Lecture 11: Retinal Ganglion Cells and Receptive fields
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What do rods contain?
rhodopsin
more light sensitive than cones
a single photon of light may be detectable by rods but not by cones
This is because the process of signal amplification is greater in rods
What do cones contain?
Coneopsin
What are the three types of coneopsin?
red, green, blue
Meaning they are more sensitive to light in the red, green and blue wavelengths
What is the difference between the 3 forms of coneopsin?
Small change in the amino acid sequence for maximal sensitivity to different wavelengths of light
What’s another reason that rods are more sensitive to light?
the outer segment of rods is larger
they have a larger surface area to absorb light
What’s another reason why rods are more sensitive to light?
Rods have more photopigment densely packed into the membrane of the optic disks so they absorb more light
Why aren’t rods functional in light while cones are?
in bright light the photopigment in rods (not cones) is saturated (bleached )
Means we have 2 parallel visual systems
one for bright light
one for very dim light
What happens to colors in night
at night colors appear muted
same spectral frequencies exist in bright and dim light
Why don’t we perceive colors in dim light?
cones don’t work in dim light
we don’t perceive color because we are using a part of the visual system that is color blind
How do RGCs code information that results in perception of the visual stimulus?
Through receptive fields
this diagram exemplifies the receptive fields of RGCs
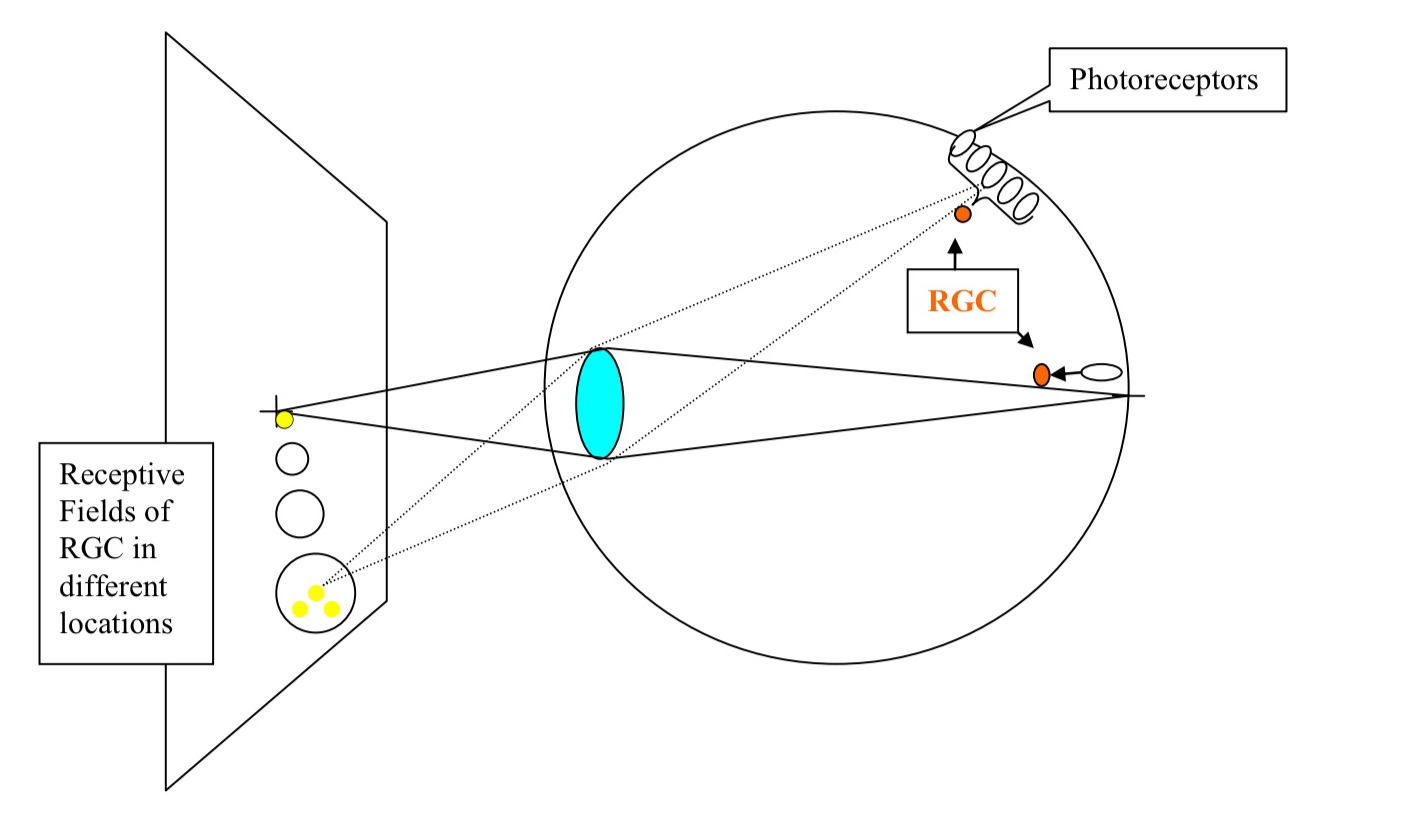
What is a neuron’s receptive field?
the location in the environment (or the surface of the body) which an appropriate stimulus will change that cell’s activity
Where are the receptive fields in different RGCs?
in different location in the visual field/retina
What are the characteristics of the receptive fields in the RGCs in the fovea?
tiny and the size of the receptive fields increases in RGCs with distance from the fovea
What changes the cell’s activity?
light anywhere within the cell’s receptive fields
What are some features of receptive fields of RGCs?
the receptive fields of RGCs are circular
vary in size
Receptive fields of adjoining RGCs may overlap
Why are the receptive fields of RGCs on the edge of the retina larger?
collect information from a greater number of photoreceptors than do RGCs closer to the fovea
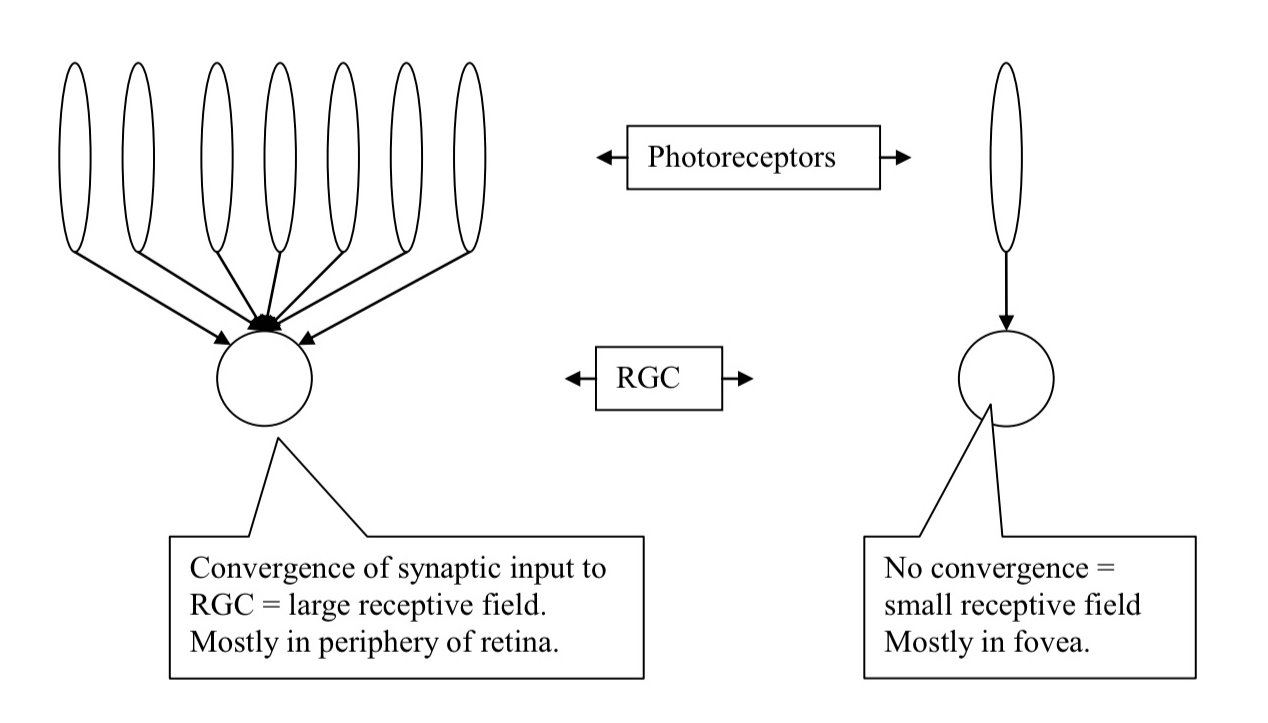
What is convergence?
a situation where many neurons converge onto a few neurons
120-130 million photoreceptors and only 1 million RGCs. Therefore there is a lot of convergence of photoreceptors onto RGCs
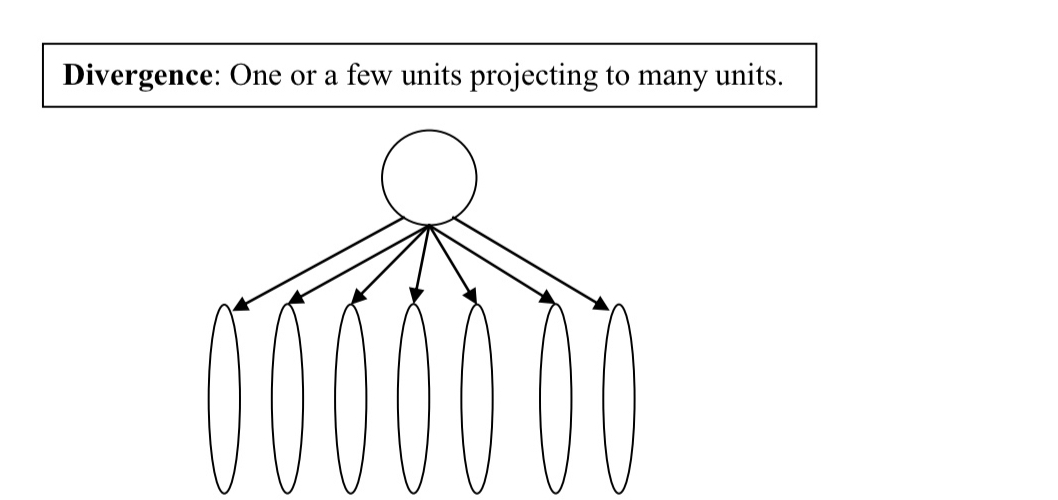
What is divergence?
few or one unit projecting onto many units
What happens in the fovea?
less convergence of photoreceptors onto RGC (via bipolar cells) than in the periphery of the retina
this is a mechanism that explains the differences in size of the receptive fields of RGCs
How does convergence explain light sensitivity?
theres less convergence in the cone system
Therefore RGCs receiving input from cones are not as sensitive to light
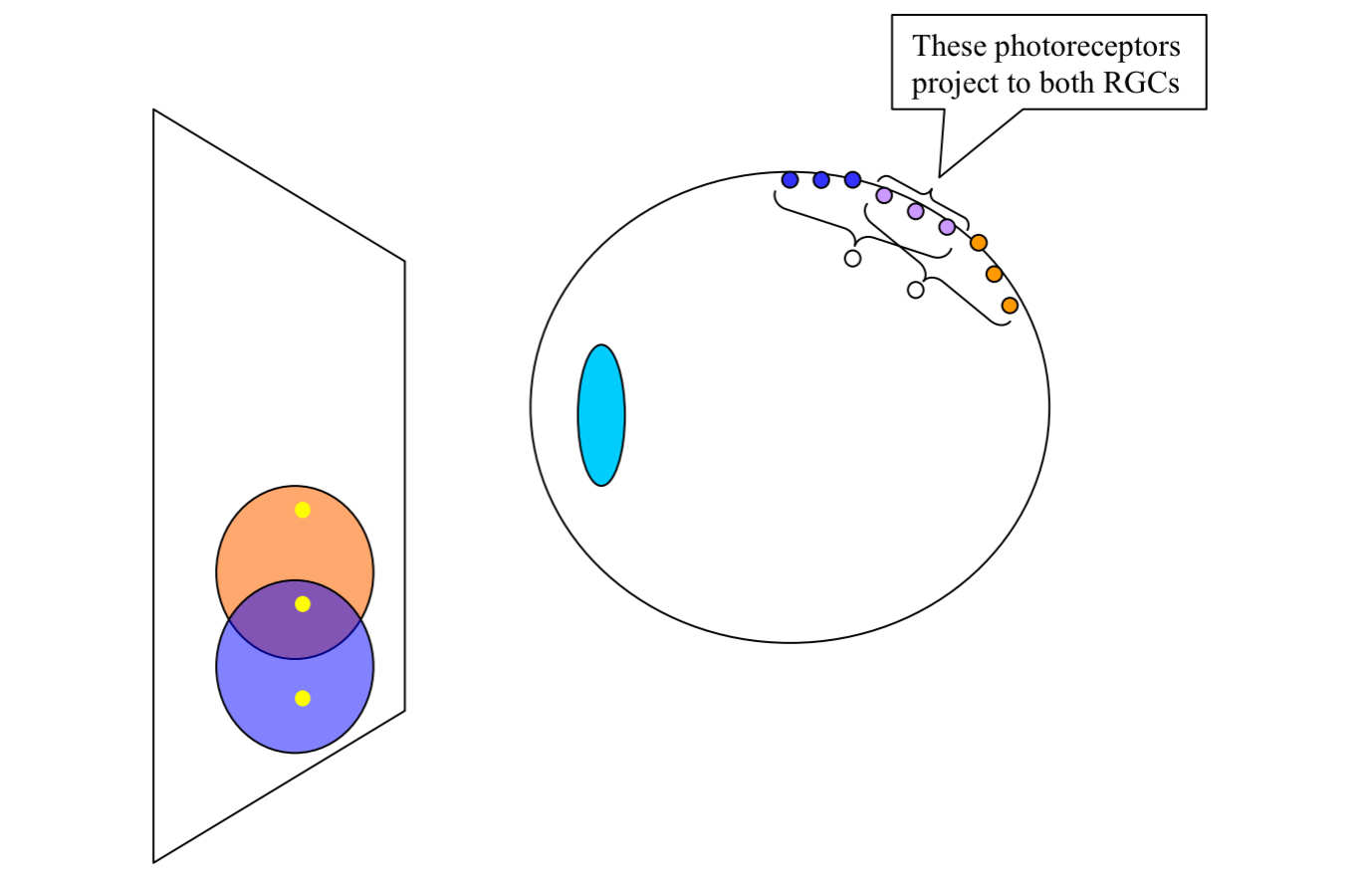
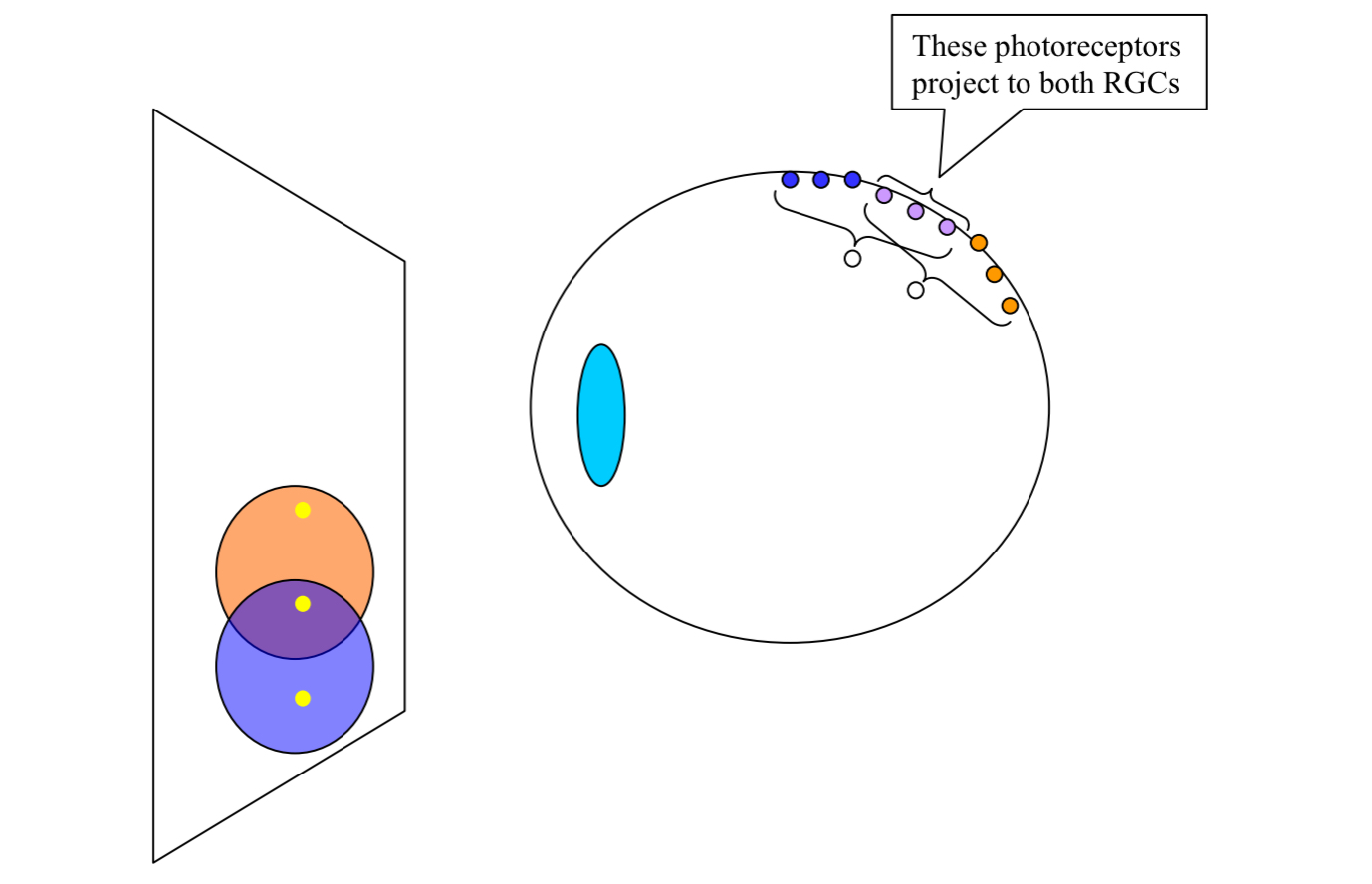
What does this diagram depict?
receptive fields overlap
Consequence: light from one point in the visual field will affect many different RGCs
How were receptive fields of retinal cells modeled?
-as concentric circles
What are the 2 types of concentric circles?
on center
off center
What are the 2 RGCs defined by?
their response to light in the center of their receptive fields
On Center RGCs: are turned on (generate AP) by light
Off center RGCs: are turned off by light in their receptive field centers
Which center RGC generates more Action potential in the dark?
Off center RGCs generate more action potential generation in the dark
Why do these concentric fields have antagonistic centers and surrounds?
b/c light falling in the center of their receptive fields has the opposite effect of light in their receptive field surrounds
Light in the center of their receptive fields has the opposite effect of light in the surrounding area.
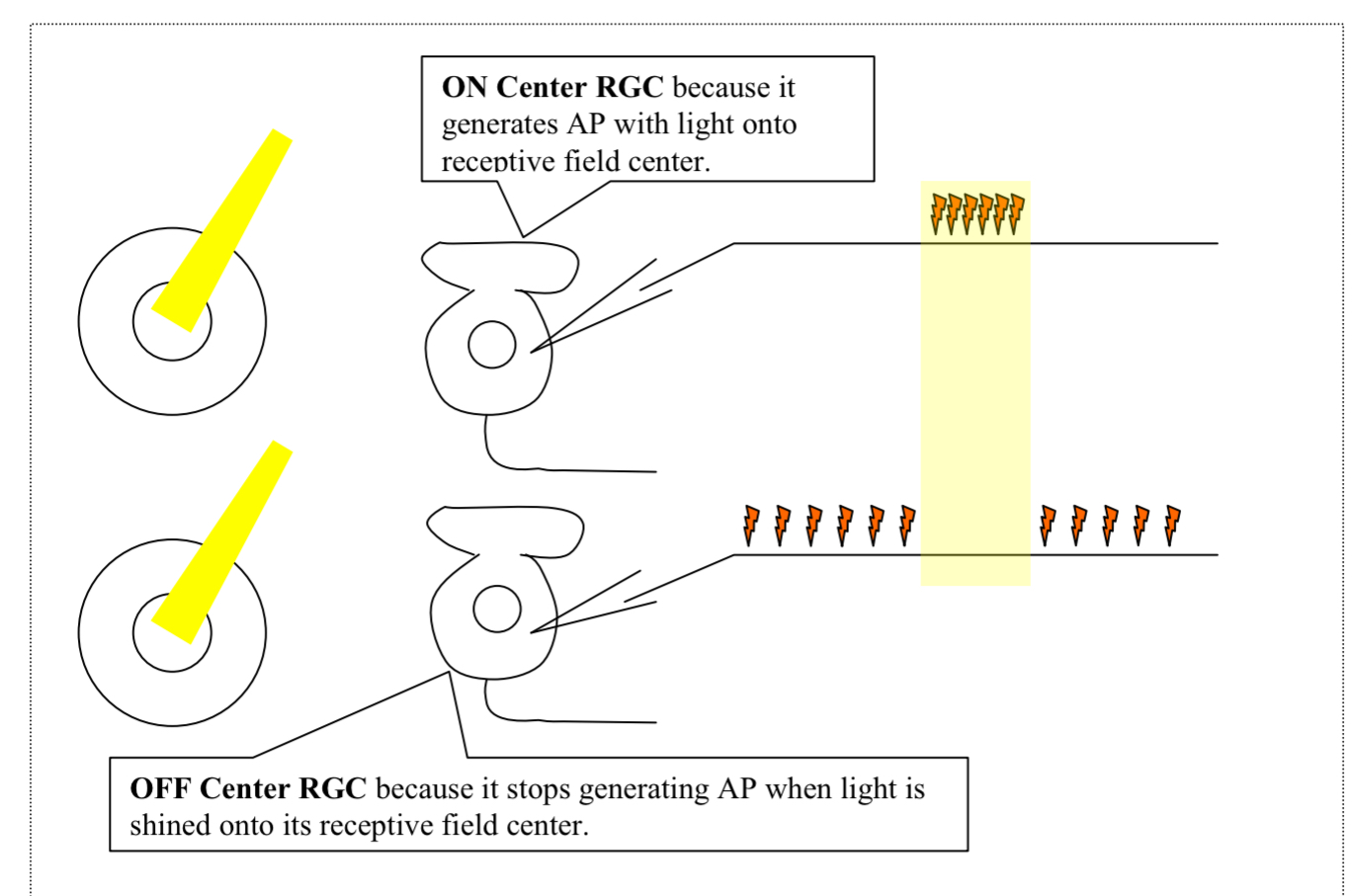
What does this diagram depict ?
shows an on and off center RGC
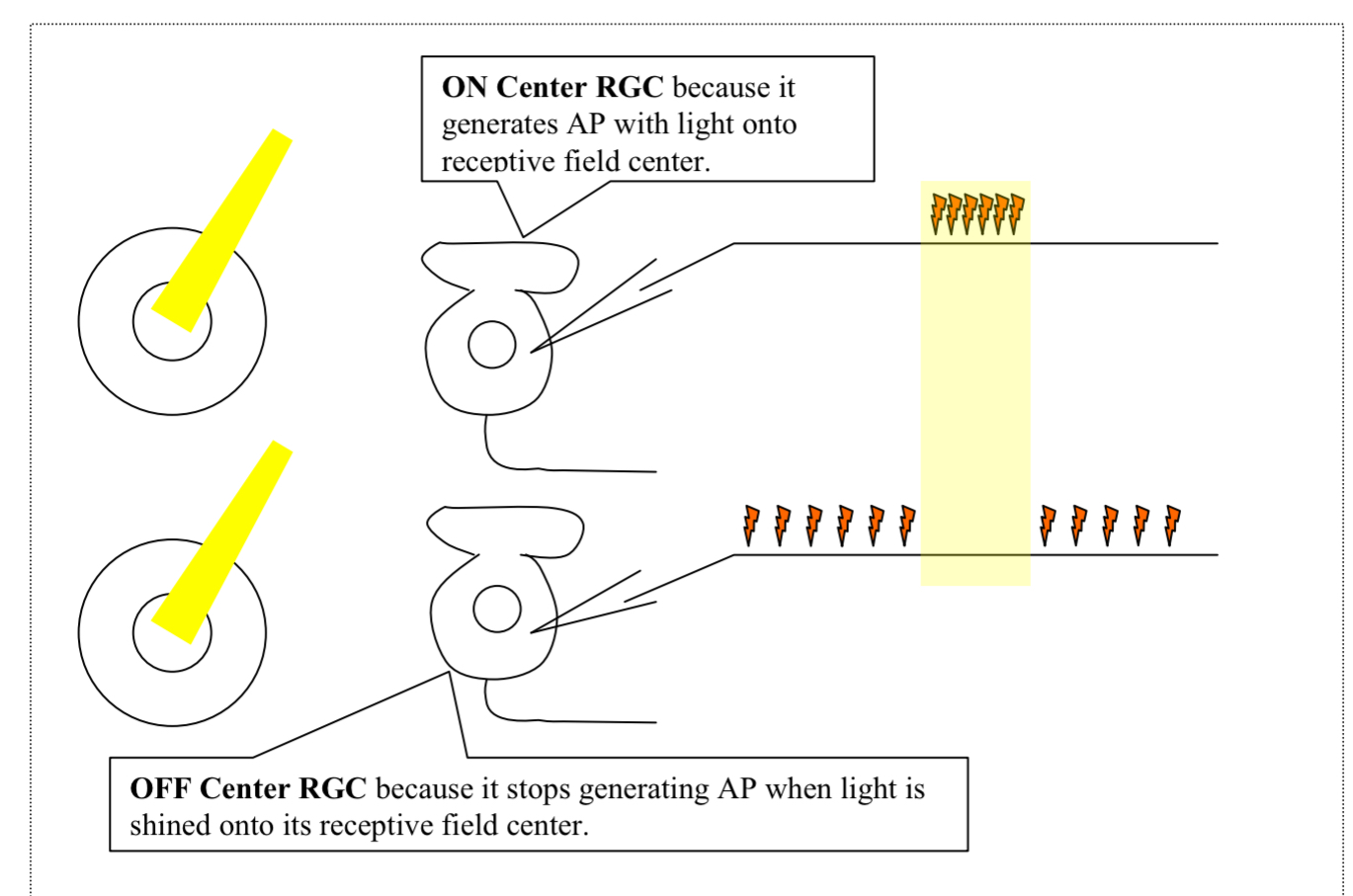
What is anatagonistic?
effect of light on the center is the opposite effect of light on the surround
if light covers both the center and the surround the effects cancel out
How is our visual system set up?
with centers and surrounds that are antagonistic to each other
What does this set up mean for the visual system?
suggest the visual system is more sensitive to contrasts in intensity of illumination than to total brightness
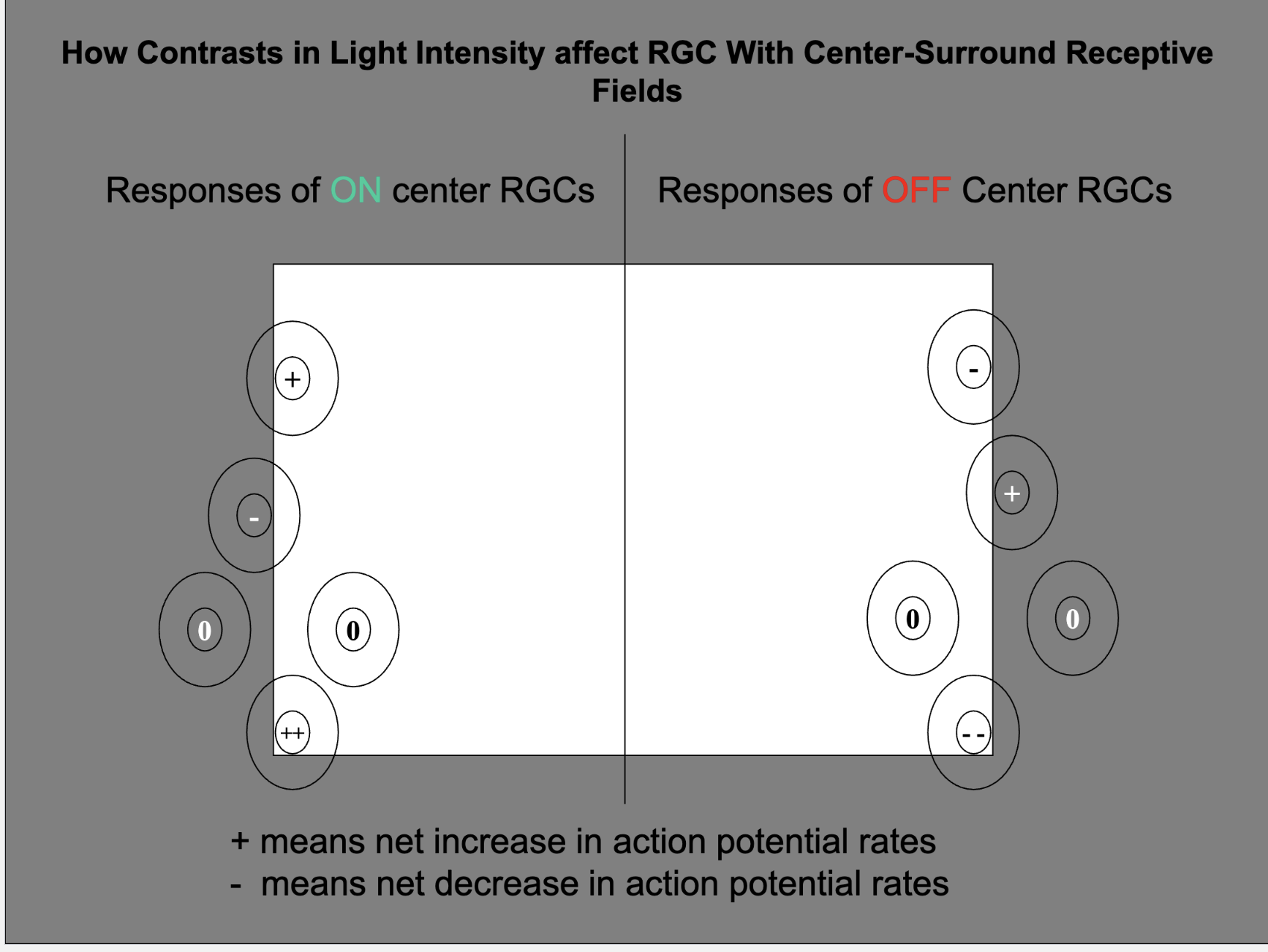
Explain what’s happening here and the responses of RGCs with different receptive fields just outside vs inside the border of the light reflected off a sheet of white paper on a black background?
On center RGC:
When the light completely fills the center, and only part of the surround: net effect is an increase in action potentials
Light falling on the receptive field surround suppresses the ongoing rate of AP production
On- and off-center RGCs overlap, and their response to light is opposite to that of each other.
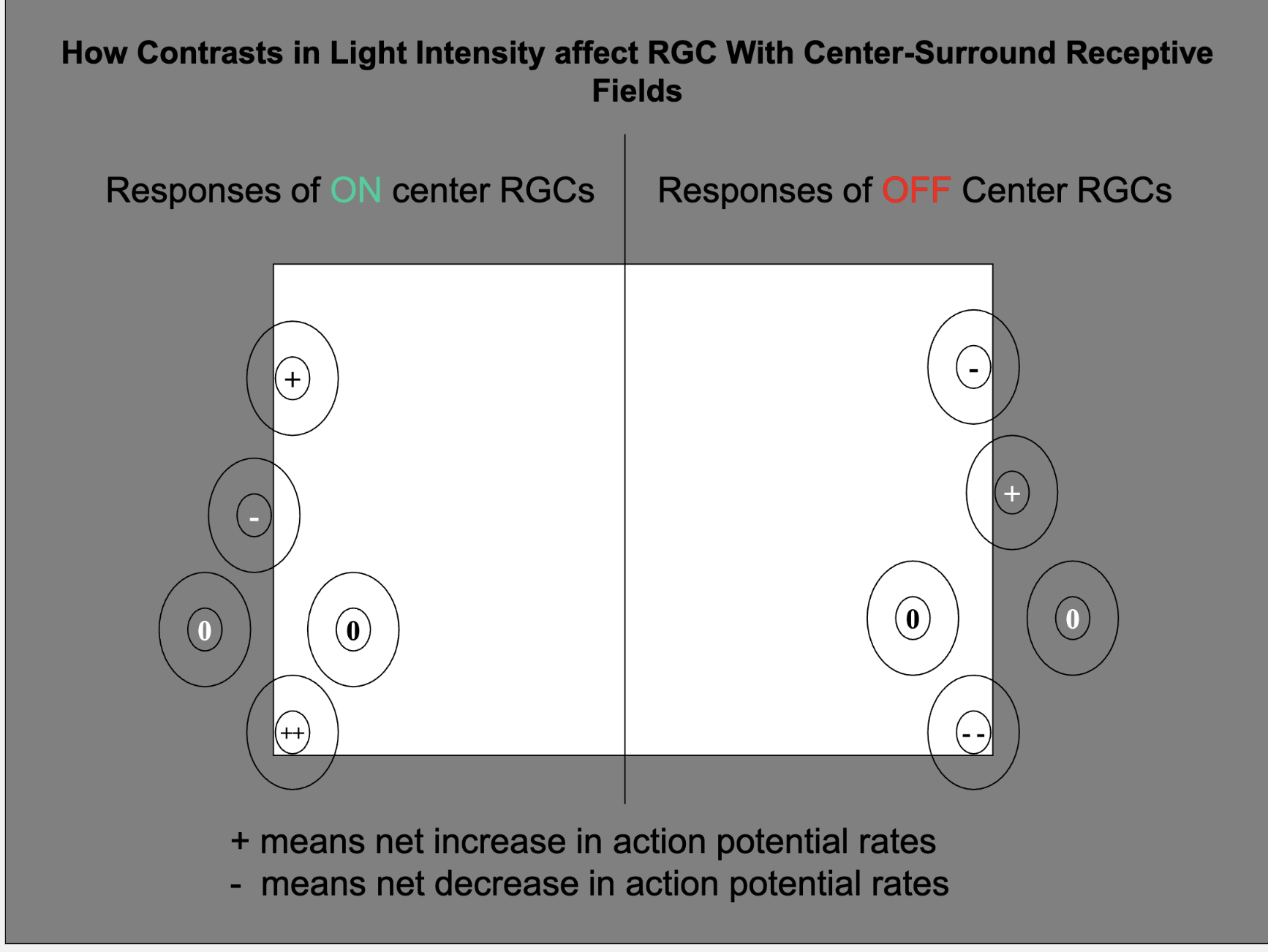
When is the action potential rate nearly the same as the baseline condition?
when light either fills both the center and the surround
or it is dark there is little to no net effect on action potential production
Why is the visual system organized to detect contrasts?
contrasts in light intensity are more informative than the overall illumination
What’s another way of saying “contrasts in light intensity are more informative than the overall illumination” ?
The amount of light reflected by an object can vary dramatically depending upon the ambient illumination
Perceptions should not vary dramatically in different lighting conditions
What is the mechanisms for on center versus off center receptive field properties?
due to the difference in receptor type expressed by BP cells
receptor is expressed by the On Center BP cell which produces an IPSP in response to glutamate
The Off Center BP cell produces an EPSP to glutamate
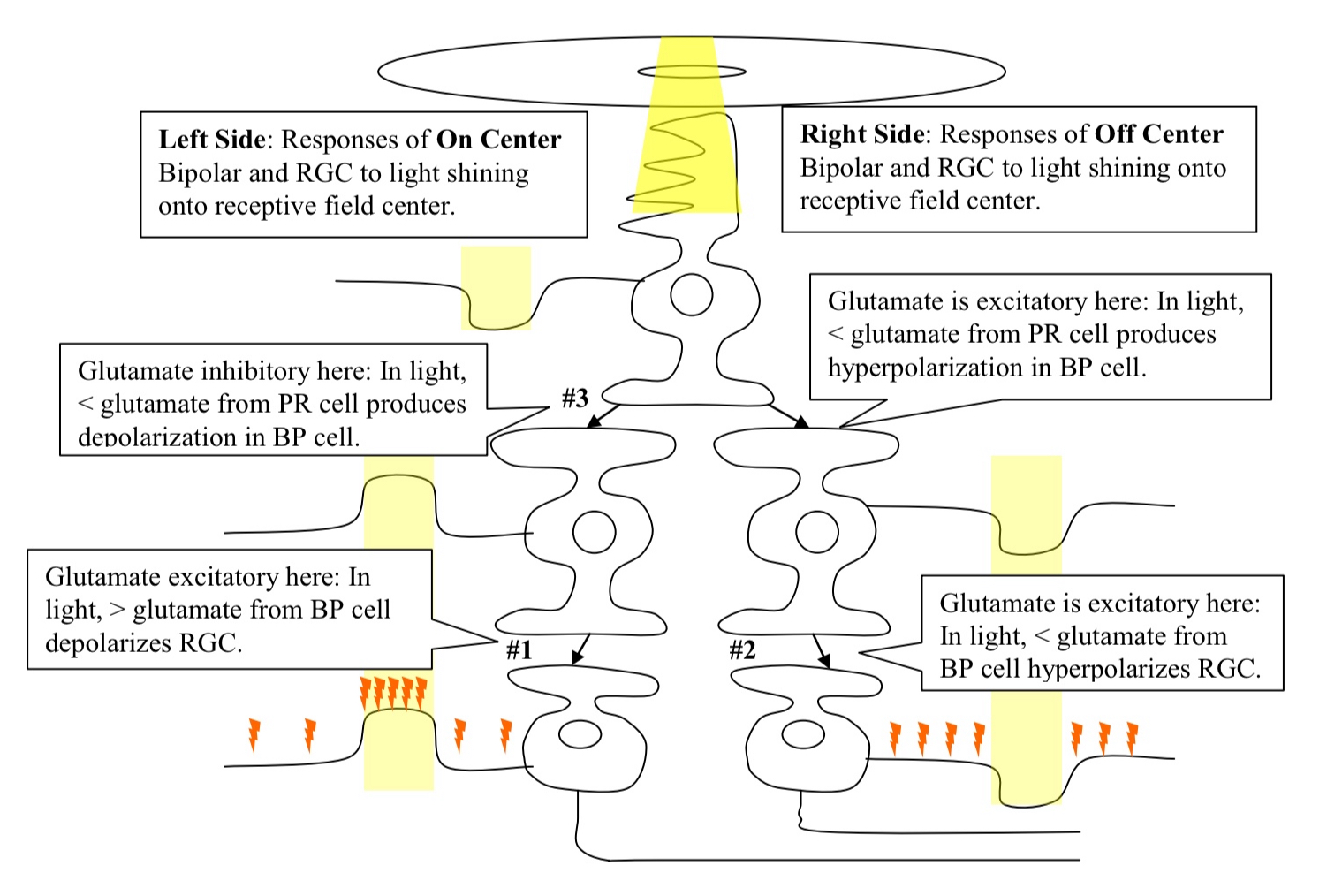
When is an Neurotransmitter excitatory?
when it’s presence produces a depolarization
What is glutamate?
transmitter released by the bipolar cells
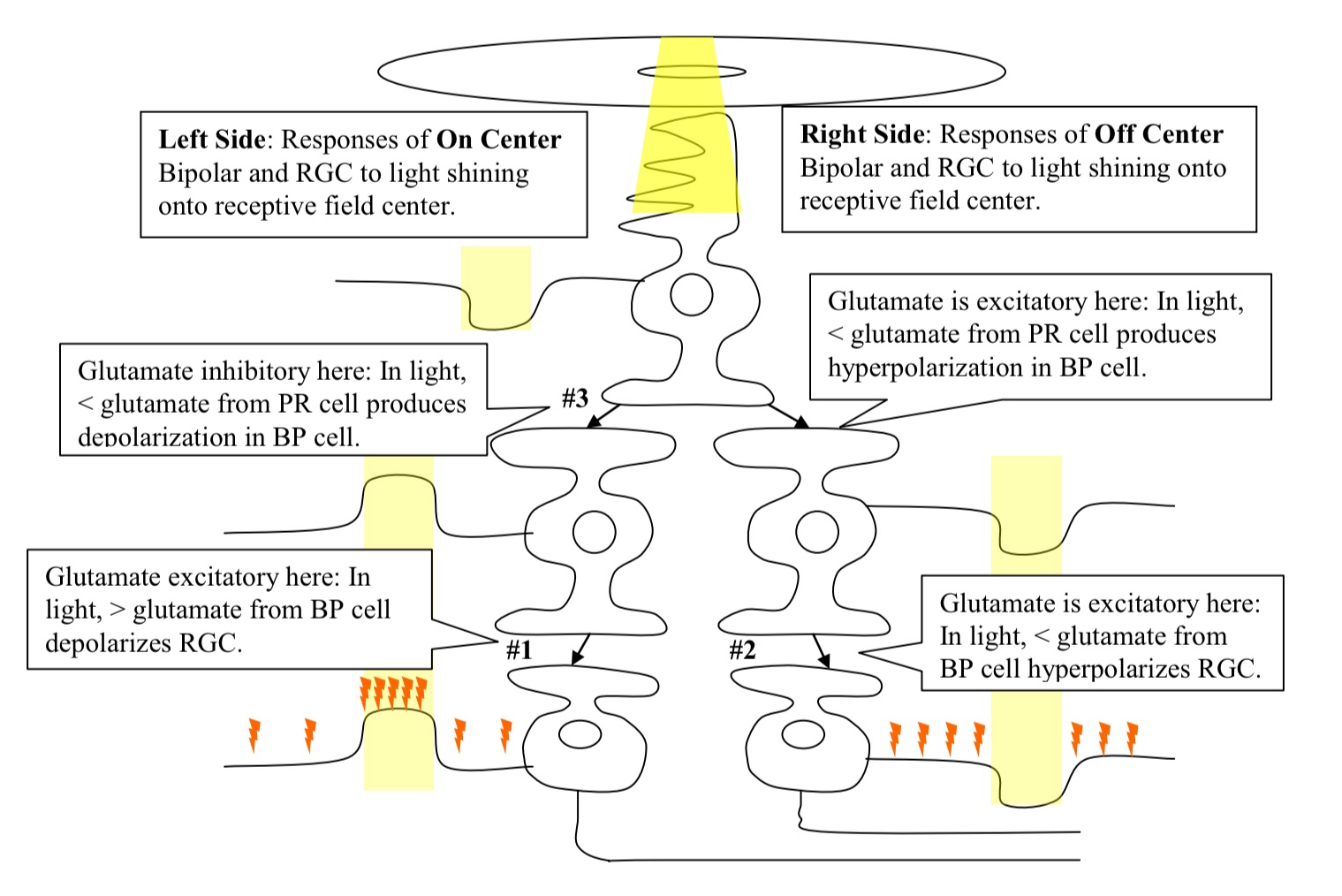
Explain what’s happening with the numbers on the diagram?
#1. Glutamate is excitatory here because an increase in NT release results in depolarization
#2. Glutamate is excitatory here because a decrease in NT release results in hyperpolarization
#3. Glutamate is inhibitory here because a decrease in NT release results in a depolarization
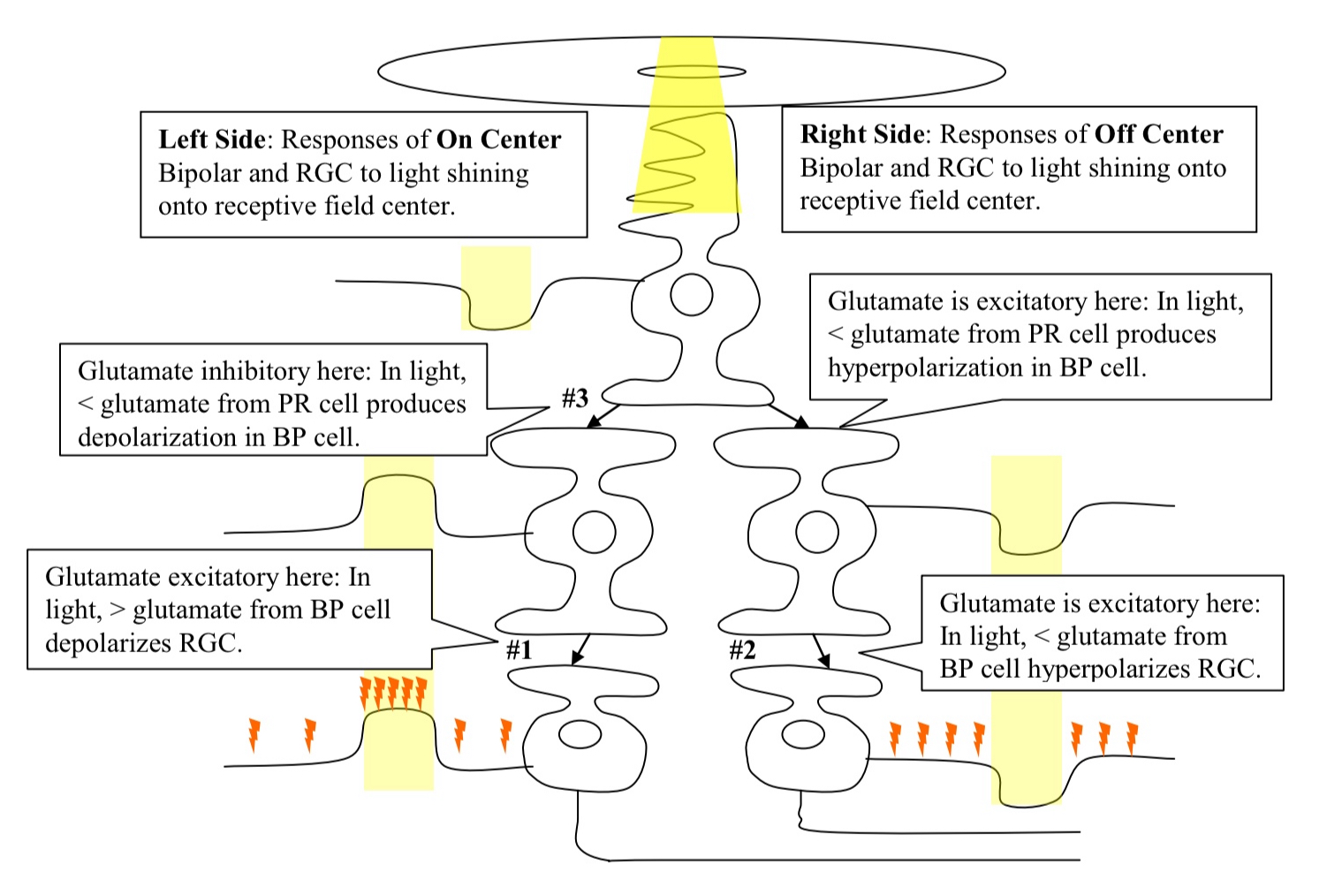
What is the general rule of thumb?
NT Excitatory: if the direction of polarization is the same in 2 neurons where one is being driven by the other
NT Inhibitory: if the direction of polarization is opposite
What’s the general rule about NT release by a presynaptic terminal?
increased by depolarization
decreased by hyperpolarization
What accounts for the difference between on and off center receptive fields?
Same NT (glutamate) is released onto both ON and OFF center BP cells
However, there are different receptors for that Neurotransmitter
Receptor expressed by ON center BP Cell : glutamate inhibits it
Receptor expressed by OFF center BP Cell : glutamate excites it
BP cells also account for the difference
Why do we have both ON and OFF center systems?
The On Center System: is most sensitive to increases in illumination
The OFF Center System: most sensitive to decreases in illumination