant micro and macroconidia
powdery granular colonies
tan to buff
rapidly growing
sterile hyphae in aging cultures
Brown or red on the reverse
What kind of specimens for the recovery of fungi are not acceptable
Swab
For which clinical specimens is the KOH direct mount technique for examination of fungal elements used?
Skin
The India ink stain is used as a presumptive test for the presence of which organism?
Cryptococcus neoformans in CSF
Cutaneous disease involving skin, hair, and nails usually indicates an infection with a
Dematophyte
What is the first step to be performed in the identification of an unknown yeast isolate?
Germ tube test
An isolate produced a constriction that was interpreted as a positive germ tube, but Candidia albicans was ruled out when confirmatory tests were performed. Which fungi is it most likely?
Candidia tropicalis
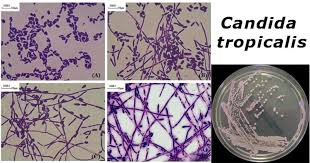
Cormenal agar with Tween 80 is used to identify which characteristic of an unknown yeast isolate?
Hyphae, blastoconidia and arthroconidia, Chlamydospores
Blastoconidia are the beginning of which structures?
Pseudohyphae
An isolate from CSF growing on cornmeal agar produces blastoconidia, but is negative for pseudohyphae, chlamydospores, and arthroconidia. Which tests should be performed next?
Birdseed agar and urease
Which of the following yeast enzymes is detected using birdseed agar?
Phenol oxidase
Which of the yeasts is characteristically positive for germ tube production?
Candida albicans
Arthroconidia production is used to differentiate which two yeast isolates?
Trichosporon cutaneum and Cryptococcus neoformans
The urease test, niger seed agar test, and the germ tube test are all used for the presumptive identification of
Cryptococcus neoformans
Which yeast produces only blastoconidia on cornmeal Tween 80 agar?
Cryptococcus spp
Ascospores are formed by which yeast isolate?
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
A germ tube-negative, pink yeast isolate was recovered from the respiratory secretions and urine of a patient with AIDS. Given the following results, what is the most likely identification?
Rhodotorula spp.
Chlamydospore production is demonstrated by which Candida spp?
C. albicans
Carbohydrate assimilation tests are used for the identification of yeast isolates by inoculating media
containing yeast extract
Yeast recovered from the urine of a catheterized patient receiving chemotherapy gave the following results
Germ tube pos
blastoconidia pos
pseudohyphae pos
chlamydospore pos
No further testing
A blood agar plate inoculated with sputum from a patient with diabetes mellitus grew few bacterial flora and a predominance of yeast. Given the following results, what is the most likely ID of the yeast isolate?
Germ tube neg
Arthroconidia neg
Chlamydospores neg
Pseudohyphae pos
Blastoconidia pos
Candida tropicalis
Dimorphic molds are found in infected tissue in which form?
Yeast phase
The mycelial form of which dimorphic mold produces thick-walled, regular, or barrel-shaped alternate arthroconidia?
Coccidoides immitis

The yeast form of which dimorphic fungus appears as oval or elongated cigar shapes?
Sporothix schenckii
The mycelial forma of Histoplasma capsulatum seen on agar resembles
Sepedonium spp
The yeast form of which dimorphic mold shows a large parent yeast cell surrounded by smaller budding yeast cells?
Paracoccoidiodes brasiliensis
Which group of molds can be ruled out when sepatate hyphae are observed in a culture?
Zygomycetes
Tinea versicolor is a skin infection caused by
Malassezia furfur
Which of the following structures is invaded by the genus Trichophyton?
Nails
An organism cultured from the skin produces colonies displaying a cherry-red color on Sabouraud dextrose agar after 3-4 weeks and teardrop-shaped microcondidia along the sides of the hyphae. the most likely ID is
Trichophyton rubrum
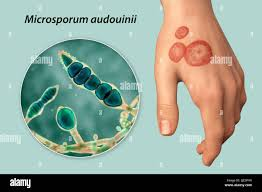
Which Micosporum species causes an epidemic form of tinea capitis in children?
Microsporum audouinii
Microscopic examination of a fungus cultured from a patient with athlete's foot shoed large, smooth-walled, club-shaped macroconidia appearing singly or in clusters of two to three from the tips of short conidiospores. The colonies did not produce microcondidia. What is the most likely ID?
Epidermophyton spp
Which Trichophyton species causes the favus type of tinea captis seen in the Scandinavian countries and in the Appalachian region of the US?
T. schoenleinii
The Hair Baiting Test is used to differentiate which two species of Trichophyton that produce red colonies on Sabouraud agar plates?
T. mentagrophytes and T. rubrum
A mold that produces colonies with a dark brown, green-black, or black appearance of both the surface and reverse side is classified as a
Dematiaceous mold
A rapidly growing hyaline mold began as a white colony but soon developed a black pepper effect on the agar surface. The older a colony produced a black matte, making it resemble a dematiaceous mold. What is the most likely ID?
Aspergillus niger
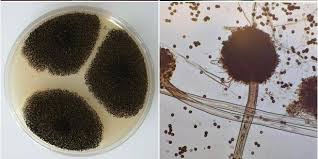
What dematiaceous mold forms flask-shaped phialides each with a flask-chaped collarette?
Phialophora spp
Which Aspergillus species, recovered from sputum or bronchial mucus, is the most common cause of pulmonary apergillosis?
A. fumigatus
A hyaline mold recovered from a patient with AIDS produced rose-colored colonies with lavender centers on Sabouraud dextrose agar. Microscopic examination showed multiseptate macroconidia appearing as sickles or canoes. What is the most likely ID?
Fusarium spp
Material from a fungaus-ball infection produced colonies with a green surface on Sabouraud agar in 5 days at 30 degrees. Microscopic examination shoed culb-shaped vesicles with sporulation only from the top half of the vesicle. This hyaline mold is most probably which Aspergillus spp?
A. fumigatus
A rapidly growing non septate mold produced colonies with a gray surface resembling cotton candy that covered the entire plate. Microscopic examination revealed sporangiophores arising between, not opposite, the rhizoids and producing pear-shaped sporangia. What is the most likely ID
Absidia spp
An India Ink test was performed on CSF from an HIV infected male patient. Many encapsulated yeast cells were seen in the centrifuged sample. Further testing revealed a positive urease test and growth of brown colonies on niger-seed agar. The diagnosis of meningitis was caused by which yeast?
Cryptococcus neoformans
A bone marrow sample obtained from an immunocompromised patient revealed small intracellular cells using a Wright's stain preparation. Growth on Sabouraud dextrose agar plates of a mold phase at 25 degrees and a yeast phase at 37 degrees designates the organism as dimorphic. The mold phase produced thick, spherical tuberculated macroconidia. What is the most likely ID?
Histoplasma capsulatum
A lung biopsy obtained from an immunocompromised patient showed many cup-shaped cysts (gray to black) in a foamy exudate (green background) using Gomori methenamine silver (GMS) stain. The organism cannot be cultured because it does not grow on routine culture media for molds. Tha patient was diagnosed with pneumonia that resisted antibiotic treatment. The most likely ID is?
Pneumocystis jirovecci (carinii)
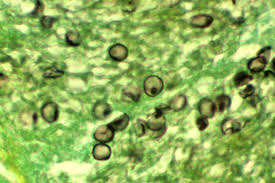
Upon direct examination of a sputum specimen, several spherule were noted that contained endospores. Growth on Sabouraud dextrose agar showed aerial mycelial elements. The septate hyphae produced barrel-shaped arthroconidia. What is the most likely ID?
Coccidioides immitis
A bone marrow specimen was obtained from an immunocompromised patient who tested positive for HIV. The organism grew rapidly at 3 days showing a mold form at 25 degrees, displaying conidiophores with four to five terminal metulae with each having four to six phialides. The conidia at the end of the phialides were oval and in short chains. They appear as a fan or broom when vewing under 10X and 40X. At 37 degrees, the yeast form grew more slowly, showing conidia that formed hyphal elements breaking at the septa to produce oval arthroconidia. This thermo-dimorphic mold is most likely:
Penicillium marneffei
What is the specimen of choice for the initial diagnosis of Pneumocysits jirovecii (carinii) in an immunocompromised patient, such as someone with AIDS?
Induced sputum
A transplant patient is suspected of having invasive Aspergillosis on the basis of clinical and radiological findings. Which specimen is best for the initial ID of aspergillosis by soluble antigen testing?
Serum or urine
What is the most common cause of mucormycosis infection in humans?
Rhizopus spp.
A thermally dimorphic fungus shows a filamentous mold form with tuberculate macroconidia at room temperature, and a yeast form above 35 degrees. Which organism best fits this description?
HIstoplasma capsulatum
After a vacation to Southwestern US, a Midwesterner complained of flulike symptoms with fever, chills, nonproductive cough, and chest pain. Microscopic exam of sputum, cleared with KOH, revealed large, thick-walled spherules containing endospores. Upon culture, the mold phase showed septate hyphae and alternating barrel-shaped arthroconidia. Which organism is most likely the cause?
Coccidioides immitis
Sexual reproduction
Fusion of 2 haploid nuclei; Spores-telemorph
Asexual reproduction
Mitotic division of haploid nucleus and budding production of conidia- anamorph
Hyphae
Tube-like structures with thick parallel walls
Septate hyphae
Has cross wall