To estimate the concentration of free chlorine in swimming pool water or bleach using: i) A comparator or ii) A colorimeter
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Theory
• Chlorine is added to swimming pools to kill bacteria
• It reacts with the water as follows:
Cl2 + H2O ← → HOCl (hypochlorous acid) + HCl
• The hypochlorous acid then dissociates as a weak acid
HOCl ← → H+ + OCl–
• The amount of free chlorine in a sample of swimming pool water can be determined by establishing a relationship between the concentration of free chlorine in a sample and the amount of light the sample will absorb
• This is done in an instrument known as a colorimeter
The concentration of a substance in a solution can be determined by measuring the intensity of its colour.
Procedure
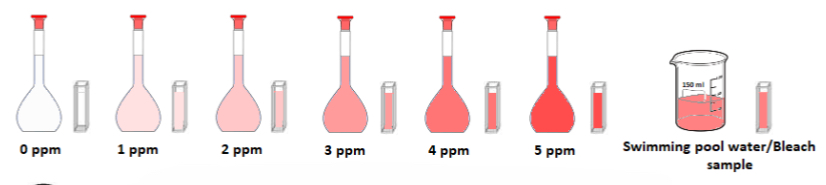
➢ Six standard solutions of chlorine are made up of concentrations:
0 ppm (deionised water only), 1 ppm, 2 ppm, 3 ppm, 4 ppm, 5 ppm
➢ A DPD tablet is added to each and shaken until it dissolves – each solution turns a pink colour of different intensity
Note: The 0 ppm (deionised water) will remain colourless
➢ Each solution is placed in a cuvette and placed in the colorimeter and an absorbance reading is taken
➢ A graph is plotted of absorbance Vs concentration of free chlorine for the six solutions
➢ A DPD tablet is added to the sample of swimming pool water being tested, it is placed in a cuvette and placed in the colorimeter and its absorbance reading is also taken
➢ The graph is used to determine the concentration of free chlorine in the sample of swimming pool water/bleach
Name two species in swimming pool water known as free chlorine
• Hypochlorous acid (HOCl)
• Hypochlorite ion (OCl–)
Free chlorine species - effective at killing bacteria
What is meant by free chlorine?
Free chlorine is chlorine present in water in the form of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) and as hypochlorite ions (OCl-)
Name a reagent suitable to test for free chlorine in a water sample
A DPD tablet
How does this reagent indicate the presence of free chlorine in a sample?
• The solution will turn pink
• The more free chlorine present, the more intense the pink colour
What is the relationship between absorbance and concentration of free chlorine?
• Absorbance of light is directly proportional to concentration of free chlorine
• A straight-line graph through the origin (0,0) is obtained for a directly proportional relationship
Give a reason why the concentration of free chlorine in treated drinking water is usually between 0.2-0.5 ppm whereas in swimming pool water it should be between 1-5 ppm
• Swimming pool water has more bacteria added by people swimming in it
• Therefore the concentration of chlorine must be greater in swimming pools than in drinking water